Amino Acids - Structure to full name
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
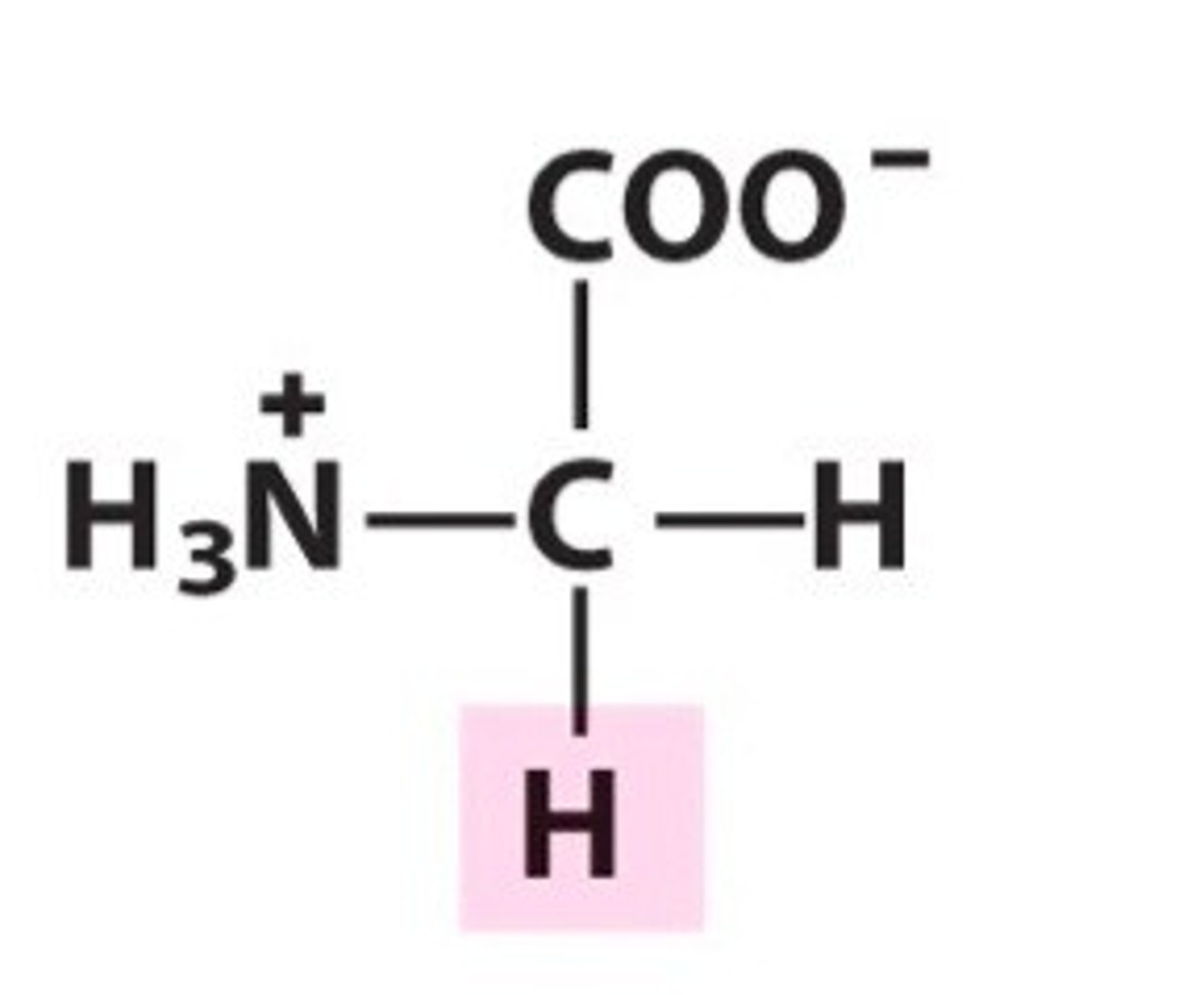
Name, 3 letter abbreviation and Classification
special features?
Glycine. Gly. Polar (up for debate)
Achiral and very small
Which amino acid may be found at tight turns in a protein due to its flexibility?
Glycine
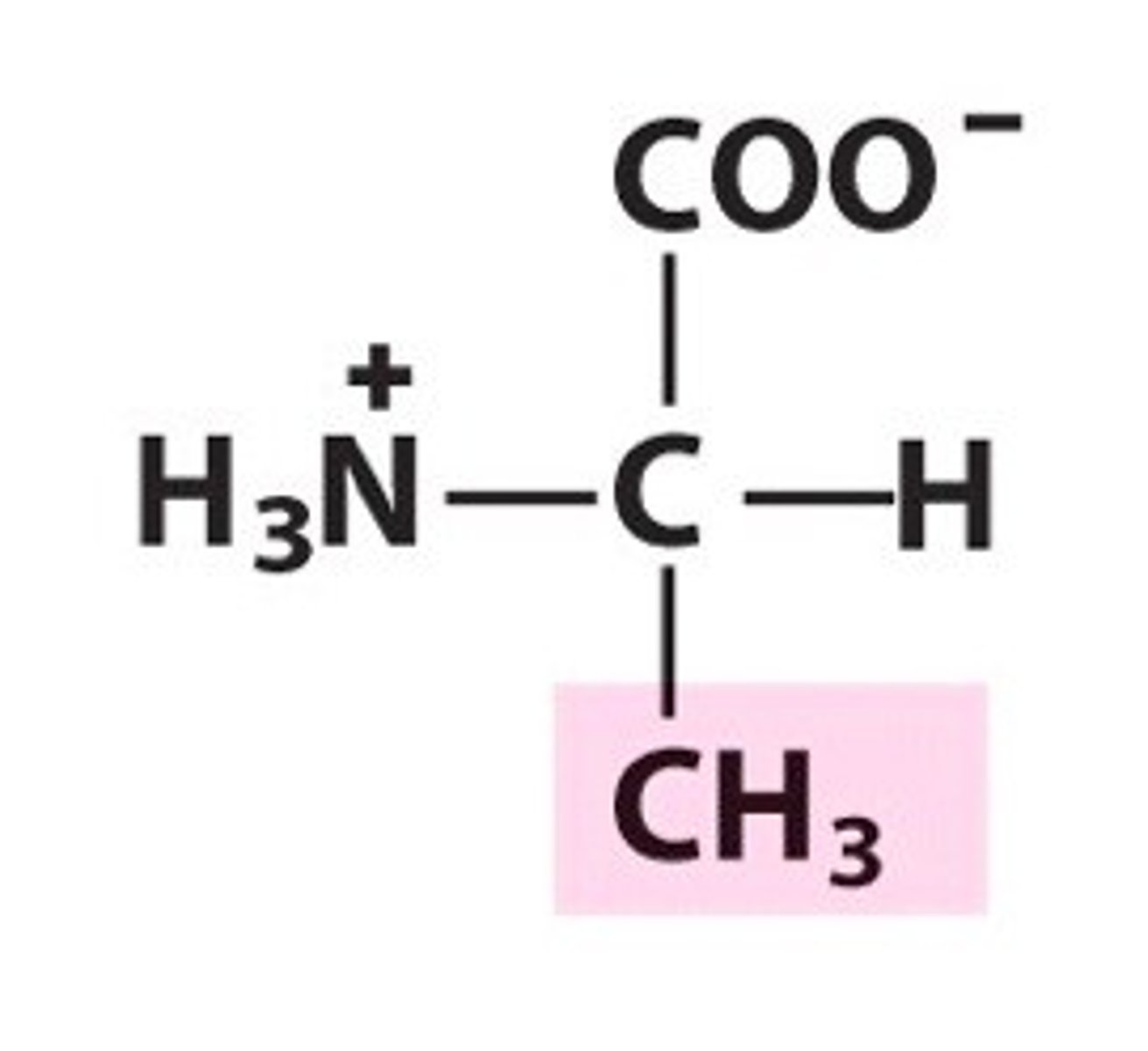
Name, 3 letter abbreviation and Classification
special features?
Alanine. Ala. Non-polar/hydrophobic
Would alanine or valine be more hydrophobic?
