17: Gene Regulation
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
metabolic regulation
regulation of enzymatic activity (i.e., affinity, activation, inhibition)
regulation of enzyme synthesis (i.e., gene expression)
operons
unit of genetic function found in bacteria with 3 elements
promoter
operator (within the promoter region)
controls the access of RNA pol to genes
cluster of genes (whose products function in a common pathway)
repressor when active
represses gene expression
repressor binds to operator, blocking RNA pol from binding
transcription decreases
elements of trp operon
3 reactions
3 enzymes
5 genes
1 promoter
1 operator
1 long mRNA
5 start codons
5 stop codons
= 5 ORFs
5 polypeptides in single mRNA
trp repressible operon
under normal conditions:
operon is ON
trpR is inactive
activated by concentration of tryptophan that activates trpR
corepressor
tryptophan
cooperates with trpR (repressor) to turn off operon
anabolic pathway
operon: ON
tryptophan expressed
increased [tryptophan]: binds to trpR and activates it
trpR binds to operator (within promoter)
operon: OFF
tryptophan not expressed (already high concentration in the cell)
negative regulation
trp operon
lac operon
positive regulation
lac operon (in the presence of glucose and lactose)
lac inducible operon
normal conditions
operon is OFF
lac repressor is active
inactivated as it binds to inducer, allolactose
elements of lac operon
1 promoter
1 operator
1 regulatory gene
lacI codes repressor
3 genes
lacZ: b-galactosidase
lacY: permease
lacA: transacetylase
catabolic pathway
lac operon OFF
lac repressor is active
lactose present
inducer allolactose binds to lac repressor to inactivate it
lac repressor inactive
lac operon ON
transcription by RNA pol II
increased lactose pathway enzymes (b-galactosidase)
hydrolysis of lactose
lactose → glucose + galactose
lac operon: positive regulation
cAMP binds to CRP (cAMP receptor protein)
once activated, CRP activator binds to lac promoter
recruits RNA pol
CRP increases gene transcription of lac operon
+ glucose
+ lactose
decreased AC
decreased cAMP
CRP inactive
decreased affinity for RNA to bind to promoter
because glucose inhibits AC; no CRP
operon OFF
*some transcription is still possible due to presence of lactose
+ glucose
- lactose
operon OFF
lac repressor active
- glucose
- lactose
operon OFF
AC active
cAMP activates CRP
lac repressor active
- glucose
+ lactose
operon ON
AC active
cAMP activates CRP
increases affinity for RNA pol
transcription of lac mRNA
eukaryotes
gene expression can be modulated at different stages
does not involve operons
depends on control elements
differential gene expression
cells from different cell types (tissues) have the same genome but a different program of gene expression
depends on the cell’s specific
function
localization
differentiation
signals
internal and external environment
control elements
serve as binding sites for transcription factors and help recruit the transcription initiation complex
cis-acting DNA control elements
control elements located on the same chromosome as the gene they regulate
promoters
enhancers
trans-acting DNA control elements
control elements that bind to the gene they regulate
transcription factors
enhancer
group of distal control elements that increase gene transcription
upstream from promoter
cis-acting control elements
proximal control elements
close to promoter
upstream from the gene
bind TFs to help gene expression
general TFs
can bind to
promoter of all protein-coding genes (TATA box)
other TFs
RNA pol II
specific TFs
can bind to
control elements (upstream and downstream)
other TFs
mediator proteins
which increase or decrease the rate of transcription
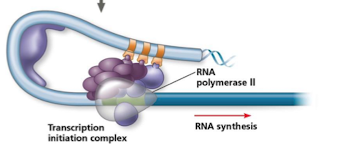
transcription initiation complex (TIC)
recruited by mediator proteins
includes
RNA pol II
general TFs
other coactivators
steps in TIC complex
TFs bind to control elements
once bound, TFs interact with mediator proteins that act like bridges
mediator proteins stabilize and recruit TIC
DNA looping brings distal elements like enhancers close to promoter region so their bound proteins can interact with transcription machinery
coordinated gene expression
for enzymes that belong to the same metabolic pathway
achieved by binding the same TFs to the same combination of control elements
differential gene expression example
different TFs are active in different cells
liver and lens cells
both contain entire genome
albumin gene - important for liver cells
crystallin gene - important for lens cells
control elements required for both genes
liver cells produce liver specific TFs that bind to albumin gene enhancers
lens cells produce lens-specific TFs to do the same with crystallin
RNA interference
process in which small RNA molecules regulate gene expression by targeting specific mRNA molecules
degradation
translation inhibition
siRNA
complementary to mRNA target
lead to degradation
ex. dicer
miRNA
partially complementary to mRNA target
forms hairpin structure structure processed into mature miRNA
leads to translation inhibition
ex. drosha
RISC (RNA-induced silencing complex)
siRNA or miRNA loaded into RISC complex
RISC uses RNA strand (siRNA or miRNA) as guide to find complementary mRNA
once it finds target:
a. if siRNA - RISC cleaves mRNA =degradation
b. if miRNA - RISC blocks translation or destabilizes mRNA