Global Marketing 363 - Ch. 1-5 Wachner
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
Customer Perceived Value
Value=Benefits/Price
-improve product
-Find new distribution channels
-Create better communications
-Cut monetary and non-monetary cost and prices
Global Industries (Definition)
An industry is global to the extent that a company's industry position in one country is interdependent with its industry position in another country
Indicators of Globalization
- Ratio of cross-border investment to total capital investment
- Proportion of industry revenue generated by all companies that compete in key world regions
- Ratio of cross-border trade to worldwide production
Why go Global
Percentage of business outside of Country
-US - 75%
-Japanese - 90%
-Germany - 94%
Global Marketing (Key Differences)
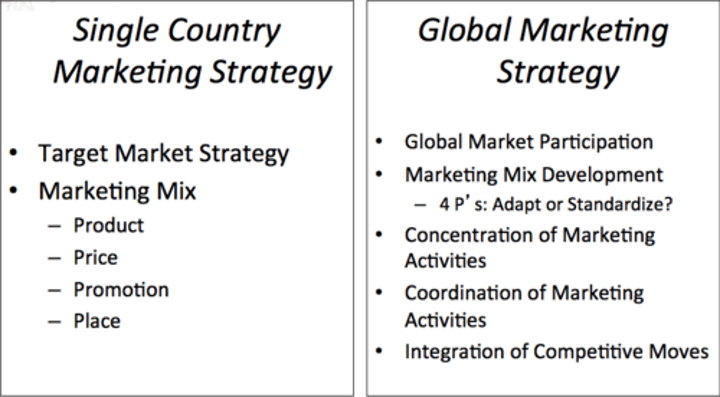
Global Marketing Examples
Cinnabon
Starbucks
Kraft
Standardization Vs. Adaptation
Globalization (Standardization)
-Developing standardized products marketed worldwide with a standardized Marketing Mix
-MASS MARKETING
Global Localization (ADAPTATION)
-Mixing standardization and customization in a way that minimizes costs while maximizing satisfaction
-Essence of segmentation
-"Think globally, act locally"
MANAGEMENT ORIENTATION
(IMPORTANT)
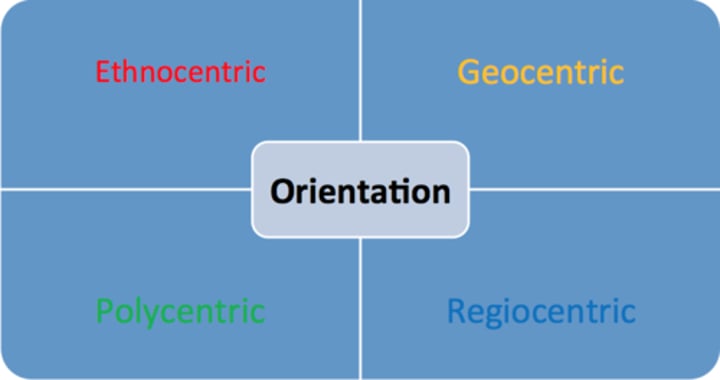
Ethnocentric
-Home Country is superior to others
-Sees only similarities in other countries
-Assumes products and practices that succeed at home will be successful everywhere
-Foreign operations or markets are viewed as inferior or subordinate to the home market.
-Leads to a standardized or extension approach
Polycentric Orientation
-Each country is unique
-Each subsidiary develops its own unique business and marketing strategies
-Often referred to as multinational
-Leads to a localized or adaptation approach that assumes products must be adapted to local market conditions.
Regiocentric Orientation
-A region is the relevant geographic unit
Ex European Union Market
-Some companies serve market throughout the world but on a regional basis.
Ex. General Motors had four regions for decades
Geocentric Orientation
-Entire world is a potential market.
-Strives for integrated global strategies
(((Also known as a global or transnational company)))
-Retains an association with the headquarters country
-Pursues serving world markets form a single country or sources globally to focus on select country markets
---- Important ----
-Leads to a combination of extension and adaptation elements.