valine since it has a larger non-polar side chain
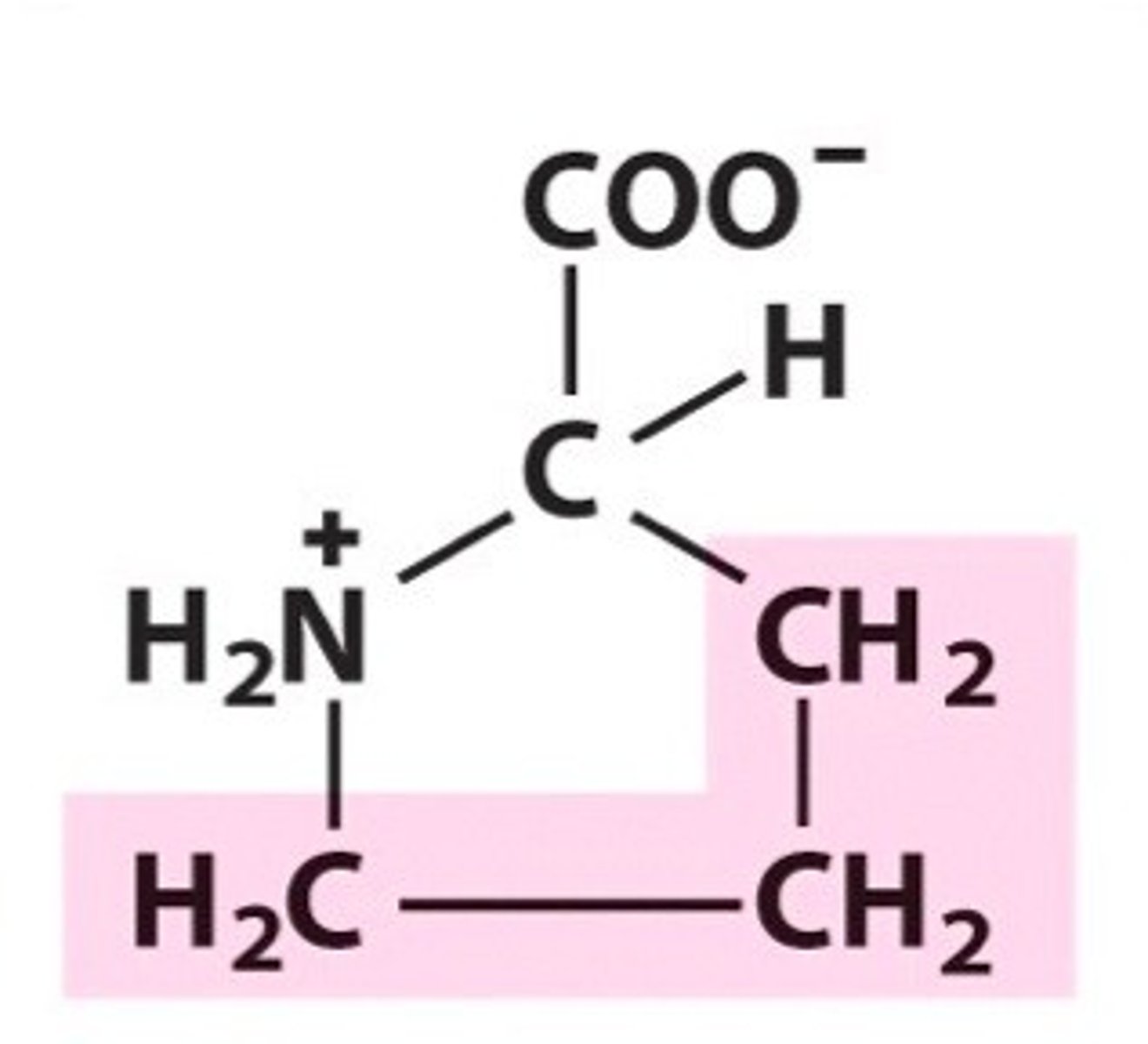
Name, 3 letter abbreviation and Classification
special features?
Proline. Pro. Non-polar/Hydrophobic.
Cyclic but not aromatic.
Is the amino group primary, secondary or tertiary in proline?
secondary
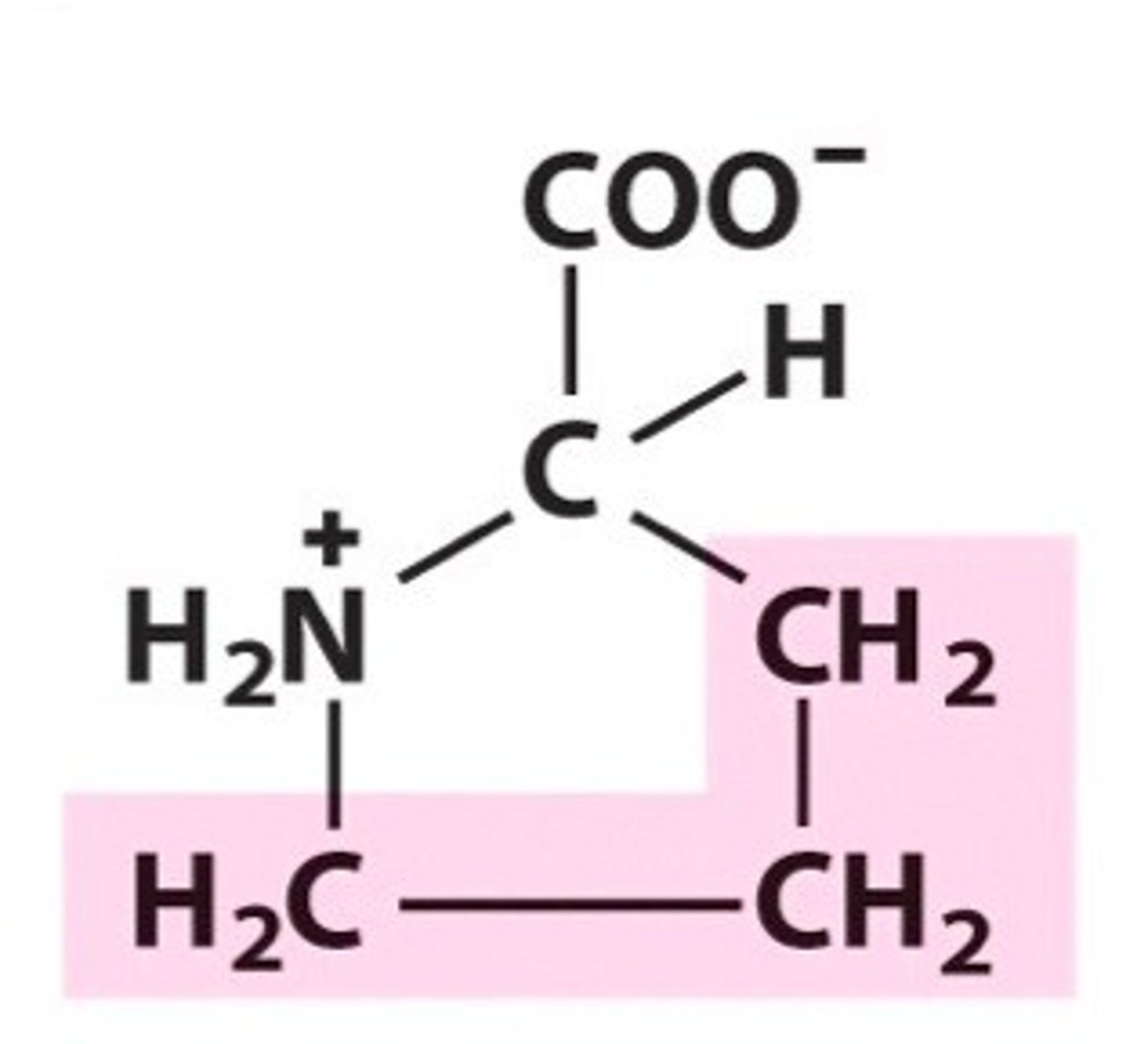
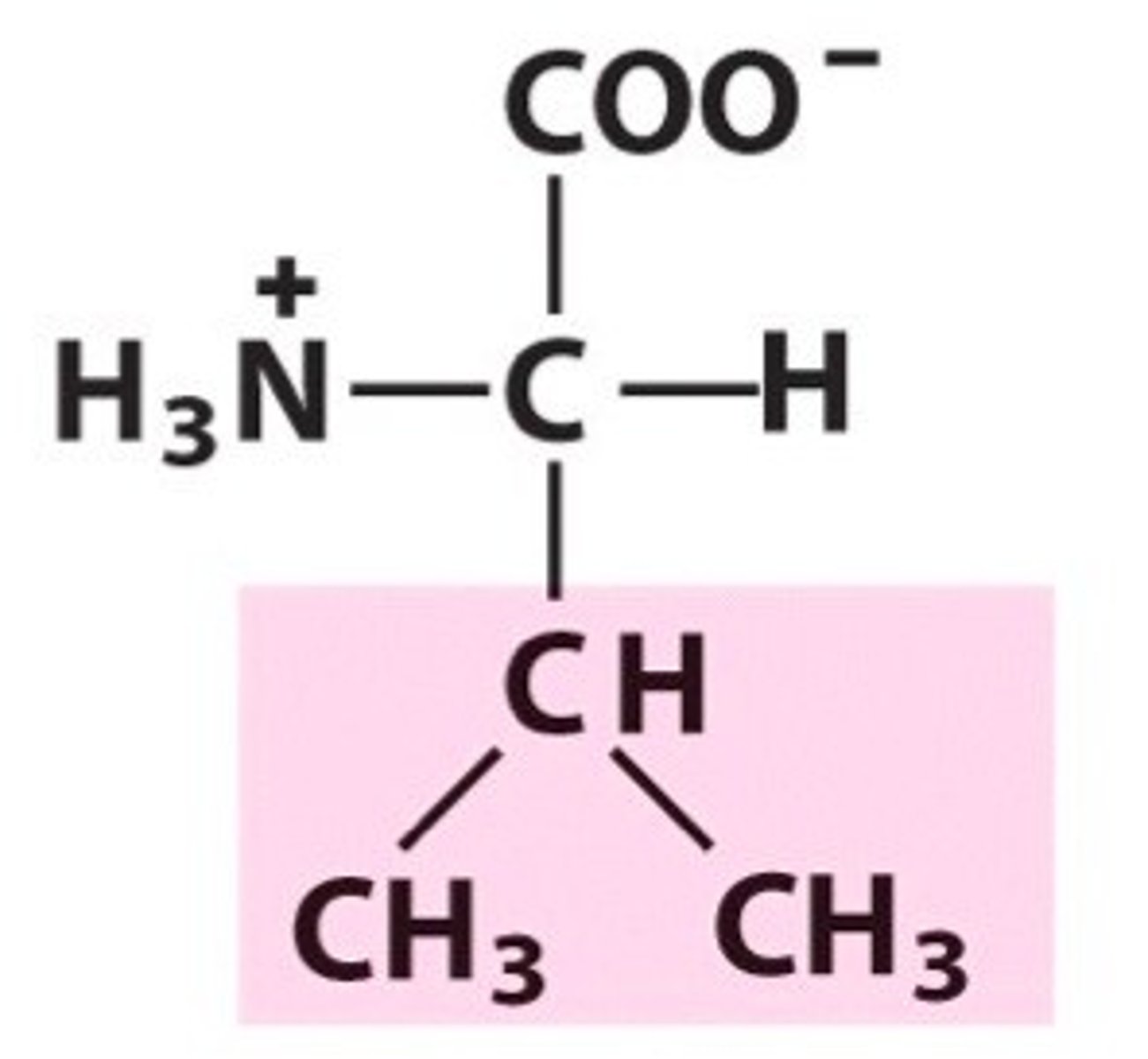
Name, 3 letter abbreviation and Classification
special features?
