Chemistry As, Unit 3
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Why do Ionic compounds have high melting/boiling points
Strong electrostatic forces of attraction between particles
What does Brittle do (ions)
Forces ions to move, causing ++ and - - charge to come together. They then repel one another and the compound breaks.
What does Isoelelectronic mean?
ions/ atoms or molecules having the same electronic structure and having the same number of electrons
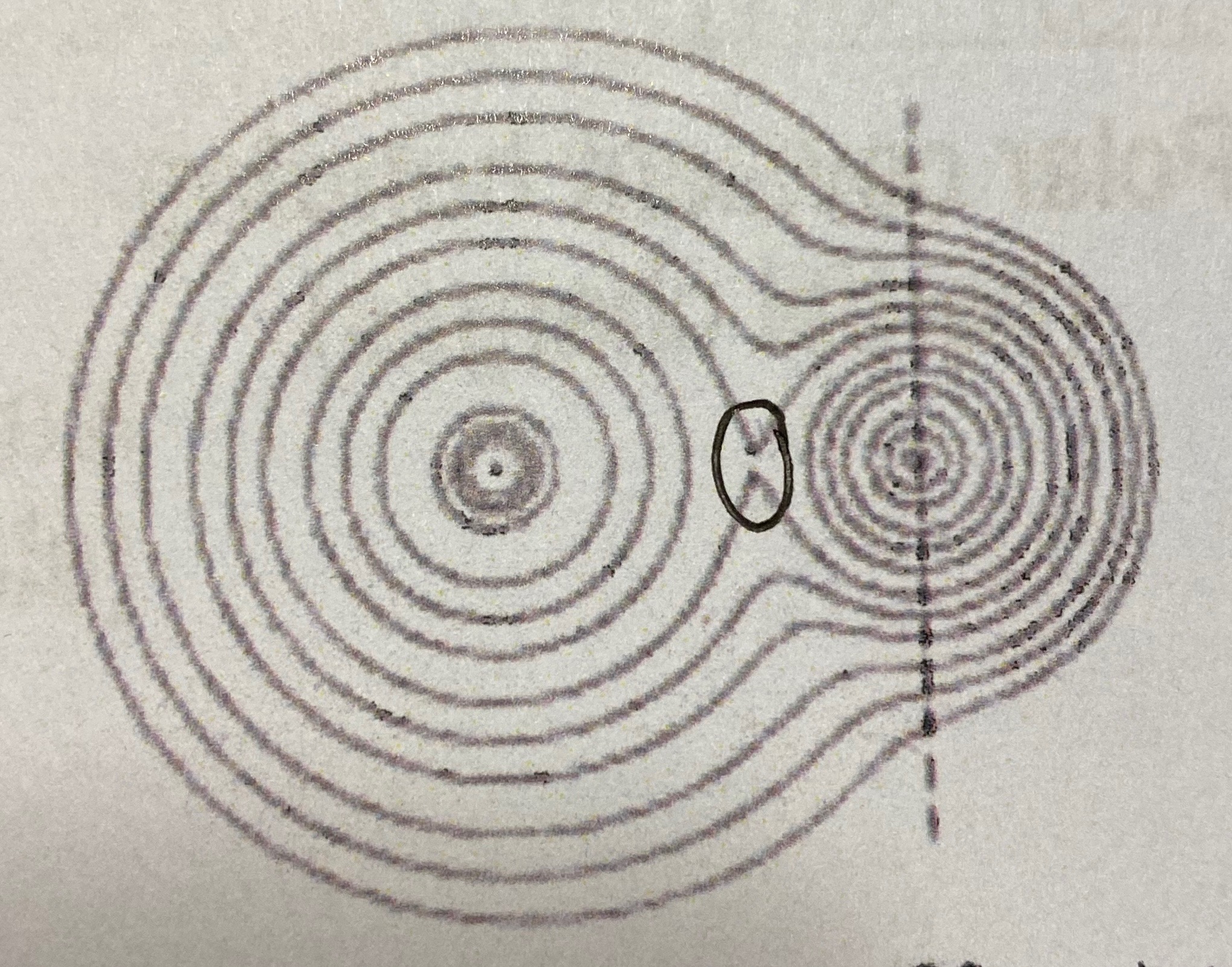
Ionic or covalent?