Forces affecting Global Integration
-Multilateral trade agreements
-Converging market needs and wants and the information revolution
-Transportation and communication improvements
-Product development costs
Forces Affecting Global Integration
-Quality
-R&D as a percent of sales
-World economic trends
-2008 global crisis
-Growing middle class in BRIC nations
-Rapid growth in China
-Movement to "free" markets worldwide.
MODULE @
THE GLOBAL ENVIRONMENT
World Economy
The New Realities
-Capital Movements have replaced trade as the driving force of the world economy.
-The world economy, not individual countries, is the dominating factor.
-Production has become uncoupled from employment
Economic Systems
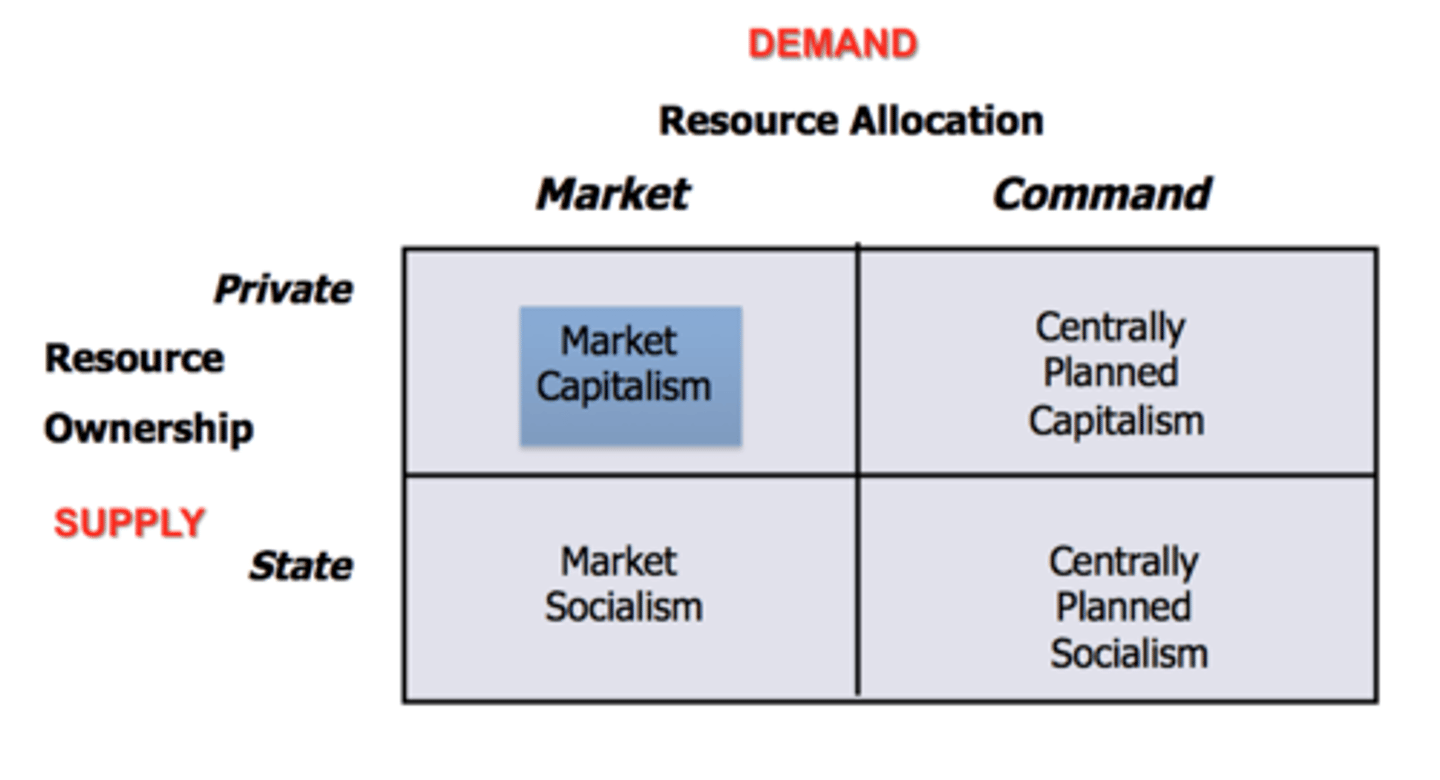
Market Capitalism
Western Market Systems
-Anglo-Saxon Model
-Social Market Economy Model
-Nordic Model

Centrally Planned Socialism
Communism
Centrally Planned Capitalism
Command resources allocation
-Private Resource Ownership
Ex. Swedish Government controls 2/3's of all spending.
