Sedimentary Processes and Soil Formation
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Sedimentary process
Formation of sediments through various environmental factors.
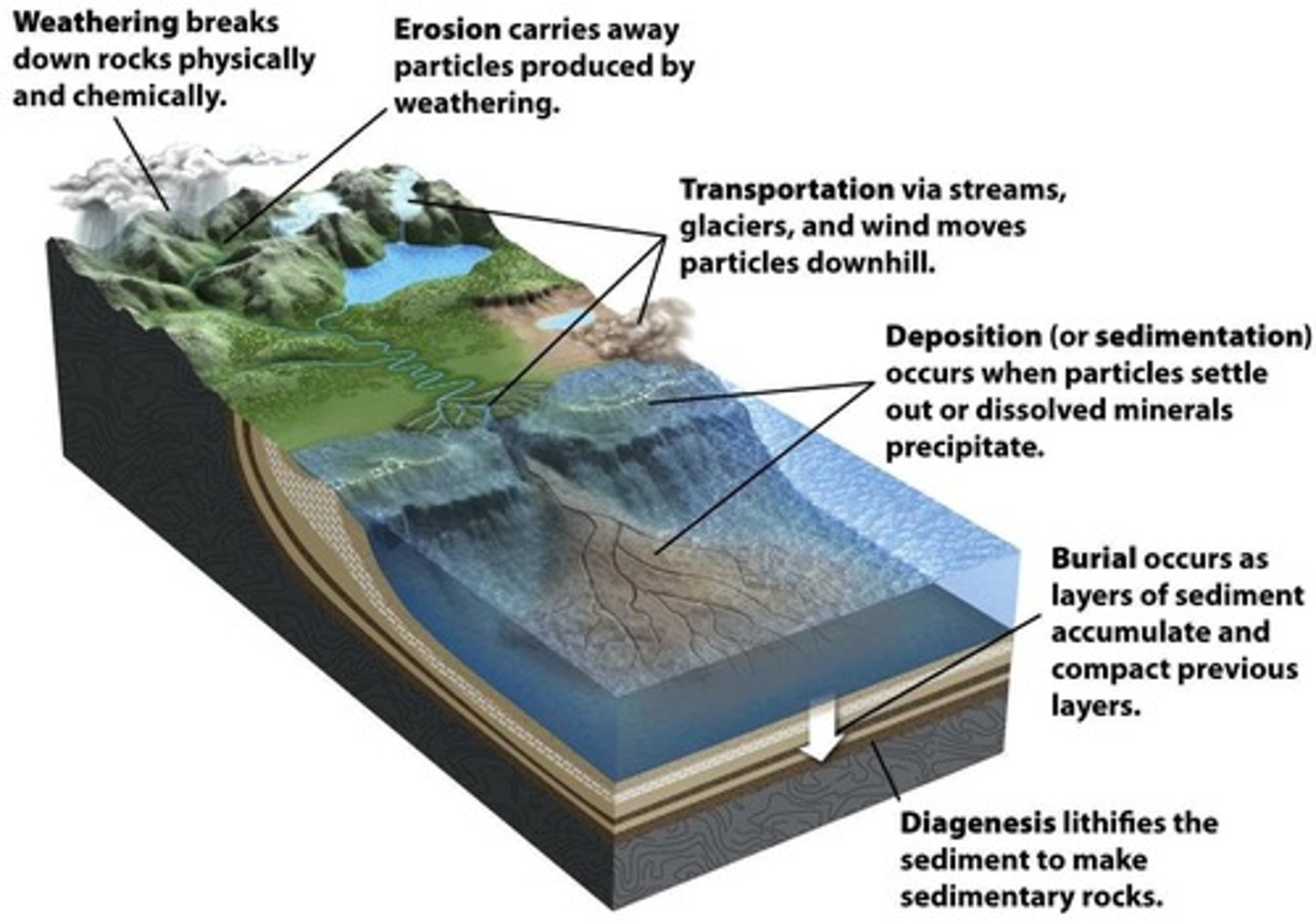
Diagenesis
Processes affecting sediments post-deposition before metamorphism.
Lithification
Conversion of loose sediment into solid rock.
Mechanical weathering
Fragmentation of rock without changing composition.