Valine. Val, Non-polar/hydrophobic
What are aliphatic amino side chains?
Aliphatic amino acids are non-polar and hydrophobic. contain only carbon and hydrogen.
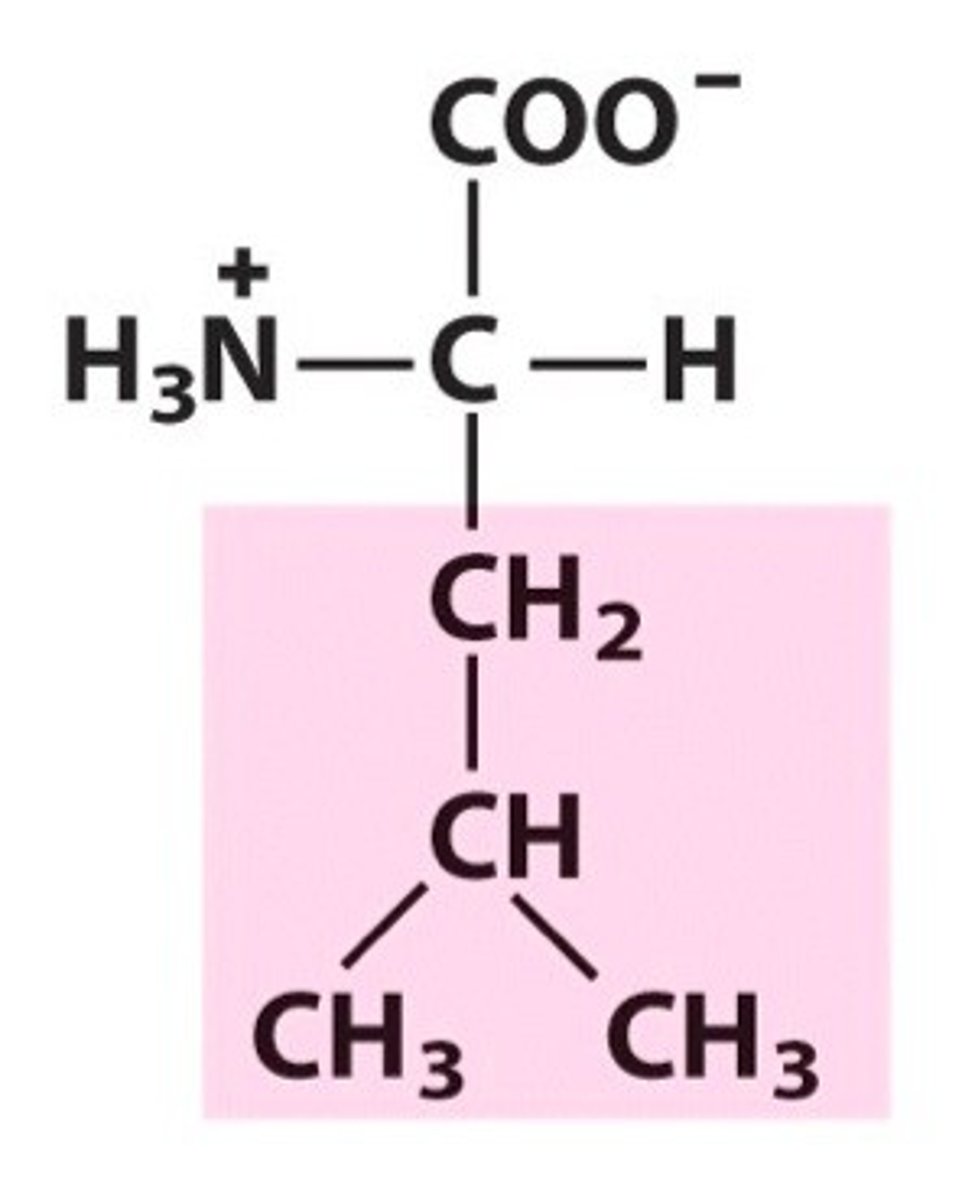
Name, 3 letter abbreviation and Classification
special features?
Leucine. Leu. Hydrophobic/Non-polar
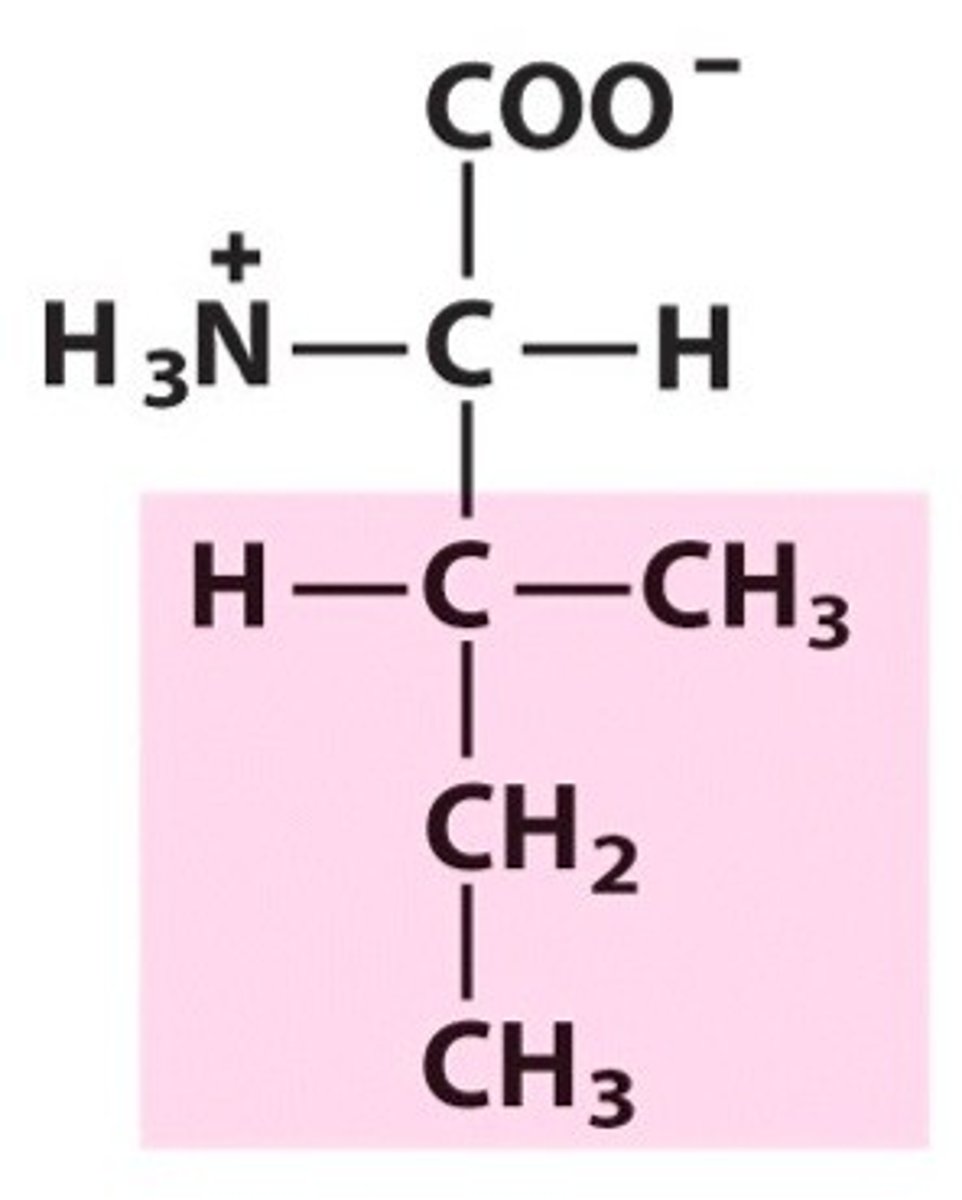
Name, 3 letter abbreviation and Classification
special features?
Isoleucine. Ile. Hydrophobic/Non-polar
2 chiral carbons!
What are all the aromatic aminos?
