ap macro terms to know (in progress)
1/75
Earn XP
Description and Tags
answer with term
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
4 factors of production
land, labor, capital, entrepreneurship
Land
one of the four factors of production, any natural resources on the land
Labor
one of the four factors of production, the effort of people
Capital
One of the four factors of products, has two types — human and physical
Human Capital
knowledge/skills gained from education and training
Physical Capital
machines, factories, tools, bridges, office buildings, etc.
Entrepreneurship
One of the four factors of production, the organizing of resources for production
Trade-off
all of the alternatives you are giving up when making a decision
Opportunity cost
the next best thing (most desirable alternative)
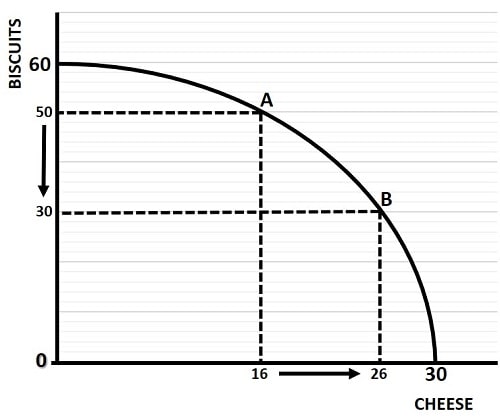
Production Possibilities Curve (PPC)
also called the production possibilities frontier (PPF); a model that shows ways that an economy can use its scarce resources
Absolute Advantage
one producer can produce more of a good than another producer given the same resources
Comparative Advantage
one producer can produce at a lower opportunity cost than another producer
Law of Demand
The higher the price for a good or service, all else equal, people will demand a lesser quantity
Factors that shift the demand curve
Tastes/preferences, change in income, change in the number of consumers, change in expectations, change in price of related goods or services
Normal good
Tise in income leads to an increase in demand
Inferior good
Rise in income leads to a decrease in demand
Law of Supply
There is a positive (direct) relationship between price and quantity supplied
Factors that shift the supply curve
Price or availability of inputs, number of sellers, technology, government action, expectations of future profit
Price ceiling
maximum price that sellers are allowed to charge; governments might be motivated to set this for basic necessities like gas, rent, or food. If this is below equilibrium price, there will be a shortage.
Price floor
minimum price that sellers must charge; governments may be motivated to set this to keep a good from going out of business. If this is above the equilibrium price, then there will be a surplus.
government spending
Government injects money into the circular flow in the from of _____.
taxes
Government causes a leak in the circular flow because of ____.
Government transfer payments
things like unemployment insurance, welfare, grants, subsidies, etc.
Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
the total value of all final goods and services produced within a country’s borders during a given time period (usually one year).
Not counted in GDP
Intermediate goods, used goods, bartering/trading, goods produced in another country, financial transactions, household production, non-market transactions, work without pay
GDP = C + I + G + NX
Equation for GSP in which C stands for consumer goods, I stands for investment spending, G stands for government spending, and NX stands for net exports
investment spending
spending by businesses
net exports
exports - imports
Expenditures approach
one method to calculating GDP in which the final value of each good/service in the economy are added up — most common + easiest to calculate
income approach
one method to calculating GDP by adding up all the income from the factors of production
value-added approach
a method to calculating GDP in which all contributions on the way to final production are added together
GDP per capita
average GDP per person; limited as a measure of overall well-being/productivity because negative things can contribute positively to GDP, good things aren’t counted in GDP at all (volunteering, etc), working within the home, trading …
unemployed
people, 16 and older, who do not have a job but are willing/able to work
Labor force
unemployed + employed
Who doesn’t count as a part of the labor force?
kids, retired persons, disabled persons who are unable to work, students, stay-at-home parents, institutionalized (prison or mental) persons, discouraged workers
labor force participation rate
(labor force size / population 16 or older) *100
Frictional unemployment
new workers entering the work force, people leaving jobs voluntarily to look for a new job, relatively normal in an economy
cyclical unemployment
unemployment due to business cycle (recession, depression, etc.)
structural unemployment
workers lack skills for the current job market, more people seeking jobs than positions available
natural unemployment
frictional + structural
actual unemployment
natural + cyclical
aggregate price level
number that attempts to measure general overall prices in an economy
market basket
hypothetical set of consumer purchases of goods/services
price index
measure of overall price level compared to some base year
consumer price index (CPI)
measure of cost for a market basket of typical urban American family; to calculate, cost of market basket in a given year divided by the cost of market basket in base year * 100.
inflation rate
[(price index in year 2 - price index in year 1)/price index in year 1] × 100
100
The CPI in the base year will always be ___.
inflation
general rise in prices; it takes more money to buy the same stuff than it used to — your dollars lose value over time when prices rise.
disinflation
rise in prices, but at a slower rate than previously
deflation
fall in prices
Borrowers; lenders
In general, ____ are helped by unexpected inflation and ____ are hurt by unexpected inflation.
Menu Costs
costs that are incurred as a result of inflation, such as restaurants having to reprint menus due to changing prices, stores having to change price tags when prices change, or changing signs/advertising due to price changes.
Shoe-Leather Costs
increased costs of transactions due to rising prices (ex. having to make additional trips to the bank).
Unit-of-Account Costs
costs that arise from the way inflation makes money a less reliable unit of measurement
Nominal interest rate
real interest rate + anticipated inflation
Nominal GDP
measured in current year prices
Real GDP
measured in constant, unchanging dollars; adjusted for inflation.
GDP Deflator
nominal gdp/real gdp *100
6 month
A recession is a ____ period of decline in Real GDP.
Aggregate Demand (AD)
all of the goods and services (real GDP) that buyers are willing and able to purchase at different price levels.
along
A change in the price level causes a movement ____ the AD curve.
Marginal Propensity to Consume (MPC)
change in consumption/change in disposable income
Marginal Propensity to Save (MPS)
change in savings/change in disposable income
1
MPS + MPC = _
Spending Multiplier
1/MPS
Aggregate Supply (AS)
Amounts of goods/services (real GDP) that firms will produce in an economy at different price levels
Short-run aggregate supply
wages and resource prices are “sticky” and will not change as price levels change.
long-run aggregate supply
wages and resource prices are “flexible” and will change as price levels change.
price level
A change in the ___ causes movement along the SRAS curve.
Shifters of the AS curve
RAP: Resources, Action by the government, Productivity
Shifters of the LRAS
change in resource quantity/quality or change in technology
Full Employment
long-run equilibrium where the economy is producing at its potential output
inflationary gap
above or beyond full employment, aka positive output gap
recessionary gap
below or less than full employment, aka negative output gap
stagflation
a recessionary gap with inflation (rising prices) and lower rGDP
right; inflationary; prices and wages; right
If there is an increase in consumer spending, in the short-run AD will shift to the ___. There will be an ____ gap. In the long-run ____ will adjust and AS will shift to the ___ to get back to equilibrium.