Market Socialism
Offshoot of Communism with social programs
Economic Freedom
Ranking of Economic Freedom Among Countries
Free - Mostly Free - Mostly Unfree - Repressed
Variables considered include such things as
-Trade policy
-Taxation policy
-Capital Flows and Foreign investment
-Banking policy
-Wage and price controls
-Property rights
-Black martket
Stages of Development
Gross National Income (GNI) is a base
BRICS - Brazil, Russia, India, China, South Africa
NIEs
Newly Industrializing Economies
-Lower middle and upper income economies with the highest sustained rates of economic growth.
G-8 (The Group of Eight)
-US
-Japan
-Germany
-France
-Britain
-Canada
-Italy
-Rusia (1998)
Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD)
-34 Nations
-Post-WW11
-Promotes Economic Growth
The Triad
US, Western Europe, and Japan
(75% of the world income.)
Overview of International Finance
-Foreign exchange makes it possible to do business across the boundary of a national currency
-Currency of various countries are traded for both immediate (spot) and future (forward) delivery
-Currency risk adds turbulence to global commerce
Economic Exposure
-Refers to the impact of currency fluctuations on the present value of the company's financial performance.
-Occurs when sales are in a foreign currency
Nestlé generates 98% of sales outside home country
Euro zone companies GlaxoSmithKline, Daimler AG, BP, for example, generate 1/3 of sales in the U.S.
Managing Economic Exposure
Some techniques and strategies
-Hedging - Balancing the risk of loss by gaining in another.
-Forward Contracts - set the price of the exchange rate at some point in the future to eliminate some risk.
GATT
General Agreement of Tariffs and Trade
-Treaty to promote trade since 1947
-Handled disputes
-Replaced by World Trade Organization in 1995
World Trade Organization
For for trade related negotiations among 153 members
-Based in Geneva
-Serves as dispute mediator
-Has enforcement power
Preferential Trade Agreements (PTA)
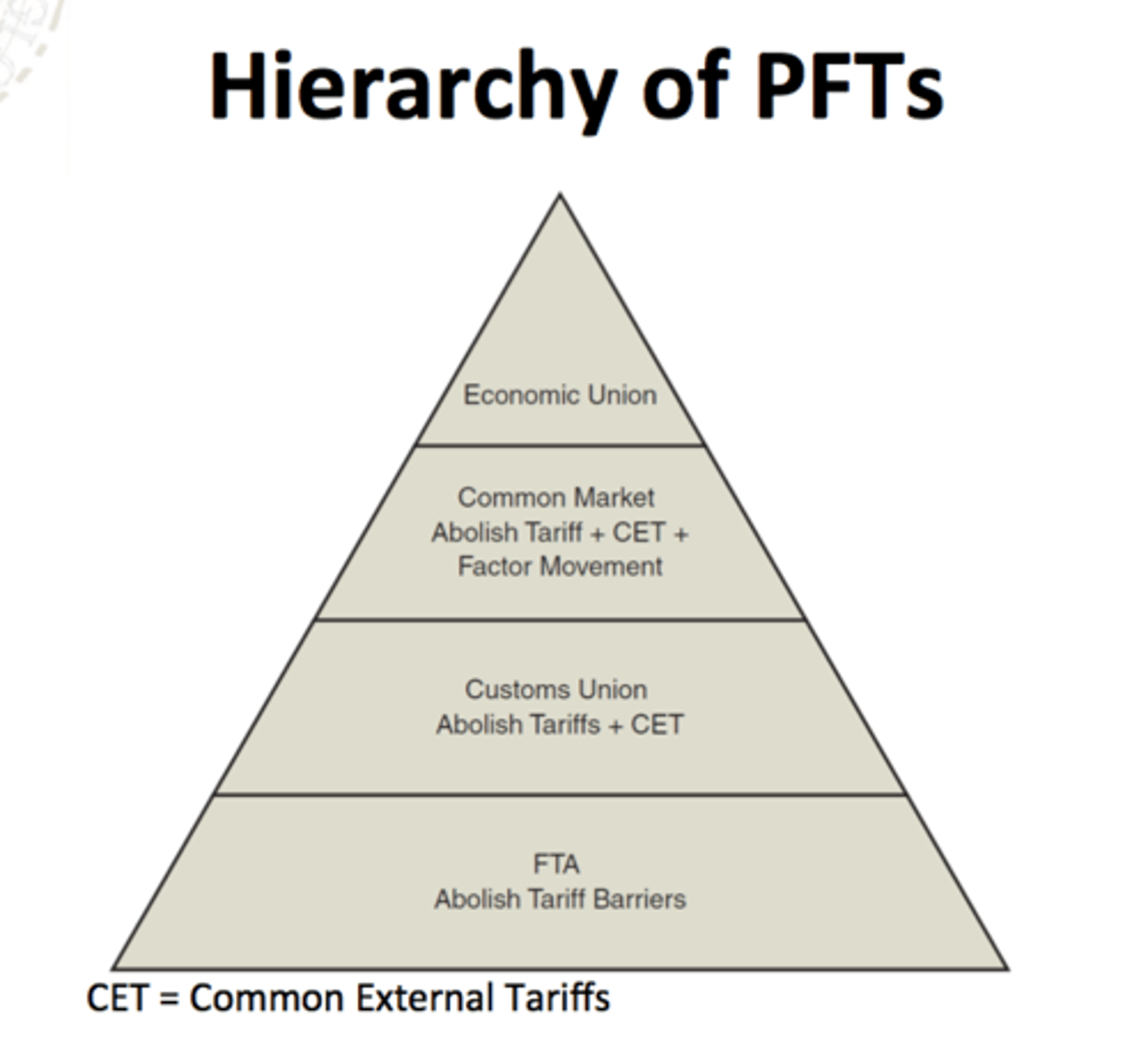
Free Trade Area
Two or more countries agree to abolish tariffs and other barriers to trade amongst themselves
