EEMB 7 - Chapter 37: Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
neurons
a nerve cell; the fundamental unit of the nervous system, having structure and properties that allow it to conduct signals by taking advantage of the electrical charge across its plasma membrane
cell body
the part of a neuron that houses the nucleus and most other organelles
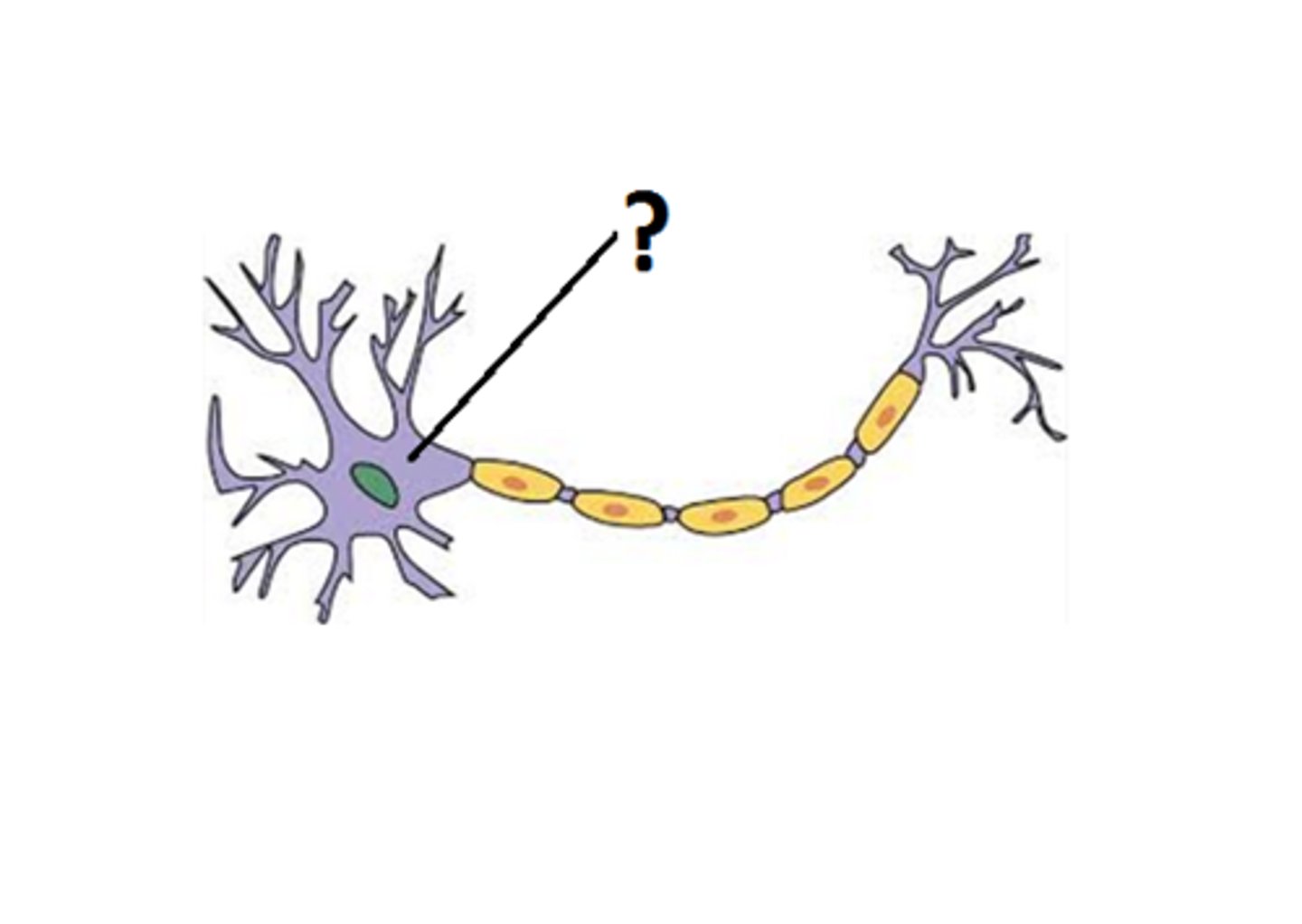
dendrites
one of usually numerous, short, highly branched extensions of a neuron that receive signals from other neurons
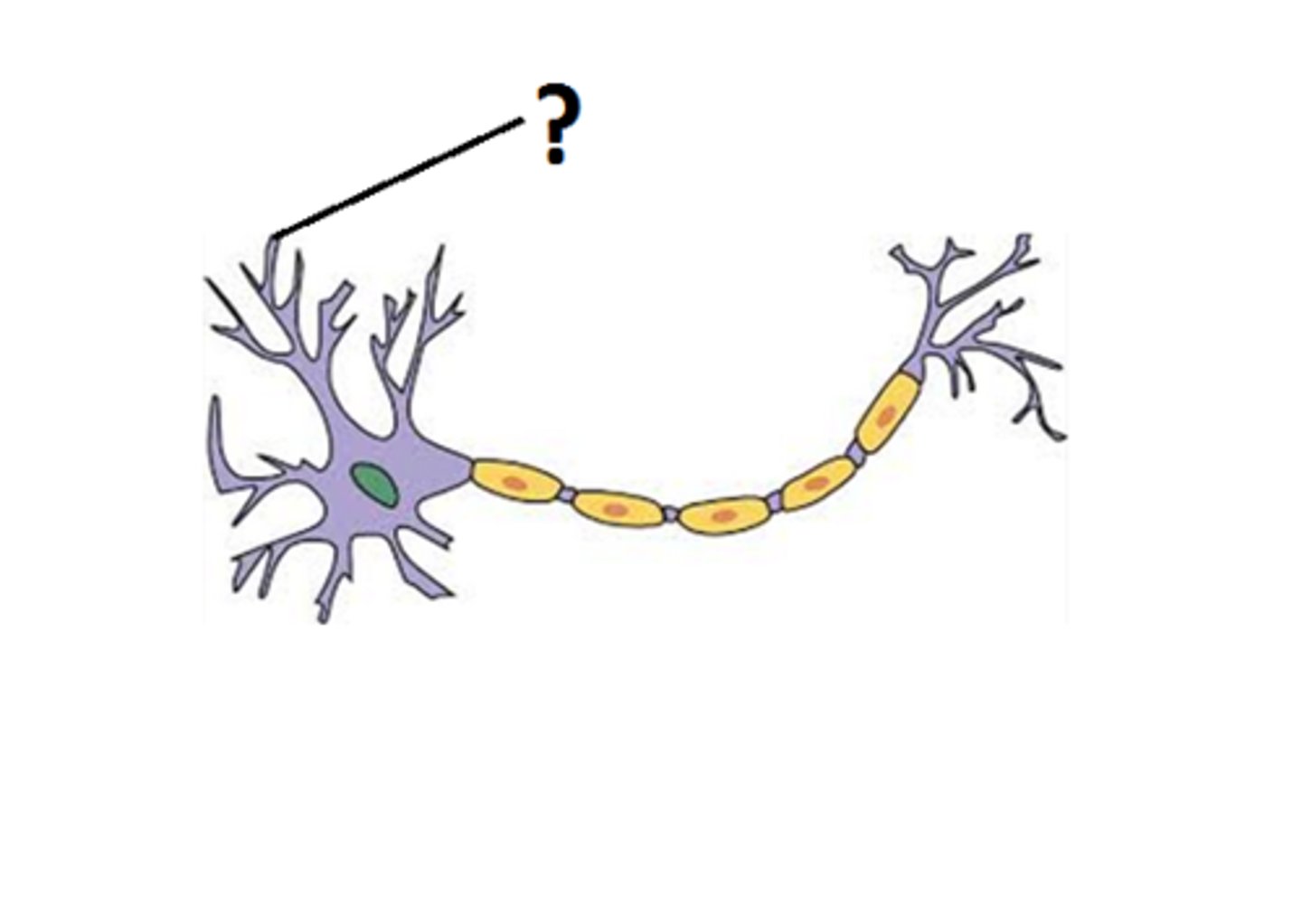
axon
a typically long extension, or process, of a neuron that carries nerve impulses away from the cell body toward target cells
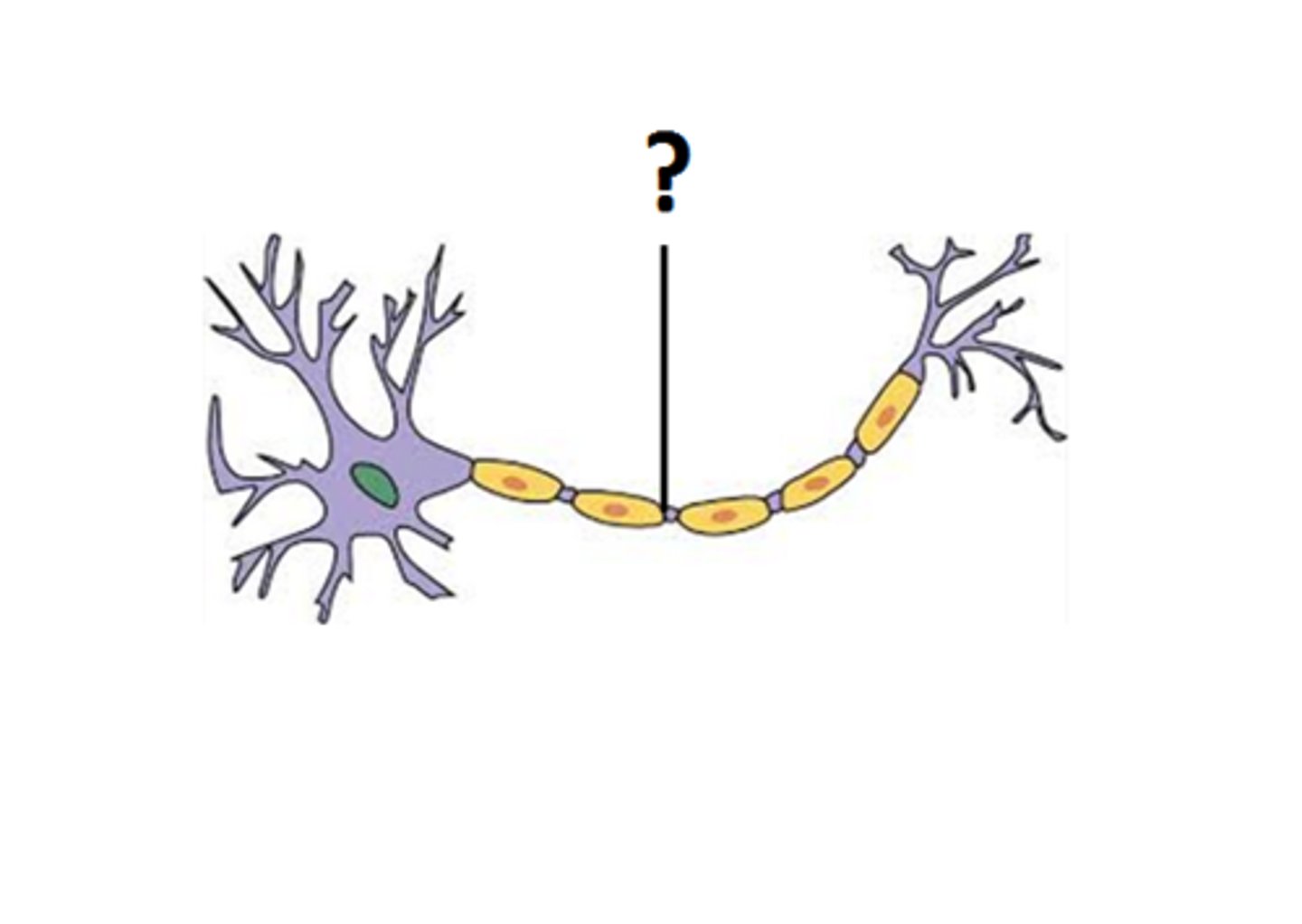
synapse
the junction where a neuron communicates with another cell across a narrow gap via a neurotransmitter or an electrical coupling
