Gastrointestinal Disorders and Pathophysiology for Nursing Students
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
GI Tract
mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small & large intestines, liver, gall bladder, pancreas & spleen

Barrett's Esophagus
Condition caused by GERD: tissues in the esophagus become dysplastic & if not treated can become cancer of the esophagus
Peptic Ulcer Disease (PUD)
Common inflammatory condition of the stomach and proximal duodenum. The mucosal lining is disturbed and acid ulcerates the underlying tissues.
Cirrhosis
an irreversible disease of the liver, where liver tissue is destroyed and replaced by fibrous tissue and nodules.
Acute Pancreatitis
life-threatening condition where pancreatic enzymes lead to auto digestion and hemorrhage of the pancreas and surrounding tissues.
Portal Hypertension
a type of hypertension present in patients with cirrhosis, as a result of fibrotic liver tissue developing resistance to normal venous flow.
Amylase and Lipase
Acute pancreatitis is diagnosed with elevation of these enzymes.
GERD
acronym for stomach disorder that results in reflux of hydrochloric acid and pepsin into the esophagus which causes heartburn or coughing within 1 hour of eating.
Cholecystitis
general term for an inflammation of the gallbladder as a result of irritation from stones present within the gallbladder.
Varices
large torturous veins, usually within the esophagus, that are associated with liver disease and a cause of upper gastrointestinal bleeding.
Epigastric Pain
frankly bloody stools; a sign of lower gastrointestinal (LGI) bleeding.
H. Pylori
a type of bacteria that disrupts the mucosa of the stomach and is commonly found in patients with peptic ulcer disease.
Diverticulitis
inflammation and/or infection of saclike outpouchings of the intestinal mucosa.
Dysplastic Tissues
abnormal tissue changes that can lead to cancer if untreated.
Auto Digestion
the process where pancreatic enzymes digest the pancreas itself.
Pancytopenia
Reduced numbers of RBCs, WBCs, and thrombocytes.
Hematochezia
area of abdomen that includes pyloric area of stomach, duodenum, and part of pancreas.
Type C Hepatitis
hepatitis where no vaccine is available to prevent the disease.
Cholelithiasis
almost always caused by gall bladder stones.
Gall stones
Formation of small (2-8mm) to large (3-4cm) stones made of cholesterol and bilirubin precipitant.
Gall bladder swelling
caused by chemical irritation of concentrated bile.
Crohn's Disease
chronic inflammation of the intestinal tract characterized by symptoms of: malabsorption, malnutrition, weight loss, bloody stool/diarrhea, abdominal pain, transmural involvement, and a patchy pattern of inflammation commonly found in the Ileum.
Ulcerative Colitis
A chronic condition of unknown cause in which repeated episodes of inflammation in the rectum and large intestine cause ulcers and irritation. Signs and symptoms of increased risk of dehydration, confluent inflammation, non-transmural, bloody stool/ diarrhea, and abdominal pain.
Hepatic encephalopathy
a change in mental status resulting from toxic levels of ammonia.
Type A
hepatitis characterized by acute onset of fever and malaise, usually transmitted via oral/fecal route.
Melena
"tarry" (tar-like/paste-like) stool signaling the presence of partially digested blood. Seen in upper gastrointestinal (UGI) bleeding.
Type B
hepatitis characterized by a subtler onset and is most typically transmitted via blood or bodily fluid.
Prehepatic
type of jaundice due to an increase in unconjugated bilirubin from a variety of hemolytic (RBC destruction) conditions.
Hypersplenism
a condition resulting from stasis of blood causing splenomegaly which leads to anemia, thrombocytopenia, and leukopenia.
Gastritis
acute or chronic inflammation of the stomach mucosa leading to erosions.
Ileus
loss of peristaltic motor activity which results in a mechanical obstruction of the intestine.
Adhesion
scar tissue formed as a result of chronic inflammation or abdominal surgery, which may cause an intestinal obstruction.
Hepatitis
general term for inflammation of the liver.
Icterus
Alternative name for the yellow-green pigment of skin, sclera, tongue, and palate resulting from an alteration in the normal bilirubin cycle.
Appendicitis
Inflammatory process that results in periumbilical and RLQ (right lower quadrant) pain with fever and leukocytosis.
