All in order isk
1/576
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
577 Terms
What is a cell?
A cell is the smallest unit of life. It is the basic, structural and functional unit of a living organism
What is the function of the cell membrane?
To control what substances enter and exit the cell.
State THREE structures found in a plant cell, that arent in an animal cell
Cell wall
Chloroplasts
Large Vacuole
The cytoplasm and nucleus together are referred to as the _______
protoplasm
What is the ‘cytoplasm’?
A gel like substance composed of about 80% water and 20% dissolved substances. It supports the organelles and is the site of many chemical reactions
Where does respiration take place in a cell?
mitochondria
What is the function of the vacuole in a plant cell?
To store nutrients, water, and waste, and to maintain turgor pressure/support the cell when turgid
State THREE differences between the structure of a plant cell and an animal cell
A plant cell has a CELL WALL while an animal cell does not
A plant cell has a fixed (usually rectangular) shape due to its cell wall while an animal cell has a variable shape
Plant cells may contain STARCH GRAINS as a food store while animal cells may contain GLYCOGEN GRANULES as a food store
Plant cells usually have chloroplasts while animal cells dont
What is the function of chloroplasts in a plant cell?
To carry out photosynthesis, converting sunlight into chemical energy and producing oxygen as a byproduct.
Chlorophyll is found in the ________
chloroplasts
What is the function of the nucleus in a cell?
The nucleus contains chromatin threads which house genetic information/the cell’s DNA. This is essential to control the functioning and characteristics of the cell.
It is also necessary for CELL DIVISION
Instead of a membrane bound nucleus, a bacterial cell has a ________
Nucleoid (single,long,coiled loop of DNA)
How do plasmids aid bacteria in carrying out their function?
Plasmids often have antibiotic resistance genes that help bacteria survive in the presence of antibiotics.
The flagellum on a bacterial cell aids in its ______
mobility/movement.
An amoeba moves via ________ while a bacterial cell has a ______ that aids in its movement
pseudopodia, flagellum
______ cells & _____ cells have a CELL WALL
plant cells, bacterial cells
To enable multicellular organisms to carry out all essential life processes efficiently, cells in their bodies must become ________ to carry out specific functions
Specialised/Differentiated
Specialised cells work together in groups called _____
tissues
Epidermal tissue is composed of __________ cells
epidermal cells
Where is epidermal tissue found?
Around the outside of leaves, young stems and roots of plants
List 3 examples of plant tissues
Packing Tissue
Epidermal Tissue
Photosynthetic Tissue
Vascular Tissue
Packing tissue is made up of _______ cells
parenchyma cells
State 2 functions of packing tissue
Fills spaces in stems and roots
Supports non-woody plants when turgid
Stores food
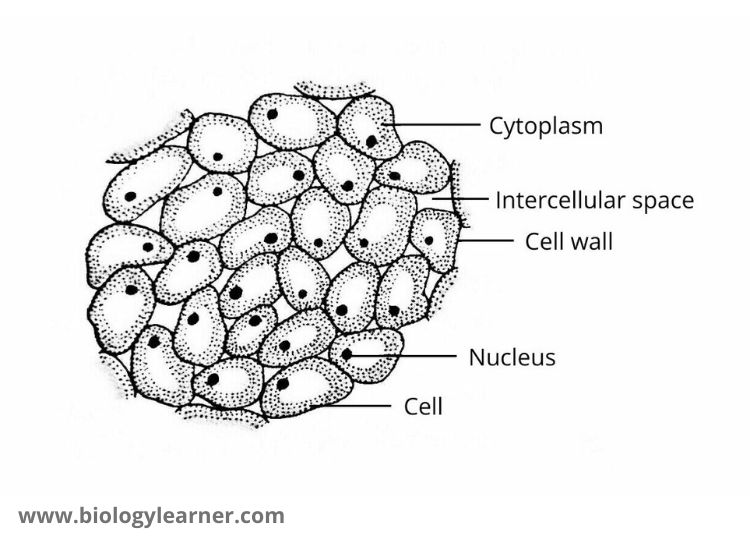
List FOUR examples of animal tissues
Nerve Tissue
Muscle Tissue
Epithelial Tissue
Connective Tissue
Cardiovascular Tissue
Give two examples of ‘connective tissue’
Blood Tissue
Adipose (Fat Tissue)
Cartilage
Bone
Give 2 functions of Connective Tissue
To transport various substances around the body
Helps fight disease
Insulates the body
Serves as a food reserve
Protects the body by acting as ‘padding’
The skin is composed of _______, ______ and ______ tissues
epithelial, connective and nerve
The leaves of plants are composed of _________,_______ and ________ tissues
epidermal, photosynthetic and vascular
Define the term ‘diffusion’
Diffusion is the process of particles moving from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration until equilibrium is achieved. The particles move down a concentration gradient.
