Practical 4: Alcohol fermentation in yeast
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
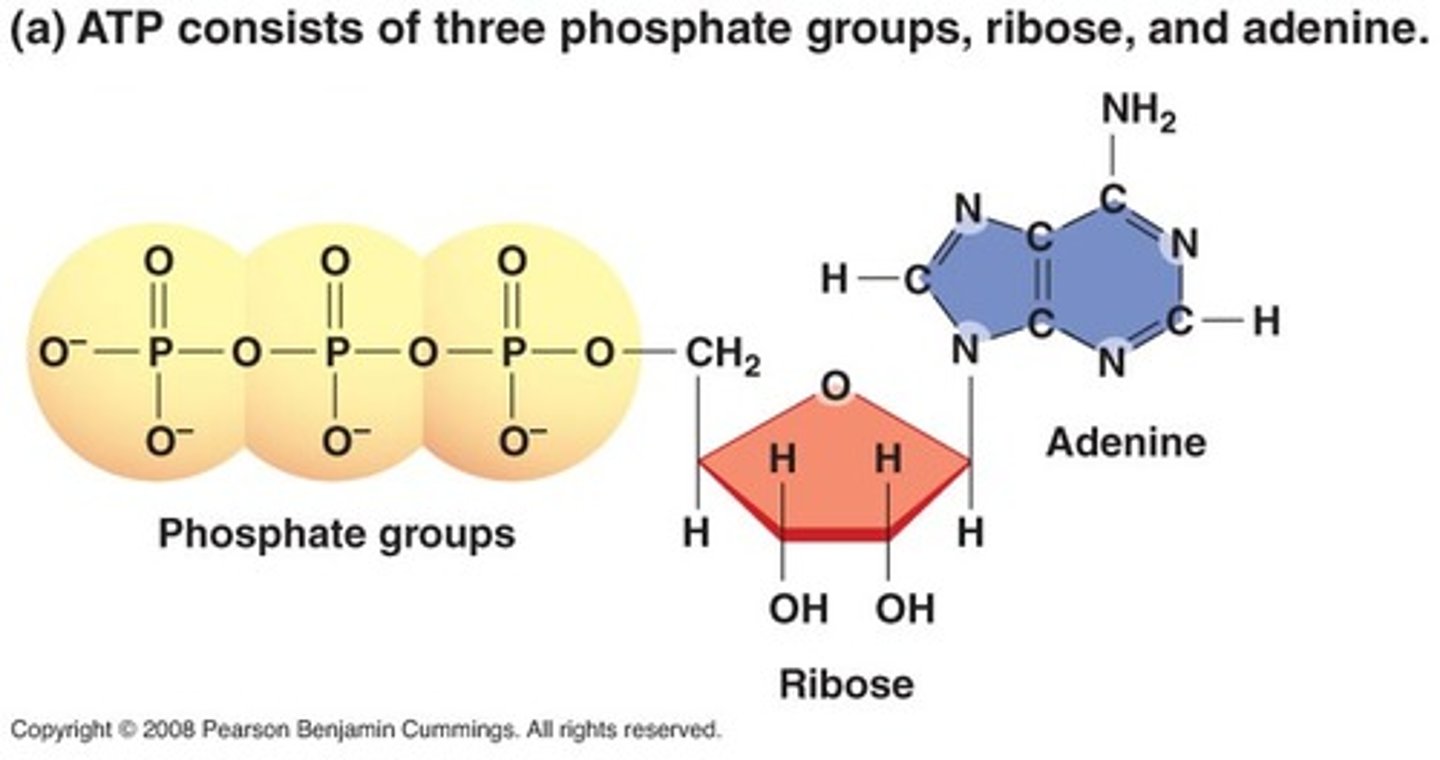
structure of ATP
adenine, ribose, 3 phosphate groups
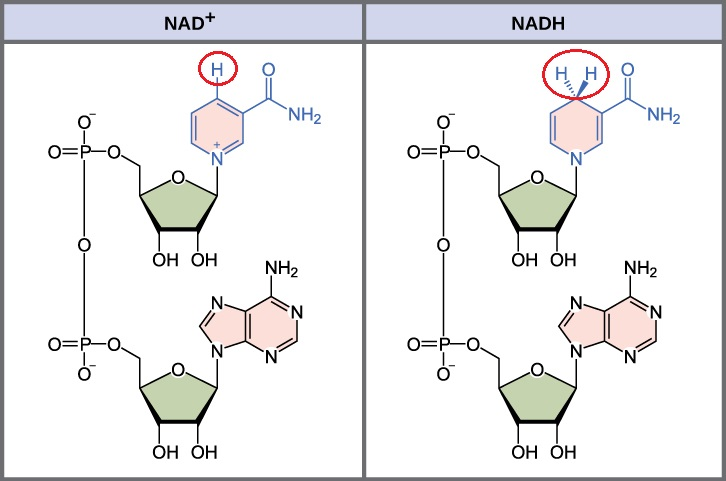
NAD+ vs NADH structure:
NAD⁺ (oxidised form) is a coenzyme composed of 2 nts: one containing adenine and the other containing nicotinamide, linked through phosphate groups.
In its oxidized form, NAD⁺ has a positive charge (+), due to the N in the nicotinamide ring being positively charged.