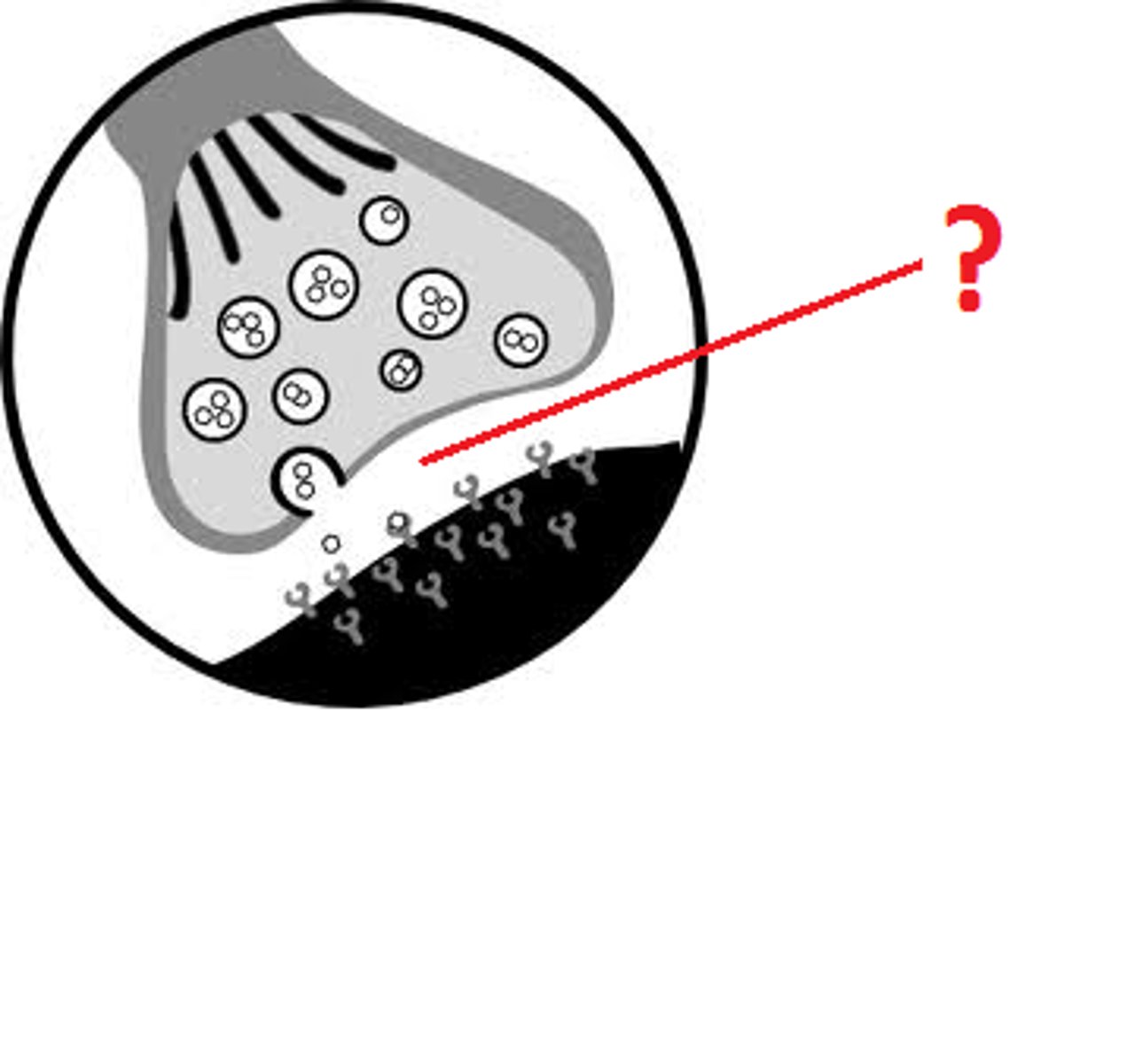
neurotransmitter
a chemical messenger that is released from the synaptic terminal of a neuron at a chemical synapse, diffuses across the synaptic cleft, and binds to the postsynaptic cell, triggering a response
glial cell/glia
cells of the nervous system that support, regulate, and augment the functions of neurons
CNS
the portion of the nervous system where signal integration occurs; in vertebrate animals, the brain and spinal cord
PNS
The sensory and motor neurons that connect to the central nervous system
membrane potential
the difference in electrical charge (voltage) across a cell's plasma membrane due to the differential distribution of ions; affects the activity of excitable cells and the transmembrane movement of all charged substances
resting potential
