MAC Module 13 Notes - Monetary Policy
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
98 Terms
The ripple effects that follow a change in the federal funds rate change three components of aggregate expenditure:
Investment & Net exports
Two alternative monetary policy rules have been proposed. They are:
An interest rate rule & A monetary base rule
Two other strategies that the Fed might use are discretionary policies that are constrained by tightly defined objectives. They are
Inflation targeting & Money growth targeting
The Federal Reserve Act requires the Fed to use
monetary policy to achieve the “dual mandate” of maximum employment and stable prices.
The Fed’s goals can-
come into conflict in the short run.
The Fed’s monetary policy instrument is-
the federal funds rate.
The Fed sets the federal funds rate at the level that makes its-
forecast of inflation and other goals equal to their targets.
The Fed hits its federal funds rate target by using-
open market operations and in times of financial crisis by quantitative easing and credit easing.
A change in the federal funds rate changes other-
interest rates, the exchange rate, the quantity of money and loans, aggregate demand, and eventually real GDP and the inflation rate.
Changes in the federal funds rate change-
real GDP about one year later and change the inflation rate with an even longer time lag
The main alternatives to the Fed’s discretionary policy are
an interest rate rule, a monetary base rule, inflation targeting, and money growth targeting.
Rules dominate discretion in monetary policy because-
they bring greater certainty about future policy actions and better enable the central bank to manage inflation expectations.
In the McCallum Rule, money is the monetary base, so the quantity theory equation becomes

The objectives of monetary policy are set out in the-
mandate of the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System, defined by the Federal Reserve Act of 1913 and its subsequent amendments, the most recent in 2000
The Fed’s mandate has two parts:
A statement of goals & prescription of the means by which a pursue those goals.
The Fed’s goals, known as the “________ “, are to achieve “_______” and “ _________”
dual mandate, stable prices, maximum employment
The goal of “stable prices” means
keeping the inflation rate low
The goal of “maximum employment” means
attaining the maximum sustainable growth rate of potential GDP, keeping real GDP close to potential GDP, keeping real GDP close to potential GDP & the unemployment rate close to the natural unemployment rate.
The 2000 law instructs the Fed to pursue-
its goals by keeping the growth rate of quantity of money in line with the growth rate of potential GDP.
The Fed is expected
To be able to maintain full employment & keep the price level stable
The Fed pays close attention to the
Business cycle & tries to steer a steady course between recession & inflation.
The Fed tries to minimize the output gap-
The percentage deviation of real GDP from potential GDP
The Fed believes that core inflation provides the best indication of whether __________ has been achieved
price stability
The annual percentage change in the Personal Consumption Expenditure deflator (PCE deflator) excluding the prices of food & fuel
Core Inflation
Since January 2012, the Fed has defined price stability as a core inflation rate of
2 percent a year
The Federal Reserve Act makes the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System & the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC)-
responsible for the conduct of monetary policy.
The FOMC makes a monetary policy decision at ____ scheduled meetings a year & publishes the minutes _____ weeks after each meeting
8, 3
Congress plays no role in making monetary policy decisions but the Federal Reserve Act requires -
The Board of Governors to report on monetary policy to Congress
The Fed makes ___ _____ to Congress each year
two reports
To conduct its monetary policy the Fed must select a -
monetary policy instrument
monetary policy instrument-
a variable that the Fed can directly control or closely target and that influences the economy in desirable ways.
The Fed’s choice of instrument is the
Federal funds rate
Federal funds rate-
the interest rate at which banks can borrow and lend reserves (Interbank loans) in the federal funds market.
The federal funds rate is also the-
opportunity cost of holding reserves.
Holding a larger quantity of reserves is-
the alternative to lending reserves to another bank.
Holder a smaller quantity of reserves is-
the alternative to borrowing reserves from another bank
So the quantity of reserves that banks are willing to hold varies with the federal funds rate:
The higher the federal funds rate, the smaller is the quantity of reserves that the banks plan to hold.
The Fed controls the quantity of reserves supplied.
The Fed can change this quantity of reserves supplied by conducting an open market operation.
