Ch5: Sex Chromosomes
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
sexual differentiation
differences in male/female body form
dimorphism
phenotypical differences to show dif sexes
heteromorphic chromosomes
XY
____, not _______ ultimately determine sex
genes ; chromosomes
What was discovered in the sperm of Protenor & Lygaeus insects in 1891?
Insects’ sperm sometimes lacked an “X-body,” showing some sperm had X, some didn’t.
heterogametic sex = M
homogametic sex = F
Klinefelter syndrome
47,XXY karyotype (extra X).
tall w/ long arms & legs, large hands & feet
Testes fail to produce sperm
occur due to nondisjunction during meiosis (chromosomes dont seperate)
Turner syndrome
45, X karyotype (only 1 X)
female external genitalia, but no ovaries
underdeveloped breasts
occur due to nondisjunction during meiosis (chromosomes dont separate)
mosaics
some of your somatic cells display two dif genetic cell lines w/ dif karyotypes
(some 45.X & others 46.XX)
Triplo-XXX
47,XXX
female w/ underdeveloped, sterility, and/or intellectual disability
47,XYY karyotype condition characteristics
males over 6 ft
may have subnormal intelligence & personality disorders
bipotential gonads
the early stage gonads (before 6 weeks) that can develop into either testes or ovaries
By the ___ week, the gonadal ridges form either ovaries or testes
5th
formation of male parts
medulla develops into testes
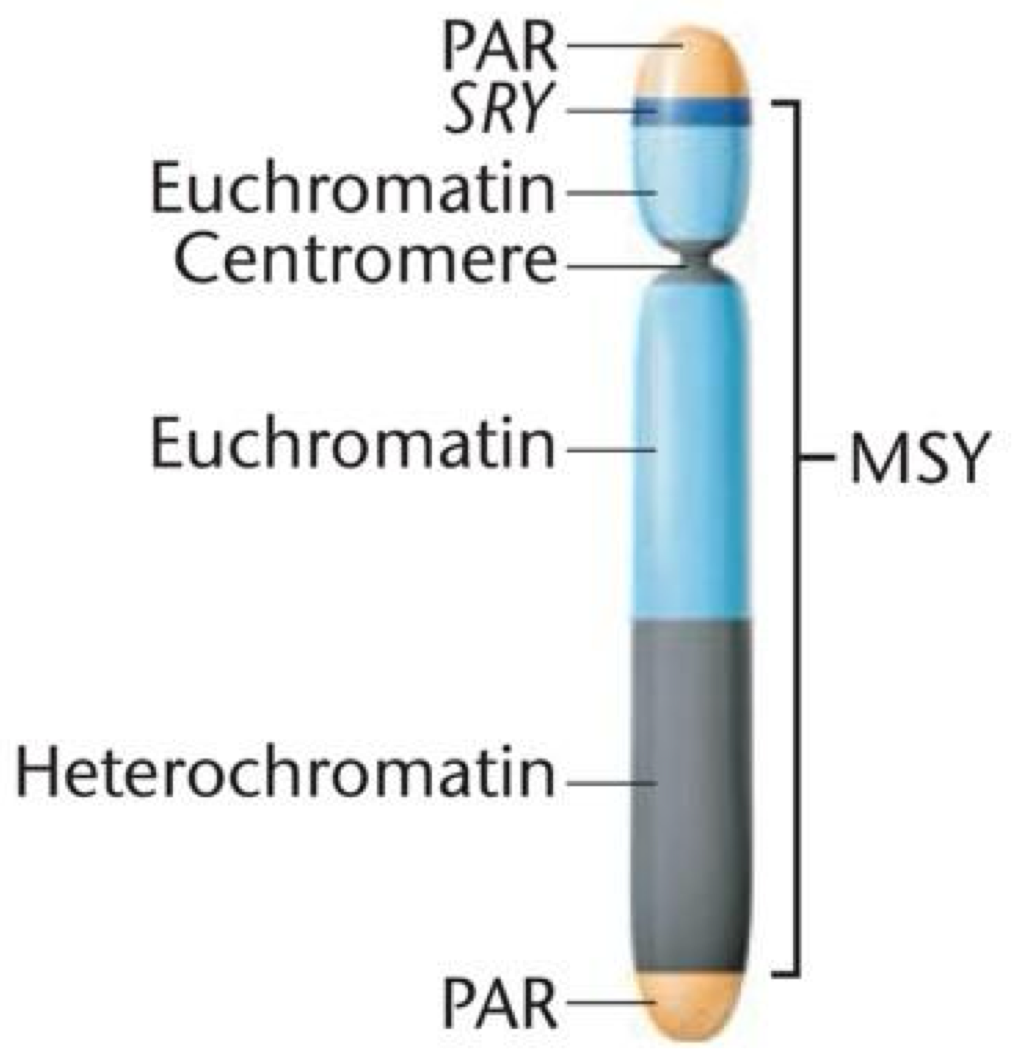
Y chromosome has at least 75 genes
95% of Y chromosome doens’t recombine w/ X = MSY (male specific region of Y)
SRY (sex determining gene of Y) activates 6-8 weeks
SRY gene encodes protein TDF = testes formation
formation of female parts
cortex of ridge forms ovarian tissue
X chromosomes has 900 - 1400 genes
mullerian duct forms oviducts, uterus, cervix, & vagina
pseudoautosomal regions (PARs)
tips of Y that match w/ X and recombine during meiosis
this pairing region is critical for segregation & combining
Transgenic mice research
Inserting SRY gene into XX mice makes them develop as males.
TDF is the “switch.”
human sex ratios
primary sex ratio: embryos conceived
secondary sex ratio: actual live births
Dosage compensation
females have 2 Xs so they could produce twice as much product for x linked genes:
solution = X inactivation (one x becomes inactive) : Barr Body
Barr Bodies
condensed inactive X chromosome after X inactivation
Lyon Hypothesis
Inactivation of X is random, but once an X is chosen to be shut off in a somatic cell, all its future copies keep that choice.