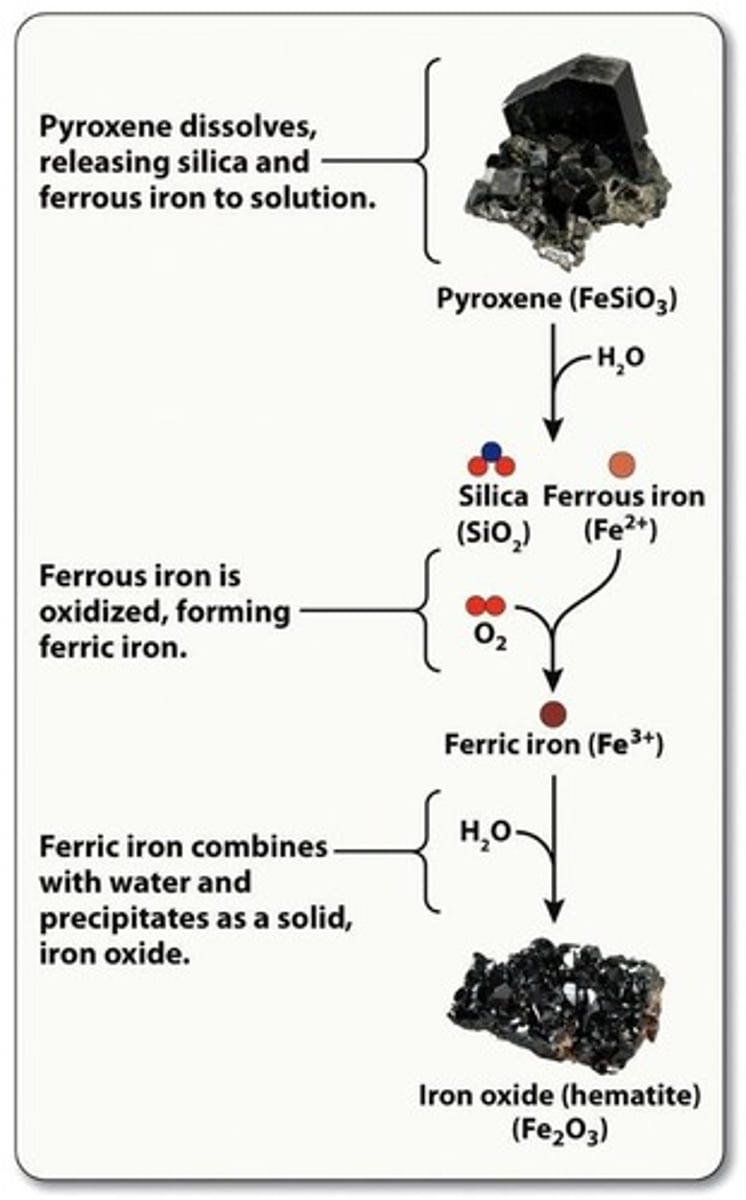
Chemical weathering
Rock alteration through chemical reactions.
Erosion
Dislodging and transporting weathered rock particles.
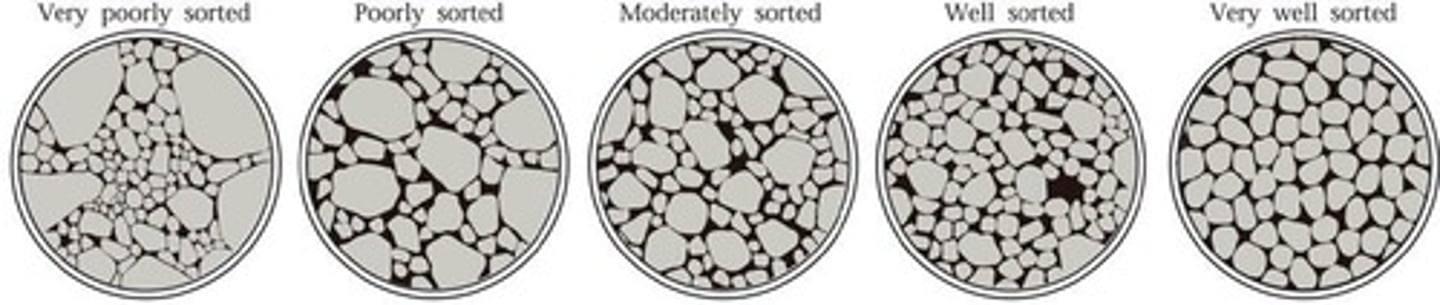
Transport and Sorting
Movement and classification of sediment by size.
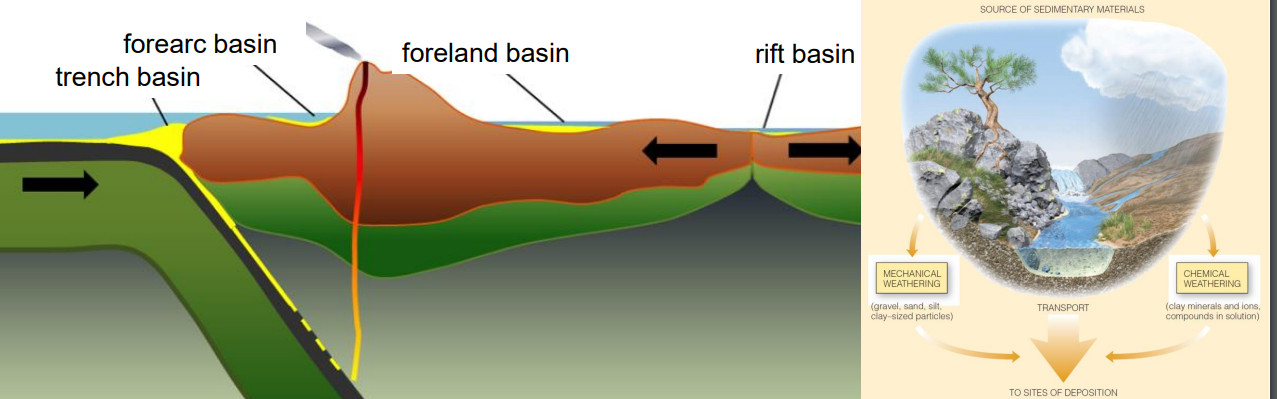
Sedimentary Basins
Depressions accumulating thick sediment layers.

