intro to animal science exam 2
1/404
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
405 Terms
what are the 9 systems of animal behavior?
sexual, caregiving(epimeletic), care-soliciting(et-epimeletic), agonistic, ingestive ,eliminative ,shelter seeking, investigative ,allelomimetic
Is there a relationship between sex drive and fertility?
not really
extreme sex drive has shown to ____ fertility
reduce
why can using an excessive number of males in a multiple-sire herd be beneficial?
it offsets poor breeders
what is a potential consequence of low fertility in a dominate bull within a herd?
it can lead to a low calf crop
how does social dominance among bull’s impact breeding within the same herd of cows?
a dominate bull may control breeding, but if he has low fertility, it negatively affects calf production
what tool is used to collect semen from bulls and stallions?
an artificial vagina
when looking at the sperm you're looking for?
sperm count and mobility, if its alive and swimming forward, and if its morphology is correct.
with castration males experience profound _____ _____…
behavioral changes (verifying importance of hormonal-directed expression)
intact males are more ____
aggressive
with cryptorchidism can the animal still breed?
yes
is cryptorchidism heritable?
yes
caregiving behavior is usually ____ oriented but ___ be ___
caregiving behavior is usually maternally oriented but can be both
what is it called when after birth the mother licks the young clean?
stimulation
stimulation after birth stimulates ___ ___ and encourages ____ and ___
stimulation after birth stimulates blood flow and encourages standing and nursing
when are pig weaned ?
3 weeks old
without strong stimulus of nursing milk output goes ____
down
creep feeding helps the dam to
start producing less milk
at what week is the peak for lactation curve
6 weeks
with reduction of nursing there is also a reduction in ____from the dam?
caregiving
cows usually give birth when?
at dark
with a reduction in milk the young are encouraged to do what?
to search for forage
care-soliciting behavior =
asking for attention/help
is care-soliciting behavior just for the young?
no also for adults when they ask for help
what’s the most effective way for a dam to recognize her offspring?
Smell
why do young nurse with rear end near female’s head?
so the female can smell them and identify them
when do young animals typically cry for help?
when they are distressed, disturbed, or hungry
how do dams and their offspring recognize each other?
through each other’s vocal sounds and smell
how dose a female determine whether to accept or reject a young animal attempting to nurse?
by recognizing its smell and vocalizations
what dose agonistic behavior include?
fight or flight response and aggressive/ passive behavior when in contact with another animal or producer
how do animals exhibit agonistic behavior when interacting with each other?
through fighting (mostly males)
when can agonistic behavior be observed?
interactions with other animals or humans and behavior during handling and restraint
when do males fight?
when they meet unfamiliar males
how are males managed during breeding season?
they are run singly
how are males managed outside the breeding season?
they are grouped with other males
what is the major cost associated with managing males?
having separate lots for each male so they don’t fight each other
what can happen when males fight? what should you do in consideration to this when you do put them together?
can fight to the point of exhaustion so put them together in early a.m. or late p.m. when temperature is low
how can fighting intensity be reduced when putting males together ?
by mixing in unfamiliar males and putting them in a neutral area (no territory)
what are the 4 stages to establish social dominance ?
offense, defense, escape , and passivity
unfamiliar males “____” after they ____ and assume _____ behavior
unfamiliar males “defeated” after they escape and assume passive behavior
why is it important to have sufficient space when putting males together?
need space for defeated male to submit
do females develop a pecking order? do they fight the same?
yes, they fight less intensely
unifiliar ___ sometimes fight. ___ rarely fight so can be grouped as strangers. (blank is a type of animal)
unifiliar sows sometimes fight. ewes rarely fight so can be grouped as strangers.
how do young animals learn social behavior?
by being raised with their own species
what can happen if young, intact males are isolated?
can attack humans
how do some animals behave before giving birth?
they withdraw from the group
how do most animals behave when there sick?
they withdraw from the group
what’s a big red flag in animal behavior?
when they withdraw from the group
what factors determine social rank in animals? (*5)
age, size, strength, experience, genetics
what happens to animals when there fed together vs when they aren’t? what is this a example of ___ ___ stimulus
they consume more food than if feed individually it’s a example of competitive environment stimulus
how dose age affects an animal’s ability to get its share of food?
older or weaker animals may have difficulty getting their share
how dose dominance in cows affect calf growth?
dominant cows wean heavier calves
what dose lip-smacking in a foal indicate?