-Countries continue independent trade policies with countries outside agreement
-Rules of origin requiremenet restrict transhipment
Common Market
-Includes the elimination of internal barriers to trade
-And establishes common external barriers to trade
-And allows for the free movement of factors of production, such as labor and information.
North America NAFTA
Since 1994
Canada - USA - Mexico
SICA
Central American Integration System
Andean Community
Bolivia, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru
Mercosur
Argentina, Brazil, Paraguay, Uruguay, Venezuela
The Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN)
Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam
Trading partners U.S., Japan, EU, China
Geographically close; historically divided
"ASEAN plus six" (Japan, China, Korea, Australia, New Zealand, India) working towards an economic community
(EU) European Union
Initially began with the 1958 Treaty of Rome
Objective is to harmonize national laws and regulations so that goods, services, people, and money could flow freely across national boundaries
The Middle East
Afghanistan, Bahrain, Cyprus, Egypt, Iran, Iraq, Israel, Jordan, Kuwait, Lebanon, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Syria, the United Arab Emirates, Yemen
Africa
54 nations over three distinct areas
Republic of South Africa
North Africa
Black Africa or sub-Saharan Africa
Chapter 4
Society, Culture and Global Consumer Culture
Task of Global Marketers
-Study and understand the cultures of countries in which they will be doing business
-Understand how an unconscious reference to their own cultural values, or self-reference criterion, may influence their perception of the market
-Incorporate this understanding into the marketing planning process
Culture
Culture-ways of living, built up by a group of human beings, that are transmitted from one generation to another
-Culture is both physical (clothing and tools) and nonphysical (religion, attitudes, beliefs, and values)
Culture has conscious and unconscious
Attitude - learned tendency to respond in a consistent way to a given object or entity
Belief - An organized pattern of knowledge that an individual holds to be true about the world.