Soil
Layer of weathered material supporting plant growth.
Regolith
Loose material covering planetary surfaces.
Compaction
Reduction of sediment volume under pressure.
Cementation
Mineral crystallization binding sediment particles.
Clastic sediments
Eroded fragments of rocks and minerals.
Chemical sediments
Minerals formed from dissolved ions in water.
Biogenic sediments
Minerals precipitated by biological processes.
Evaporite environments
Mineral deposits formed from evaporating seawater.
Carbonate environments
Sedimentary environments producing carbonate minerals.
Siliceous environments
Sediments formed from silica precipitation.
Abrasion
Scouring of surfaces by moving particles.
Dissolution
Soluble minerals dissolved in flowing water.
Hydrolysis
Chemical breakdown of minerals by water.
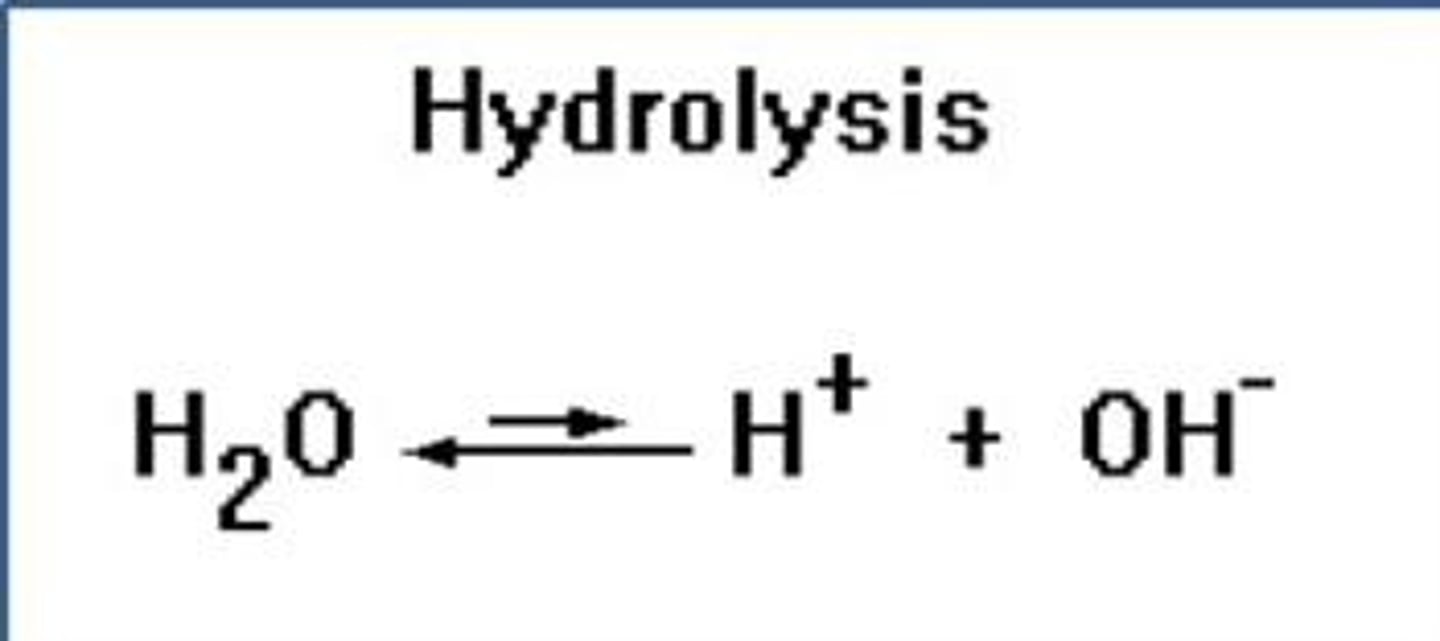
Oxidation
Chemical reaction involving oxygen altering minerals.
Forearc basin
Sedimentary basin located between a trench and an island arc.
Rift basin
Depression formed by tectonic plate divergence.