Articulation Disorders Exam 2
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
111 Terms
The shape of the face tells you about the shape of the ___________
Dental structure
Nasal Cavity
Oral cavity
phonological processes
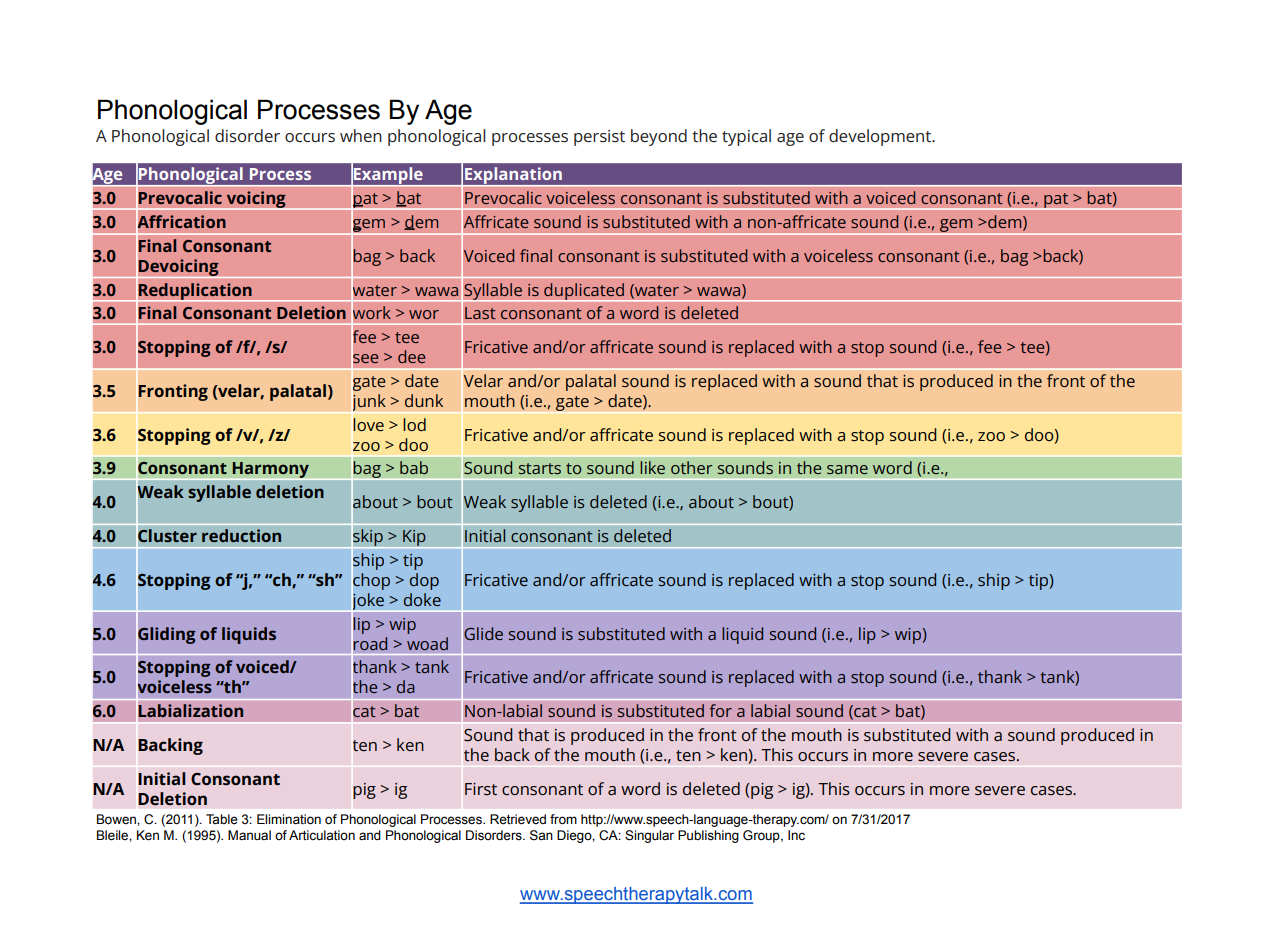
metaphon approach
for children who have failed to acquire the rules of the phonological system
minimal pairs - improves awareness of sounds
phase 1 - identify
phase 2 - awareness & application
Which contrastive approach differs by a single phoneme?