NADH (reduced form of NAD⁺) The main structural difference is that NADH has 2 additional electrons and a proton compared to NAD⁺
State: The nicotinamide ring in NADH has accepted these two electrons and one proton, neutralizing the positive charge.
This allows NADH to store energy and carry electrons to other reactions (e- carrier to be used in OP)
TRUE OF FALSE
NADH is coupled with ATP production
TRUE
where is NADH recycled and by who?
by electron transport system in mitochondria
Why is the recycling of NAD+ from NADH important in anaerobic cellular respiration?
as glycolysis cannot continue unless NAD+ can accept e-, as there is no oxygen available to accept electrons compared to oxidative phosphorylation
how many molecules of pyruvate are produced per 1 glucose?
2
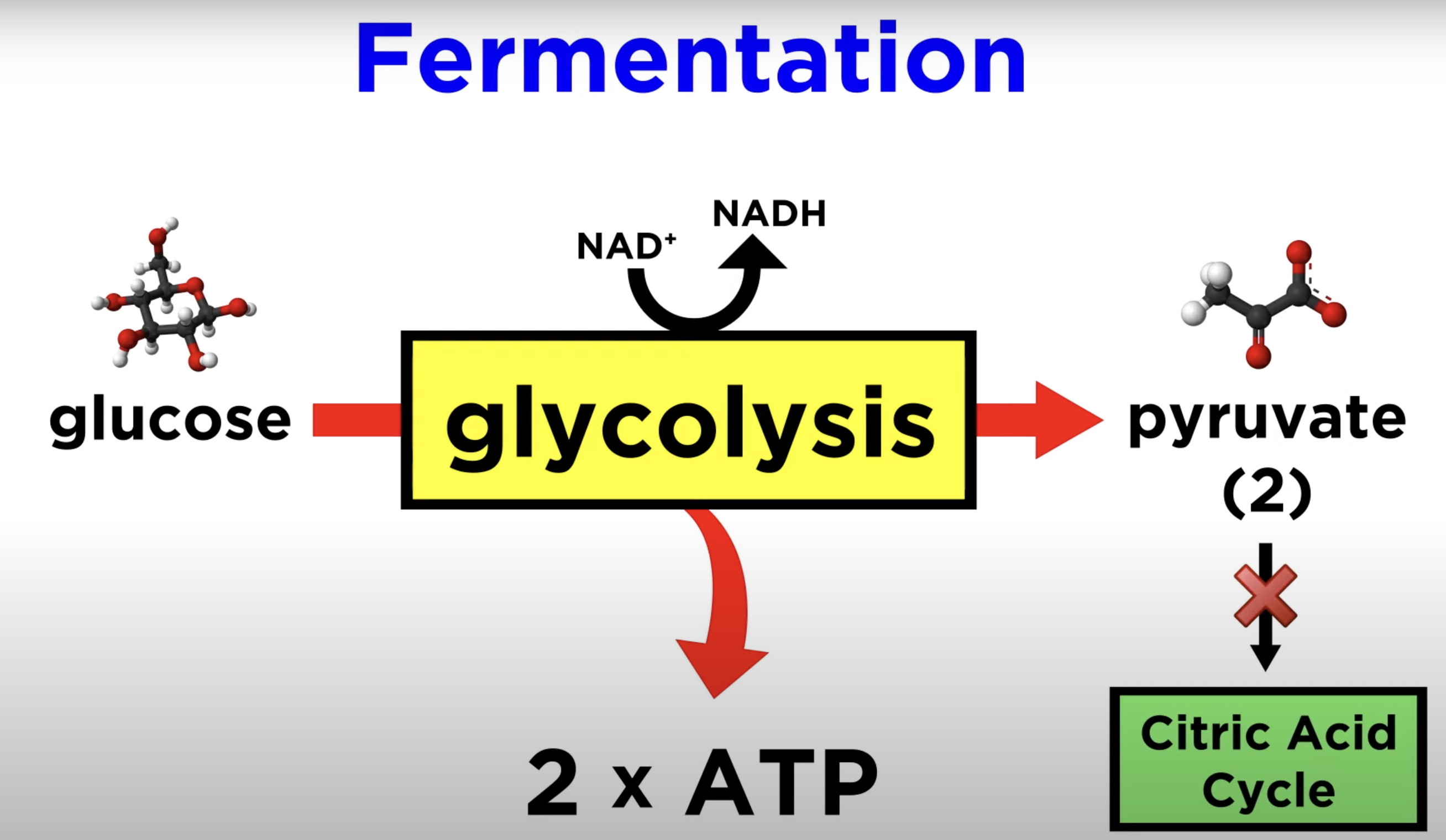
in the net outcome of glycolysis, ____ ATP , ___ NADH and ___ pyruvate are formed
2 ATP, 2 NADH, 2 pyruvate

where is NAD+ derived from?
Niacin (Vitamin B3)
TRUE OR FALSE:
Alcohol Dehydrogenase is reversible enzyme
TRUE
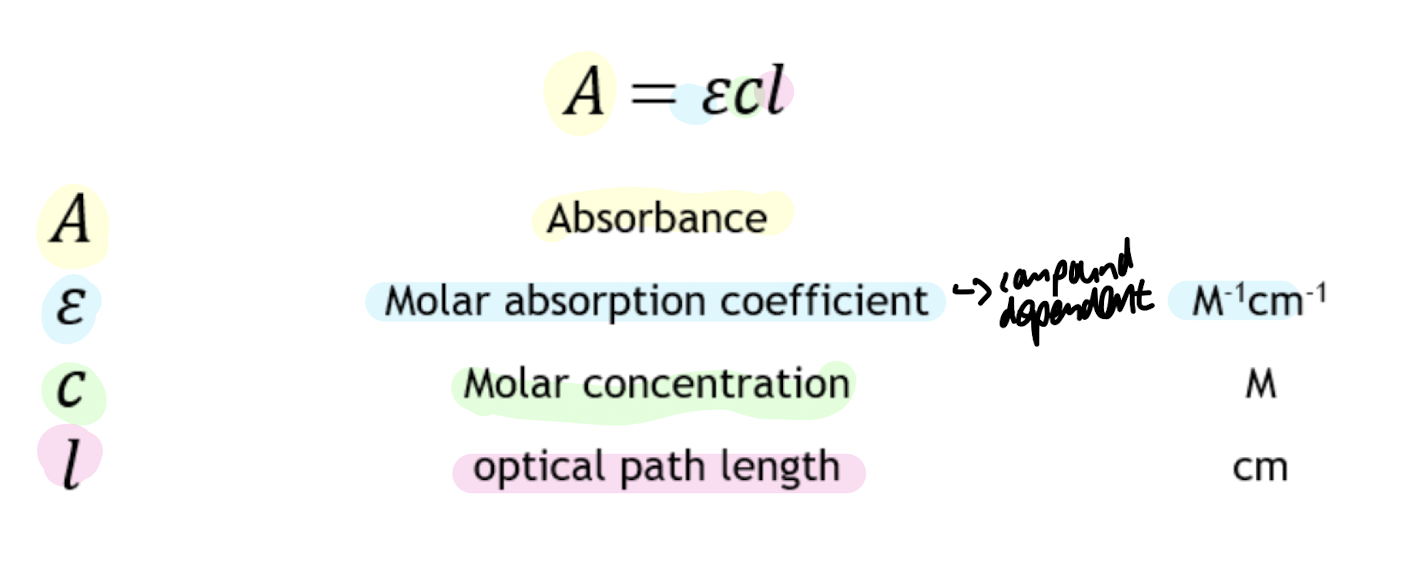
absorbance for NADH
340 nm
eq glycolysis to ethanol
C6H12O6 + 2HPO42- + 2ADP --> 2CH3CH2OH + 2ATP + 2H2O + 2CO2
number of steps in glycolysis
10 steps with 10 distinct enzymes that control the speed of glycolysis (to avoid spontaneous combustion)
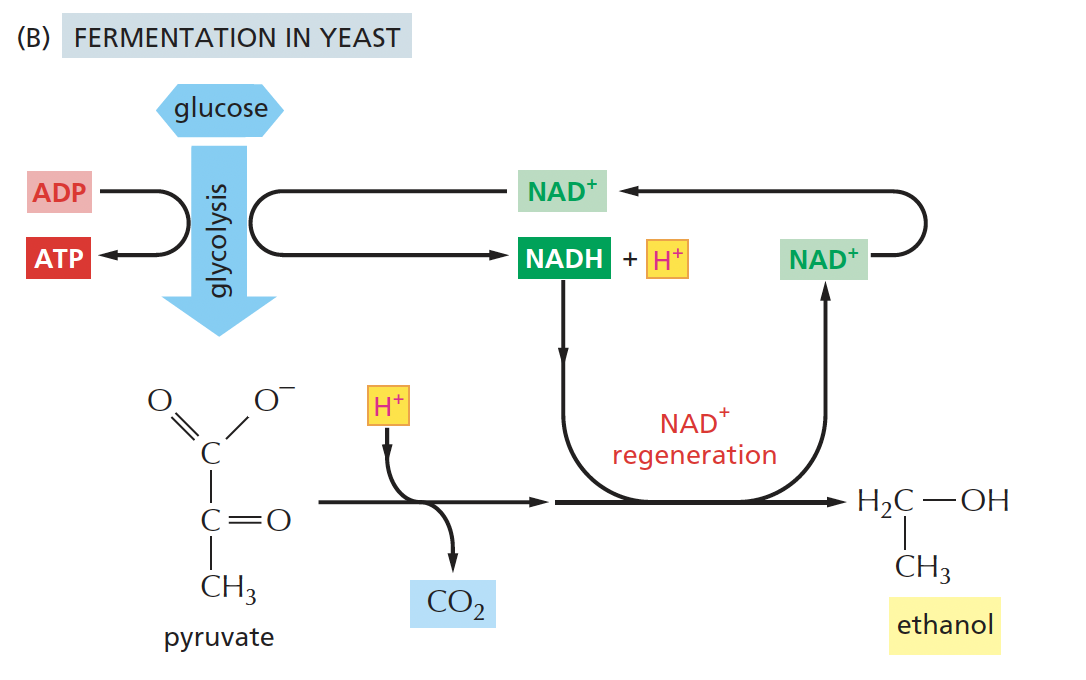
alcoholic fermentation break down
pyruvate → acetaldehyde → ethanol
*pyruvate is converted to ethanol (EtOH) + CO2, regenerating NAD⁺ in the process.
