Genetics Ch 16 Lac Operon, Transcription Regulation
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
what cellular processes is gene regulation important for?
1. metabolism
2. response to environmental stress
3. cell division
When can gene expression be regulated?
- before transcription
- during transcription
- after transcription but before translation
- at translation
- after translation
how can gene expression be regulated before transcription
DNA methylation
how can gene expression be regulated during transcription
transcription factors, attenuation
how can gene expression be regulated at translation
translational repressor proteins, riboswitches, antisense RNA can bind to mRNA and prevent translation
how can gene expression be regulated after translation
phosphorylation (covalent modification), feedback inhibition
repressors
proteins that inhibit transcription
Negative Control
operon
group of 2 or more genes under the control of one promoter
- codes for polycistronic mRNA
-> so you only have to upregulate one promoter to control all of the genes
how is the lac operon regulated?
It is turned off by repressors and turned on by the presence of lactose.
catabolite activator protein (CAP)
An activator protein that can bind to the CAP binding site upstream of certain prokaryotic operons, facilitating binding of RNA polymerase and stimulating gene expression.
enzyme adaptation
an enzyme only appears in the cell after it has been exposed to the enzyme's substrate
what regions does the lac operon contain
1. promoter (signals beginning of transcription)
2. CAP site (positive regulation)
3. operator (negative regulation)
4. protein coding genes (lacZ, lacY, LacA)
5. terminator (signals end of transcription)
Operator
negative regulation when bound by repressor protein (the lacL gene product)
lacA
encodes galactosidase transacetylase
--> which covalently modifies lactose by adding a hydrophobic acetyl group which allows it to diffuse outside of the cell
Where is the lac repressor located?
anywhere in the cell because it is a protein that can diffuse
what happens when a repressor protein binds to the operator
it forms a loop --> this structural change in the DNA molecule prevents RNA polymerase from moving
catabolite repression
a second way the lac operon can be transcriptionally regulated
when glucose is depleted _________ is alleviated and the lac operon is _________
catabolite repression; expressed
cyclic AMP (cAMP)
small effector molecule in catabolite repression
how is cAMP formed
from ATP by adenylate cyclase enzyme
when glucose is high, concentration is cAMP in the cell _________
decreases
what happens when CAP is bound to the CAP site
it stimulates the transcription of the lac operon
+lactose, -glucose
high transcription rate of lac operon
-lactose, -glucose
low transcription rate of lac operon
+lactose, +glucose
low transcription rate of lac operon
-lactose, +glucose
very low transcription rate of lac operon
constitutive gene expression
Constant expression of a gene
ex: "housekeeping genes" that are necessary for survival of the organism
housekeeping genes
a gene that is transcribed continually because its product is needed at all times and in all cells
regulated gene expression
the encoded protein is only produced when it is needed
-> expression may be increased or decreased depending on demand
cell signaling
The process of cell-to-cell communication that regulates gene expression
why is gene regulation important for response to environmental stress
living organisms have to adapt to detrimental conditions (ex: low water conditions)
how can gene expression be regulated after transcription but before translation
RNA splicing
activators
proteins that increase transcription
Positive Control
what is the most common way to regulate gene expression in prokaryotes?
at transcription initiation
small effector molecules
molecules that can bind to activators and repressors to influence transcription
what are the two ways inducers can act
1. bind activators and cause them to bind to DNA
2. bind repressors and prevent them from binding to DNA
inducible genes
genes that are normally off but can be turned on in the presence of inducer effector molecules
bacteria have a _______ switch, whereas eukaryotes have a _____ switch
on/off; dimmer
what are the two ways inhibitors can act?
