Reactions of Amines
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
State the reactions of amines you need to know.
Ethanoylation of amines
Reaction with nitric (III) acid / nitrous acid
Coupling reactions with benzenediazonium salts.
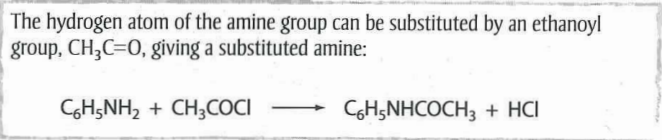
What is ethanoylation?
When a hydrogen atom in an amine is replaced with the ethanoyl group (CH3CO).
An acid chloride e.g. ethanoyl chloride is used; the product formed is an amide.
How can you determine if a compound is an aliphatic or aromatic amine?
By reactions of nitrous / nitric (III) acid.
Briefly describe nitrous / nitric (III) acid.
Nitric(III) acid (or nitrous acid), HNO2, is unstable and is always prepared in situ.
in the reaction mixture (as it is needed).
How is nitric (III) acid formed?
By reacting sodium nitrite (NaNO2) with hydrochloric acid.
NaNO2 + HCl = HNO2 + NaCl
Describe the reaction of nitrous / nitric (III) acid with aliphatic amines.
Aliphatic amines react with nitrous acid at any temperature to form:
Alcohol
Water
Nitrogen gas
Within this reaction, effervescence is observed.
Describe the reaction of aromatic amines (e.g. phenylamine) with nitrous acid at room temperature (above 10°C).
At room temperature, aromatic amines react similarly to aliphatic amines, producing:
Phenol
Water
Nitrogen gas
Effervescence is observed.
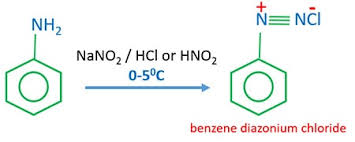
Describe the reaction of aromatic amines (e.g. phenylamine) with cold nitrous acid at room temperature (below 10°C).
A stable benzenediazonium ion is formed.
No effervescence is observed.
Summarise what coupling reactions are.
Benzenediazonium compounds are extremely reactive and, below 10°C, they react with phenols and aromatic amines in alkaline solution.
The compounds formed contain the -N=N- azo group, which links the two benzene rings together.
Coupling reactions are used to form what?
Azodyes.
Azodyes contain the -N=N- azo group, which links the two benzene rings together.
What is a chromophore?
A structural unit of a molecule which is responsible for the absorption of a certain wavelength in the visible spectrum.
Chromophores are responsible for giving a molecule its colour.
What rule of thumb can be used to determine the colour of a compound using its absorption?
The colour seen of a compound is OPPOSITE to the colour absorbed.
E.g. Red and blue are on opposite sides of the visible spectrum.
if a compound shows a maximum absorption at the blue section of the spectrum, the colour seen will be red / orange/ yellow.