State 3 ways in which diffusion is important to living organisms
Oxygen produced in photosynthesis, moves out of plant cells and leaves by diffusion
Oxygen for use in aerobic respiration moves into organisms through gaseous exchange surfaces and into cells by diffusion
Some glucose and amino acids produced in digestion are absorbed through cells in the ileum and capillary walls into the blood by diffusion
Carbon Dioxide, for use in photosynthesis, moves into leaves and plant cells by diffusion
Carbon Dioxide produced in aerobic respiration, moves out of cells in organisms through gaseous exchange surfaces by diffusion
What is ‘osmosis’?
Osmosis is a special form of diffusion. It is the movement of water molecules from an area of higher concentration to one of lower concentration through a semi-permeable/differentially-permeable membrane, until equilibrium is achieved.
Briefly state what would happen to an animal cell that was placed in a hypertonic solution
The animal cell would lose water and shrink due to the higher concentration of solutes in the surrounding solution.
Briefly state what would happen to an animal cell that was placed in a hypotonic solution
The animal cell would gain water and swell, potentially leading to bursting, due to the lower concentration of solutes in the surrounding solution.
State what would happen to a plant cell that was placed in a hypertonic solution
The plant cell would lose water and undergo plasmolysis (vacuole and membrane pull away from the cell wall), causing it to become flaccid due to the higher concentration of solutes in the surrounding solution.
A plant cell in water or a solution that is more dilute than its cytoplasm and cell sap will ___ ____ and become _____.
gain water/ swell; turgid
State 3 ways in which osmosis is important to living organisms
All cells are kept hydrated by water moving into them by osmosis
Plant cells are kept turgid to support non-woody plants to stand upright and keep leaves firm
Water is kept moving through plants by osmosis occurring in the cells of roots and leaves
Water is reabsorbed into the blood from the filtrate in the kidney tubules by osmosis.
The size of stomatal pores is regulated by osmosis occuring in the guard cells (controls water loss)
What is ‘active transport’?
Active transport is the movement of particles from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration until equilibrium is achieved. Active transport requires energy produced during respiration to take place.
State 3 ways why active transport is important in living organisms
Mineral ions move from the soil to plant roots
Sugars produced in photosynthesis move into the phloem
Some of the glucose and amino acids produced in digestion are absorbed from the ileum into the blood
Useful substances are reabsorbed from the filtrate in the kidney tubules into the blood
Define the term ‘nutrition’
The process by which living organisms obtain or make food.
What are the two types of nutrition?
Heterotrophic & Autotrophic Nutrition
What is an ‘autotroph’?
An organism that uses simple inorganic compounds to manufacture complex organic food substances.
State the 3 types of Heterotrophic Nutrition
Holozoic, Parasitic and Saprophytic
Animals, fungi and most bacteria are _______. Humans feed by means of _______ nutrition.
Heterotrophs, Holozoic
What is a saprophyte?
An organism that feeds by obtaining organic food from dead remains of other organisms. They digest the complex organic food outside of their bodies and then absorb the simpler inorganic substances.
What is meant by the term ‘photosynthesis’?
Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose by using sunlight energy absorbed by chlorophyll in the chloroplasts. Oxygen is released as a byproduct
What is the chemical equation for photosynthesis?
6CO2+6H2O —→ light energy in chlorophyll = C6H12O6 + 6O2
What occurs in the light stage of photosynthesis?
The light energy captured by the chlorophyll splits water molecules into Hydrogen and oxygen. The oxygen is released as a gas (waste product)
The dark stage of photosynthesis is also called the?
Light Independent Stage
What occurs in the dark stage of photosynthesis?
The hydrogen atoms are used to reduce the Carbon Dioxide molecules to form glucose.
The dark stage of photosynthesis takes place whether or not light is present. However, the dark stage requires ______
enzymes
State the 6 conditions needed for photosynthesis to take place
Carbon Dioxide
Water
Sunlight
Enzymes
Chlorophyll
A suitable temperature (5-40^C)
What is the role of chlorophyll in photosynthesis?