Tryptophan, Histidine, Tyrosine, Phenylaline
Which 2 aminos have >1 chiral carbon
isoleucine and threonine
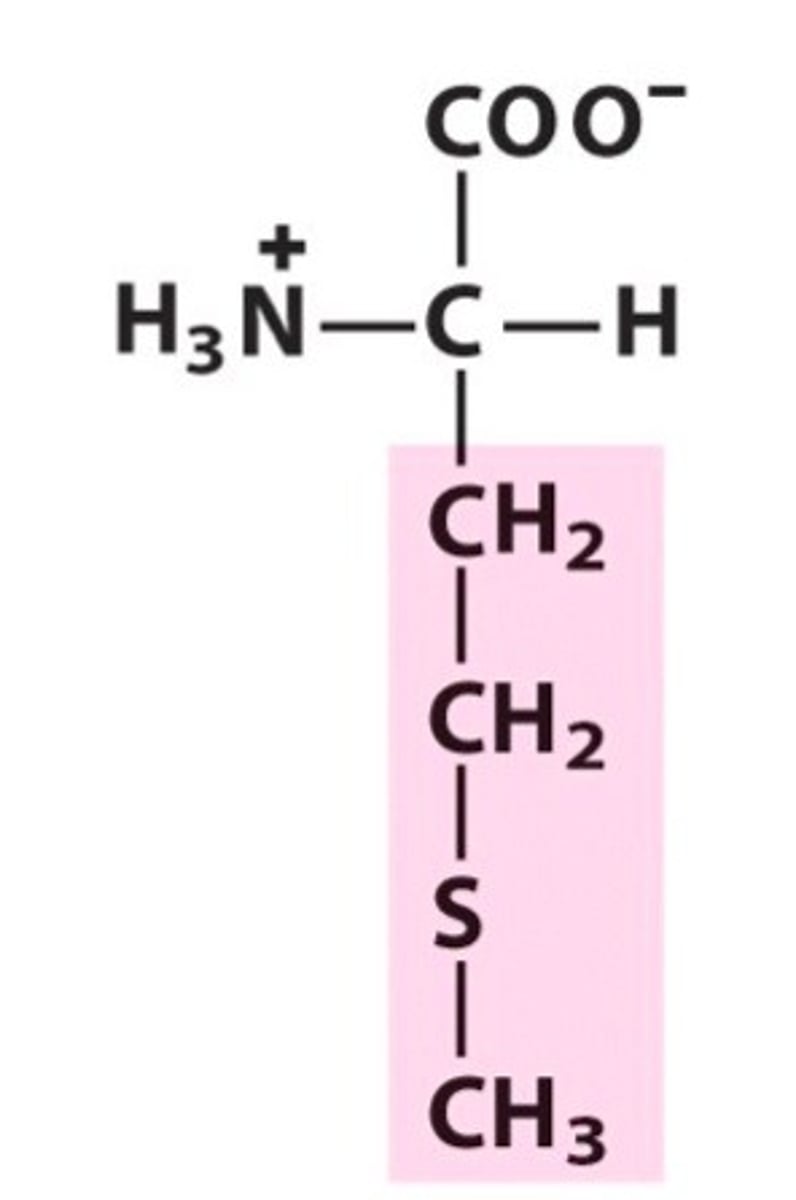
Name, 3 letter abbreviation and Classification
special features?
Methionine. Met. Hydrophobic
even though sulfur is present (thioether), it is a non-polar side chain.
Unlikely to form H bonds.
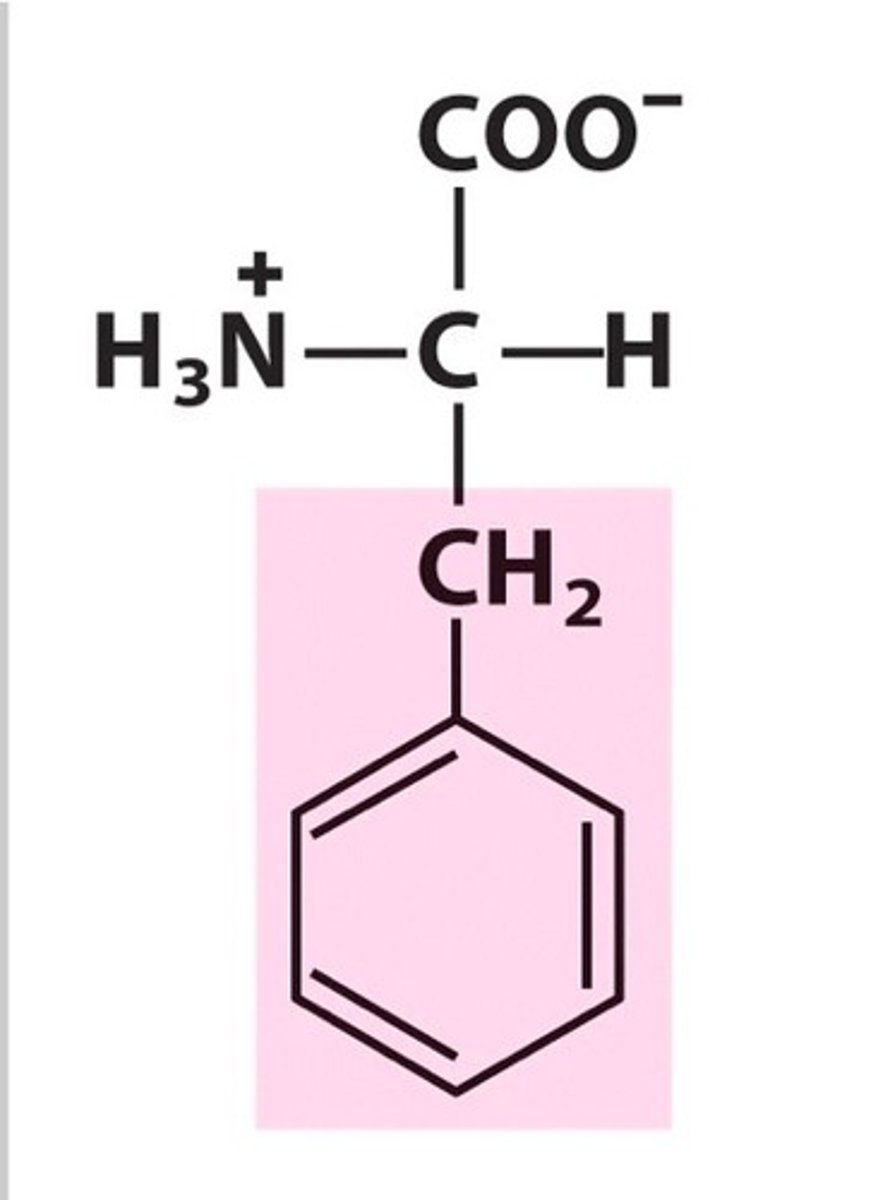
Name, 3 letter abbreviation and Classification
special features?
Phenylalanine. Phe. Hydrophobic
Aromatic R group: absorbs UV very weakly at 280nm
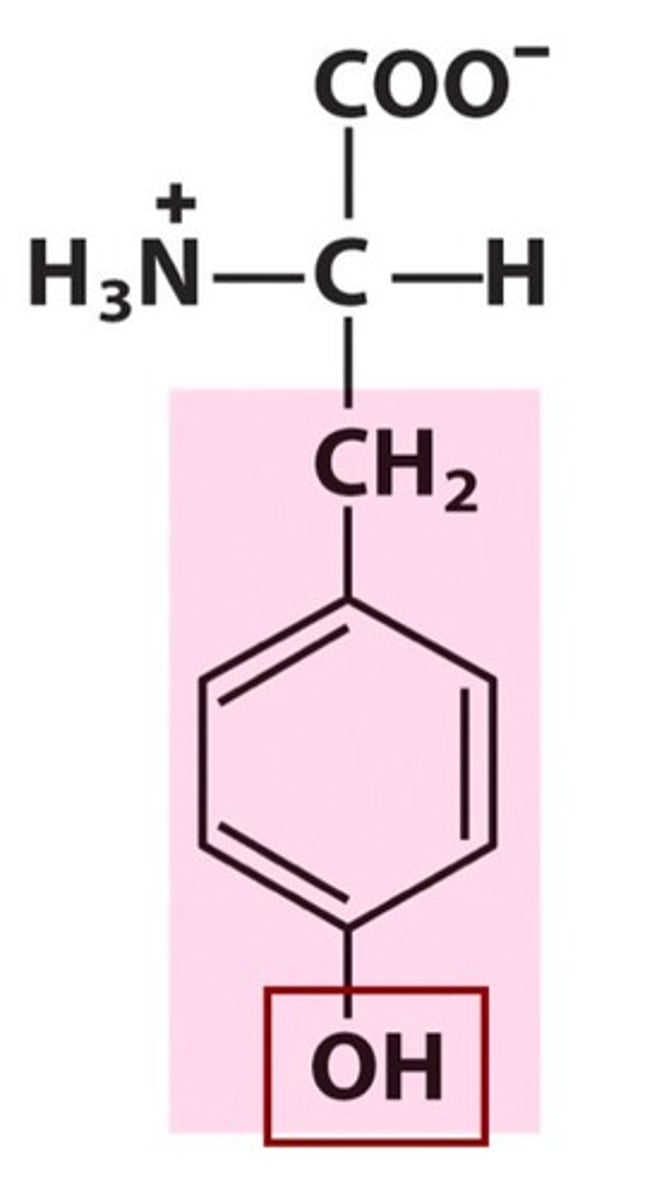
Name, 3 letter abbreviation and Classification
special features?
Tyrosine. Tyr. Polar.
Can form H-bonds but also participate in hydrophobic interactions!!
Absorbs UV at 280nm
due to OH group, it can be phosphorylated
pKa = 10.5 therefore has H under biological conditions (negative charge at pH 14)
Which 7 aminos have ionizable R groups?
