Chapter 12: Forensic DNA Profiling
0.0(0)Studied by 11 people
Card Sorting
1/70
Last updated 12:12 AM on 1/12/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
1
New cards
Karl Landsteiner
The foundations of forensic genetics were laid down when ________ described ABO blood group systems in 1901.
2
New cards
post mortem
In ________ cases DNA can be obtained from body tissues.
3
New cards
probability of discrimination
The frequencies of the markers are important as these are to be used in calculating the ________ and /or match by multiplying them together.
4
New cards
genetic characteristics
It defines that individuals ________ contains a large number of polymorphisms that can be used for human identification.
5
New cards
DNA methods
________ avoid any complications of dominance or recessives.
6
New cards
Genotype of the Person
allelic configuration at a locus
7
New cards
Profile of the Person
genotypes at different loci
8
New cards
Variable number of tandem repeats (VNTRs)
minisatellite polymorphisms in a large number of tandemly repeating units of a particular sequence typically 16-80 bp long
9
New cards
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
an in vitro molecular photocopying process that generates millions of copies of the target DNA sequence the boundaries of which are defined by synthetic oligonucleotide primers that are complementary to the 3' ends of the sequence
10
New cards
Denaturation of DNA
The two strands of DNA are wrapped around each other, for replication the DNA has to unwind to have a single strand available for the synthesis of the new strand
11
New cards
AmpFLPs
smaller minisatellite loci which had alleles from 9-15 bp, composed of short core repeat units**
12
New cards
Short Tandem Repeats (STRs)
microsatellites that are an abundant class of DNA polymorphisms
13
New cards
Multiplex PCR
this is where each primer pair would amplify a specific sequence or STR
14
New cards
Multiplexing
a technique where a number of STR loci are amplified in a single tube PCR
15
New cards
Allelic ladder
consists of a number of alleles of a STR system and is used as a reference to designate the alleles
16
New cards
Genotyper
the programme would call the allele on the basis of the established windows, which is called the ‘absolute window method
17
New cards
DYS19
described as the first STR on the human Y-chromosome, which was found to be polymorphic and suitable for sex and paternity determination in deficiency cases
18
New cards
Match Probability
the probability that the two randomly selected individuals will have identical genotype
19
New cards
Power of Discrimination
the probability that two randomly selected individuals will have different genotypes
20
New cards
Karl Landsteiner
He introduced the ABO blood group systems.
21
New cards
Sir Alec Jeffrey
He introduced VNTRs
22
New cards
Complex repeats
consider two alleles of locus D21S11
23
New cards
DNA
the biological blueprint of life.
24
New cards
deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
The structure of ______ was described by *James Watson* and *Francis Crick* in 1953.
25
New cards
right-handed double
DNA was determined to be a ________ helix.
26
New cards
nucleotides
DNA’s repeating subunits
27
New cards
Nuclear DNA
is inherited equally from both mother and father.
28
New cards
Mitochondrial DNA
is inherited only from the mother, and therefore it can be used to match with the maternal lineages.
29
New cards
**chromosomes**
* There are 3 billion base pairs (bp) in a single copy of the human genome.
* These are arranged in compact structures, which we all know as **_______**.
* These are arranged in compact structures, which we all know as **_______**.
30
New cards
diploid cells
There are 23 pairs of chromosomes in all the cells of humans and so are called ______.
31
New cards
haploid cells
Only in the gametes, one copy of each chromosome is present and these are called _______.
32
New cards
coding and non-coding
The DNA in the chromosomes is arranged as ______ regions.
33
New cards
Introns
functional portions of the genes.
34
New cards
Exons
non-functional regions of the genes.
35
New cards
Loci
polymorphic markers have been detected in the areas of the human genomes.
36
New cards
Alleles
an alternative form of the marker at a particular locus.
37
New cards
Homozygote
it is if the alleles are the same.
38
New cards
Heterozygote
it is if the alleles are different.
39
New cards
Genotype of the Person
allelic configuration at a locus.
40
New cards
Profile of the Person
genotypes at different loci.
41
New cards
tandemly repetitive DNA
Segments of DNA are arranged as a particular sequence being repeated more than once, a sequence GGGCCCTTAA might be repeated many times
42
New cards
Variable number of tandem repeats (VNTRs)
minisatellite polymorphisms in many tandemly repeating units of a particular sequence, typically 16-80 bp long.