Chlorophyll captures sunlight energy
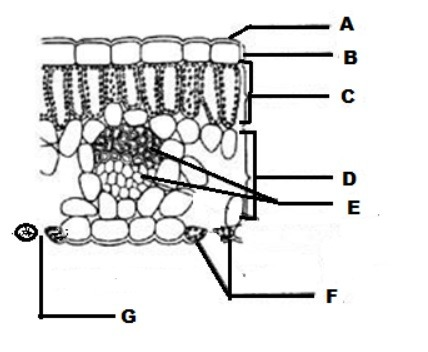
Label the image of the internal structure of a leaf from A-G
A - Waxy Cuticle
B - Upper Epidermis
C - Palisade Mesophyll Layer/Cells
D - Spongy Mesophyll Layer/Cells
E - Vascular Tissue (Xylem & Phloem)
F - Guard Cells
G - Stomatal Pore
How is the external structure of a leaf adapted to carry out photosynthesis efficiently?
The lamina is broad and flat, providing a large surface area to maximize sunlight and carbon dioxide absorption
The lamina is thin to allow sunlight energy and carbon dioxide to reach all cells
The lamina is held out flat by the veins - maximise sunlight absorption
The lamina usually lies at 90 degrees to the sunlight
The laminae are spaced out around stems, giving each maximum exposure to sunlight
How is the internal structure of a leaf adapted to carry out photosynthesis efficiently?
Waxy cuticle - waterproof so prevents excess water loss that is needed for photosynthesis
Stomatal pores - allow carbon dioxide to diffuse into the leaf and oxygen to diffuse out
Palisade Mesophyll Cells - Directly below upper epidermis and closest to sunlight, contain large amounts of chloroplasts to maximise sunlight energy absorption, arranged at 90 degrees to the leaf’s surface (allows chloroplasts to move to the top in dim light)
Intercellular Air Spaces - Diffusion of gases
Phloem Sieve Tubes - Transport the soluble food made in photosynthesis from the mesophyll cells to other parts of the plant
Xylem Vessels - Supply all the mesophyll cells with water and mineral ions.
The four main factors that affect the rate of photosynthesis are ______, _____ ______, _______ and ______
light, Carbon Dioxide, Temperature and Water
When does temperature become a limiting factor of photosynthesis?
During winter months in temperate climates
When does water become a limiting factor of photosynthesis?
Dry season in tropical climates
When the ground is frozen in temperate climates
What 3 things can happen to the glucose produced during photosynthesis?
Used in respiration to produce energy
Converted to starch and stored
Converted to other organic substances - amino acids, protein, vitamins, etc.
What is Nitrogen used for in plants?
Nitrogen is needed for the formation of proteins used for plant growth and it’s also used to make chlorophyll
State some visible characteristics that can be observed from a plant deficient in Nitrogen
Stunted growth
Chlorosis (yellowing of leaves)
Underdeveloped Leaves
What is Magnesium used for in plants?
To make chlorophyll; magnesium forms a part of the chlorophyll molecule
Outline the steps in testing for Protein in a substance
Add an equal volume of sodium hydroxide solution to the substance and shake.
Add a few drops of dilute Copper Sulfate Solution and shake.
Or add an equal volume of biuret reagent and shake
If protein is present the solution will turn purple
______ ______ is used to test for Reducing Sugars
Benedict’s Solution
Explain the necessity for hydrolysis and neutralisation in testing for non-reducing sugars.
Non-reducing sugars, like sucrose, do not react with Benedict’s solution because they do not have the chemical group needed to reduce it. To test for them, the sugar must first be broken down into simpler sugars that can react. This is done by boiling the solution with a little dilute acid, which breaks the non-reducing sugar into reducing sugars — a process called hydrolysis. After this, the solution is acidic, so it needs to be neutralised using an alkali like sodium hydroxide. Once the solution is neutral, Benedict’s solution can be added again and heated. If a non-reducing sugar was present, the test will now give a positive result, usually shown by a colour change from blue to brick red.
List 2 chemical properties of monosaccharides and disaccharides
Have a sweet taste
Soluble in water
List the 3 monosaccharides
Fructose
Glucose
Galactose
List the 3 disaccharides
Maltose
Sucrose
Lactose
Disaccharides are formed by chemically joining two monosaccharide molecules via a process called ________
dehydration synthesis OR condensation
__________ is the process used to split disaccharide/polysaccharide molecules
Hydrolysis
A lipid molecule is composed of 4 smaller molecules: ___ Fatty Acid molecules and 1 ______ molecule
3; glycerol
State 1 examples of a soluble protein and 1 example of an insoluble protein
Soluble - haemoglobin, albumin
Insoluble - collagen
What is mechanical digestion?
