Consumer Behavior Exam 3
5.0(2)
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/53
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
1
New cards
microcultures
a group who share similar values and tastes that are subsumed within a larger culture
Affect consumer culture, culture is universal and hierarchical
individuals may belong to many cultural groups at once
Affect consumer culture, culture is universal and hierarchical
individuals may belong to many cultural groups at once
2
New cards
socialization
learning about everyday experience through observation
3
New cards
how is culture learned
through socialization , enculturation, acculturation, and ethnic identification
4
New cards
enculturation
learning native culture
5
New cards
acculturation
learning about culture other than native one
6
New cards
ethnic identification
degree to which consumers feel a sense of belonging to their culture
7
New cards
consumer ethnocentrism
Belief native products are superior
8
New cards
Modeling
process of imitating others' behavior
9
New cards
shaping
adapt to a culture rewards and sanctions
10
New cards
verbal communication
transfer of info through spoken or written word
Dialects- Specific to a region
Dialects- Specific to a region
11
New cards
Metric equivalence
numeric uniformly across cultures
12
New cards
globish
Reduces the English vocabulary to around 1500 words
13
New cards
Globalization
marketing strategy may be global but the implementation and tactics should be local
14
New cards
Five Step Decision Making Process
1. Problem Recognition
2. Information Search
3. Evaluation of Alternatives
4. Purchase Decision (Choice)
5. Post-Purchase evaluation
2. Information Search
3. Evaluation of Alternatives
4. Purchase Decision (Choice)
5. Post-Purchase evaluation
15
New cards
low involvment
low risk, habitual decision making
16
New cards
high involvement
high risk. extended decision making
17
New cards
involvement
the degree of personal relevance that a consumer finds in a CB act
18
New cards
types of risk
financial, social, performance, physical, time
19
New cards
decision fatigue
emotional and mental strain resulting from a burden of choices
- may lead to physical and emotional distress
- may lead to physical and emotional distress
20
New cards
search behavior
Ongoing
Pre Purchase
Internal
External
Pre Purchase
Internal
External
21
New cards
ZMOT
zero moment of truth
22
New cards
Evaluative criteria
Attributes
Features
Potential benefits
Features
Potential benefits
23
New cards
Determinant criteria
The most carefully considered criteria
Directly related to choice made
Directly related to choice made
24
New cards
How do marketers determine which criteria consumers use?
Techniques:
Surveys
Warranty registrations
Conjoint analysis
Perceptual mapping
Surveys
Warranty registrations
Conjoint analysis
Perceptual mapping
25
New cards
Situational factors
Value varies with situations
contextual effects that are not enduring
Temporary conditions- that impact CB
contextual effects that are not enduring
Temporary conditions- that impact CB
26
New cards
antecedent conditions
time, shopping orientation, personal traits, resources, mood, security/fear
27
New cards
purchase environment
servicescape, atmospherics, nudges, experience, ownership
28
New cards
postpurchase processes
consumer satisfaction, product disposal, alternative markets
29
New cards
Time and consumer behavior
Time pressure sense of urgency
Time of year seasonality
Time of day circadian cycle
Time of year seasonality
Time of day circadian cycle
30
New cards
Shopping orientations
Acquisitional, Epistemic, Experiential, Impulsive
31
New cards
Acquisitional
Activity shopping for a specific purchase
Ex: Have a headache, need to buy an Advil
Ex: Have a headache, need to buy an Advil
32
New cards
Epistemic
Activities oriented towards gathering knowledge
33
New cards
Experiential
Fun, excitement, interest, relaxation
Ex: Buy a wedding dress or make it an experience
Ex: Buy a wedding dress or make it an experience
34
New cards
Impulsive
Orientation of spontaneity
35
New cards
Three additional antecedent conditions
Resources: budgeted amount
Mood: exaggerates everything
security/fear
Mood: exaggerates everything
security/fear
36
New cards
Servicescape
services physical environment
37
New cards
Atmospherics
feelings created by the total aura of physical environment
38
New cards
Atmosphere elements
Odors, music, merchandising, social setting, color
These can all nudge!!
These can all nudge!!
39
New cards
recommerce
Selling or trading your possessions (squeeze more value from them)
40
New cards
swishing
Organizing parties to exchange clothing/accessories
41
New cards
Underground economy
Used product sales (flea markets, garage sales, etc)
42
New cards
disposal
Trash
Recycling
Recommerce
Swishing
Underground economy
Recycling
Recommerce
Swishing
Underground economy
43
New cards
Green marketing
products that supposedly satisfy both the need of consumers and society in a sustainable way
44
New cards
greenwashing
unsubstantiated
and/or exaggerated claim(s) to
deceive consumers into believing
that a company's products are
environmentally friendly.
and/or exaggerated claim(s) to
deceive consumers into believing
that a company's products are
environmentally friendly.
