Communication Disorders
1/150
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
151 Terms
Communication
the exchange of ideas from one person to another
There must be sender, a message, and a receiver
Sociolinguistics
How society affects language
Cultural Identity - Age, gender, ethnic background, education
Setting- where communication takes place
Participants - who’s engaged in conversation
Language
A socially shared code or conventional system for representing concepts or ideas through the use of arbitrary symbols and rule governed combinations of those symbols
Language is
-socially shared
-a code which is a system of words, letters, and figures that represent ideas
Language is both..
dynamic - changes over the centuries and decades
generative - we don't speak in memorized forms. (i.e when a professor teaches the same material to a new class they don’t use the same exact words)
Receptive Language
-Understanding
-Comprehension
-Discrimination
-Following Directions
Expressive Language
-What we verbally convey
-Sentence Formulation
-Putting together grammar verbally
-Naming, Describing
Linguistic intuiton
A natural understanding of the rules
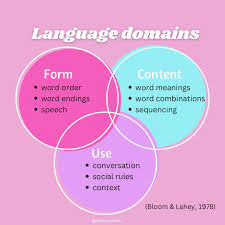
The Bloom and Lahey Model of Language
content, form, use
Form
Structure of language. Includes phonology, morphology, and syntax
Content
Meaning of language - Includes semantics
Use
Social conventions of language, pragmatics
Phonology
study of the sounds of a language
a phoneme is a minimal unit of sound
Morphology
a morpheme or word is a minimal unit of meaning
word structure can change by adding an ending such a as (s) or (ing)
Syntax
grammar of the language
governs how we put words together in a sentence
Pragmatics
-the social part of language
-ex: turn taking, eye contact,
speech
-verbal output
-physical rather than cognitive
Speech incorporates
-fluency (rate and smoothness of speech)
-respiration(breath support)
-phonation(use of voice)
-resonation(the oral, nasal, pharynx enhancing sound)
-articulation(the shaping of sounds with the tongue, lips, teeth, hard palate)
Anamtomical systems of speech and hearing
Nervous System
Respiratory System
Phonatory/ Voice System
Articulatory System
Auditory System
Parameters of Voice
-Loudness
-Pitch
-Quality
-Variability
Artifacts
How we decorate self or environment
Kinesics
the movement of the body as a means of nonverbal communication
proxemics
the distance between individuals during communication
intimate (gf/bf)
social (friends hanging out)
formal (professor teaching students)
public (president making speech)
Chronemics
the study of how time affects communication and the way people perceive and value time in interactions.
Dialect
-Variation/subset within a language. It is not a disorder. (eg. think of military branches
-Includes pronunciation
-Includes vocabulary
-Includes grammar
-very specific consistent phonological rules. (eg. Del of Cons cluster)
John ran fast (fas)
Genderlect
-People communicating differently based on the social cues, constructs and societal expectations of gender.
Idiolect
an individual’s unique way of speaking.
Communication Disorder
Impairment in the ability to receive, send, process and comprehend concepts or verbal/non-verbal and graphic symbol systems.
Etiology - the cause of a disease
acquired (caused over time) vs congenital (caused at birth)
delay (when a child is developing behind, but on the right track) vs. deviance (when a child is off the track with unusual patterns that don't match typical development)
organic (a disease thats neurological or physical) vs functional (no clear cause)
Language Disorders
Disorders of Form, Content and Use
expressive, receptive or both
impacts phonology, morphology, syntax, semantics, pragmatics.
Speech Sound Disorder
Articulation
Actual production of specific sounds. Deletions, substitutions, distortions ( eg. lisp)
phonological
Breaks the rules for producing and combining speech sounds in a language.
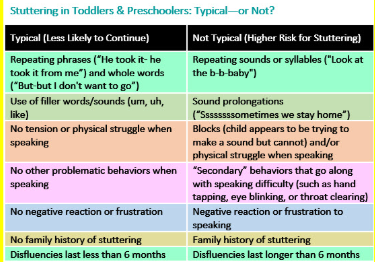
Fluency Disorders
Stuttering - affects rates, rhythm, timing of speech
includes: audible blocks, syllable reps, prolongations
Voice Disorder - Affects pitch, loudness, quality
Polyps, tumors, nodules,ulcers
Vocal abuse
Bad vocal habits
Neurogenic diseases (damage to nervous system)
Hearing Disorders - Deafness
When person’s ability to perceive sound is limited to such an extent that the primary sensory input for communication is other than the auditory channel.
