Aldol Condensation
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
aldol condensation rxn
additional of an enol or enolate to an aldehyde or ketone
what must the second species have?
alpha protons
how do u combine the aldehyde/ketone and second species ?
by work up with base or an acid
what is the final species after dehydration?
an alkene
what’s the first part of the mechanism of aldol condensation?
the base attacks an alpha proton reforms an alkene and gives O a negative charge
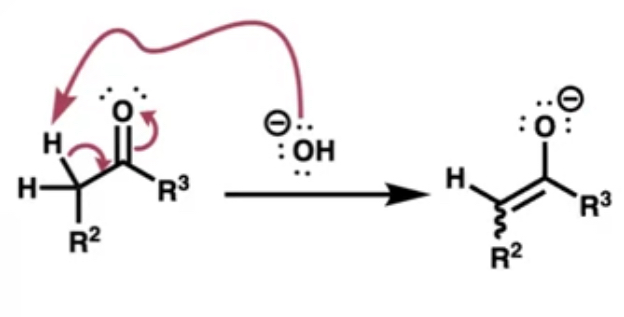
what does the first step of the mechanism result in?
enol resonance forms (carbanion)
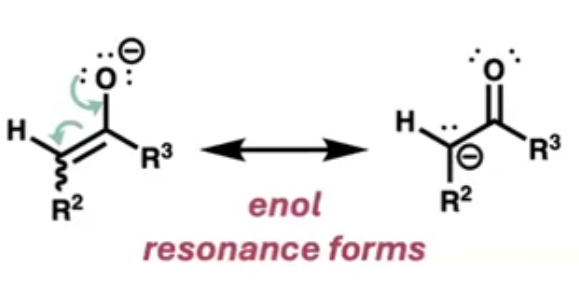
what does the carbanion act as?
a nucleophile attacking the carbonyl of the other species forming the C-C bond
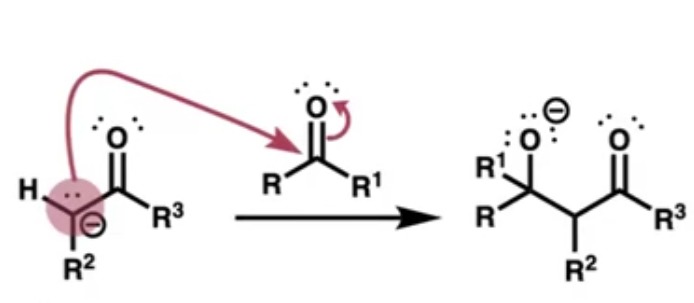
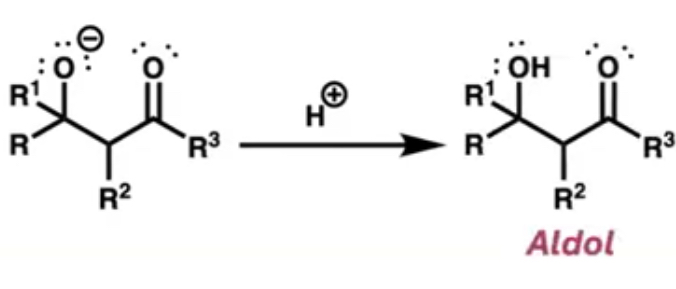
after the other species attaches what is added next?
acid(H+) which creates the aldol by connecting to the negatively charged O
what was used during the experiment ?