“don’t kill me “
how to producers rank animal disposition?
from docile to wild
what can evaluating an animals posture help with?
interpreting mood and intent of the animal
what factors influence an animal’s disposition? (*3)
treatment, handling, and genetics
true or false producers don’t cull based on animal disposition?
false some do cull based on animal disposition
why do some producers cull based on disposition?
potential for injury, economic loss (fence/ facility) ,and it reduces excitability of other animals
what dose ease of handling depend on? (*4)
animal temperament, size, previous experience, and facility design
What are some factors that make an animal difficult to handle based on facility design? just name atleast 2
lighting, shadows, eye level, footing, etc….
your approach influences how the animal responds true or false
true
what can understand animal behavior help prevent with when handling? (*3)
prevent injury, undue stress, and physical exertion for all
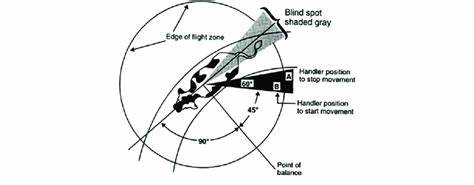
who made this?
Temple grandin
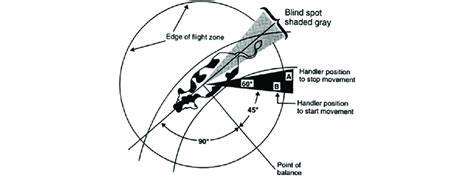
where should handler position not be? where should they be ?
should not be behind or Infront, should be off to the side
the size of an animal’s flight zone depends on?
the tameness or wildness of the animal
what type of odor is offensive to animals?
blood odor
what visual sensitivities do cattle have?
sensitive to shadows and unusual movement
what is the range of vision for cattle?
310-360 degrees
what type of handling equipment minimizes stress for cattle?
curved, solid-sided chutes
why are round pens preferred for animal handling?
they eliminate corners where animals might bunch up
what’s ingestive behavior?
eating or drinking
what do ruminants do before ingesting/swallowing food?
lubricate it with saliva it helps with fermentation
what do ruminants do after swallowing food?
they ruminate or regurgitate food for further chewing known as chewing their cud
do ruminates graze far away from water?
no
what areas do ruminates tend to overgraze?
tend to overgraze near water areas
chewing cud terms …
eruptate=
gas=
eruptate= bleach
gas= carbon dioxide
what can you do to encourage animals to move away from water?
fencing and placing a salt block away from water
what teeth do cows not have?
upper incisors
____ behavior varies among species and involves how animals void waste
eliminative
cattle, sheep, goats, and chickens void ____, meaning they do not have a specific area to defecate
indiscriminately
swine tend to defecate in ____ areas
specific
shrink occurs when animals lose at least ___ of their liveweight during transport
3%
horses prefer to void on sent piles left by other horses true or false?
true
true or false weight loss due to shrink occurs mostly during the first hour of transport?
true
how can weight loss from shrink be reduced ?
by careful handling
cattle and sheep seek ___ areas for rest and rumination during hot weather
shady
pigs search for ___ areas in hot weather
wet
if the weather is cold pigs crowed against one another when lying down which can result in ….
them smothering each other
true or false: shivering is a sign of heat stress in animals?
false that’s a sign of cold stress
__ and __ are signs to looks out for when monitoring animals for temperature discomfort
panting and shivering
what type of hazard do the animals incur when they take shelter under trees?
lighting hazard
what is investigative behavior?
when the animal goes up and investigates nonthreatening objects
pig sheep and goats are very ___ while sheep are more __ (think about investigative behaviors)
pig sheep and goats are very curious while sheep are more timid
what is allelomimetic behavior?
when animals of a species tend to do the same thing at the same time (think about the bathroom rule with girls)
what are some examples of allelomimetic behavior?
graze and ruminate at the same time, gather at watering hole
how is allelomimetic behavior useful for producers? (*3)
to observe behavior, identify any outliers or unusualties , and helps move groups from one place to another
what’s a zygote?
fertilized egg
what’s the name for a female gamete and male gamete?(2 diff names)
a female gamete is a egg and a male gamete is sperm
what’s the starting point of most life cycles?
zygote
true or false: zygote divides many times to produce an adult organism
true