Ionic
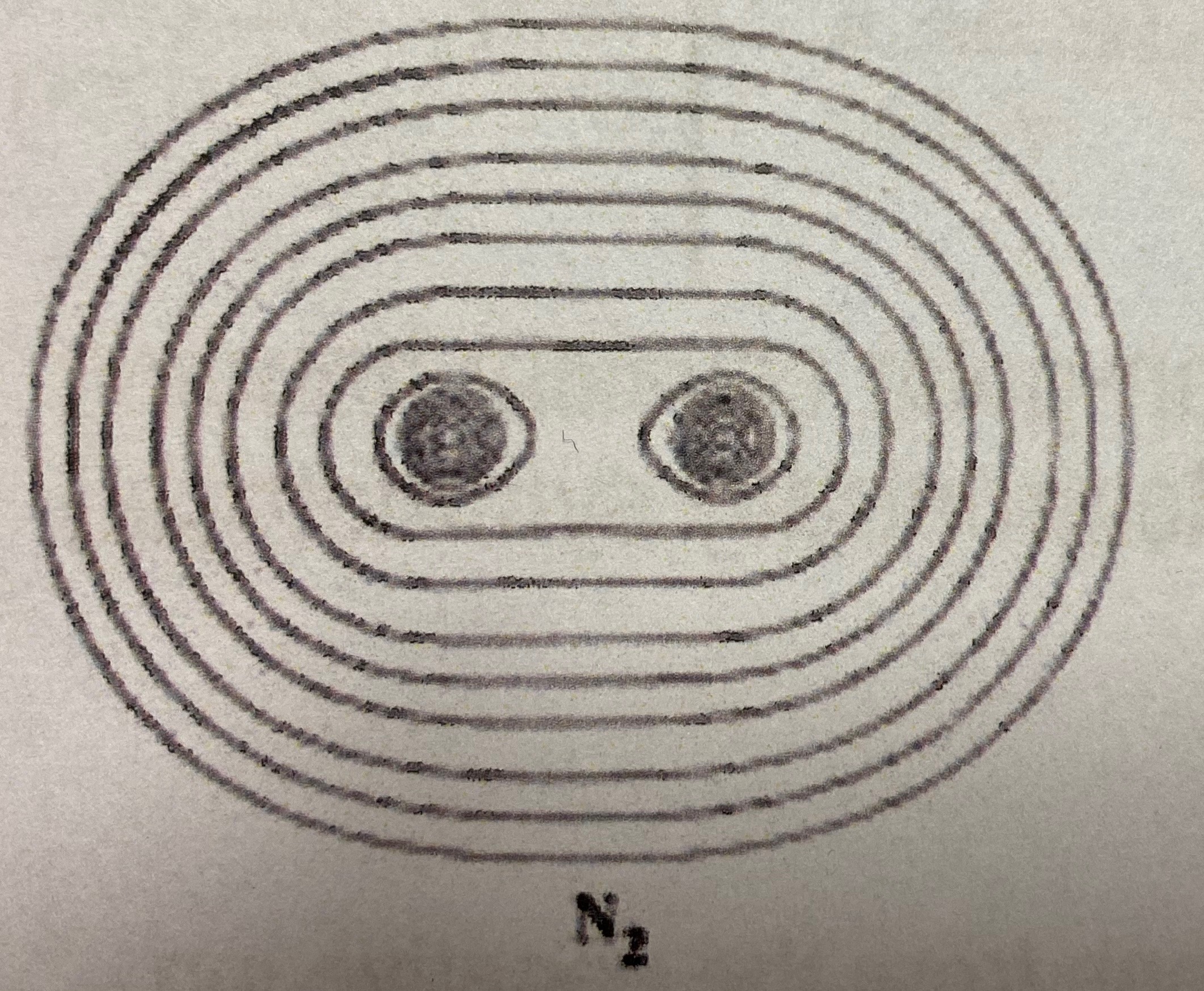
Ionic or covalent?