To hit the federal funds rate target, the Fed conducts open market operations until the supply of reserves is at just the right quantity to hit the target federal funds rate.
If the Fed wants to raise the federal funds rate
It must decrease the monetary base
If the Funds want to lower the federal funds rate
it must increase the monetary base.
1) FOMC meeting-
(a) The Fed tightens - the Fed raises the federal funds rate
(b) The Fed eases- The Fed lowers the federal funds rate
2) Same day/ Next day
(a) The Fed tightens - Other short-term interest rates rise & the exchange rate rises
(b) The Fed eases - Other short-term interest rates fall & the exchange rate falls
3) A few weeks through a few months later
(a) The Fed tightens- The quantity of money & supply of loanable funds decrease
(b) The Fed eases- The quantity of money & supply of loanable funds increase
4) A few weeks through a few months later
(a) The Fed tightens- The long-term real interest rate rises
(b) The Fed eases- The long-term real interest rate falls
5) Up to a year later
(a) The Fed tightens- Consumption expenditure, investment, & net exports decrease
(b) The Fed eases- Consumption expenditure, investment, & net exports increase
6) Up to a year later
(a) The Fed tightens- Aggregate demand decreases
(b) The Fed eases- Aggregate demand increases
7) About a year later
(a) The Fed tightens- Real GDP growth rate decreases
(b) The Fed eases- Real GDP growth rate increases
8) About two years later
(a) The Fed tightens- Inflation rate decreases
(b) The Fed eases- Inflation rate increases
The monetary policy transmission process is
long & drawn out
The time lags in the adjustment process are-
not predictable, but the average time lags are known.
After the Fed takes action, real GDP beings to change about ______ later & the inflation rate responds with a lag that averages around _____
1 year, 2 years
Monetary policy is either ______ or _______
discretionary, rule-based
The Fed’s monetary policy is _________: It sets the federal funds rate at the level it believes will best achieve its mandated policy goals.
Discretionary
A rule-based monetary is
one based on a rule for setting the policy instrument
Two alternative monetary policy rules have been proposed:
An interest rate rule
A monetary base rule
The Taylor Rule
a formula for settling the federal funds rate
The McCallum Rule
a formula for setting the monetary base growth rate
Two other strategies that the Fed might use are discentary policies that are constrained by tightly defined objectives. They are
An inflation targeting rule
A money targeting rule
Inflation targeting
a monetary policy regime in which the central bank makes a public agreement with the government to achieve an explicit inflation target and to explain how its policy actions will achieve that target.
Inflation targets are specified in terms of a range for the ____ ______ _____
CPI Inflation rate
Because the lags in the operation of monetary policy are long, if the inflation rate falls outside the target range,
The expectation is that the central bank will move the inflation rate back on target over the next two years.
The idea of inflation targeting is to state publicly the goals of _______ _______, to establish a framework of _________, and stable while maintaining a high & stable __________.
Monetary policy, accountability, employment
k-percent rule
makes the quantity of money grow at a rate of k percent a year, where k equals the growth rate of potential GDP.
Money targeting works when the
demand for money is stable & predictable
But technological change in the banking system leads to unpredictable changes in the
demand for money, which makes money targeting unreliable
financial stability-
of enabling financial markets and institutions to resume their normal functions of allocating capital resources and risk.
discretionary monetary policy
sets its policy instrument at the level it believes will best achieve its mandated policy goals.
A monetary policy instrument is a variable that the _____ can directly control or closely target and that influences _____ in desirable ways.
B. Fed; the economy
The federal funds rate is the interest rate at which banks can borrow and lend _____ in the _____ market.
C. reserves; federal funds
A discretionary monetary policy is a monetary policy that is based on an expert assessment of the current _____.
C. economic situation
The k-percent rule is a monetary policy rule that makes the quantity of _____ grow at k percent per year, where k equals the growth rate of _____.
D. money; potential GDP
The Fed’s “dual mandate” is to achieve ________.
B. low inflation and maximum employment
The Fed’s operational goals include ________.
A. a core inflation rate between 1 and 2 percent a year and an output gap as small as possible
The Fed’s monetary policy instrument is the ________.