Glutamate, Aspartate, Lysine, Arginine, Tyrosine, Histidine, Cytsteine
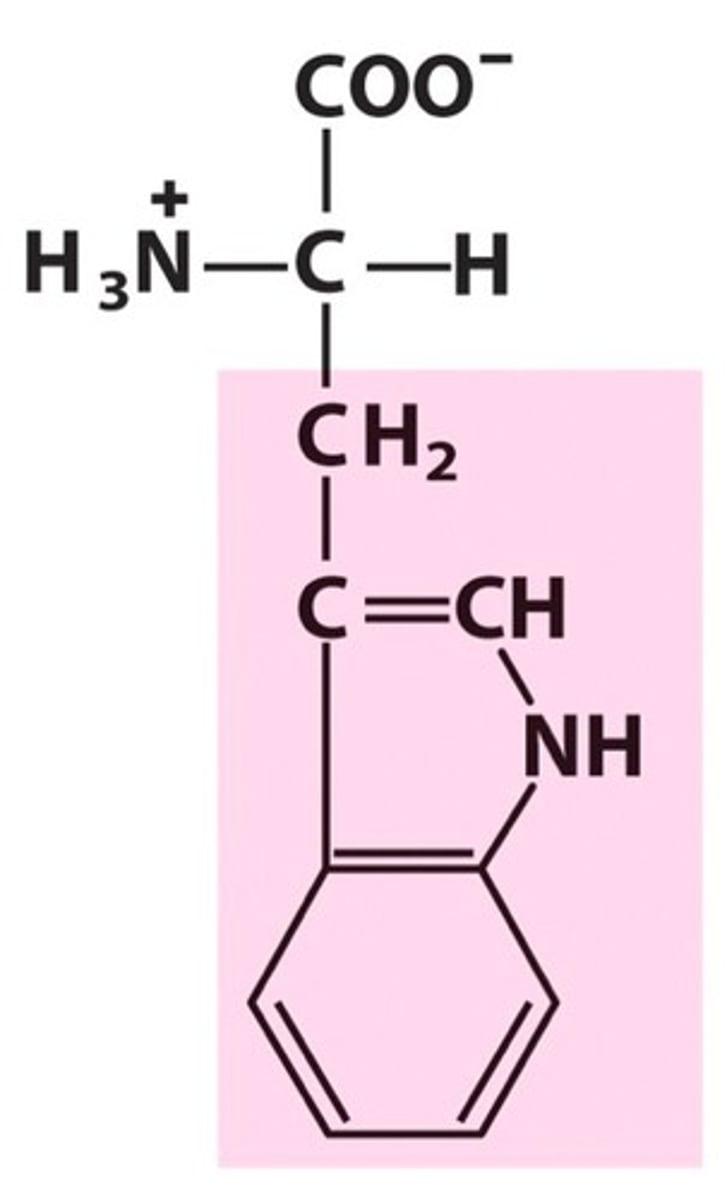
Name, 3 letter abbreviation and Classification
special features?
Tryptophan. Trp. Hydrophobic.
Biggest and bulkiest side chain. Hydrophobic but can form an H bond.
Heterocyclic and Absorbs UV Strongly at 280nm
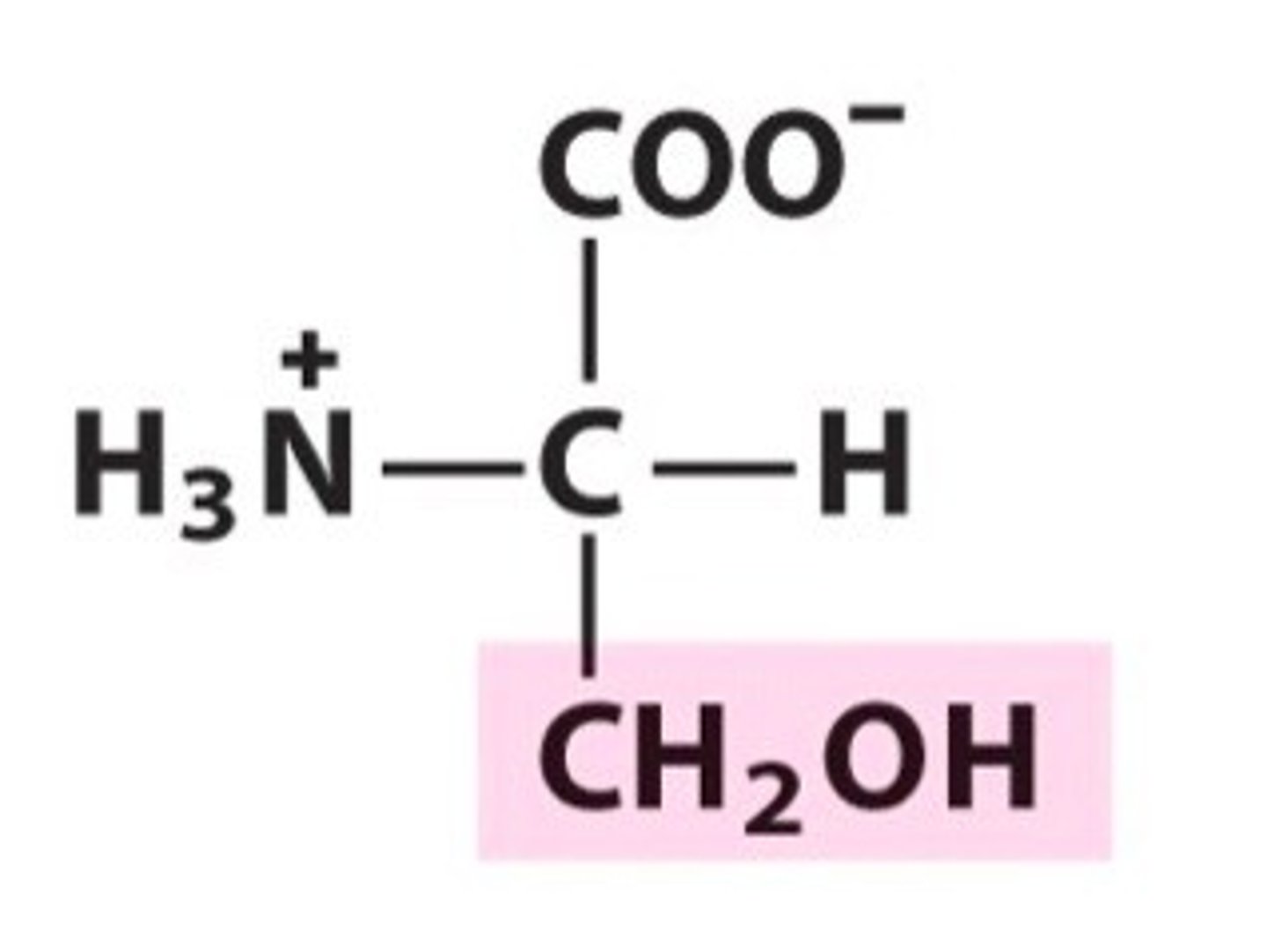
Name, 3 letter abbreviation and Classification
special features?
Serine. Ser. Polar
Can be phosphorylated due to OH group.
Participates in H bonding.
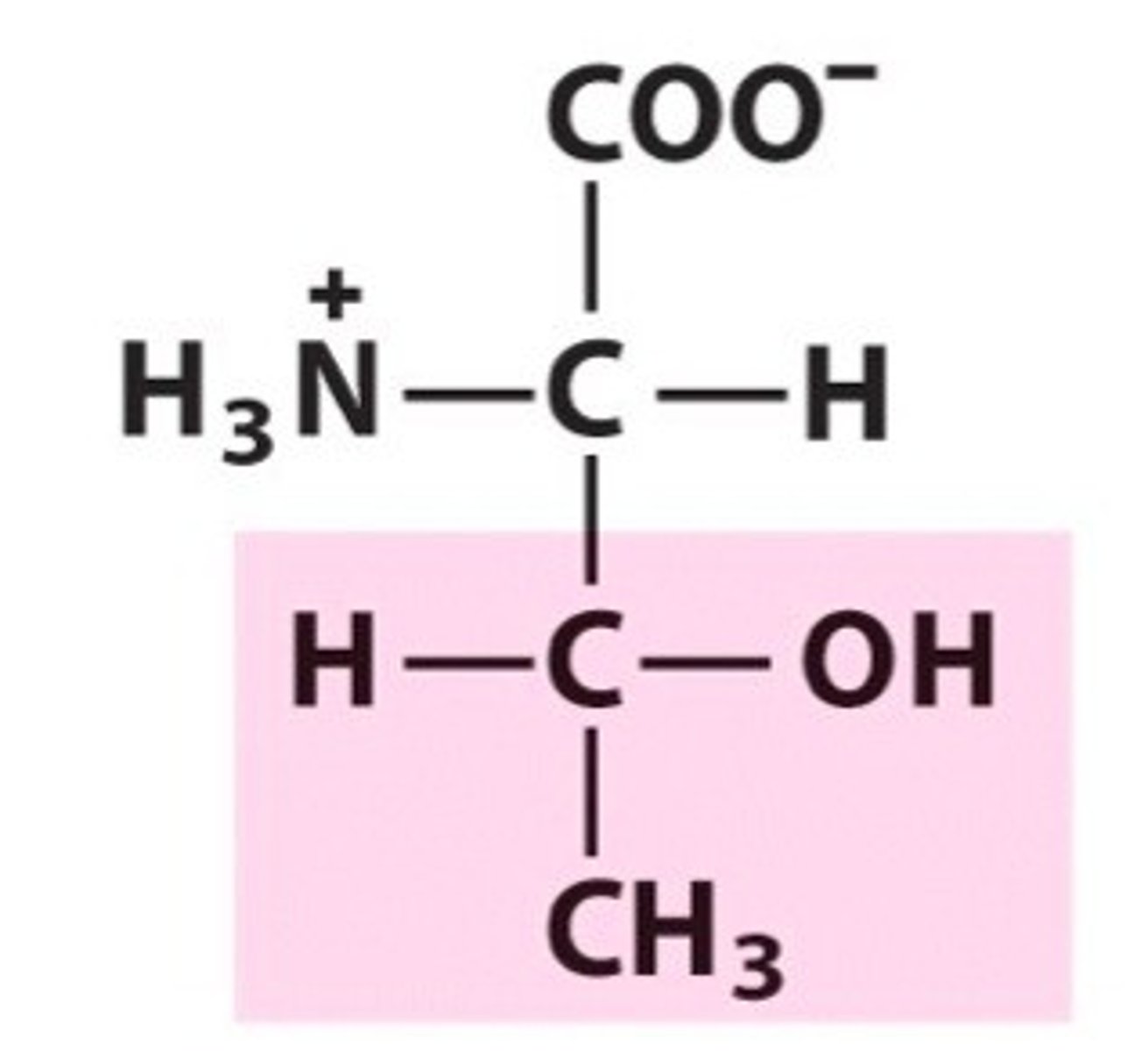
Name, 3 letter abbreviation and Classification
special features?