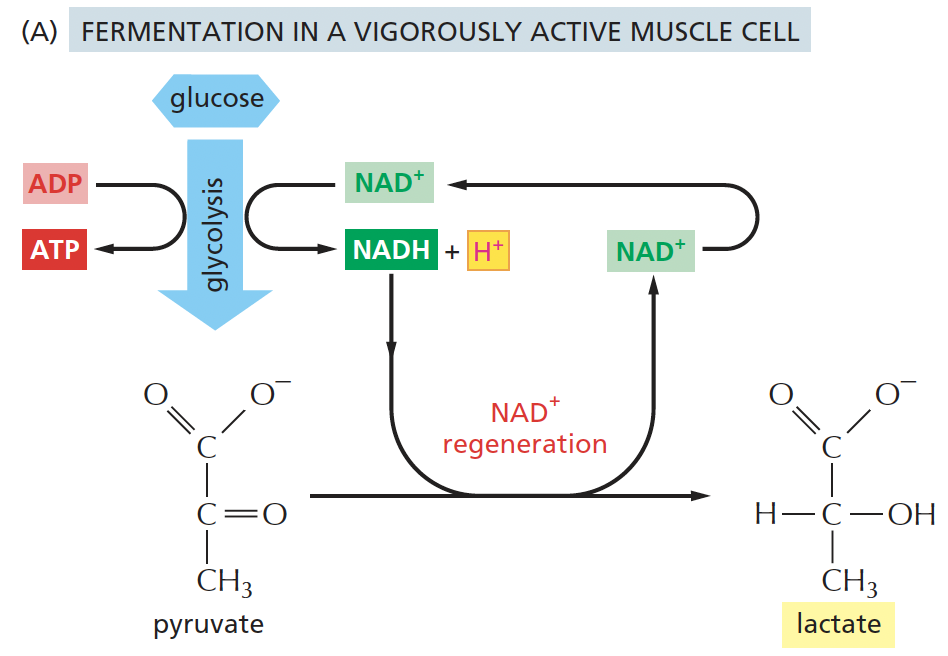
lactic acid fermentation i.e in muscle cell
pyruvate → lactate
*pyruvate is reduced to lactate, and NADH is oxidised to NAD⁺.
reduction of ethanol equation
CH3CH2OH (ethanol) + NAD+ → alcohol dehydrogenase CH3CHO (acetaldehyde) + NADH + H+
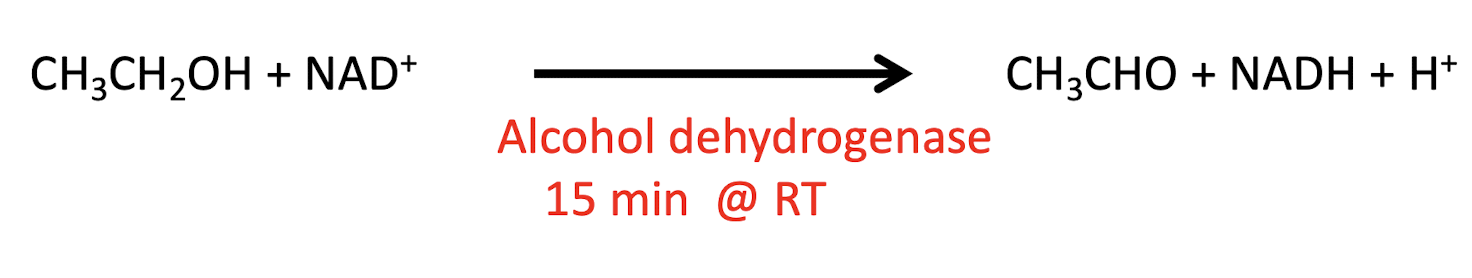
enzyme for reduction of ethanol
alcohol dehydrogenase
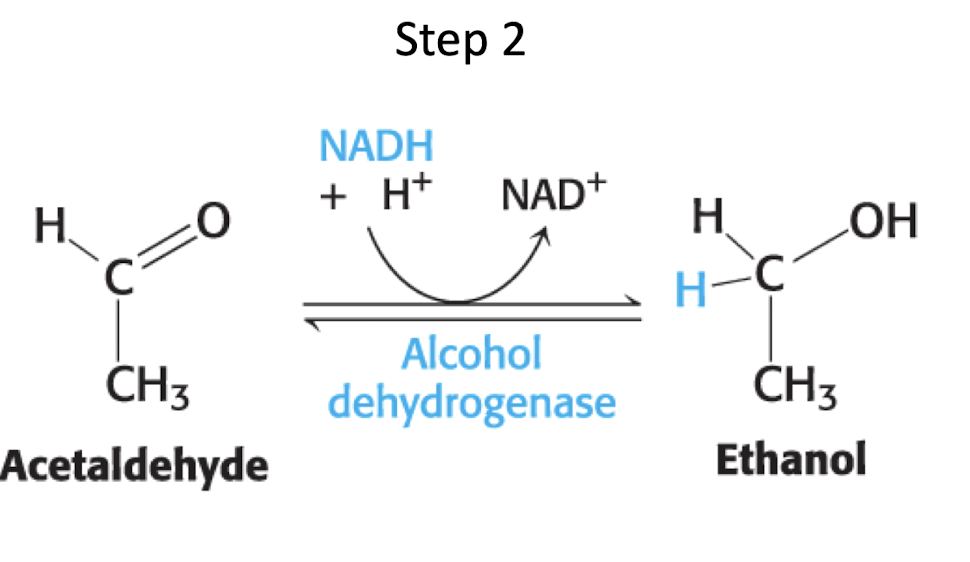
enzyme that converts pyruvate to acetaldehyde
pyruvate decarboxylase
yeast is
A) anaerobic
B) aerobic
C) facultative anaerobic
C) facultative anaerobic
what is iodoacetate?
iodoacetate is a glycolysis inhibitor