Covalent
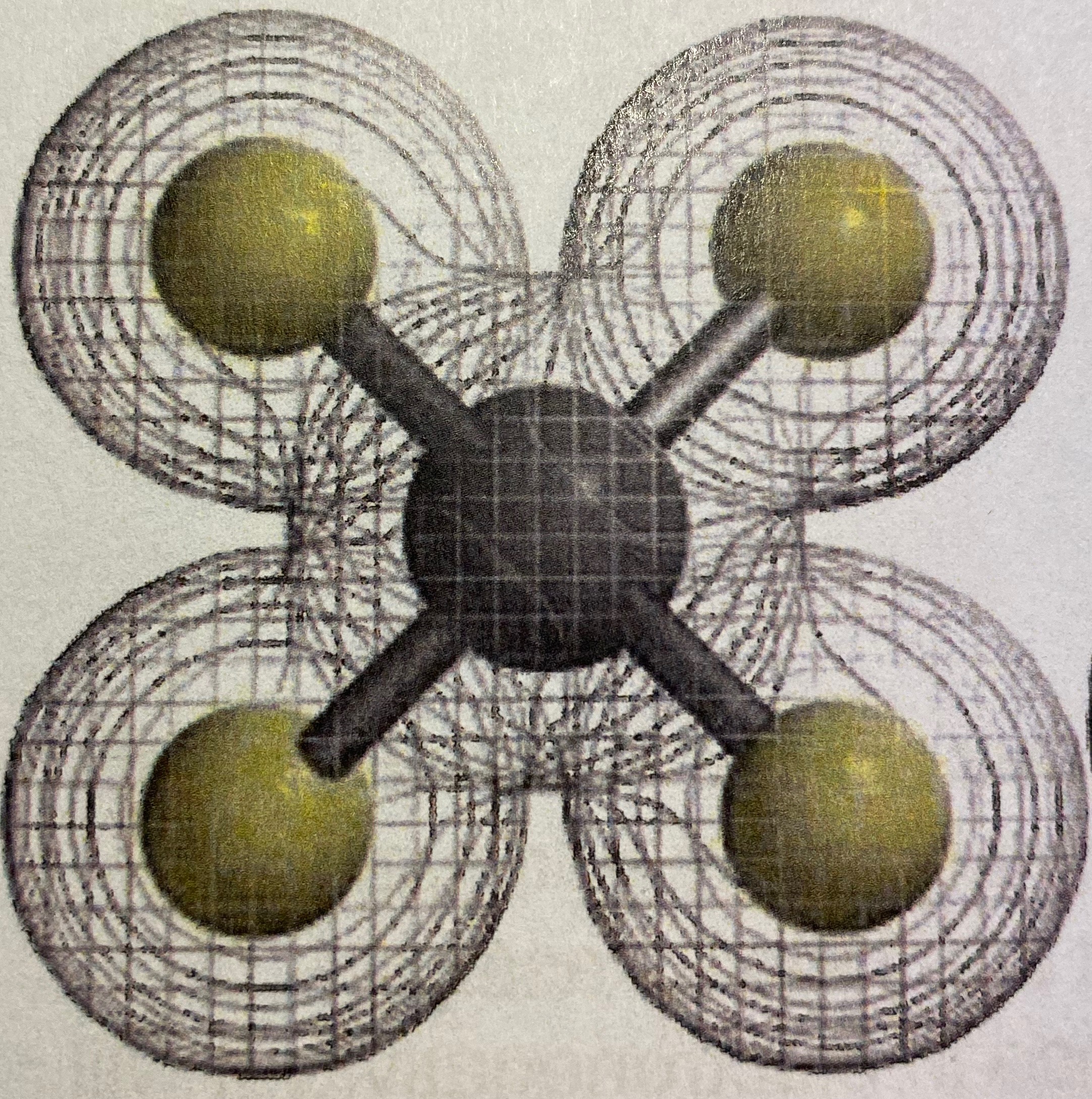
Ionic or covalent?