Minimal pairs
What has the most impact on intelligence?
Omissions
Metaphon theory is a good approach for children who exhibit...
Limited phoneme inventories
Display numerous phonological processes
Exhibit unusual phonological processes
What are the late 8 phonemes?
ʃ ɵ s z ð ʒ r l
What are the levels, in the correct order, of phase 1 of metaphon theory?
Concept, sound, phoneme, word
What does the Van Riper/ traditional approach rely on?
Clinician modeling
Which of the following is NOT a component of evidence- base practice?
Literature review
What is a good example of a minimal pair to use during therapy?
ring/wing
What are the contrasting approaches?
Conventional minimal pairs
Multiple oppositions - contrasts mult sounds w/ 1 error difference
Maximal approches - comparing very different words (distinction)
What is the most important criteria to consider when crossing therapy goals?
Intelligibility
What is a characteristic of a square face?
Abnormally wide palate
Problems with lateral margin stabilization
Problems with palatal sounds
What is an important detail to remember when administering phase 1 of metaphon theory?
Child should not
What percentage of children with SSD exhibit academic difficulty through high school?
50-70%
What is the purpose of the oral mech exam?
To identify or rule out structural or functional factors that relate to a communication disorder
What is not important when picking treatment targets?
Quantity of words
What is an example of a minimal pair?
luck/yuck
ring/bling
What are the SMART goals?
specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, timely
What speech errors are most common when having a long face?
Frontal lisp
What type of child would you use the cycles approach with?
Severe phonological disorder
Which is NOT a part of the MAYO 10? (used of CAS apraxia)
Faster rate of speech
How many phonemes differ in minimal pairs?
1
middle 8 sound?
/t, ŋ, k, g, f, v, tʃ, dʒ/
At what age should a child typically be 100% intelligible?
7
Which minimal pair is most appropriate to use to hear gliding?
ring/ wing
Which is NOT a part of an oral mech exam?
Hearing screening
Phonetic inventory is any sound a child can produce
True
Which is NOT a late 8 phoneme?
/w/
What do dysarthria and CAS have in common?
They are both motor speech based
Which of these minimal pairs would be best targeted in therapy for stopping?
/sɑg/ + /dɑg/
Which of these best describes knowledge of results?
Outcome accuracy
Which is not an aspect of the cycles approach?
Multiple oppositions
Which characteristic describes a phonological disorder?
Consistent patterns of error
Which of these is not a part of the assessment process?
Reliability
What do the phonological therapy approaches focus on?
Function of speech
How intelligible should a child be at 2 years old?
50%
Which type of feedback is most important?
Extrinsic
Muscular control: respiration, phonation, resonance, articulation, and prosody are the speech characteristics of dysarthria?
True
Which is an impairment in planning and programming the movements necessary to produce speech sounds?
Childhood Apraxia of Speech
What is the most ideal face shape?
Mesocephalic
Who is the grandfather of speech pathology?
Charles Van Riper
How many words are selected for the core vocabulary approach?
50
A speech difference must meet what criteria to be an SSD?
Arises during childhood & is not directly attributable to damage to speech mech
Not result of dialect or accent
Child or members of child's community consider it a speech problem
What is the key characteristic of CAS which differs from dysarthria?
Difficulty with motor planning
Which is NOT an element of the Van Riper Approach?
Core activity
What option best describes a phonological disorder?
Consistent errors, form patterns, unintelligible
Which aspect is NOT a precursor of motor learning?
Stimulability
Which most accurately describes the cycles approach?
Stimulates the...
What therapy focuses on production using contrasting word pairs instead of individual sounds?
Contrast therapy
How many steps are in the Hodson's steps of phonological acquisition?
7
What measures the individuals development of particular skills in terms of absolute levels of mastery?
Criterion- referenced test
What is damaged in the brain to cause Ataxic dysarthria?
Cerebellum
When considering appropriate statements to focus on during therapy, which statement would be most appropriate?
'Great! I can understand that word when you say is with your clear /s/!"
Which is not appropriate to consider when choosing which goals to target first?
Stimulability
Family Dynamic
What makes metaphon therapy different than other treatment approaches?