-can be congenital (from birth) or acquired
Hearing loss may be…
Bilateral vs Unilateral
Mild vs Severe
Conductive (damage to the outer ear/middle ear) vs. sensorineural (damage to inner ear/cochlea)
Central Auditory Processing Disorder
Normal hearing but difficulty understanding or comprehending speech.
Education of the Handicapped Act/IDEA- INDIVIDUALS WITH DISABILITIES ACT
-Free and equal education for children with disabilities in LEAST RESTRICTIVE ENVIRONMENT
-Originally covered ages 5 thru 21
-Ensures all children with an identified disability receive special education and related services to address their individual needs.
-Ensure that all children with disabilities be prepared for employment and independent living.
Education of Handicapped Act Amendment -1986
Provide services when identified
Infants and toddlers are eligible for services for free through public schools
The Rehabilitation Act -1973
-Prohibits discrimination against people with disabilities
-with agencies that receives federal funds like schools
-section 504 of the law remained unenforced
Americans with Disabilities Act 1990
prohibits discrimination against people with disabilities in key areas of public life, including employment, state and local government services, public accommodations, transportation, and telecommunications. It mandates that employers with 15 or more employees provide reasonable accommodations, ensures equal access to public services, and requires private businesses to be accessible, while also covering access to telecommunications (allow people with hearing and speech disabilities to communicate)
Assistive Technology Act 2004
provides federal and state funding for programs to help individuals with disabilities gain access to and use assistive technology
offer services such as device demonstrations, loans, financing options, and training to help people obtain the AT needed for independent living, education, and employment
Speech Language Pathologist
assess, diagnose, treat disorders of speech, language and hearing
need to complete undergrad, and complete a masters degree, must receive 200 hours of clinical training, must complete clinical fellowship, must get CCC (Certificate of Clinical Competence), must get a state license
Audiologist
diagnoses, assesses, treats hard of hearing & deafness, dispenses hearing aids
4 year undergrad, 4 year audiology, must get a phD to become an audiologist
Psychologists
assesses, counsels cognitive issues (ADHD, Anxiety, OCD, bipolar, depression etc)
physical therapist
gross motor skills (i.e transfer/ learn how to move from one place to another, walking, running, )
Occupational Therapist - fine motor skills
teaching how to write,crafts, drinking, using scissors
Prelinguistic Period
The prelinguistic period is the developmental stage, from birth to around 18 months, when infants communicate and develop foundational language skills before they begin to use meaningful words or signs. During this time, babies progress through various vocalizations and non-vocal communication, including crying, cooing, babbling, making eye contact, gesturing, and responding to social cues, all of which lay the groundwork for future language acquisition.
The Neonate (less than a month old)
-Sleep approx 17 hours
-Cat naps followed by bursts of constant hunger.(brain is growing)
-Reflexive/ Vegetative sounds appear (burps, cries, discomfort)
Neonate is a bundle of reflexes/ neural connections and they grow with age
The standout features for the newborn are reflexes
Reflex is an automatic, involuntary motor pattern
Reflexes protect the baby from things in their environment
Ensures survival, protects vital systems
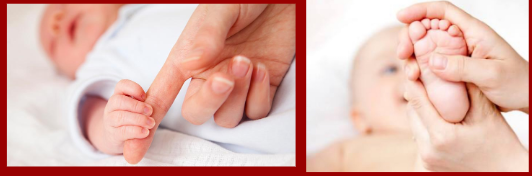
Palmer and Plantar Grasp Reflex
Stick finger in palm, baby will have firm grip on finger, Stroke ball of the foot, and toes will curl under

Rooting reflex
opening their mouth in response to a touch on their cheek or mouth

Babkin
applying pressure to palms will cause the baby to open mouth and close eyes
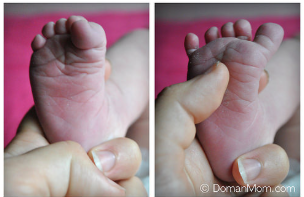
Babinski
stroke the back of foot and the toes will stretch out
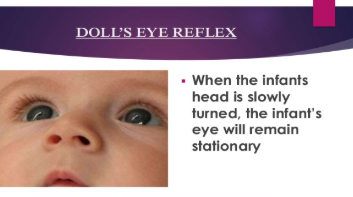
Doll’s Eye
when the infant’s head is slowly turned the infant’s eye will remain stationary