1. co-repressors bind to repressors and cause them to bind to DNA
2. inhibitors bind to activators and prevent them from binding to DNA
repressible genes
genes that are normally transcribed but can be turned off in the presence of inhibitor effector molecules
polycistronic mRNA
molecules of mRNA that code for multiple proteins
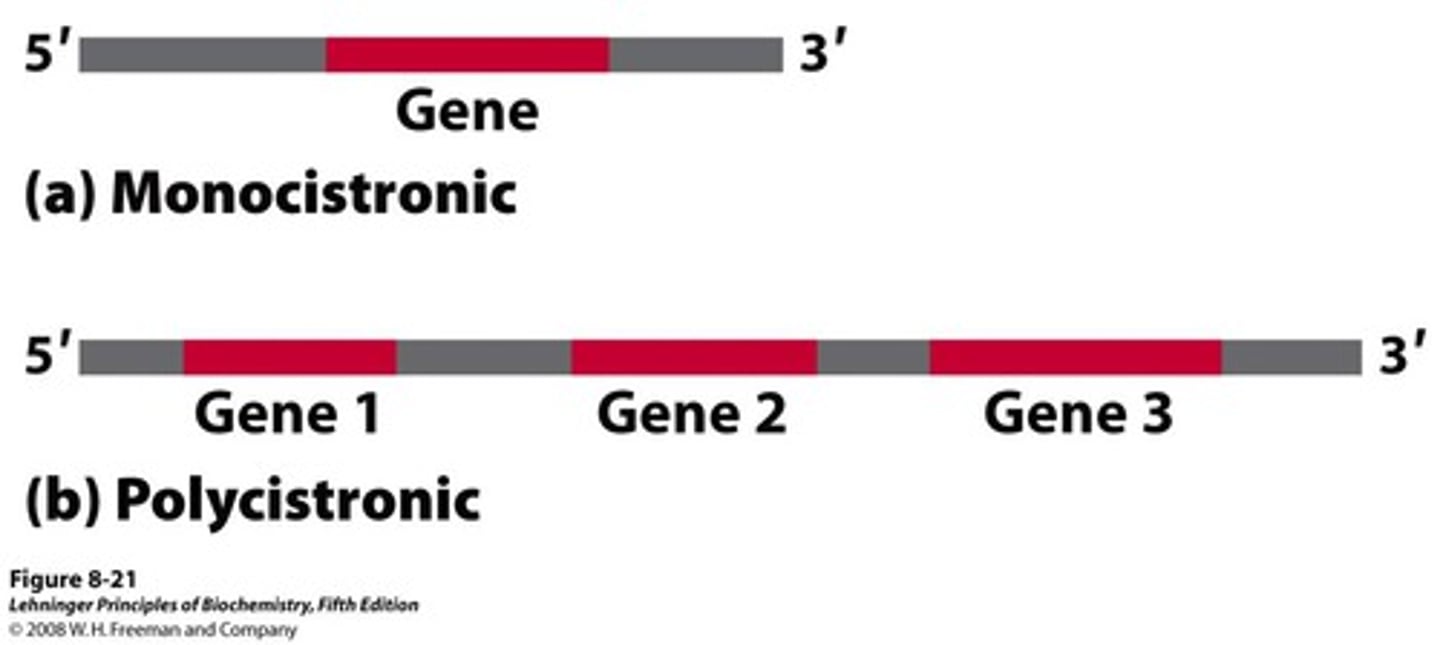
what is the lac operon necessary for?
encoding the genes necessary for lactose metabolism
CAP site
Positive regulation-site for catabolite activator protein (CAP)
lacZ
encodes B-galactosidase
-> cleaves lactose
*allows us to measure production or utilization
lacY
encodes lactose permease
*allows lactose to get into the cell (TRANSPORT protein)
stages of breakdown of lactose
1. lactose imported
2. trapped inside cell
3. broken down into galactose and lactose
how is lactose transported into the cell
Active transport where a symporter (lactose permease - encoded by lacY) uses energy from the H+ gradient
why is glucose used before lactose?
it takes much less energy expenditure for the cell
Lac operon is _____ under _____ control
inducible; negative
when the repressor protein binds to the operator region it____
prevents RNA polymerase from transcribing the lac operon
when allolactose (or lactose) binds to the repressor it_____
inactivates the repressor so that it cannot bind to the operattor
the lac operon is _______
inducible (meaning it is only turned on in the presence of lactose)
does the presence of a repressor protein completely inhibit transcription of the lac operon?
no, there are always low levels of basal transcription
-> so that initially the cell can respond to a little bit of lactose
allolactose
inducer molecule that binds to lac repressor; allowing transcription of lacZ, lacY, lacA
diauxic growth
the sequential use of two sugars by a bacterium
what does the laci gene do
encodes the lac repressor
allosteric site
The site on a protein where a small effector molecule binds to regulate the function of the protein.
catabolite repression
lactose metabolizing genes are repressed when the cell can use glucose
System of gene control in some bacterial operons in which glucose is used preferentially and the metabolism of other sugars is repressed in the presence of glucose.
attenuator sequence
A sequence found in certain operons (e.g.,trpoperon) in bacteria that stops transcription soon after it has begun.
osmoregulation
the ability of the cell to regulate how much water it has in it
micF
inhibits the expression of ompF at high osmolarity
ompF
produced at low osmolarity
how does the antisense RNA from the micF gene inhibit translation of the ompF mRNA
the micF RNA physically blocks the ribosome from binding to the ompF mRNA