45
New cards
Sustainable marketing concept
Genuinely delivering value to customers in a way that natural and human capital are preserved or enhanced
46
New cards
Linear economy vs. circular economy
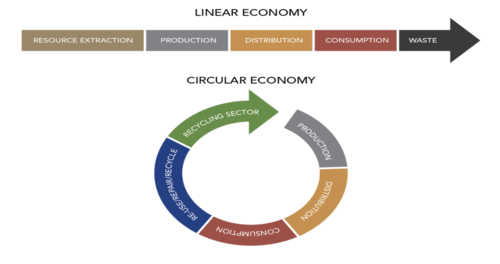
47
New cards
marketing's impact on environment
Stimulating (over-) consumption
Use of environmental goods to increase profit margins
Unnecessary packaging
Long supply chains
Use of environmental goods to increase profit margins
Unnecessary packaging
Long supply chains
48
New cards
garbage patch
parts of the ocean with a high density of human trash, primarily plastics, that weighs over 250,000 tons
49
New cards
what can we do as marketers about moving from green to sustainable?
- Integrate a sense of mission into the core of business
- Integrating social and environmental causes into products
- Focus on long term financial gains. Financial gains by companies that integrated sustainability into their core business up 40% in 2013 due to consumer demand
- Top down, rather than bottom up approach
Sustainability as a competitive advantage***
- Integrating social and environmental causes into products
- Focus on long term financial gains. Financial gains by companies that integrated sustainability into their core business up 40% in 2013 due to consumer demand
- Top down, rather than bottom up approach
Sustainability as a competitive advantage***
50
New cards
ventoso ship supply case
Italian sailboat manufacturer looking to change consumer behavior with specific targeting marketing campaigns and understand the purchasing rationale of the Italian consumer to aid development of a new international marketing campaign
Conducted interviews with potential buyers within a similar demographic to investigate the concept of an "ideal sailing boat", looked into Photosort, and Sensory Marketing
Conducted interviews with potential buyers within a similar demographic to investigate the concept of an "ideal sailing boat", looked into Photosort, and Sensory Marketing
51
New cards
Marketing Rebellion - Chapter 11
notes: transforming culture was not just the right thing to do, it was the profitable thing to do
care about employees and culture will extend to caring about processes products and customers (ex: when paul fired an employee over safety for the nuns in mexico)
practical cultural change looks like demonstrating change at the top from the ceo, unifying measurement that drives the right behaviors, make visible what is hidden, submit to the truth that customers are the marketers, take control and not look for the easy way out, do something dramatic
the traditional CMO is dead, main functions of a successful CMO are to educate, analyze, and collaborate (advertising agencies are dying)
measurement will be a signifiant hurdle to winning int he world of the third rebellion
fans vs customers, fans want to be part of what you do, customers dont really care about your team or culture, wistia created fans
if you truly connect in a personal human way, your marketing can end, if you are delivering a product that solves a problem, then the human centered culture of your company and organic customer connection drives demand and sales
care about employees and culture will extend to caring about processes products and customers (ex: when paul fired an employee over safety for the nuns in mexico)
practical cultural change looks like demonstrating change at the top from the ceo, unifying measurement that drives the right behaviors, make visible what is hidden, submit to the truth that customers are the marketers, take control and not look for the easy way out, do something dramatic
the traditional CMO is dead, main functions of a successful CMO are to educate, analyze, and collaborate (advertising agencies are dying)
measurement will be a signifiant hurdle to winning int he world of the third rebellion
fans vs customers, fans want to be part of what you do, customers dont really care about your team or culture, wistia created fans
if you truly connect in a personal human way, your marketing can end, if you are delivering a product that solves a problem, then the human centered culture of your company and organic customer connection drives demand and sales
52
New cards
Ted Radio Hour (2017) "Decisions decisions decisions"
how we make the choices we make, and how we learn to live with them
examples in the podcast: diet pepsi that there is more than one perfect product, campbell's prego made extra chunky sauces giving consumers many choices
choice overload problem, companies are overloading consumers with choice ( the advice for companies was to cut, less is more) ex: head and shoulders went down to 15 types and saw an increase in sales
paralyzed by choice, heart vs mind and gut vs reason ( constantly asking yourself what I want and what should I chose, they don't give the same answer), choice is learned
chose is the great american virtue, correlation of culture with choice and individualism
the value of choice depends on our ability to perceive differences between the options
- easy choice is that one alternative is better than the other, hard choices are hard because there is no best option (make it easier is to commit)
examples in the podcast: diet pepsi that there is more than one perfect product, campbell's prego made extra chunky sauces giving consumers many choices