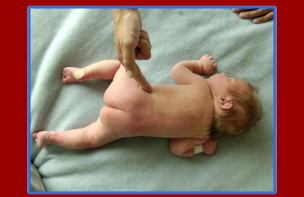
Galant
Stroke the back to one side of the spine, what will happen is that the trunk will arch towards the side being stroked
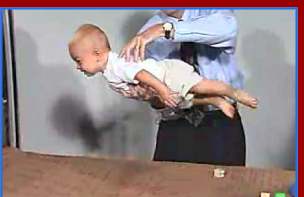
Perez
Stroke the baby’s spine from tail to head, Head will flex out and body will go straight, It also can cause baby to urinate

Parachute
Toss babies up in air, baby will place arms and legs out like a parachute
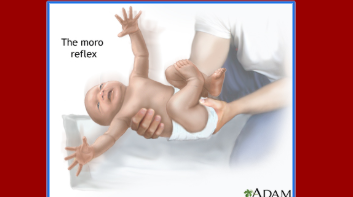
Moro/Startle
Make a sudden, jarring noise, drop the head back a few inches, drop the baby a few inches

Landau
Lay a baby down on tummy, will open arms out to the side and feet go up like swimming

Asymmetrical Tonic Neck Reflex also known as Fencing reflex (may be seen with Cerebral Palsy)
gently turn the baby's head to one side while they are lying on their back. The infant's arm on the same side as their face will extend straight out, while the arm on the opposite side will bend at the elbow
Developmental milestones
Holds up Head: 2-3 mths
Grasps Toy: 4 mths
Sit supported: 5 mths
Rolls over both sides: 6 mths
Sit unsupported: 7 mths
Pulls up squat: 8-10 mths
Crawls: 8-10 mths
Srands Supported 9-10 mths
Stands no support: 11-12 mths
Walks no support - 1 year
Communication milestones:
Distinguish caregivers from strangers: 2 weeks
Eye contact with caregiver: 6 weeks
Gazing and making sounds: 1 month
Vocalization pattern more speech like: 3 months
Rituals/ repeated habits (peek-a-boo, feeding routines): 3-4 months
Interest in toys: 6 months
Pointing at objects (signs of intentional communication): 9 months
PCFs or Vocables, when babies create sound patterns consistently to mean something even if its not a real word (I.e when a baby says baba everytime they want picked up)
Nelson, 1973 First Words & Why they are important
Naming (Nominals): Mama, Cat
Actions: drink, kiss, eat wash
Descriptions: big, little
Personal/Social: hi, bye bye
Functional: this, that, for
Vocabulary of 12-18 month/ Toddler
Lexicon reflects child’s environment
12 months - first meaningful word
12-18 months, 50 word vocabulary
starts combining words around 18 months (kiss baby, push ball)
Short term memory increases for longer constructions
By 24-3- months 150-300 words
overextension - applying a word to multiple things (dog, kitty, pig) or calling a babysitter “mama)
underextension - when the word isn’t extended one enough (if a baby calls their own dog by dog, but they won’t call a different kind of dog by its name)
variability - the child calls something by multiple names (calling a cat, kitty, lion, kiki, etc)
Phonological idioms and regression
when a child used to say something perfectly but it seemed like they went backwards and said the word “different” or “wrong”
Fast Mapping
Happens around age 2
Where children learn words and grow their lexicon rapidly because of words they already know
Phonological Processes
Syllable Structure processes- When you change the syllable of the word
Unstressed syllables reduction (block and block)
cluster reduction (bag and ba)
Substitution processes - changing one word for another)
Gliding (rabbit and wabbit)
Assimilation - substituting one sound for another one that sounds like it (pie and bye)
Metatheses- switching words around
Vision at Birth
Nearsighted at birth
Limited vision
Preference for high contrast
Hearing at Birth
Middle ear fluid filled
Respond to sounds
Able to distinguish loudness and duration
Preference for human speech
Can discriminate sounds
Muscle Control at Birth
Downward progression
Walks around 12 months
Dependent on adults for protection & well-being through age 2
Motherese
The innate way that adults talk to babies
Example: Speak in a higher pitch, exaggerate consonants & stretch vowels, and vary your volume.
Stage 1 - Phonation Stage (0-1 Month)
Newborns produce basic vocal sounds—mainly reflexive noises and comfort sounds—without clear speech intent.
Phonation: Sound production from the vocal cords.
Closed-mouth phonation: Humming or throat sounds made without opening the mouth.
Examples: Soft cooing or grunting, throaty hums like “mmm” or “uhh.”
Stage 2 - The Goo Stage (2-3 Months)
Infants begin to make back-of-the-mouth (velar) consonant sounds.