Value - Enduring belief or feeling that a specific mode of conduct is personally or socially preferable to another mode of conduct.
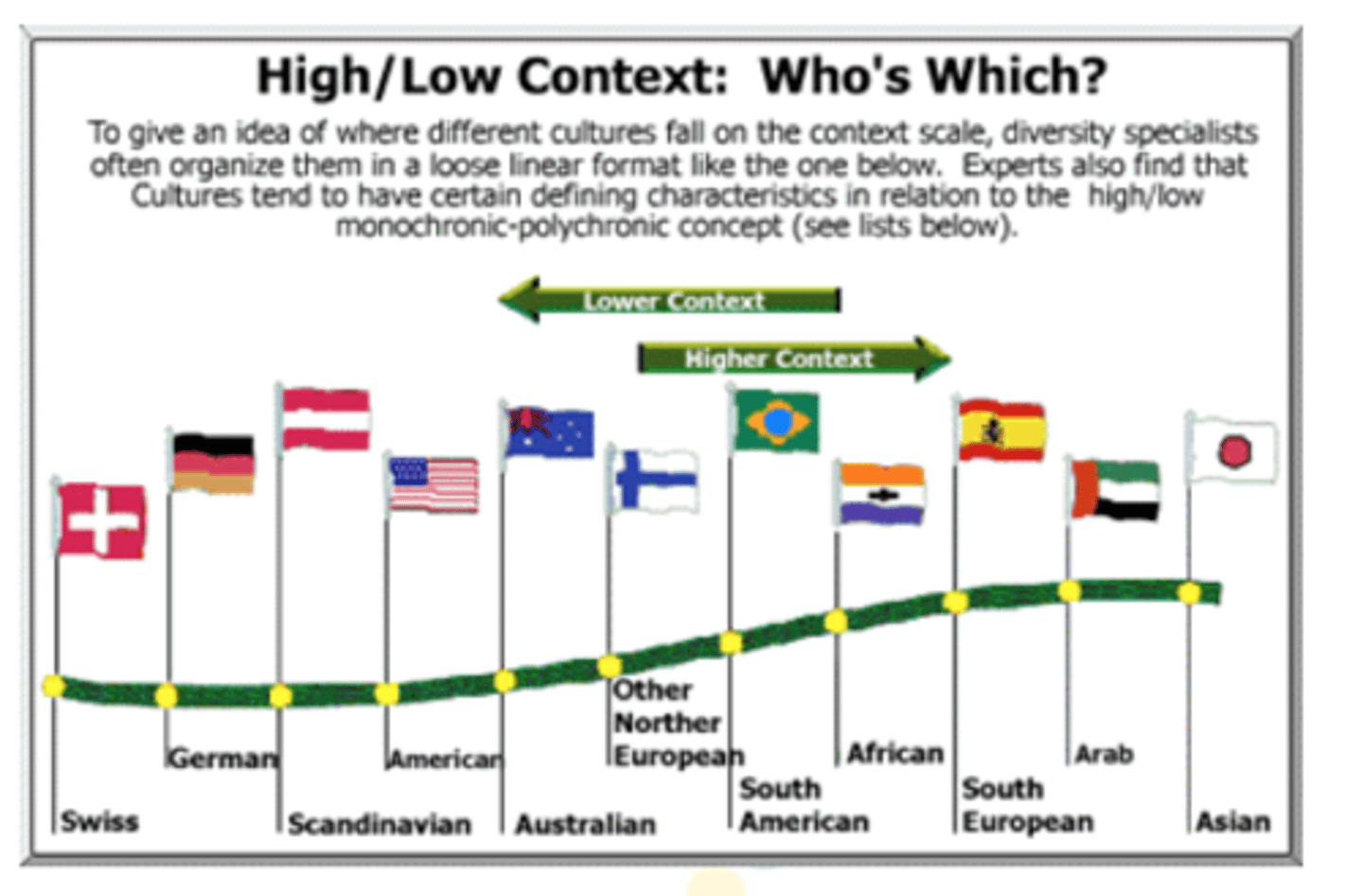
High and Low Context Cultures
See the following
High Context
-Information resides in context
-Emphasis on background, basic values, societal status
-Less emphasis on legal paperwork
-Focus on personal reputation
Saudi Arabia, Japan
Low Context
Low Context
-Messages are explicit and specific
-Words carry all information
-Reliance on legal paperwork
-Focus on non-personal documentation of credibility
Switzerland, U.S., Germany
Who is which?