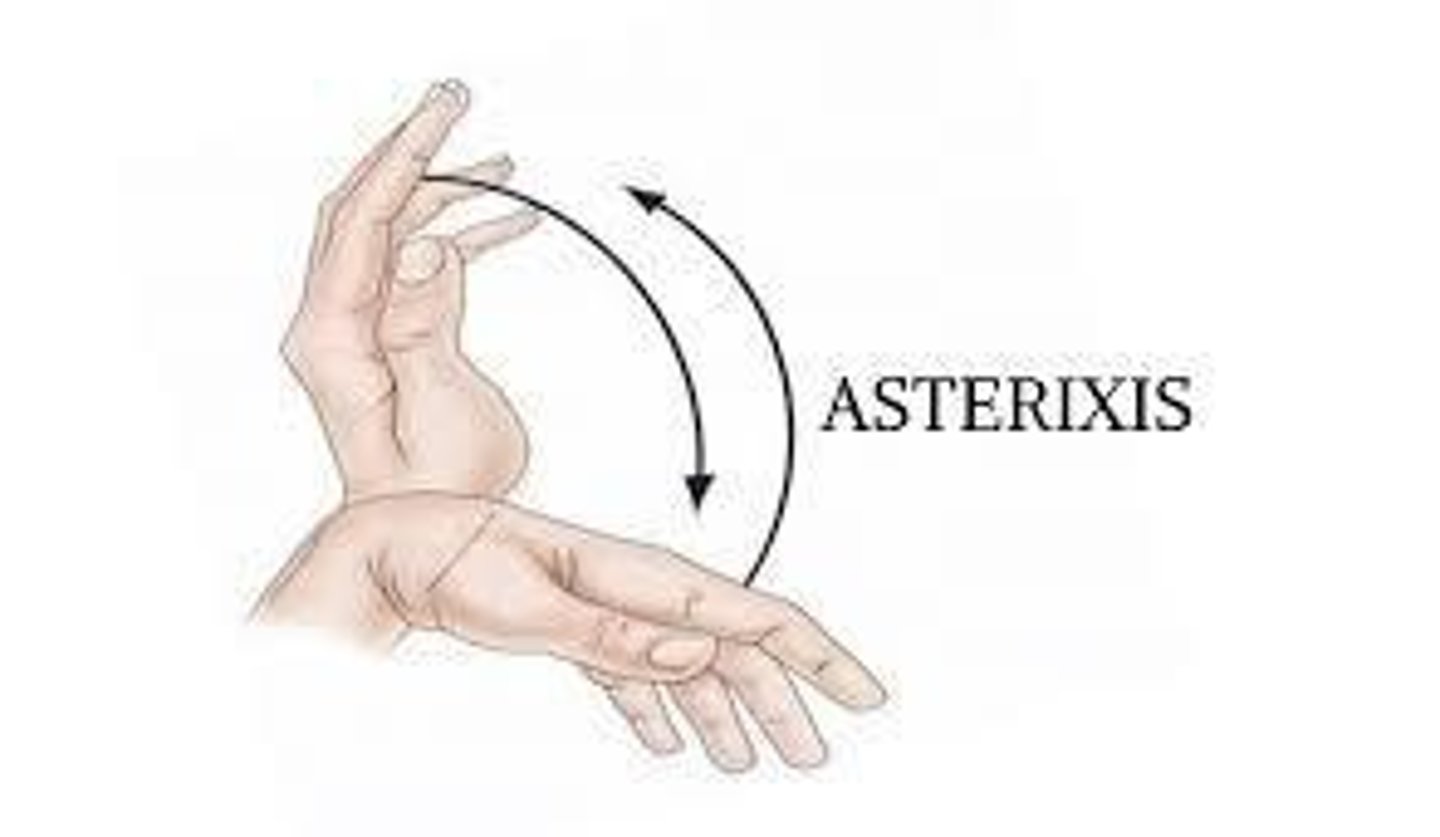
Asterixis
an early sign of impaired ammonia metabolism in a patient with cirrhosis characterized by flapping tremor of hands.
Hematemesis
term indicating blood is visibly present within vomitus. Seen in upper gastrointestinal (UGI) bleeding.