Key Terms:
Velar consonants: Sounds produced with the back of the tongue against the soft palate (e.g., /k/ and /g/).
Examples: “goo,” “coo,” or “gah.”
Stage 3 - The Expansion Stage (4-6 months)
Babies experiment with a wider variety of vocalizations and learn control over pitch and volume.
Key Terms:
Bilabial trills: Vibrating both lips together (like blowing a “raspberry”).
Strong vowels: Clear, loud vowel-like sounds.
Growling/Squeals: Low-pitched growls and high-pitched squeals showing vocal range.
Examples: “aaaaah,” raspberries (lip buzzes), squealing with excitement, or playful growling.
Stage 4 – The Canonical Stage (7–10 months)
Infants start producing repetitive consonant-vowel combinations that resemble real words.
Key Terms:
Canonical babble: Strings of repeated syllables.
Reduplicated babble: Same syllable repeated (e.g., “mama,” “dada,” “baba”).
Non-reduplicated babble: Varied syllables (e.g., “ada,” “maboo”).
Examples: “mama,” “baba,” or “ada.”
Stage 5 – The Variegated Babble Stage (11–12 months)
Babble becomes more diverse and speech-like, with varying consonant and vowel combinations, gibberish words, and expressive intonation patterns.
Key Terms:
Variegated babble: Mixed syllables that sound more like adult speech rhythm.
Intonation: Changes in pitch and melody, imitating conversational patterns.
Examples: “bada,” “gaboo,” or gibberish that mimics the tone of real conversation (“ba-da-goo?” said like a question).
Preschoolers (2 ½ yrs to 5 years) The Active learner
Language learning is active process
Learn from interactions
Caregivers provide feedback & models
Start to absorb the rules
3 yr old should:maintain 2-3 conversation turns
Begin to consider speaker’s perspective using words like: here, there, this, that
-90% of adult syntax acquired by age 5!
complex combinations (the big doggie)
MLU-mean length of utterance is longer
nouns, verbs, pronouns, articles prepositions, adverbs, adjectives, negatives
who, what, where, why, when, how
Joining phrases to make compound sentences (Ex: The cat is sleeping and the dog is running)
communication disorder
an impairment in the ability to receive, send, process or comprehend concepts or verbal, nonverbal, or graphic systems
Delay vs. Deviance
Follows a normal course but at a slower rate vs. unusual/different
School-Age Thru Adolescence (6 yrs+)
Most communication now is outside the home
Concrete thought → abstract thinking
Left temporal cortex used in language encoding and decoding
Addition of reading and writing
Metalinguistic skills (Ex: the conscious awareness and ability to reflect on, analyze, and manipulate language as an object or system)
Theory of Mind
Develops between age 4 through 5
It is the ability to recognize that other people see the world differently from the way you do.
Kindergarten variables predicting success by 2nd grade
Letter identification
Oral sentence imitation
Phonological awareness
Rapid oral naming
Receptive and Expressive language skills
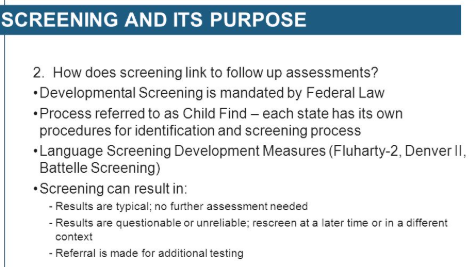
Screenings
IDEA mandates all children from birth to 20 are given opportunity for special services if needed.
Lots of kids can be seen quickly
Gives limited information. Just a pass/fail.
-Assessments give us more detailed information, but a screening WILL NOT
Hearing Screening
Clinician presents pure tone at 20 DBHL or (25 depending on condition)
500, 1000, 2000, 4000 HZ
Child raises hand when hears tone.
Red is always- Right ear
Blue is always - Left ear
otoscope is used to look in the ear
Screening Outcomes
False Positive- results suggest problem, but person may not have a problem.
Test may suggest a problem and person may actually have one.
Test results show may show no problem and none may exist.
False Negative- Test results may show no problem, but the person may actually have a problem.
Goals of Assessment
Verification of the problem
Description & quantification of strengths and weaknesses
Statement of severity ( mild, mod, severe, profound)
Treatment Plan- (plan of action)
Prognosis-(will person get better)
What happens in an assessment?
Case history
Interview
General observations
*Testing
Close interview
Score tests
Determine diagnosis
Write report
Important: Make sure assessment is culturally sensitive! Different languages are not disorders. Dialects are not disorders. If someone doesn’t speak the same language you need an interpreter or a bilingual clinician to provide services in the native language of your client.