43
New cards
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
an invitro-molecular photocopying process that generates millions of copies of the target DNA sequence, the boundaries of which are defined by synthetic oligonucleotide primers that are complementary to the 3' ends of the sequence.
44
New cards
Denaturation of DNA
The two strands of DNA are wrapped around each other, for replication the DNA has to unwind to have a single strand available for the synthesis of the new strand.
45
New cards
AmpFLPs
A smaller minisatellite loci that had alleles from 9-15 bp, composed of short core repeat units.
46
New cards
Short Tandem Repeats (STRs)
microsatellites that are an abundant class of DNA polymorphisms.
47
New cards
DNA analysis
STRs form the basis of forensic _____.
48
New cards
Multiplex PCR
this is where each primer pair would amplify a specific sequence or STR.
49
New cards
Forensic Science Services (FSS)
The first multiplex PCR kit was developed by the _______ of the UK and it comprised four STR loci, THO1, vWA, FES/FPS, and F13A1.
50
New cards
second generation multiplex (SGM)
The FSS then launched its ________ comprising of six STR loci THO1, FGA, D8S1179, D18S51 and D21S11.
51
New cards
Simple consisting of 1 repeating sequence
an STR locus has several alleles but each allele differs only in several repeats but the sequence of the repeats is the same.
52
New cards
Simple with non-consensus alleles
consider two alleles of locus HUMTHO1.
53
New cards
Compound with non-consensus alleles
considers two alleles of the locus vWA.
54
New cards
Complex repeats
consider two alleles of locus D21S11
55
New cards
Hypervariable repeats
SE33. Few loci have not only different repeat regions; they also have them arranged in many different ways.
56
New cards
slipped strand mispairing
Sometimes, ‘________’ leads to a mutation in regions of the genome, having abundant simple repetitive sequences which have been recognized as the major mechanism involved in their generation.
57
New cards
ABI GeneScan®
The automated systems such as ________ allowed electrophoretic information to be stored and tabulated as the alleles migrated through a gel matrix and pass a laser detection window.
58
New cards
Multiplexing
a technique where several STR loci are amplified in a single tube PCR.
59
New cards
Allelic ladder
consists of several alleles of an STR system and is used as a reference to designate the alleles.
60
New cards
Genotyper
the program would call the allele based on the established windows, which is called the ‘absolute window method’.
61
New cards
Maternity identification
is necessary to identify the mother in cases of child abandonment or infanticide or swapping of neonates.
62
New cards
Paternity identification
is important in cases of sexual assault in which pregnancy occurs and pregnancy is either terminated or goes to full term.
63
New cards
AMPFLSTR® SGM Plus
The FSS has started profiling criminal cases using the 11 loci _______kit.
64
New cards
DYS19
Described as the first STR on the human Y-chromosome, which was found to be polymorphic and suitable for sex and paternity determination in deficiency cases.
65
New cards
Y STR analysis
____ can be valuable in mixture interpretation in multiple rape cases or the detection of male specific profile in azoospermia/vasectomized male suspects when spermatozoa are not available.
66
New cards
multiplex systems
The ______ are mostly used as both are robust and reproducible and, together, allow seven Y STRs to be analyzed. These systems are therefore favored at the moment.
67
New cards
Y-PLEXTM 6
A new multiplex capable of amplifying seven Y STR loci, the ‘______’ has been recently developed by a commercial firm Reliagene, Technologies, Inc. USA.
68
New cards
Match Probability Formula
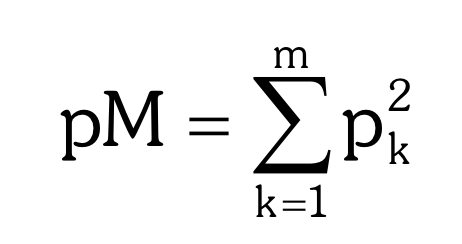
69
New cards
Power of Discrimination Formula
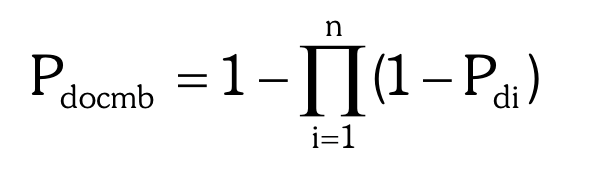
70
New cards
Match Probability
the probability that the two randomly selected individuals will have identical genotypes.
71
New cards
Power of Discrimination
the probability that two randomly selected individuals will have different genotypes. This is the reciprocal of the probability of a match.