Blood test results for prehepatic jaundice
Total serum bilirubin- High
Indirect bilirubin- High
Direct bilirubin- Normal
Posthepatic jaundice
Occurs when bile flow is obstructed between the liver and the intestine, resulting in the backup of conjugated bilirubin, causing leakage. S&S: grey stool
Hepatic jaundice
due to congenital liver disease, cirrhosis of the liver, or hepatitis, which causes an increase in unconjugated bilirubin. The liver cannot handle conjugating all the unconjugated bilirubin, so the conjugated bilirubin will be low.
Blood test results for posthepatic jaundice
Total serum bilirubin- High
Indirect bilirubin (unconjugated)- Normal
Direct bilirubin (conjugated)- High
Blood test results for hepatic jaundice
Total serum bilirubin- Norm
Indirect bilirubin- High
Direct bilirubin- Low
Complications of cirrhosis
Portal hypertension
Esophageal and gastric varices
Peripheral edema and ascites
Hepatic encephalopathy
Hepatorenal syndrome
What are the risk factors for a Brain attack/stroke
History of Atherosclerosis, Hypertension, Increased Age, Family History of DM, Smoking, Increased Fatty Diet - Poor Lifestyle Choices
What are the differences between a TIA and a CV (brain attack)?
Transient <24 hrs, is a warning
What is often the first sign of a neurologic event
Changes in LOC - Dec Alertness, lethargic, coma, Not Ox4 (some or all), Can't follow commands, garbled speech or no speech, confusion, withdrawal or aggression.
What types of "special functions" deficits would a person with a left-hemispheric stroke have?
Dysphagia - difficulty understanding words, difficulty putting words together to make meaning, aphasia - loss of ability to understand or express speech.
What types of special functions defects would a person with a right-side hemispheric stroke have?
Difficulty with spatiality, left-sided neglect, a decrease in creativity, face recognition, and music ability
What are the first signs and symptoms of a brain stem stroke
Dec LOC, Brain Stem probs - coma or near coma state most often seen, HR & BP Changes, Resp. changes - Apnea or Cheyne stoke breathing (seen in coma pts who aren't on a ventilator), muscle strength decrease, Decerebrate & decorticate posturing - sneezing, coughing. reflexes are weaker (usually symmetrical) sometimes Bilateral Babinski's Reflex seen.
What are the STAT interventions performed by medical personnel when a patient is having a stroke?
Oxygen, BP Management, HOB Up 30o, Diuretics, ICP Monitor, Clot busters - Anticoagulant treatment or surgery depending on type of stroke
What is the definition of dementia and what disease does it manifest in?
Alzheimer's - type of forgetfulness, emotional changes, behavioral changes
What are the effects of acetylcholine? Dopamine? How do these relate to Parkinson's disease?
Acetylcholine - Excitatory Dopamine- Inhibitory R/T Parkinson's - Decreased Dopamine, have Increased Excitatory Effect - hypertonia (rigidity) & dyskinesia (movement disorder)
What is multiple sclerosis? What are some s/s?
Autoimmune D/O - person's T-cells attack the myelin protein of brain neurons -> loss of functioning. S/Sx: parasthesis, weakness - Asymmetrical (one-sided), ataxia, dysarthria, double vision, bladder control issues
Name some differences between Grand seizures and Partial seizures
General Szs: Always Unconscious - movement is tonic-clonic -> alternating rigidity & contraction of muscles. Partial Szs: Locally, Varied LOC /unconsciousness
What disease correlates to a positive Brudzinski's sign?
Bacterial or Viral Meningitis - Brudzinski's Sign - when the neck is flexed, if the patient has severe neck stiffness, causes the patient's hips & knees to fle
Bacterial vs. Viral Meningitis
BACTERIAL - More virulent; High fever; Marked LOC change; Can be fatal; Nuchal rigidity; Droplet precautions
VIRAL - Less virulent; Low-grade fever; No LOC change; Rarely fatal; Some nuchal rigidity; Hospitalized to R/O
Mydriasis
Pupillary dilation. Usually equal in both eyes - responding to exposure of less light
What are the main concerns of Cushing's disease?
Hyperglycemia - DM 2, truncal obesity, Inc Risk Atherosclerosis, Hypercortisolism & Hyperaldosteronism. Hypercortisolism -> Inc Adrenocorticotropic (Pituitary Gland) Hormone (ACTH) &/or the Adrenal Cortex has a tumor or other malfunction which causes it to excrete cortisol. Hyperaldosteronism -> Adrenal Cortex oversecretes Aldosterone.