APUSH Period 1
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 4:15 PM on 3/13/25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
1
New cards
maize
The Mayas and the Incas cultivated this crop; important stable food supply.

2
New cards
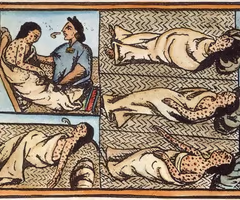
diseases
When Europeans came to America they brought smallpox and measles to which the natives had no resistance and millions perished.
3
New cards
Encomienda
A grant by the Spanish king or queen that allowed a person to demand tribute and forced labor from the Native people in a defined territory.

4
New cards
slavery
As far back as the 1500s the Spanish brought captured Africans to America to provide free labor.

5
New cards
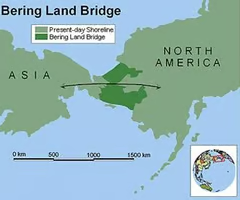
land bridge
Some time between 10,000 and 40,000 years ago, people migrated from Asia to the Americas, across this area that connected Siberia and Alaska.
6
New cards
Adena-Hopewell
This American Indian culture centered in Ohio created large earthen mounds as tall as 300 feet.

7
New cards
Hokokam, Anasazi, and Pueblos
These American Indians were located in the New Mexico and Arizona region. They developed farming using irrigation systems.

8
New cards
Lakota Sioux
American Indian tribe that started using horses in the 17th century. This allowed them to change from farming to nomadic buffalo hunting.

9
New cards
Mayas
From A.D. 300 to 800, this highly developed civilization built large cities in what is today's southern Mexico and Guatemala.

10
New cards
Incas
This highly developed civilization developed a vast South American empire based in Peru.

11
New cards
Aztecs
Civilization flourished in central Mexico starting around 1300.

12
New cards
Conquistadors
These Spanish explorers and conquerors of the Americas sent ships loaded with gold and silver back to Spain making it the richest and most powerful nation in Europe.

13
New cards
Hernan Cortes
He conquered the Aztecs in Mexico.

14
New cards
Native Americans
The first people to settle North America arrived as many as 40,000 years ago. They came from Asia and may have crossed by a land bridge connecting Siberia and Alaska.

15
New cards
Francisco Pizarro
He conquered the Incas in Peru.

16
New cards
Roanoke Island
In 1587, Sir Walter Raleigh attempted to establish a settlement here, but it failed.

17
New cards
compass
One aspect of the Renaissance was a gradual increase in scientific knowledge and technological change. Europeans made improvements in the inventions of others. this invention was used in sailing.

18
New cards
printing press
This invention in the 1450s spread knowledge across Europe.

19
New cards
Ferdinand and Isabella
They united Spain, defeated and drove out the Moors. In 1492, they funded Christopher Columbus's voyage to America.

20
New cards
Protestant Reformation
In the early 1500s, certain Christians in Germany, England, France, Holland, and other northern European countries revolted against the authority of the pope in Rome.

21
New cards
Henry the Navigator
Portuguese prince who promoted the study of navigation and directed voyages of exploration down the western coast of Africa.

22
New cards
Christopher Columbus
He mistakenly discovered the Americas in 1492 while searching for a faster route to India.

23
New cards
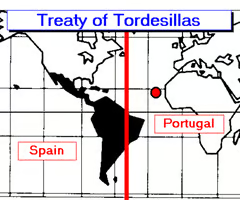
Treaty of Tordesillas (1494)
An agreement between Portugal and Spain which declared that newly discovered lands to the west of an imaginary line in the Atlantic Ocean would belong to Spain and newly discovered lands to the east of the line would belong to Portugal.
24
New cards
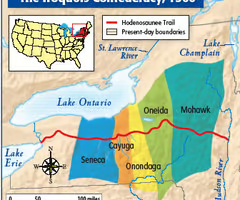
Iroquois Confederation
A political union of five independent American Indian tribes in the Mohawk Valley of New York.
25
New cards
longhouses
American Indians along the Pacific Coast lived in the these plank houses.
26
New cards
John Cabot
An Italian sea captain who sailed under contract to England's King Henry VII. He explored the coast of Newfoundland in 1497.

27
New cards
Jacques Cartier
In the period for 1534 to 1542, he explored the St. Lawrence River.

28
New cards
Samuel de Champlain
He established the first permanent French settlement at Quebec, a fortified village on the St. Lawrence River.

29
New cards
Henry Hudson
This English sailor was hired by the Dutch government to seek a westward passage to Asia through North America. In 1609, while searching for the passage, he sailed up a broad river that would later be named in his honor.

30
New cards
Bartolome de Las Casas
Spanish priest who was an advocate for more humane treatment of Native Americans.

31
New cards
Valladolid Debate
1550-1551, Formal discussion in Spanish city, concerning the role of American Indians in the Spanish colonies and use of the encomienda system.

32
New cards
Juan Gines de Sepulveda
Spaniard who argued that the Native Americans were less than human and that harsh treatment was necessary.