Tests should be..
Norm referenced (compare a student’s performance against the performance of their peers)
Reliable (consistent and unchanging) and valid
yield raw scores, percentiles, standard scores, age equiv
in the child’s native language
Establishing goals and objectives
-X does Y with ____% success in a specified condition.
-Provides a starting point for planning & measuring progress
Audience
Behavior
Condition
Degree
Example: Eliana will use the /s/ sound in the beginning, middle and final position of words with 80% accuracy

Clinical Elements of Assessments
-High (ex: specific games/plans for specific skills) vs. Low structure (general/less planned games)
-Counseling (equipping parents/counseling parents in how to communicate with children instead of sending children to therapy)
-Pull out (taking children out of the classroom for therapy and then sending them back) vs. Push in models (teachers go in to the classrooms and teach all kids)
-Family and Environmental involvement
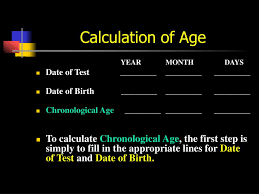
Calculating Chronological Age
Date of Testing - Date of Birth
(Flip dates backwards, year, month, day)
Basal and Ceiling
Basal is the point where a test-taker is assumed to have answered all previous items correctly, allowing the examiner to skip easier questions and save time.
Ceiling is the point where the test-taker is assumed to have answered all future items incorrectly, stopping the test to prevent fatigue and discouragement from overly difficult questions
these rules create an "effective range" of items, making the assessment more efficient and accurate for the individual
Definition of LANGUAGE DISORDER
A heterogeneous group of developmental and/or acquired disorders/delays characterized by deficits and/or immaturities in the use of spoken or written language for comprehension and/or production purposes that may involve form, content and/use of language in any combination.
Types of Disorders
Developmental Disability
Learning Disability
Specific Language Impairment (SLI) also called DLD
Pervasive Developmental Disorder PDD or Spectrum Disorder (Autism)
Neglect/Abuse
Developmental Disability/Delay
Substantial limitations in present functioning (tying shoes, making bed, everyday activities)
2. Significantly subaverage intellectual functioning. (90-110 is average IQ, below 90 can be alarming and IQ score is consistent with reading score, etc)
3. Concurrent related limitations in 2 or more adaptive skill areas. (acitivities of daily living for example struggling with a job)
4. Manifests before age 18
Developmental Delay Causes
Social/Environmental - (poor housing, poor hygiene, inadequate diet, lack of medical care)
Biological - Genetic: Specific characteristics or traits passed from one generation to another or Maternal Infections:such as HIV, Cancer, STD’s, Hepatitis B, Bacterial, Alcohol, smoking, abuse, mercury, marijuana, raw eggs, gestational diabetes or Brain differences: Cerebral Palsy, Spina Bifida, Microcephaly, Hydrocephalus, Meningitis)
Causes of Genetic Disorders
-Each chromosome is made up of genes. Genes make proteins which promote growth of body functions
-1 or more genes or chromosomes may be missing or mutated.
Chromosomal Disorders
Disorder in structure or number of chromosomes or both.
- 23 pairs. The 23rd pair differs between male & female.
-Female- 2 XXs, Male 1X 1Y
Syndrome
-Disease or disorder that shares more than 1 identifying feature or symptom.
-Each genetic syndrome will have many typical features
Besides similar outward physical features….
-shared problems with organs (heart, kidneys, brain, bones)
Down Syndrome/ Trisomy 21
-3 copies of chromosome 21
-1/600-800 live births
-mild to severe
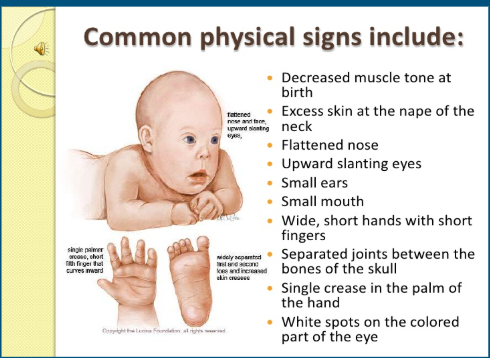
Down Syndrome’s Speech and language skills
-Decreased Intellectual abilities (lower IQ)
-Decreased lexicon
-Memory problems
-Articulation problems
-Speech problems
-conductive hearing loss
-concrete language (idiomatic expressions can be difficult to understand such as “it’s quarter past 5”)
-behavioral problems
-reading is level higher than language & cognitive (reading score is not consistent with iQ score)