Threonine. Thr. Polar
2 chiral carbons!
Can be phosphorylated
H-bonds as donor and acceptor
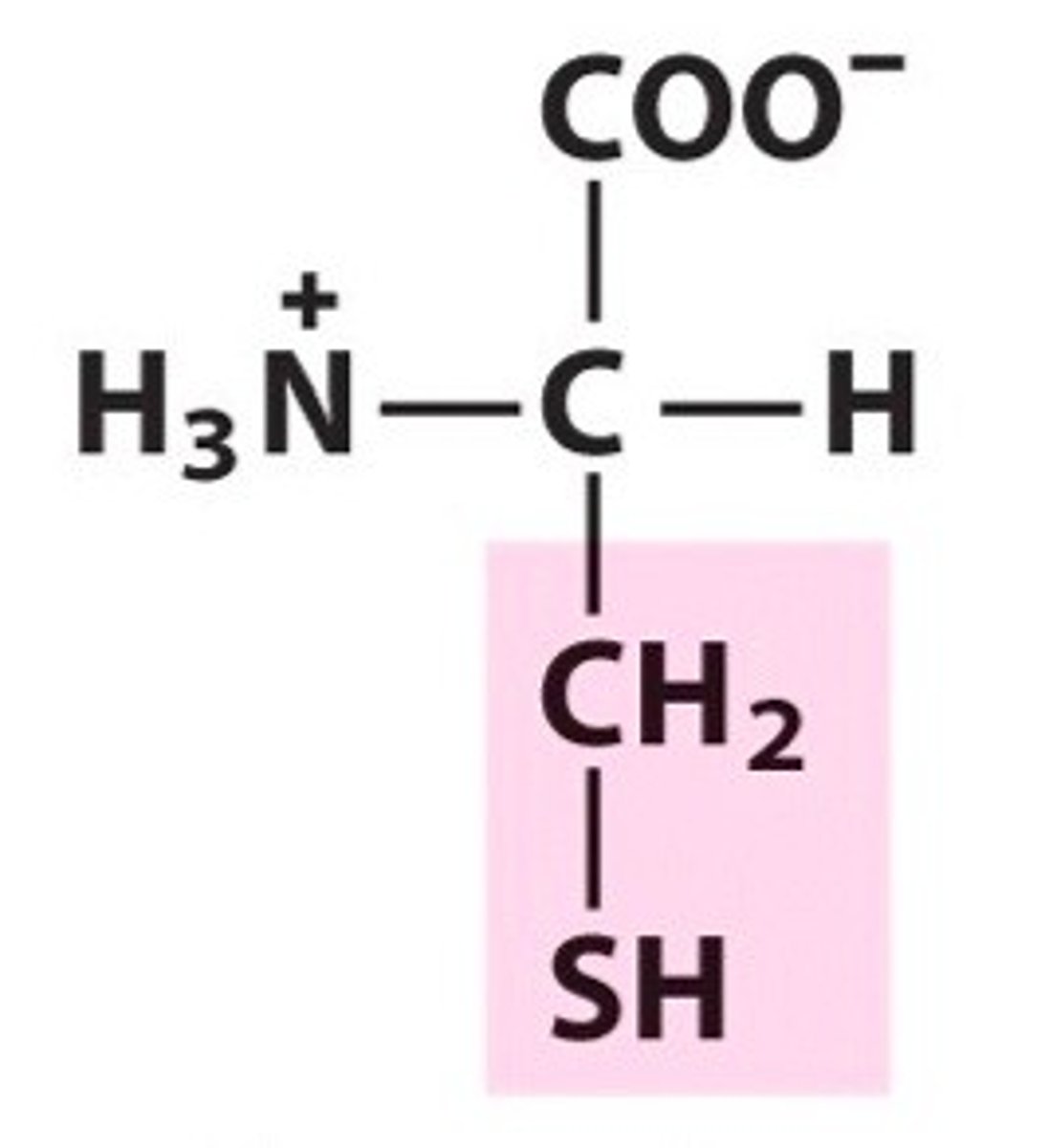
Name, 3 letter abbreviation and Classification
special features?
Cysteine. Cys. Polar.
Can form disulphide bridges/bonds with other Cys.
Can form H-bonds but doesn't act as an acceptor
pKa = 8.5 can give up H at pH 14
What are the necessary conditions to form a disulphide bridge and where can this occur?
Two Cys residues must be close enough to form a bond
Oxidizing environment such as the mitochondria or the extracellular fluid
If S-S bonds are formed in an oxidizing environment, what breaks a disulphide bond?
A reducing env.
What is Cystine? Is it polar or hydrophobic?
Two cysteine side chains interacting in a disulphide bond.
Relatively hydrophobic (S-S bond not S-H)
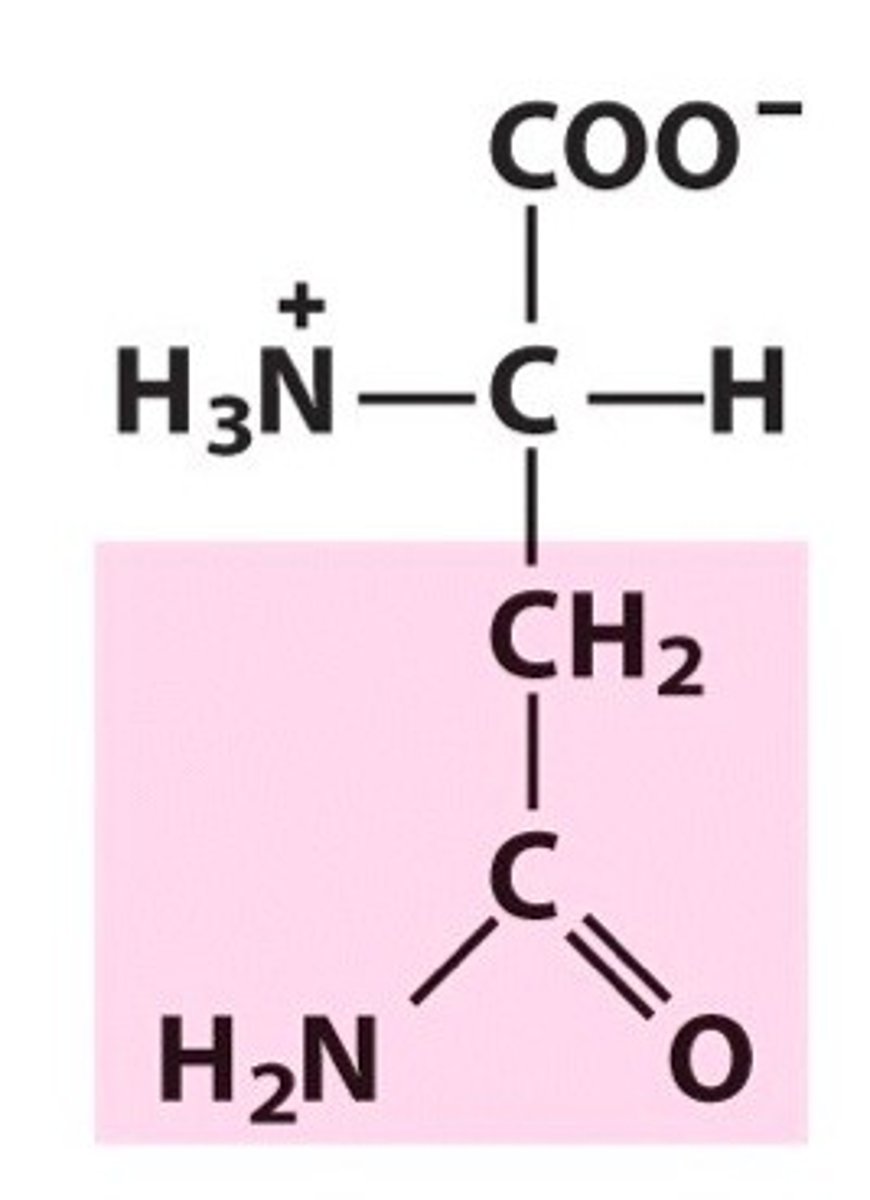
Name, 3 letter abbreviation and Classification
special features?
Asparagine. Asn. Polar.
