lec 10 - epithelial transport
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
functional classifications of epithelia
specialised for absorption, secretion, or to act as a barrier
protective epithelia - cornea, skin
transporting epithelia - secretory epithelia, absorptive epithelia
exchange epithelia - endothelium of blood vessels
highly specialised epithelia - podocytes
ohms law equation
R=V/I
transepithelial resistance (RTE)
a meaasure of how much the epithelium opposes ion flow
in ohms
R=V/I
transepithelial conductance (GTE)
the inverse of resistance
indicates how easily ions move across the epithelium
relationshipb between R and G
if the resistance is small, the conductance will be high
if the resistance is large the conductance will be low
epithelia as electrical circuits
can be modelled as a group of resistors
two pathways in parallel:
transcellular - (Ra+Rb in series), paracellulae = tight junctions
ion channels and transporters alter the transcellular conductance
nephron low resistance, bladder epithelium super high
transepithelial voltage
the difference in electrical potential across the epithelium (lumen vs interstitial)
the interplay of electrogenic transport and junctional resistance influences the ability of an epithelium to maintain a significant transepithelial volrage
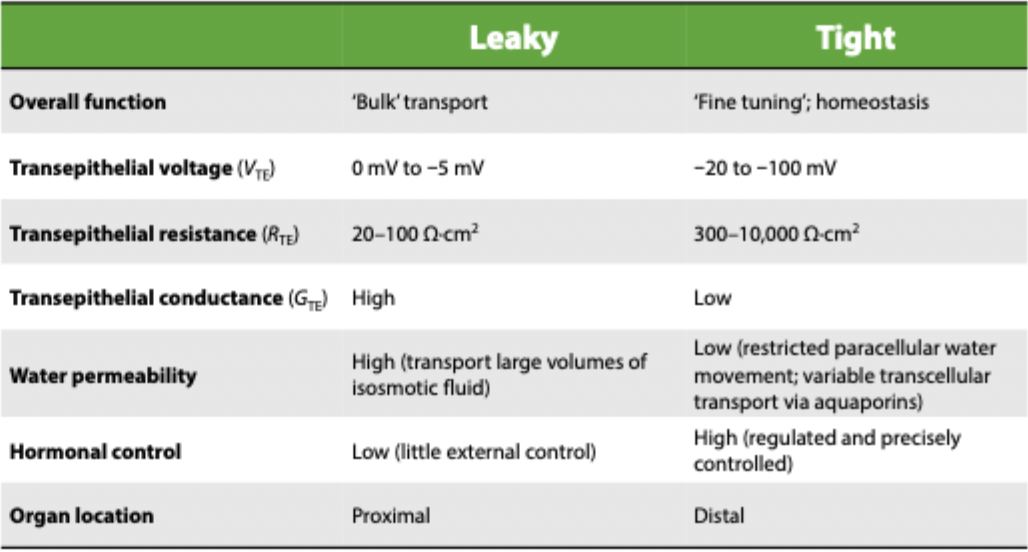
epithelial voltage in tight vs leaky epithelia
tight = large VTE - limited paracellular ion flow
leaky = small VTE - low resistance TJ enable paracellular ion flow
electrical properties of leaky epithelia
high current flow through both the paracellular and transcellular pathways
low transepithelial resistance - 10-10 ohms/cm
transepithelial voltage is -5 to 0mV
hormonal control is low to absent - prioritise speed and bulk recovery over precise regulation
electrical properties of tight epithelia
tight junctions restrict paracelliular ion movement, and low ion transport through the transcellular pathway
transepithelial resistance 300-10000 ohm/cm
transepithelial voltage -20 to -100mV
hormonal control - highly regulated
activity and expression of ion channels and transporters are under close control
transport can be precisely adjusted to maintain homeostasis
water permeability in leaky vs tight epithelia
leaky - hgih hydraulic conductivity - hgih expressio fo AQPs, TJs allow paracellular movement, transport large aounts of isosmotic fluid
tight - low hydraulic conductivity, tight junctions restrict or prevent paracellular water transport, low transport via AQPs, required for regulation of fluid osmolarity (e.g. urine concentration in medulla)
ADH and water permeability
ADH increases water permeability in tight distal nephron segments
leaky epithelia (proximal tubule) have intrinsically high water permeability
right epithelium has low baseline water permeability
can be upregulated by the hormone ADH to increase expression of AQP in the apical membrane
tight vs leaky epithelial location
leaky - proximal regions of organs (PCT, duodenum and jejunum of the small intestine)
tight - distal regions of organs (DCT, distal colon of large intestine)
epithelial summary table