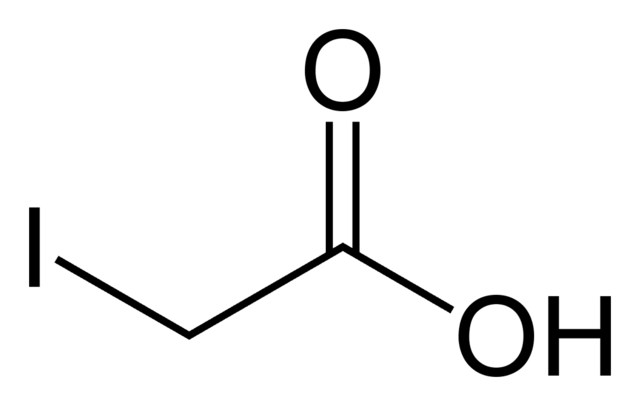
iodoacetate binds to the glycolytic enzyme ____________________ , where the ______ residue present in the enzyme binds to iodoacetate and forms a ______ bond, causing an irreversible reaction.
The enzyme cannot bond to its substrate and form ethanol due to the inhibition of _________ as the process stops
glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH), cysteine, thioether bond, glycolysis
*GAPDH catalyses the conversion of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate to 1,3-biphosphoglycerate resulting in production of NADH → GAPDH is dysfunctional = no NAD
Beer-Lambert law: