Unit 4 AP Chemistry Study Guide
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
WHAT I DID NOT INCLUDE - the 2nd type of phase diagram STUDY IT (pg 5 in notes) -all formulas used (will be provided on the test but familiarize yourself with it) -INTRAMF (covalent,ionic,metallic,etc)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
Ion-Dipole
Ionic attracted to polar
the strength of ion-dipole makes it possible for ionic substances to dissolve in polar solvents
Dipole-Dipole
molecules with permanent dipoles → attracted to each other
the positive side of 1 molecule is attracted to the negative end of another molecule
the more POLAR the molecule → the higher the boiling point
London Dispersion (Shape, Molecular Weight)
When particles get closer to each other they start to exhibit some attraction
Shape (organics): long, skinny molecules have stronger LD than shorter fat molecules
Weight: Larger atoms have larger electron clouds which are easier to polarize
Which has the greater effect? Comparable size and shape + One larger than another
Comparable size and shape: dipole-dipole and London forces
One larger than another: London dispersion forces will likely determine its physical properties
Increase Trends for IMFS
increase in size
increase in electron density
increase in LD strength
increase in temporary dipole strength
H-Bonds
extreme dipole-dipole
when H is bonded to a highly Electronegitative element (FON) because the H bond is exposed to a strong attractive force
Strongest IMF to Weakest
ion-dipole>H-Bond>dipole-dipole>LD
What is Viscosity?
resistance to flow, related to how molecules move past each other
flows by sliding molecules past one another
What does viscosity depend on?
Attractive forces b/w molecules: Stronger the IMF the higher the viscosity
Tendency of molecules to become entangled: More entanglement → greater viscosity
Viscosity decreases with an increase in temperature
Surface Tension
Surface molecules are only attracted inward towards the “bulk” molecules → causes a liquid to have a “skin”
Stronger IMFs → higher surface tension
Cohesive forces
IMFs b/w molecules of the SAME TYPE
Adhesive forces
IMFs b/w molecules of DIFF TYPES
Capillary Action
a process where the liquid rises in a tube bc of a combo of adhesion to the walls of the tube & cohesion b/w the liquid particles
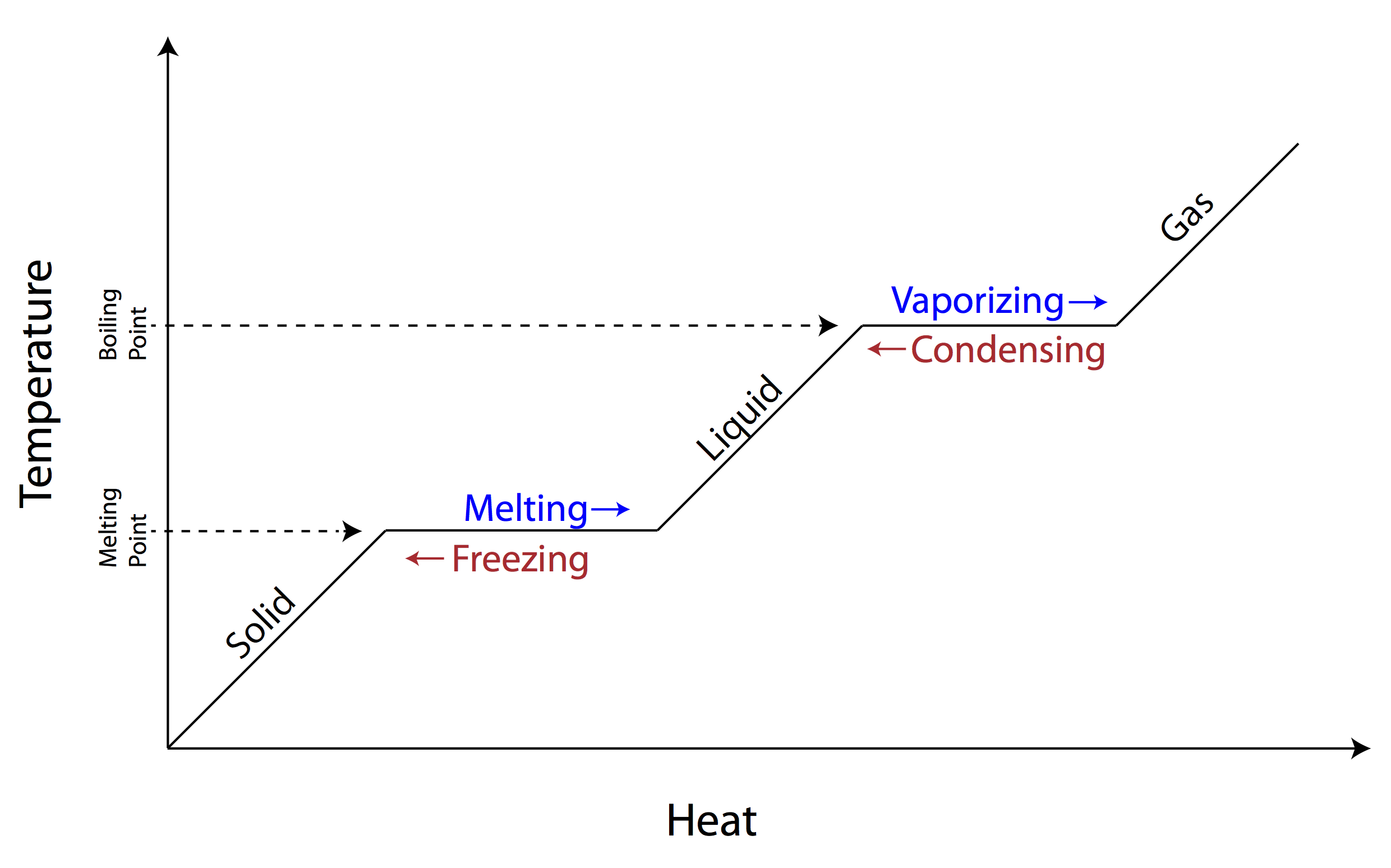
Draw out/Memorize the Phase Change Diagram
A) Soild →B) Freezing/Melting → C) Liquid → D) Condensation/Vaporization → E) Gas
Sublimation (solid→gas)
Deposition (gas→solid)
Vapor Pressure
interaction of the molecules on the surface of the liquid that had escaped to a gas and the gas molecules striking the surface and returning to a liquid
vapor pressure of a liquid is the pressure exerted by the vapor when the liquid and vapor are in dynamic equilibrium
-the pressure of gas becomes constant = dynamic equilibrium
-If equilibrium never established vapor continues to form an eventually the liquid dries out
Liquids that evaporate easily are ________
volatile
Liquids boil when _________________________
the external pressure at the liquid surface = the vapor pressure (norm boiling point is at the standard pressure 1 atm 760 torr, etc)
Temperature of the boiling point increases with ____________
increase in external pressure
Two ways to boil
Increase temp
Decrease pressure
Solute
substance that is dissolved in a solvent to form a solution
typically present in smaller quantities compared to the solvent
Solvent
a substance capable of dissolving other substances to form a solution.
Solvate
pulls solute particles apart and surrounds them
Miscible