Hofstede's Six Value Dimensions
Individualism/Collectivism
Power Distance
Masculinity
Uncertainty Avoidance
Long-term Orientation
Indulgence vs. Restraint (new addition!)
Examples
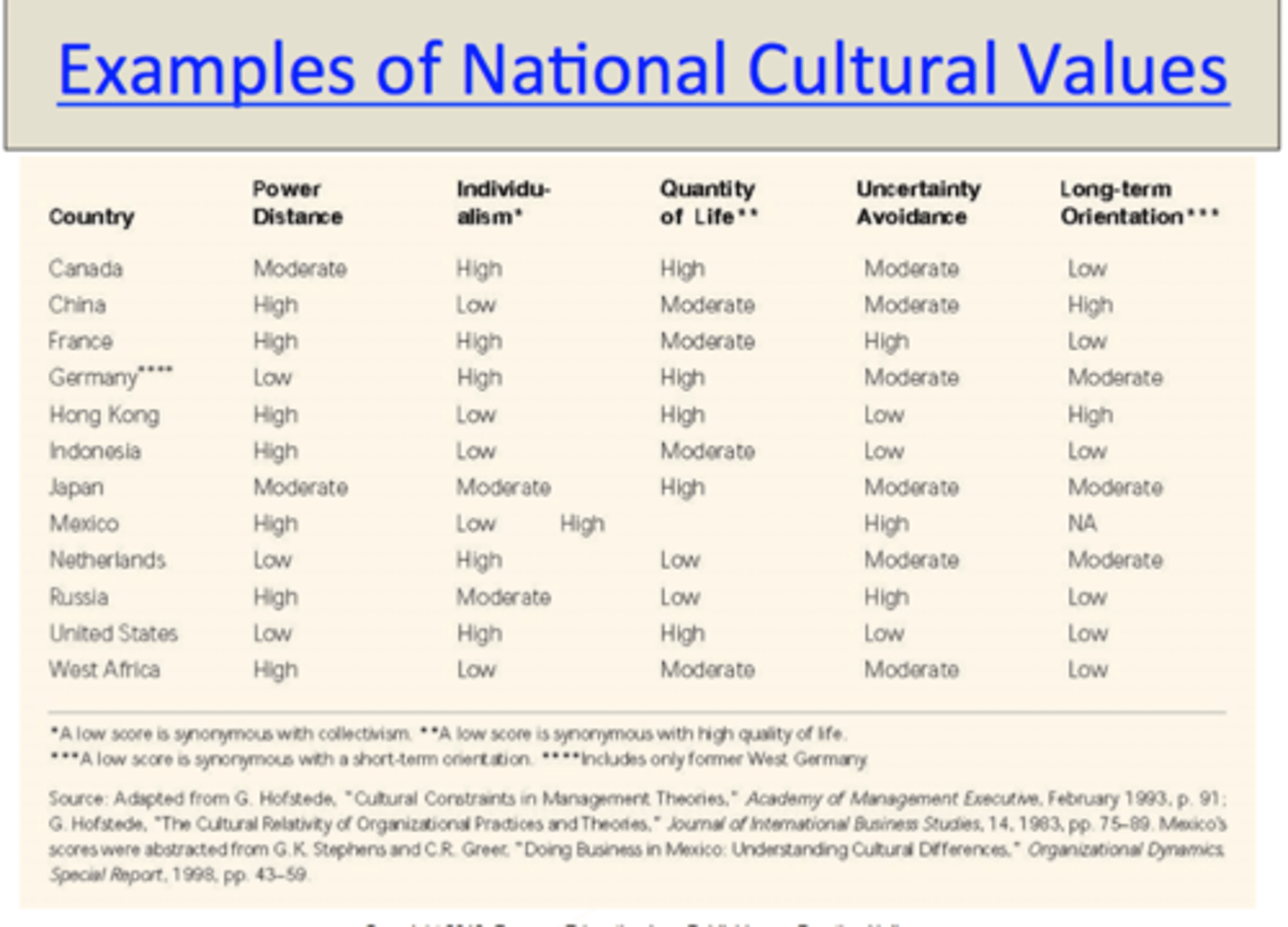
(Important)
Self-Referencing Criterion & Perception
Unconscious reference to one's own cultural values; creates ((cultural myopia))
How to Reduce Cultural Myopia
-Define the problem or goal in terms of home country cultural traits
-Define the problem in terms of host-country cultural traits; make no value judgments
-Isolate the SRC influence and examine it
-Redefine the problem without the SRC influence and solve for the host country situation
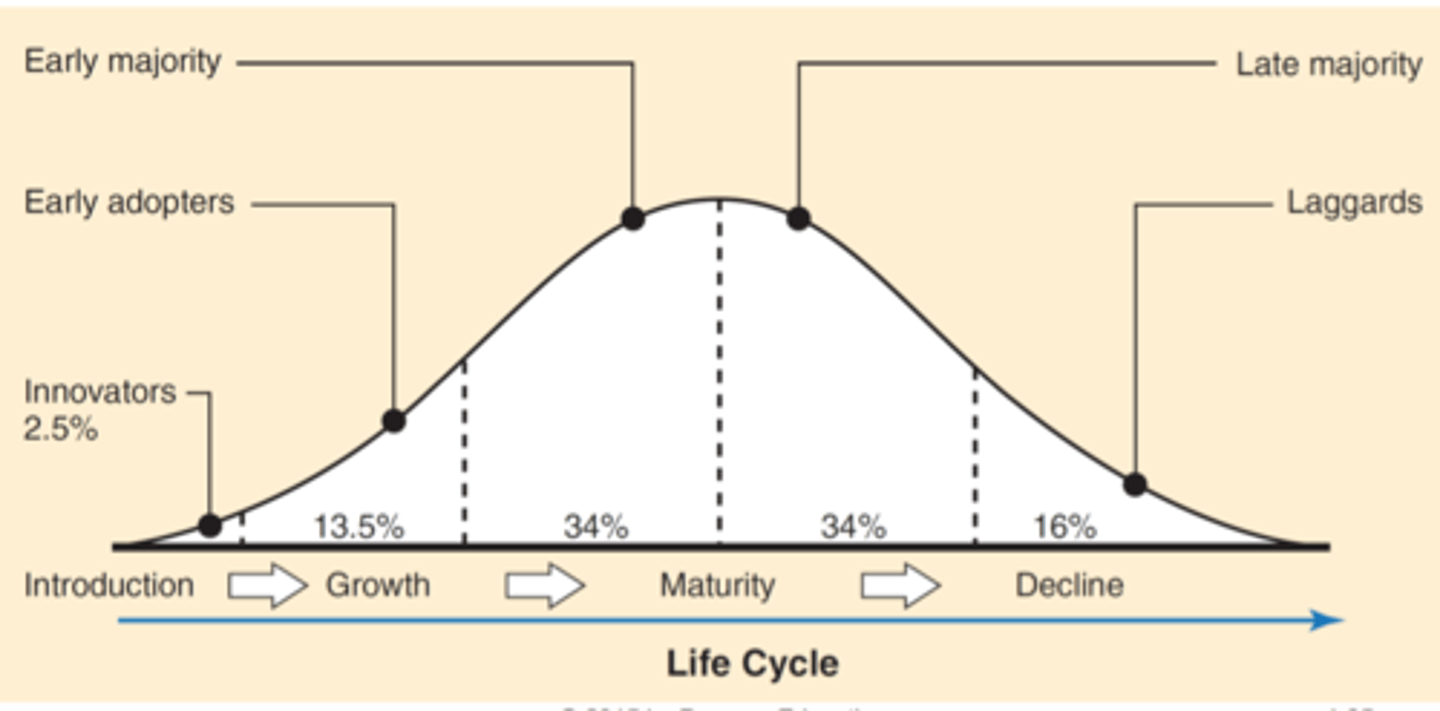
Diffusion Theory:
The Adoption Process
"Product adoption or purchase"
-Awareness
-Interest
-Evaluation
-Trial
-Adoption
Diffusion Theory:
Characteristics of Innovations being adopted
-Relative Advantage
-Compatibility
-Complexity
-Divisibility
-Communicability
Adopter Categories
Environmental Sensitivity
Food is the most culturally-sensitive category of consumer goods
UNIT 3 -Chapter 5-
Political, Legal, and Regulatory Environments
Political Risk
Risk of change in political environment or in government policy that would adversely affect a company's ability to operate effectively and profitably
When perceived political risk is high, a country will have