B. federal funds rate
The Fed fights inflation by ________.
B. raising the federal funds rate, which raises interest rates and decreases aggregate demand
To fight unemployment and close a recessionary gap, the Fed ________.
A. stimulates aggregate demand by lowering the federal funds rate, which increases the quantity of money
The Fed’s choice of monetary policy strategy is ________.
C. adjusting the federal funds rate to best fulfill its dual mandate
A monetary policy role is ________ to discretionary monetary policy because ________.
C. superior; a rule keeps inflation expectations anchored
First Banks (Scotts Lecture)
1- Bank for Banks
2- Assist financial transaction for U.S.
First Bank of the United States (Scotts Lecture)
1791-1811
Second Bank of the United States (Scotts Lecture)
1816-1836
National Banking (Scotts Lecture)
-Imposes single currency
-Fed Government gives means to burrow
Board of Government (BOG) (Scotts Lecture)
7 members
1- Appointed by the president
2- Confirmed by Senate
3- Serve 14 year terms
4- Term exploration expire every other year
12 regional banks (Scotts Lecture)
1- Collect data w/n districts
2- Implement Fred policies w/n district
1935 (Scotts Lecture)
Establish current Fed structure
Federal Open Market Committee (Scotts Lecture)
1- Seven BOGs 12 members
2- Permanent & New York
3- Four rotating with 3 year term
Fed Tools (Scotts Lecture)
1- Fomo
2- Discount Rate
3- Reserve Regulation
Federal Open Market Committee (Scotts Lecture)
12 members
7 BOG
5 Bank Pres
Discount rate (Scotts Lecture)
rate the Fed bonds to banks to meet overnight reserve regulations
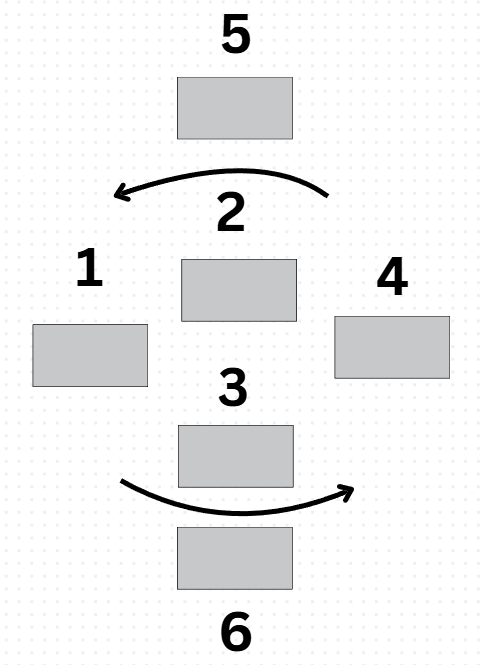
What does each number represent? (Scotts Lecture)
1- Fed 2- Bonds 3- Cash/Money 4- Primary Dealer 5- Open Market Purchase 6- Open Market Sell
What is the Monetary Policy Formula? (Scotts Lecture)
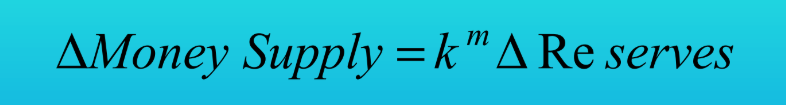
Federal Open Market Operation (Scotts Lecture)
The Federal Reserves buys and sells government securities that member banks hold to change bank’s reserves.
The Fed buys securities when (Scotts Lecture)
it wants to increase the money supply, therefore, decrease interest rates.
The Fed sells securities when (Scotts Lecture)
it wants to decrease the money supply, therefore, increase interest rates.
The discount rate in the rate that the Fed lends (Scotts Lecture)
money to banks to meet their overnight reserve requirements.
During a contraction (Scotts Lecture)
the Fed decreases the discount rate.
During an expansion (Scotts Lecture)
the Fed increases the discount rate.
Reserve Requirement in a contraction (Scotts Lecture)
the Fed decreases the reserve requirement.
Reserve Requirement in an expansion (Scotts Lecture)
the Fed increases the reserve requirement.