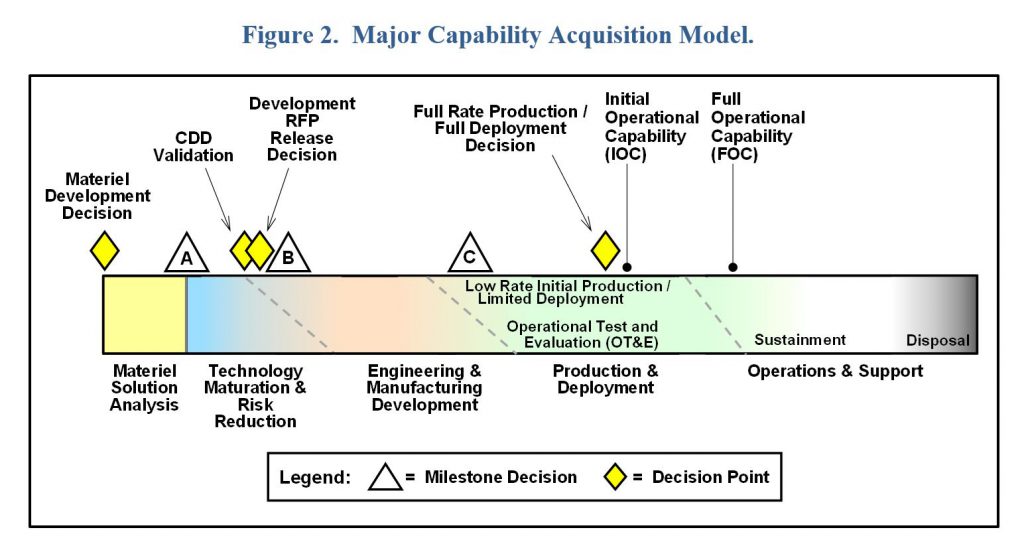
Major Capability Acquisition (MCA) Pathway
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Milestone Decision Authority (MDA)
The approval authority responsible for a program as it progresses through the MCA pathway
Describe the Materiel Development Decision (MDD)
Purpose: The starting point for all programs where the entry phase is determined
Inputs:
ICD that identifies gap
Analysis of Alternatives (AoA) Study
Affordability Analysis to determine if budget can support effort
Outputs:
Acquisition Decision Memorandum (ADM) that decides the program’s next phase
Describe the purpose of the Materiel Solution Analysis (MSA) Phase
Purpose: Assess all solutions to determine what system will meet the capability gap
Inputs:
ICD
AoA Study
Outputs:
Completed AoA with materiel solution recommendation
Draft CDD that translates gap to system requirements
Milestone A
Purpose: Select the materiel solution
Inputs:
ICD
AoA recommendation
Outputs:
ADM for chosen materiel solution
Acquisition Strategy (AS)
Describe the purpose of the Technology Maturation and Risk Reduction (TMRR) Phase
Purpose: Reduce risks enough to feel confident about successful program execution
Inputs:
AS
Outputs:
Fully developed and validated CDD
Preliminary Design Review (PDR) to identify the high-level system architecture
Request for Proposal (RFP) to solicit contractor design bids
Identify the purpose of Milestone B
Purpose: Officially initiate program
Inputs:
TMRR results (risk acceptability, program affordability, technology maturation)
Outputs:
Acquisition Program Baseline (APB) to create and commit to program
Engineering Manufacturing Development (EMD) contract awarded to company
Engineering Manufacturing Development (EMD) Phase
Purpose: Produce a requirements-meeting system and prepare for full production
Inputs:
CDD
Outputs:
Critical Design Review (CDR) to determine maturity, documentation, and risk
Production Readiness Review (PRR) to determine if the design and production are capable
Identify the four main work efforts of the EMD phase
1.) Design the System
2.) Build the Prototype
3.) Test Prototype
4.) Prepare for Production, Deployment, and Sustainment Decisions
Design the System
Define the system, complete hardware/software design, and reduce system level risk
CDR is performed after this step to initiate prototyping
