3.7 AP Psych
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Who was Ivan Pavlov?
-1836-1936
-research physiologist
-conducted experiments
-studied digestion of dogs
-developed stimulus and made a response model
-laid the foundation for behaivoral psychologists such as John Watson
What was Pavlov’s experiment?
Thesis: Understanding the digestion of dogs and the appearance of mysterious secretions at the sound of a bell.
What did Pavlov learn from his experiment?
Pairing food with a bell caused the dog to salivate= Association/Acquisition
-Any stimulus that can be paired with another to make an association
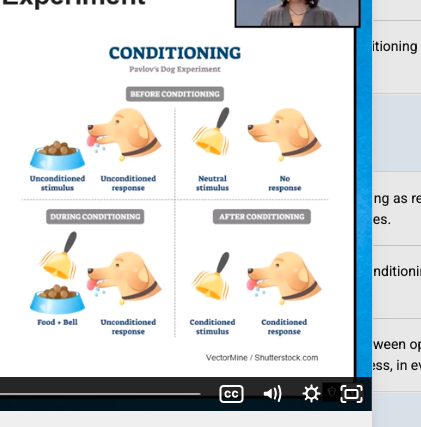
Unconditioned Stimulus (US/UCS)
Any stimulus that will always and naturally ELICIT a response.
Unconditioned response (UR. UCR)
Any response that always and naturally OCCURS at the presentation of the US.
Nuetral Stimulus (NS)
Any stimulus that doesn’t naturally ELICIT a response associated with the USR. Or something which does not produce a specific, desired behavior. If a scientist is training people to produce knee-jerks when they hear a bell, the bell would initially be a neutral stimulus because prior to conditioning it does not produce the desired behavior.
Training Trials for Clasical Conditinoing
Order of presentation of the CS with the UCS is important to successful acquisition
NS and UCS must be paired ½ second apart
Intensity of the UCS effects how many training trials are neccesary for conditioning to occur.
Extinction trials for classical condtioning
-A CR can become extinct when the CS is no longer paired with the UCS.
-A formerly extinct CR can be sponetanously recovered when the CS and UCS are paired together again.
Classical conditioning
a form of learning which involves one stimulus pairing with neutral stimulus to produce a response typically associated with the original stimulus.
What did the Little Albert experiment contribute to understanding of classical condtioning?
Thesis: Like phobias, emotional reactions can be taught
-Watson was able to carry out the process of classical conditioning on Little Albert, since he was able to take a neutral stimulus (white rat) and pair it with the unconditioned stimulus (loud noise) to create the conditioned stimulus (white rat) and conditioned response (fear).
-This taught us that fear can be taught, and generalization is a possibility
-performed by John B Watson
Generelization
Responding (CR) in the same way to a similar stimulus (CS)
Discrimination
Responding CR differently to a similar stimulus (CS)
Extinction
No longer responding (CR) to the original stimulus
Sponatenous recovery
reapperance of conditioned responses after a period of extinction or dimished responses
Higher order conditinoing (second order condtioning)
Conditioned stimulus (CS) can be used as a new unconditinoed stimuls (UCR) to produce the original conditioned response (CR).
emotional response counterconditinoi
positive or negative emotion when experiencing a stimulus accompanied by a present or painful event
counterconditinoing
a theraupuetic intervention for many mental disorders
Taste Aversion
One trial learning (UCS+CS) occurs which is so strong that another occurs and is not needed to produce the response (CR)
Biological Preparedness
Animals are predisposed to learn stimulus response pairing