The beginning requires the client to just listen respond verbally
What step in the Van Riper approach does Dr. Highfill omit?
Step 2: production of sound in isolation
What are characteristics of phonological speech errors?
Consistent, predictable
Which of the following is NOT a contrastive approach?
Cycles approach
Which child would NOT benefit from metaphon therapy?
Children who display one process
Which of the following is an example of stopping?
/ʃu/ --> /tu/
Select characteristics of CAS (multiple)
Voicing errors
Equal stress
Which of the following is considered the "traditional" approach, characterized by targeting individual phonemes?
Van Riper Approach
If you have a client who presents with a motor- speech disorder, which concept would you apply in treatment?
Principles of motor speech
What does SMART stand for?
Specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, time- bound
Given the minimal pair "bat" and "cat", which phonological process would you be targeting?
Backing
What is the key difference between CAS and dysarthria?
Sequencing v. coordination
Bobby pronounces /t/ in place of /b/, as in /tæt/ for /bæt/, what is this?
Alveolar assimilation
What is the purpose of the oral mech exam?
Assess for any abnormal facial structures that contribute to communication disorder
What kind of patient would you use the multiple oppositions approach on?
Moderate to severe speech sound disorders
What is the first step of differential diagnosis?
Assessment
What is the first step of the traditional approach?
Ear training
Which of the following is a lesser known/seen phonological process?
Metathesis
What is a characteristic of CAS?
Difficulty with planning & programming of motor speech movements
Which is an example of stridency deletion?
Soup--> toup /s/ --> /t/
Feet--> teet /f/-->/t/
Which treatment approach targets 50 vowels in total, but 10 per session?
Core vocabulary approach
What type of child would the phonological therapy approaches be used one?
Consistent errors that form patterns and has unintelligible speech
What phonemes are included in the early 8?
m n, j b w d p h
What characteristics indicate childhood apraxia of speech?
Inconsistent errors, prosody, groping, planning, difficulty
If a child replaces the phoneme /d/ for /g/ in the words, /go/, what is this called?
Fronting
Which diagnostic tool would best help a clinician assess stimulability for specific speech sounds?
Imitation tasks during a speech assessment
What is the primary goal of the cycles approach>
To gradually increase intelligibility by targeting phonological patterns in cycles
A child with a diagnosis of dysarthria is most likely to exhibit which of the following symptoms?
Difficulty with articulation due to an underlying motor control problem
What is the primary purpose of a speech sample analysis in diagnosing speech sound disorders?
To evaluate spontaneous speech production and phonological patterns
A child exhibits consistent errors, such as omitting final consonants in words and backing of sounds, suggesting a likely diagnosis of:
Phonological process disorder
Which of the following is most likely to cause a speech disorder sue to neurological impairment or muscle weakness in a child?
Dysarthria
Which of the following is a characteristic of articulation disorder but not typically seen in Childhood Apraxia of Speech
Consistent errors in producing specific phonemes
Which activity would most likely be used in a session using the Multiple Oppositions Approach?
Practicing works like "tip, ship, chip, slip" if the child substitutes all of them with "dip"
What does diadochokokinetic (DDK) rate testing assess in a speech sound evaluation?
Oral motor control and speech
Which of the following signs might indicate velopharyngeal insufficiency during an oral mechanism exam?
Nasal emission during speech
Compared to minimal oppositions therapy, maximal oppositions therapy focuses on:
Greater Feature differences
Knowledge of Results (KR) feedback focuses on:
Whether the response was correct
Which of the following is most commonly observed in children with dysarthria?
Imprecise and slurred speech with reduced intelligibility
Why is the Cycles Approach considered a "cycle"?
It targets several patterns in succession and then repeats them
A child substitutes /t/ for /k/ (e.g., "tat" for "cat"). This is an example of which process?
Fronting
What is one advantage of delayed feedback in speech motor learning?
Forces reliance on internal feedback
Which technique is commonly used in the traditional approach to correct misarticulations?
Drill and practice
Which child would be the most appropriate candidate for the Cycles Approach?
A child with multiple consistent phonological processes reducing speech intelligibility
In the Core Vocabulary Approach, the primary goal is to:
Achieve consistent word production