dibenzyl ketone and benzyl and added KOH & EtOH heating it to make the TPCP product
can dibenzyl ketone be enolized?
yes it has alpha protons
can benzil be enolized?
no it has no alpha protons
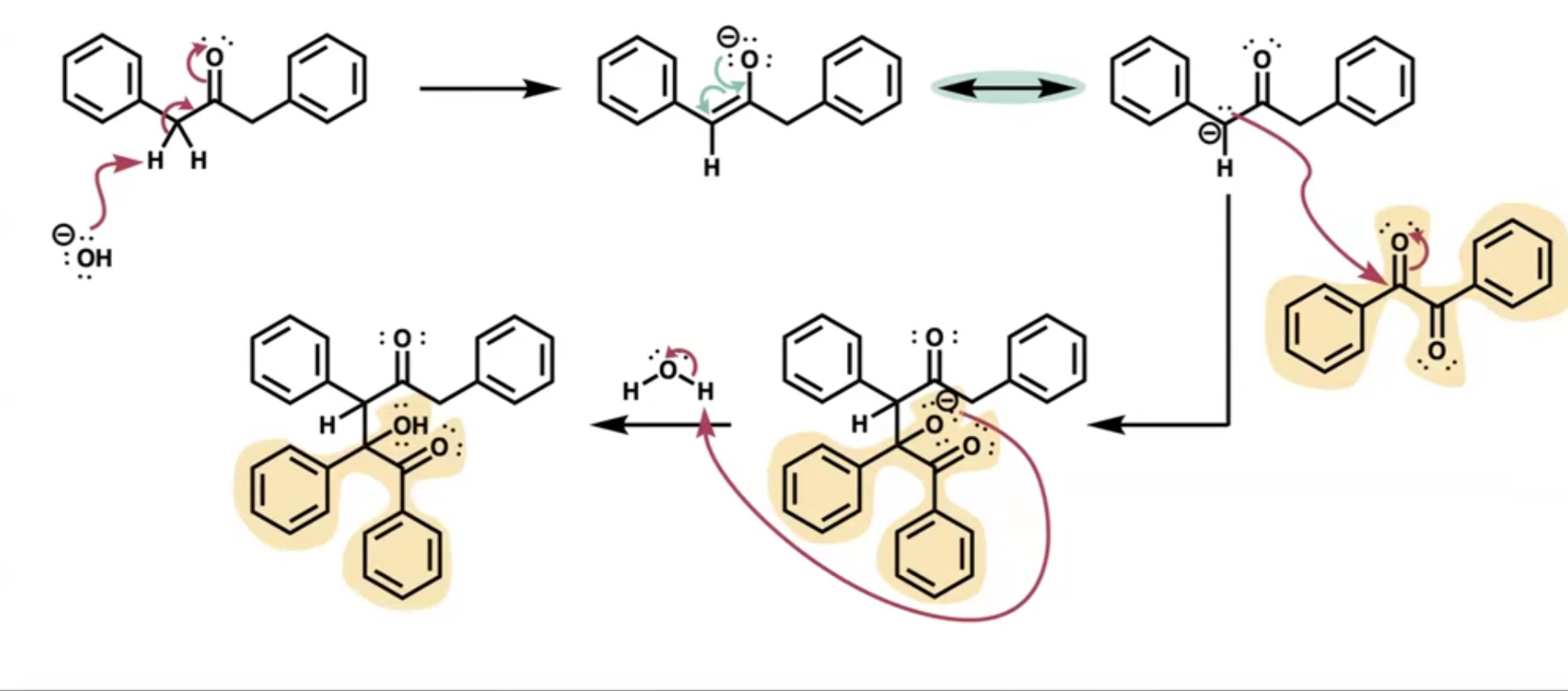
mechanism of dibenzyl ketone and benzil to make TPCP
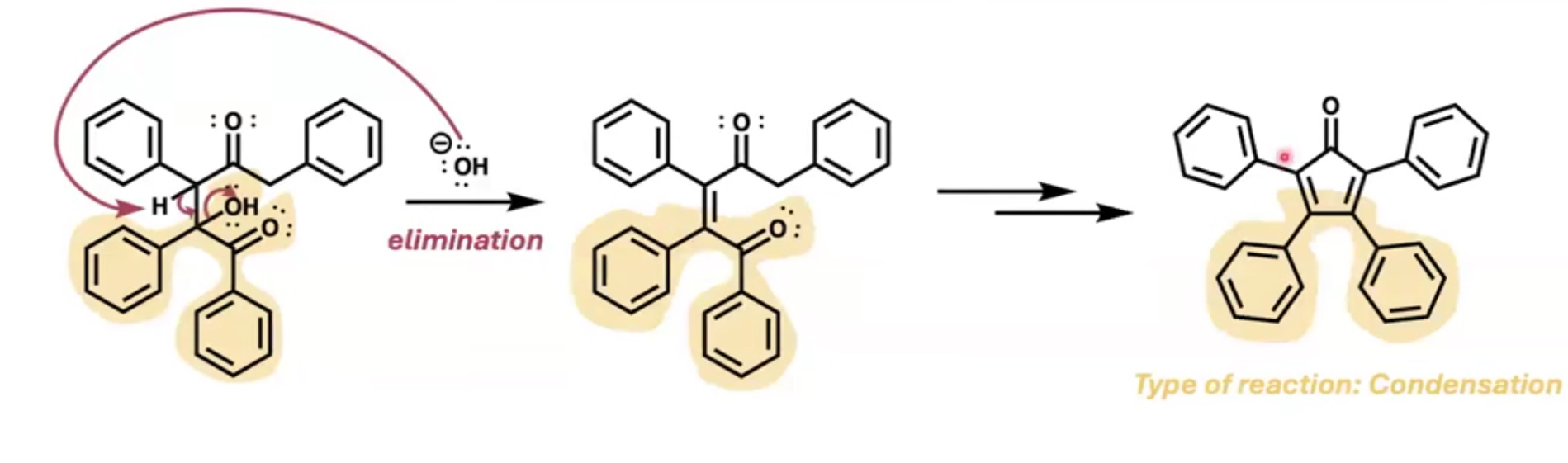
what 3 steps were done during the experiment for aldol condensation?
synthesis
isolation
MP, TLC, and UV-Vis
UV-Vis measures electronic transitions from?
200 nm to 700 nm
compounds have specific UV-Vis spectra due to?
their electronic structure
where do compounds w/color have absorbances?
in the visible region from 400 nm to 700 nm
atomic orbitals
describe where to expect electrons in a single atom
molecular orbitals
describe where to expect electrons in an entire molecule
excitation
electrons can move b/w molecular orbitals when hit w/energy or light
lamda max values
the wavelengths at which there is a peak in the spectrum; lambda w/ the maximum in absorbance
lambda max values are a measure of?
energy b/w molecular orbitals