Amide group and forms hydrogen bonds (O acceptor, N donor)
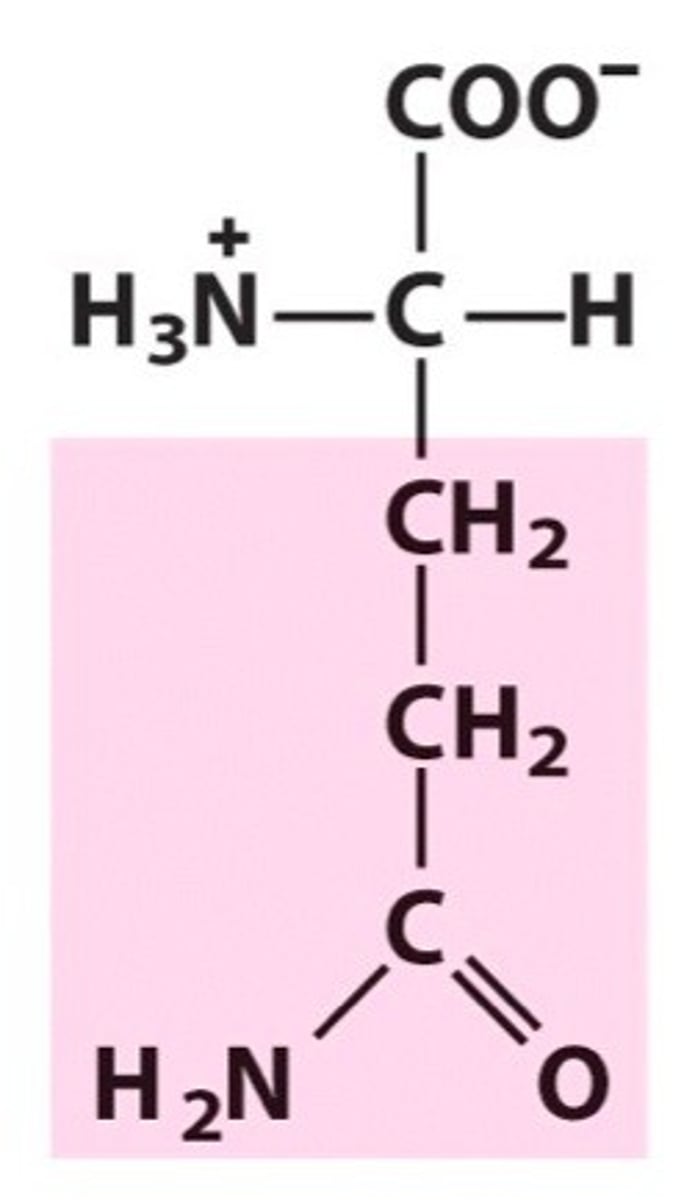
Name, 3 letter abbreviation and Classification
special features?
Glutamine. Gln. Polar
Amide group, forms H-bonds
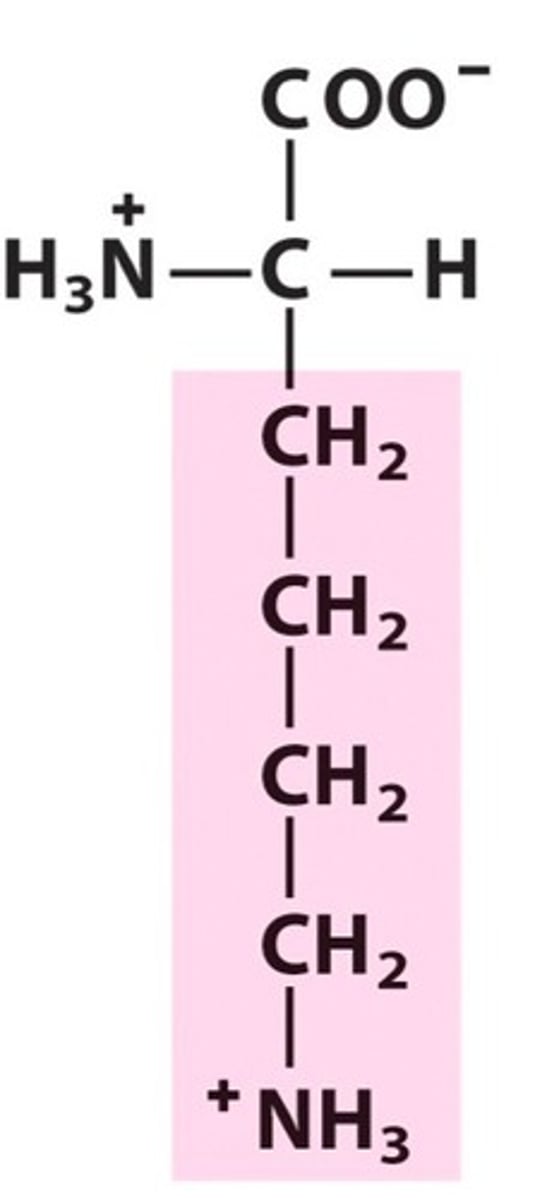
Name, 3 letter abbreviation and Classification
special features?
Lysine. Lys. Charged.
Positive charge from NH3 at pH 7
pKa = 10.5 therefore neutral/loses H at pH 14. Basic amino acid
Long CH chain is hydrophobic?
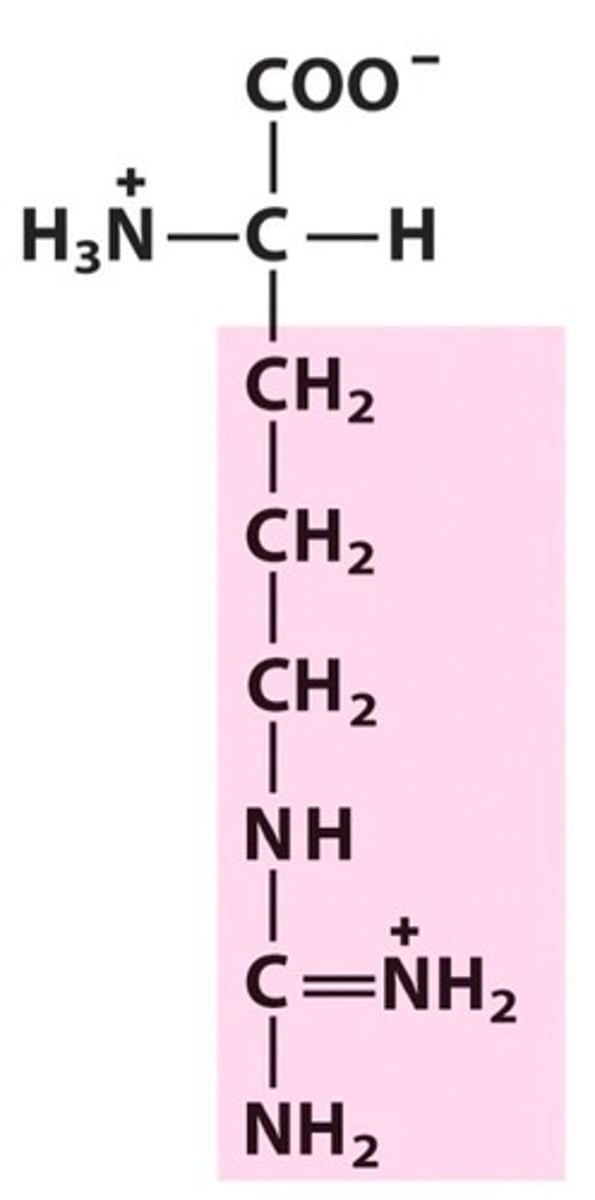
Name, 3 letter abbreviation and Classification
special features?
Arginine
Basic, but never deprotonated under biological conditions
pKa = 12.5
H bond donor only!
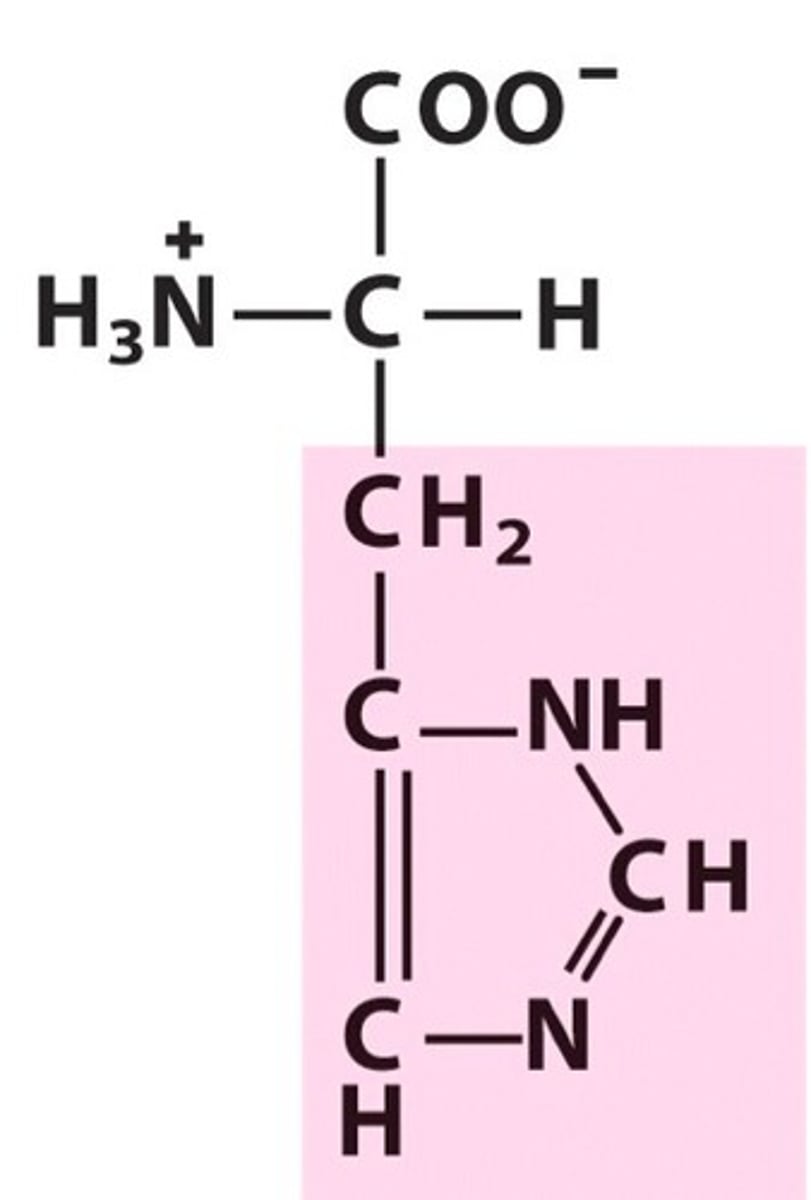
Name, 3 letter abbreviation and Classification
special features?