Covalent
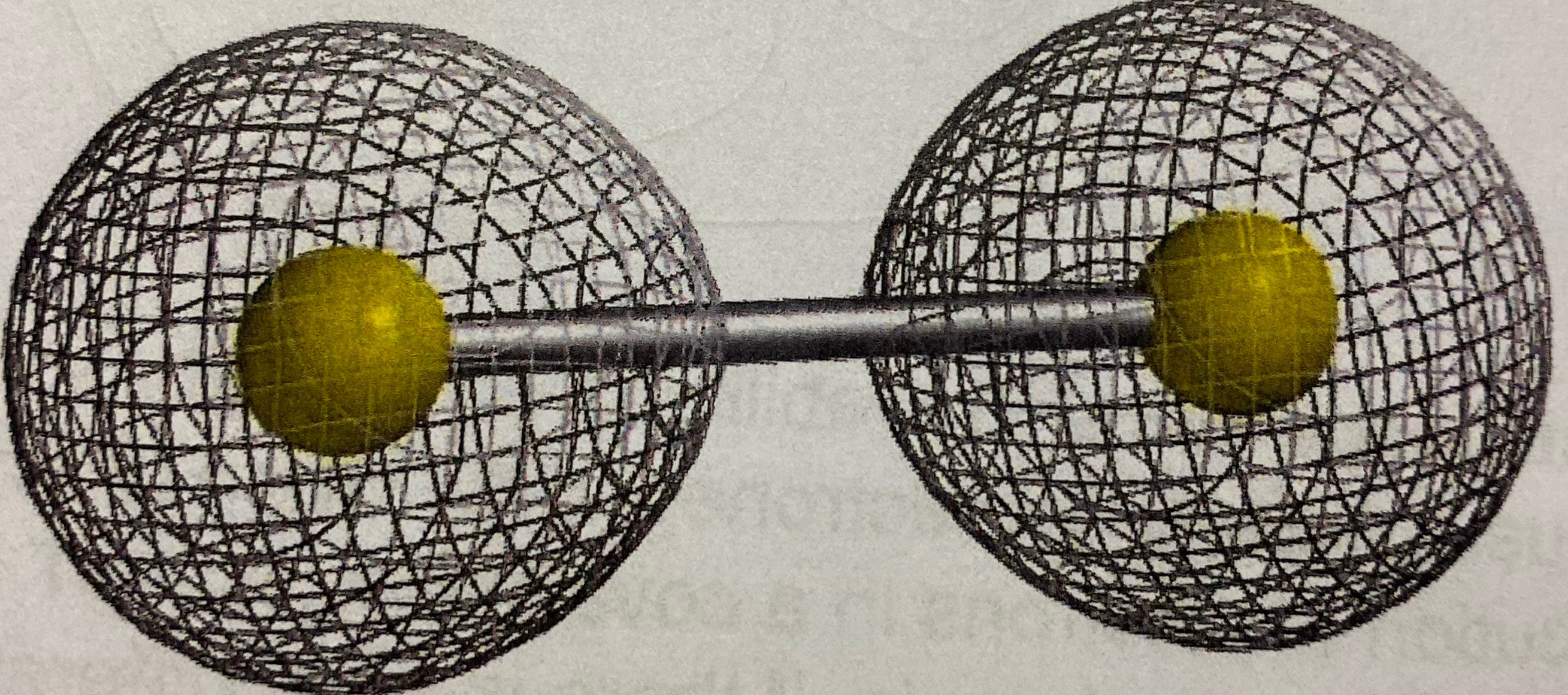
Ionic or covalent?
Ionic
What is polarisation
When a positive ion pulls the electrons from the negative ion towards it
Define Electron negativity
The ability for an atom to pull electrons towards itself
What does polar mean?
The separation of a charge with a clear positive/negative end
What is a polar covalent bond
Bond where one bond has a slight positive charge and one slight negative charge
How do we know if bond is polar?
central atom has a lone pair
All atoms are the same
Less EN atom gets a +S charge
More En atom gets a -S charge
Electron negativity definition + when it decreases or increases (periodic table)
The ability of an atom to attract a shared pair of electrons.