Build the Prototype
System prototype is built from CDR specifications
Test Prototype
Perform Development Test and Evaluation (DT&E) on the prototype to prove the system meets requirements
Prepare for Production, Deployment, and Sustainment Decisions
PRR is completed to ensure the design is stable and meets requirements, manufacturing/processes risks are controlled, and supplier qualifications are complete
Milestone C
Purpose: Authorize the system to enter the Production and Development (P&D) phase
Inputs:
CDR, DT&E, and PRR results
Program affordability
Outputs:
Updated APB
P&D contract to production company
Identify the purpose of the Production and Deployment phase
Purpose: Produce and delivery capability-closing system to receiving organizations
Inputs: N/A
Outputs:
Low-Rate Initial Production (LRIP)
Operational Test and Evaluation (OT&E)
Full Rate Production (FRP) Decision
Reach Initial Operational Capability (IOC)
Low-Rate Initial Production (LRIP)
Manufacturing of a small quantity of assets to determine large-scale production risks and inefficiencies
Operational Test and Evaluation (OT&E)
Operational testing of the system are conducted in threat environments to assess effectiveness, suitability, and survivability
Full Rate Production (FRP) Decision
OT&E results and manufacturing/development activities are assessed before moving to full production
Initial Operational Capability (IOC)
The minimum number of systems necessary to conduct operations are delivered
Operations and Support (O&S) Phase
Purpose: Ensure the product is fully supported and sustained throughout the system’s lifecycle
Outputs:
Reach Full Operational Capability (FOC)
System turnover of operation and maintenance
Disposal plan
Full Operational Capability (FOC)
All units scheduled to receive the system have obtained it and can employ and maintain it
Describe the [5] unique characteristics of space programs
1.) One Shot at Launch
2.) Operate in Harsh Environment
3.) Requires Sufficient Fuel and Redundancies to Last
4.) Limited Maintenance Options
5.) More Expensive Per Program (inverse cost curves)
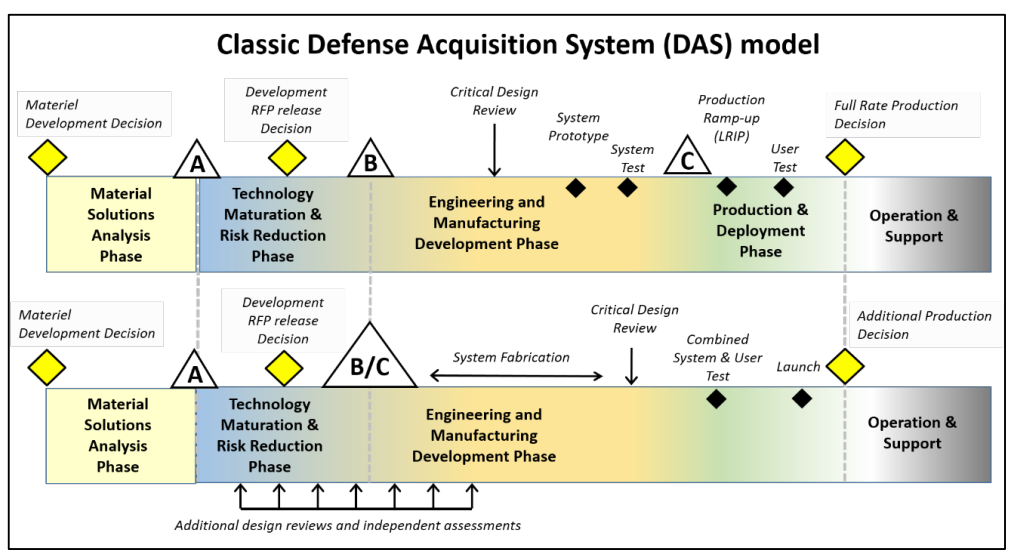
Identify how MCA is tailored to support space programs
1.) More design reviews and independent assessments
2.) Milestones B and C are combined
3.) No prototyping is done; a single system is created and tested
4.) System and User Test are combined