2 liquids dissolved in each other
Immiscible
2 liquids that don’t dissolve in each other
Saturated
(as much as it can be)
hold the most solute at that temp
Unsaturated
(excess)
at that temp the solvent could hold more
Supersaturated
(rare+unstable)
holds more than it can actually can at that temp
Factors Affecting Solubility
“like dissolves like”
more similar IMF → more likely to dissolve
gases increase w increase in mass → stronger LD
gases increase with increase in pressure
solid & liquid increase w temp
gas decrease w increase in temp
How to calculate Solution Concentrations in mass percentage
(mass of A in solution)(100)/total mass of solution
How to calculate Solution Concentrations in ppm
(mass of A in solution) (10⁶) / total mass of solution
How to calculate Solution Concentrations in ppb
(mass of A in solution) (10⁹) / total mass of solution
How to calculate Mole Fraction
X(a) = mole of / total moles of solution
What is the mobile phase?
when the liquid/gas is moving up
What is the stationary phase?
the solid/liquid used (separates the mixture)
Gas Chromatography
separating & analyzing compounds that can be vaporized w/o decomposing
Liquid Chromatography
separates, identifies, and quantifies components of a mixture (used to find vitamin D lvls in blood)
Paper Chromatography
separating dissolved chem substances by taking advantage of the diff rates of which they move up the paper
Solvent: non-polar
Paper= polar
What is the Rf Value?
the distance the sample moves along the paper compared to the overall distance the solvent travels
Gas Characteristics & Pressure
gas molecules expand to fill their containers
pressure: the amount of force applied to the area P=F/A
Standard Air Pressure
1 atm
760 torr
760 mm Hg
101.3 kPa
Avogadro’s Law
The vol of gas at constant temp & pressure is directly proportional to the # of the moles of the gas PV=nRT
What happens to the density of gas as the gas is heated in a constant-volume container?
no effect
What happens to the density of gas as the gas is compressed at constant temp?
gas density increase & vol decreases
What happens to the density of gas as additional gas is added to a constant-volume container?
gas density increase & greater mass
Kinetic Molecular Theory Part 1
Gases consist of large #s of molecules that are in continuous random motion
Kinetic Molecular Theory Part 2
The combined volume of all molecules of the gas is negligible relative to the total volume which gas is contained
Kinetic Molecular Theory Part 3
Attractive & repulsive forces b/w gas molecules are negligible (gas particles are too far apart so they don’t attract/repulse)
Kinetic Molecular Theory Part 4
Energy transferred b/w molecules during collisions (energy transfers to the one it collides with)
Kinetic Molecular Theory Part 5
The average kinetic energy of the molecules is proportional to the absolute temp
Diffusion
The spread of 1 substance throughout a space or second substance [high(concentration] - [low]
Effusion
The escape of gas molecules through a tiny hole into an evacuated space
Maxwell-Boltzman Curves SAME sub DIFF temp
higher peak = lower temp
lower peak = higher temp
Maxwell-Boltzman Curves DIFF sub SAME temp
higher peak = biggest
lower peak = smallest
Real Gas Traits (all 3)
Deviate most from ideal gas behavior at extremely high pressure and low temperatures
All gas particles have some volume bc of the size of their atoms and lengths or their bond
All gas particles are subject to IMFs
Deviations real gas under ______ circumstances
non ideal under very high pressure and low temperature
the more polar a gas it the more the gas will deviate from ideal behavior