a difficult time attracting foreign direct investment.
Examples of Political Unrest
War
Social unrest, fractionalized by language, ethnic and/or religious groups
Orderly political transfer
Politically motivated violence
Change in government/pro-business orientation
Social conditions (population density and wealth distribution)
Corruption, nepotism
Crime
Labour costs
Tax discrimination
Exchange controls, tariff barriers
Seizure of Assets (By a Foreign Government)
"Expropriation"
"Confiscation"
Expropriation
-governmental action to dispossess a foreign company or investor
Compensation should be provided in a "prompt, effective, and adequate manner"
Confiscation occurs when no compensation is provided
Seizure of Assets
"Nationalization"
Nationalization-a government takes control of some or all of the enterprises in an entire industry
Acceptable according to international law if:
satisfies public purpose
includes compensation
Creeping Expropriation
-limits economic activities of foreign firms
May include:
Limits on repatriation of profits, dividends, or royalties
Technical assistance fees
Increased local content laws
Quotas for hiring local nationals
Price controls
Discriminatory tariff and nontariff barriers
Discriminatory laws on patents and trademarks
Taxes
Government taxation policies
-High taxation can lead to black market growth and cross-border shopping
Corporate taxation
-Cash transactions and bartering can increase
International Law
-The rules and principles that nation-states consider binding among themselves
-Disputes between nations are issues of public international law
--World Court or International Court of Justice (ICJ);
--Judicial arm of the United Nations
Intellectual Property
Intellectual property must be registered in each country where business is conducted
-Patent-gives an inventor exclusive right to make, use, and sell an invention for a specified period of time
-Trademark-distinctive mark, motto, device, or emblem used to distinguish it from competing products
-Copyright-establishes ownership of a written, recorded, performed, or filmed creative work
Infringements
-Counterfeiting-unauthorized copying and production of a product
-Associative Counterfeit/Imitation-product name differs slightly from a well-known brand
-Piracy-unauthorized publication or reproduction of copyrighted work
Licensing
Licensing is a contractual agreement in which a licensor allows a licensee to use patents, trademarks, trade secrets, technology, and other intangible assets in return for royalty payments or other forms of compensation
Trade Secrets
Trade secrets are confidential information or knowledge that has commercial value and is not in the public domain and for which steps have been taken to keep it secret