Histidine. His. Polar
Aromatic - abs weakly at 280nm
pKa = 6 therefore neutral at 7 but becomes protonated at pH 1 with a positive charge!
Histidine can act as an acid or a base in reactions and also participates in H-bonding.
At pH 10 and 1 is histidine protonated or not? what is its pKa
pKa = 6 therefore;
10 = no
1 = yes
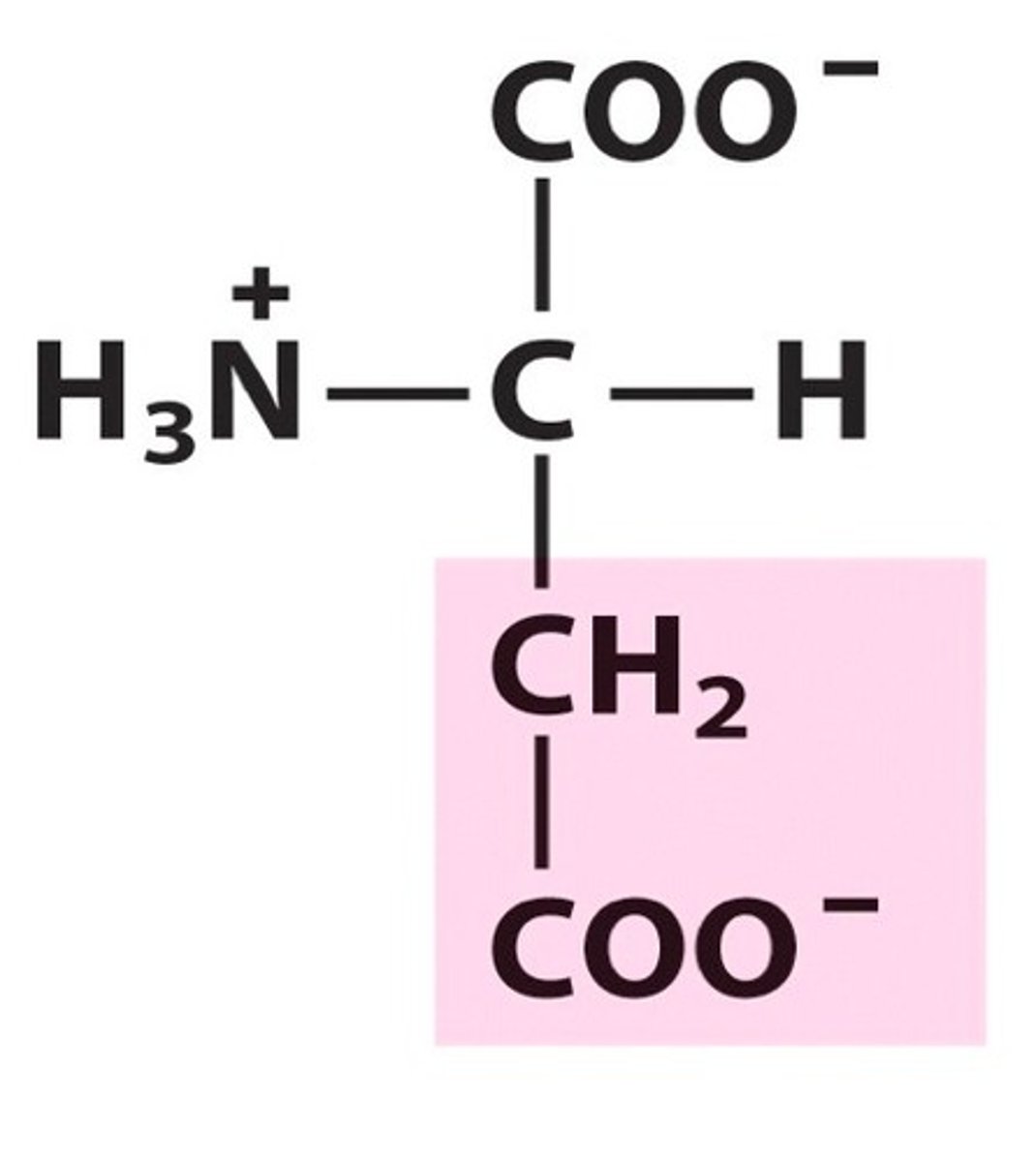
Name, 3 letter abbreviation and Classification
special features?
Aspartate. Asp. Charged
acidic amino acid. pKa = 4.0
Negative charge at pH = 7 but called aspartic acid at pH 1 since it becomes protonated
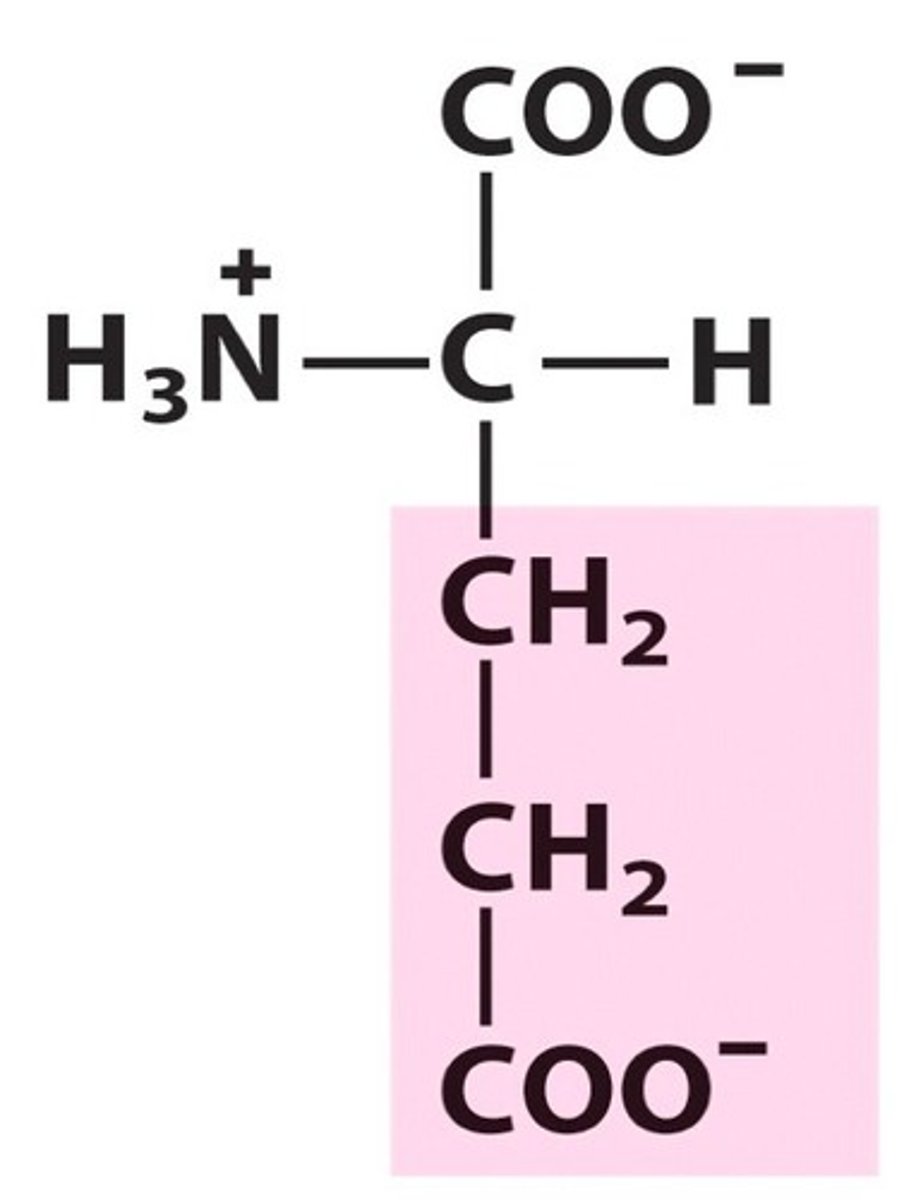
Negatively Name, 3 letter abbreviation and Classification
special features?
Glutamate. Glu. Charged.
pKa = 4: Negative at pH 7
acidic amino acid
called glutamic acid at pH 1 since becomes protonated