The breaking up of large pieces of food into smaller pieces. It gives digestive enzymes a larger surface area to act upon and makes food easy to swallow.
Mechanical digestion begins in the ______ where it is carried out mainly by the ______
mouth;teeth
List the 4 types of teeth in a human
Incisors (8) - to cut food, to bite of food
Canine (4) - to grip and tear food
Premolars (8) - To crush and grind food
Molars (12) - To crush and grind food
A tooth is divided into 2 parts: the _____ and the ______
root and the crown
Why are fibres important in the structure of a tooth?
To anchor the tooth in the jawbone and to allow slight movement for shock absorption
What is an enzyme?
Enzymes are biological catalysts that speed up chemical reactions occuring in living organisms without being changed themselves.
State FOUR properties of an enzyme
Enzymes work at a particular temperature knows at the optimum temperature
Enzymes are specific - each only catalyzes one type of reaction
High temps denature enzymes
Enzymes work best at an optimum pH (pH 7)
Extremes of acidity or alkalinity denature most enzymes
The action of enzymes is inhibited by certain poisons
State the name of the enzyme found in saliva and its use
Salivary Amylase - breaks down starch into maltose
Name 2 enzymes found in the stomach and their uses
Pepsin - begins the breakdown of protein into peptides
Rennin - produced in infants to clot soluble proteins in milk so protein is retained in the stomach
Where is bile stored?
In the gall bladder
Organic bile salts are used to emulsify lipids. What is meant by this?
They break down lipid droplets into smaller droplets increasing their surface area for digestion.
List the 3 digestive enzymes in Pancreatic Juice and their uses
Pancreatic Amylase - continues to breakdown starch into maltose
Pancreatic Lipase - digests lipids into fatty acids and glycerol
Trypsin - continues to break down protein into peptides
State 3 enzymes found in intestinal juice
Maltase, Sucrase Lactase, Peptidase
List THREE ways that the ileum is adapted to efficient absorption
It is very long providing a large surface area for rapid absorption
Its inner surface has thousands of villi - surface area
Each villus has a network of capillaries and a lacteal inside. These provide a means of rapidly transporting products of digestion
The wall of each villus known as the epithelium, is only one cell thick
The epithelial cells have microvilli
What is the function of the lymphatic vessel in the villi
To transport fatty substances to the blood before it enters the heart
List 4 substances that are absorbed in the ileum
Water
Vitamins
Minerals
Monosaccharides
Fatty acids & glycerol
Amino Acids
What two things are absorbed in the colon?
Water and mineral salts
What does the term ‘assimilation’ mean?
The process by which the body uses the products of digestion.
What happens to excess amino acids when they’re absorbed by the body
When excess amino acids are absorbed by the body, they can't be stored like fats or carbohydrates. Instead, the liver breaks them down in a process called deamination. This removes the part of the amino acid that contains nitrogen, which is turned into urea and passed out of the body in urine. The rest of the molecule can be used for energy or turned into fat and stored.
Two hormones secreted into the blood by the pancreas are responsible for blood sugar control. They are _______ and ______
glucagon and insulin
What happens in the body when blood sugar falls?
The pancreas secretes glucagon which stimulates the liver to convert stored glycogen back to glucose for respiration.
What happens in the body when blood sugar rises?
The pancreas secretes insulin which stimulates body cells to absorb glucose for respiration. The liver converts excess glucose to glycogen and stores it.
State 3 uses of lipids in the body
To make cell membranes of newly formed cells
To provide energy when carbohydrates have been used up
For storage
For insulation
What is Xerophthalmia and what nutrient deficiency is it cause by?
Xerophthalmia is when the eyes fail to produce tears leading to a dry damaged cornea and sometimes blindness. It is caused by a Vitamin A deficiency
State 1 function of Vitamin B1 in the body
Important for the proper functioning of the nervous system
Aids in respiration to produce energy
List 3 symptoms of scurvy
Swollen, red, gums
Loose teeth
Wounds do not heal
Red-blue spots on the skin
State two benefits of a vegetarian diet?
The diet is low in saturated fats and cholesterol, therefore vegetarians are less prone to obesity, heart disease, hypertension, diabetes and gall stones.
The diet is high in dietary fibre, therefore, vegetarians are less likely to suffer from constipation, colon cancer, and certain other types of cancer
Distinguish between natural and artificial immunity
Natural immunity refers to the protection that an individual gains through their own immune system after exposure to a pathogen, while artificial immunity is acquired through medical means, such as vaccinations or antibody injections.