Climate Change
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/36
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
1
New cards
Biosphere
thin layer of earth that has conditions suitable for supporting life
2
New cards
Atmosphere
layers of gases that surround the Earth (nitrogen, oxygen and other gases)
3
New cards
Atmosphere layers
troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere
4
New cards
Hydrosphere
consists of all the water on earth, solid, liquid and gas
5
New cards
Lithosphere
solid portion of the Earth that sits above the mantle
6
New cards
Solar Energy
radiant energy, it is transmitted as electromagnetic waves
7
New cards
Insolation
amount of solar energy received by a region of the Earth’s surface
8
New cards
Angle of inclination
degree that the Earth’s poles are tilted from the perpendicular plane of orbit
9
New cards
Angle of incidence
angle between a ray falling on a surface and the line perpendicular to that surface
10
New cards
Seasonal changes
latitudes north and south of the equator are the result of the Earth’s angle of inclination and the resulting changes in the angle of incidence
11
New cards
Summer solstice
June 21
12
New cards
Winter solstice
December 21
13
New cards
Albedo effect
percentage of solar radiation that it reflects
14
New cards
Cloud cover
reflects incoming solar radiation
15
New cards
Atmospheric dust
reflects incoming solar radiation
16
New cards
Natural greenhouse effect
absorption of outgoing infrared radiation by naturally occurring water vapor, carbon dioxide, and other gases (methane, nitrous oxide) into the atmosphere
17
New cards
Net radiation budget
difference between the amount of incoming radiation and outgoing radiation emitted from the Earth’s surface and atmosphere
18
New cards
Incoming radiation
all of the solar energy that reaches the Earth’s surface, not including the solar radiation that is reflected by the albedo of the earths surface
19
New cards
Outgoing radiation
thermal radiation that is remitted by the earths surface and atmosphere
20
New cards
net radiation budget deficit
more outgoing radiation then incoming, in the regions near the poles
21
New cards
net radiation budget surplus
More incoming radiation than outgoing radiation, in the regions near the equator
22
New cards
Thermal energy transfer
movement of thermal energy from an area of higher temperature to an area of lower temperature
23
New cards
Radiation
emission of energy as particles or waves that may be reflected or absorbed by particles of matter
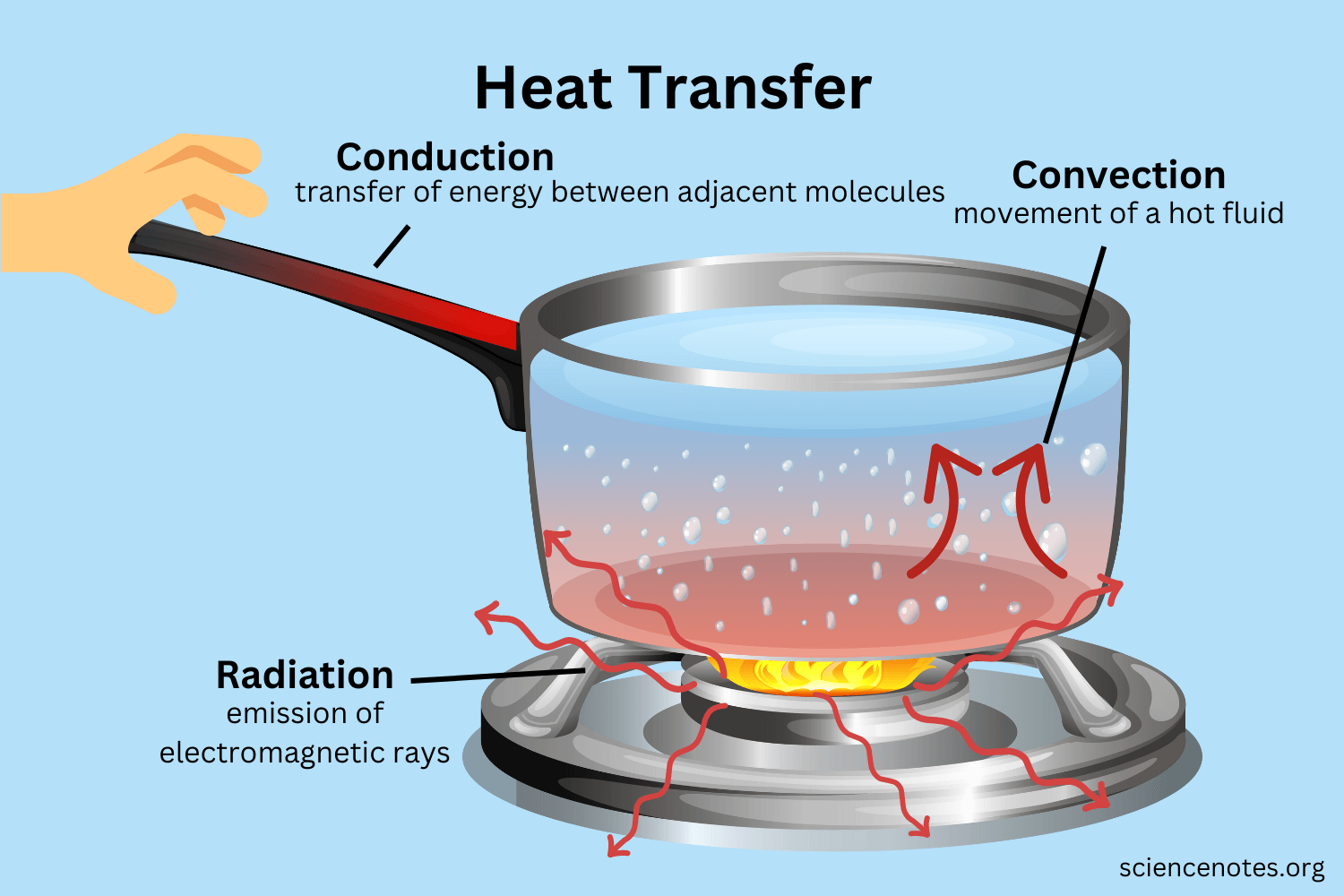
24
New cards
Conduction
transfer of thermal energy (heat) through direct contact but not moving to a new location
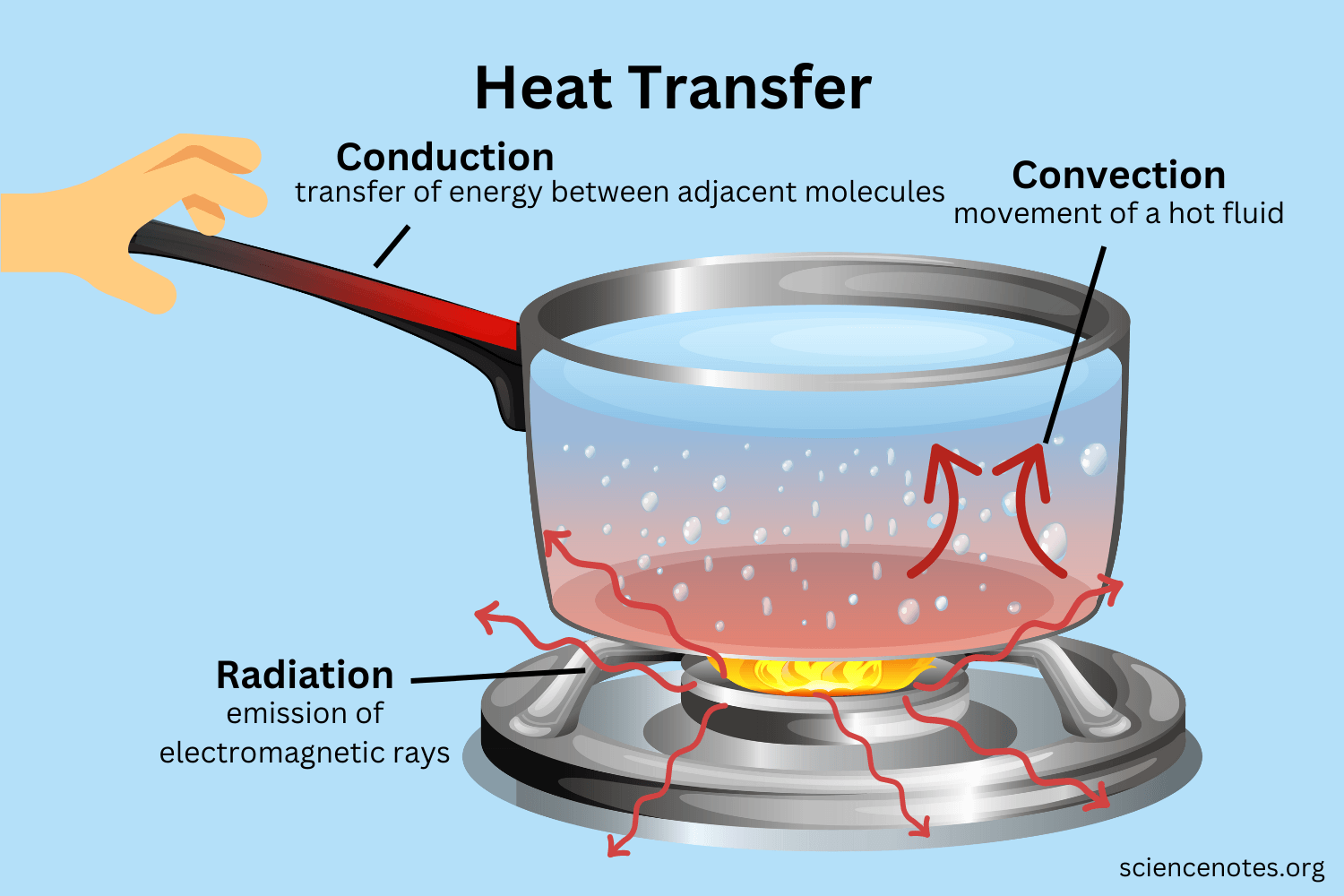
25
New cards
Convection
transfer of thermal energy through the movement of particles from one location to another
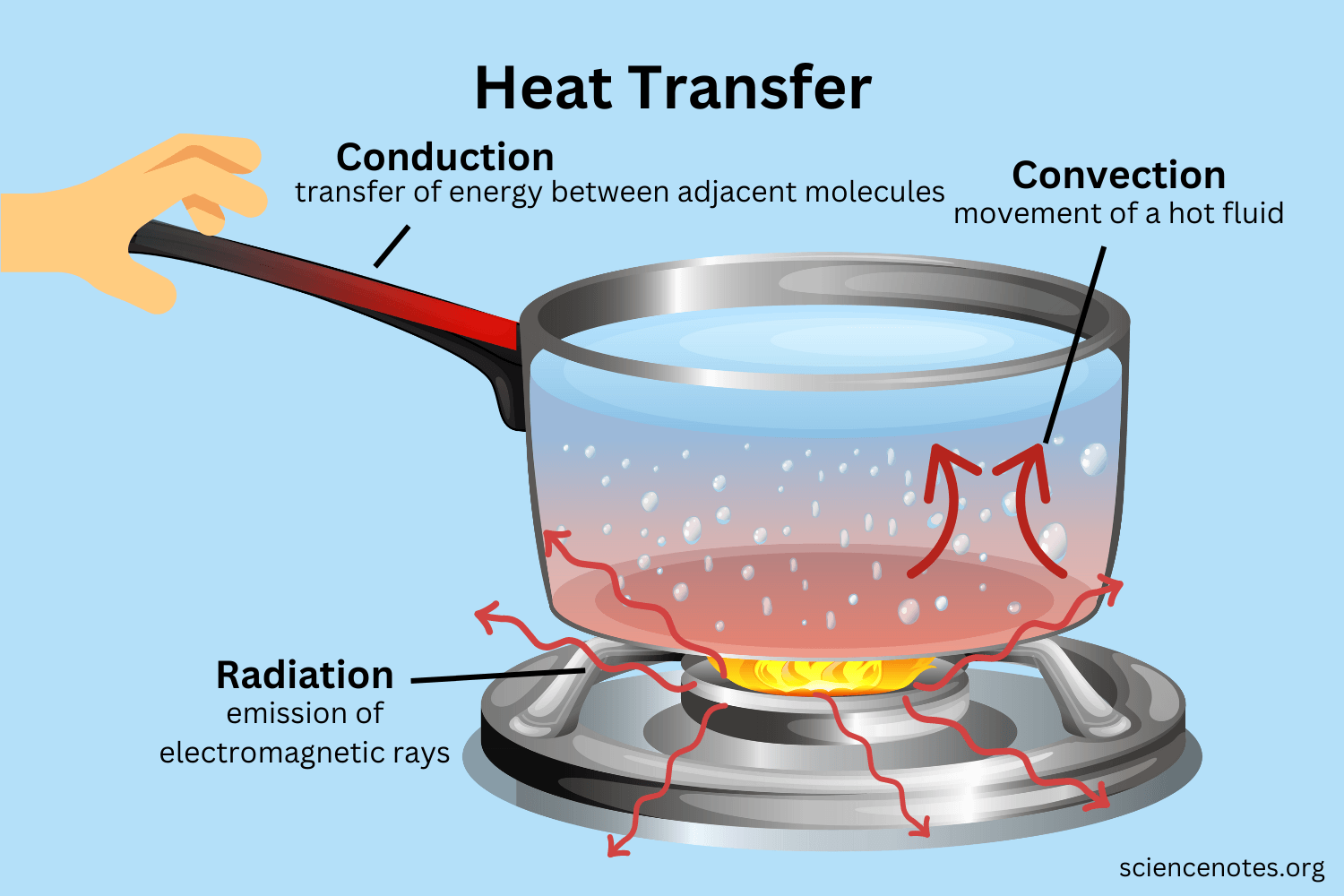
26
New cards
Convection currents
how thermal energy is transferred through he atmosphere
27
New cards
Atmospheric pressure
pressure exerted by the mass of air above any point on earth’s surface
28
New cards
Wind
movement of cool air from areas of higher pressure to areas of low pressure
29
New cards
Coriolis effect
deflection of any object from a straight-line path due to the rotation of the earth (moves air in the Northern Hemisphere to the right and air in the southern hemisphere to the left)
30
New cards
Global wind patterns
transfer thermal energy from areas of net radiation budget surplus to areas of net radiation budget deficit, warming areas further away from the equator
31
New cards
Sea breeze
as the sun rises, the land warms faster than the water and as the warmer air rises, cooler air from over the water moves in to replace it
32
New cards
Land breeze
at night, the water cools more slowly than the land and the breeze reverses itself
33
New cards
how do the hydrosphere transfer thermal energy
it transfers thermal energy from the warmer latitudes near the equator to cooler areas near the poles, through the action of global winds
34
New cards
Surface currents
moved by global wind patterns
35
New cards
How is thermal energy transferred through oceans
convection currents
36
New cards
Hydrologic cycle
Water molecules are constantly moving among the components of the biosphere through the action of the **hydrologic cycle**.
37
New cards
heating curve of water
the temperature changes of solid water as it is heated to a liquid and then to a vapour.