Going from left to right EN increases
Going down the group EN decreases
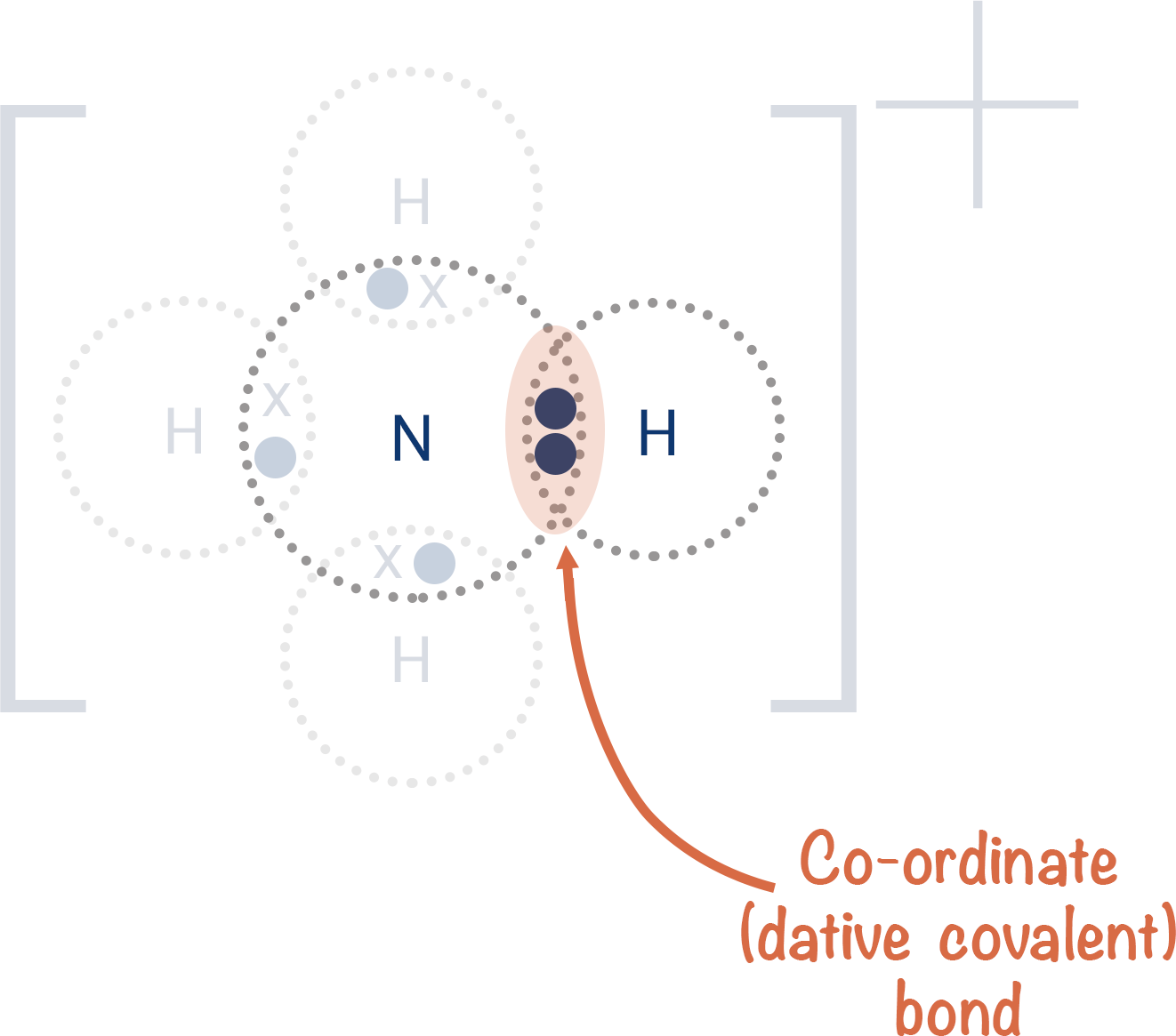
Define and explain Dative covalent bond
The complete shared pair of electrons given by a single atom (Donner)
Linear
Draw, degree, bond count, lone pair
Cl - Be - Cl
180’
Bond, 2
Lone, 0
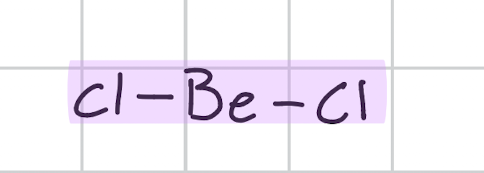
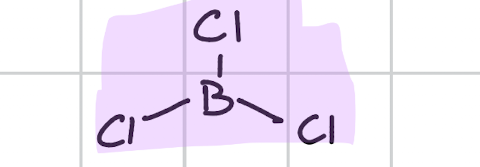
Trigonal planer
Draw, degree, bond count, lone pair
120’
Bond, 3
Lone, 0
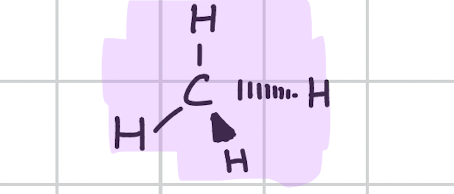
Tetrahedral
Draw, degree, bond count, lone pair
109.5’
Bonds, 4
Lone, 0
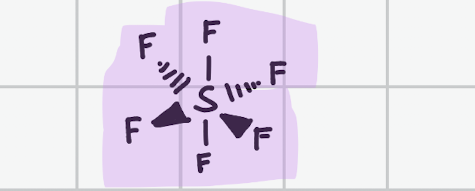
Trigonal Bipyramidal
120’ , 90’
Bond, 5
Lone, 0
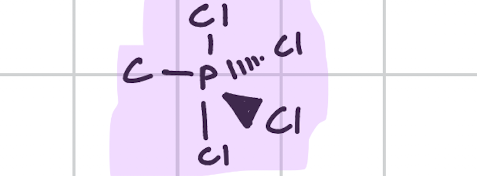
Octahedral
Draw, degree, bond count, lone pair
90’
Bond, 6
Lone, 0
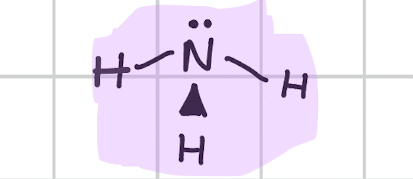
Trigonal pyramidal
Draw, degree, bond count, lone pair
107’
Bond, 3
Lone, 1
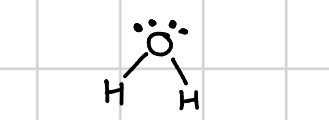
V- shaped
Draw, degree, bond count, lone pair
104.5’
Bond, 2
Lone, 2
Simple molecular structure
eg H2, O2, Br2
Week intermolecular forces between molecules
Joined by covalent bond
Low melting/ boiling points
Giant covalent structure
Elements: Si, Diamond, graphite, graphene
Lattice structure where all atoms joined together by covalent bonds
High melting/ boiling point
Ionic structure
compounds with metal and non-metal
Lattice structure of positive and negative ions
Ion held by strong forces of attraction with + and - ions
High melting/ boiling points
Metallic structure
Element: metals
Lattice structure of metal atoms where outer shell electrons from each atom are delocalized.
Strong attraction between positive nucleus of atoms in a sea of delocalised electrons.
High melting/ boiling points
Finding non-polar molecules
if molecule has same atoms eg O2, N2
Made of only carbon and Hydrogen atoms
Central atoms:
-Has no lone pair
-same bonded around the central atom
Malleable
Materials ability to deform or shape into thin sheets without breaking
Ductile
Ability to stretch material into thin or thread without breaking when pulling
Brittle
A material that fractures with little to no deformation under a pressure
Characteristics of a Sigma bond
made of head-to-head overlap between orbitals
Shared electron density lies along the central line
Strong bond
Characteristics of a PI-bond
made of a sideways overlap between orbitals
Shared electron density lies above and below the central line
Weak bond
What is the electron-pair repulsion theory?
Both repel each other therefore now move as far apart as possible to reduce repulsion.
Difference of bond length and angle
One length is the distance between 2 bonded atoms
Bond angle is the angle between 2 bonds that share common atoms