choice overload problem, companies are overloading consumers with choice ( the advice for companies was to cut, less is more) ex: head and shoulders went down to 15 types and saw an increase in sales
paralyzed by choice, heart vs mind and gut vs reason ( constantly asking yourself what I want and what should I chose, they don't give the same answer), choice is learned
chose is the great american virtue, correlation of culture with choice and individualism
the value of choice depends on our ability to perceive differences between the options
- easy choice is that one alternative is better than the other, hard choices are hard because there is no best option (make it easier is to commit)
53
New cards
TED Radio Hour (2018) "Nudge"
It's hard to change habits, but a gentle push can move us in the right direction
deceptively simple "nudges" for managing our kids, our health, and our aspirations
small tweaks in the words we use and behaviors can have huge impacts and outcomes
the easiest way to make someone to make the right choice is to reverse the choice, make people to chose to opt out instead of opting in
make kids eat more apples by putting them in a bag and cutting them up
paradoxial nudge that smoking is bad when they go through mindfulness
growth mindset is that you can grow your skills and abilities, praising intelligence puts kids in a fixed mindset
girls desire to be in careers they wont fail in because they were taught to smile pretty and not fail while boys were taught to play rough
raising girls to be perfect and boys to be brave
teach girls to be brave, show progress not perfection ex: girls who code
nudging people is to understand the choice, finding the psychological blockage, change from a choice to a rule (ex: brushing your teeth isnt a choice it is a rule unlike working out)
deceptively simple "nudges" for managing our kids, our health, and our aspirations
small tweaks in the words we use and behaviors can have huge impacts and outcomes
the easiest way to make someone to make the right choice is to reverse the choice, make people to chose to opt out instead of opting in
make kids eat more apples by putting them in a bag and cutting them up
paradoxial nudge that smoking is bad when they go through mindfulness
growth mindset is that you can grow your skills and abilities, praising intelligence puts kids in a fixed mindset
girls desire to be in careers they wont fail in because they were taught to smile pretty and not fail while boys were taught to play rough
raising girls to be perfect and boys to be brave
teach girls to be brave, show progress not perfection ex: girls who code
nudging people is to understand the choice, finding the psychological blockage, change from a choice to a rule (ex: brushing your teeth isnt a choice it is a rule unlike working out)
54
New cards
HBR IdeaCast (2021) "How Business Leaders Can Fight Climate Change"
notes:
- bill gates pays attention to climate change, wants to get to net zero of carbon admissions by 2050, we can't get all the countries of the world to be a part of this
we need good policies but we need to increase the supplies of global innovation
consumers can move to needle through clean products (impossible burger, beyond burger), buying an electric vehicle that uses less materials, drive green premium to zero
employers can move the needle by they have a lot of purchasing power, buy clean aviation fuel for when their employees travel, take capital and invest in these breakthrough companies, make sure they are not holding back policies
synopsis: Bill Gates, philanthropist and founder of Microsoft, argues that, even as we work to end the global pandemic, we can't lose sight of another existential threat: climate change. He says that we need to take aggressive action to get to net zero carbon emissions by 2050 and insists that regulation isn't enough. Businesses need to pave the way forward by investing much more heavily in climate-friendly innovation. Gates speaks with HBR editor in chief Adi Ignatius about his new book, "How to Avoid a Climate Disaster: The Solutions We Have and the Breakthroughs We Need.
- bill gates pays attention to climate change, wants to get to net zero of carbon admissions by 2050, we can't get all the countries of the world to be a part of this
we need good policies but we need to increase the supplies of global innovation
consumers can move to needle through clean products (impossible burger, beyond burger), buying an electric vehicle that uses less materials, drive green premium to zero
employers can move the needle by they have a lot of purchasing power, buy clean aviation fuel for when their employees travel, take capital and invest in these breakthrough companies, make sure they are not holding back policies
synopsis: Bill Gates, philanthropist and founder of Microsoft, argues that, even as we work to end the global pandemic, we can't lose sight of another existential threat: climate change. He says that we need to take aggressive action to get to net zero carbon emissions by 2050 and insists that regulation isn't enough. Businesses need to pave the way forward by investing much more heavily in climate-friendly innovation. Gates speaks with HBR editor in chief Adi Ignatius about his new book, "How to Avoid a Climate Disaster: The Solutions We Have and the Breakthroughs We Need.