the membrane potential characteristic of a nonconducting excitable cell, with the inside of the cell more negative than the outside
sodium-potassium pump
a transport protein in the plasma membrane of animal cells that actively transports three sodium out of the cell and two potassium into the cell
ion channels
a transmembrane protein channel that allows a specific ion to diffuse across the membrane down its concentration or electrochemical gradient
equilibrium potential
the magnitude of a cell's membrane voltage at equilibrium
gated ion channels
a gated channel for a specific ion; the opening or closing of such channels may alter a cell's membrane potential
voltage-gated ion channels
a specialized ion channel that opens or closes in response to changes in electrical membrane potential, altering conformation of channel proteins
hyperpolarization
a change in a cell's membrane potential, inside is more negative than outside; reduces the chance that a neuron will fire (inhibitory)
depolarization
a change in a cell's membrane potential; inside is less negative than outside
graded potential
in a neuron, a shift in the membrane potential that has an amplitude proportional to signal strength and that decays as it spreads
action potential
an electrical signal that propagates (travels) along the membrane of a neuron or other excitable cell as a nongraded (all-or-none) depolarization; good for transmitting signals over longer distances
threshold
the minimum potential that an excitable cell membrane must reach for an action potential to be initiated
myelin sheath
wrapped around the axon of a neuron, a lipid insulating coat of cell membranes from Schwann cells or oligodendrocyte; interrupted by nodes of Ranvier, where action potentials are generated
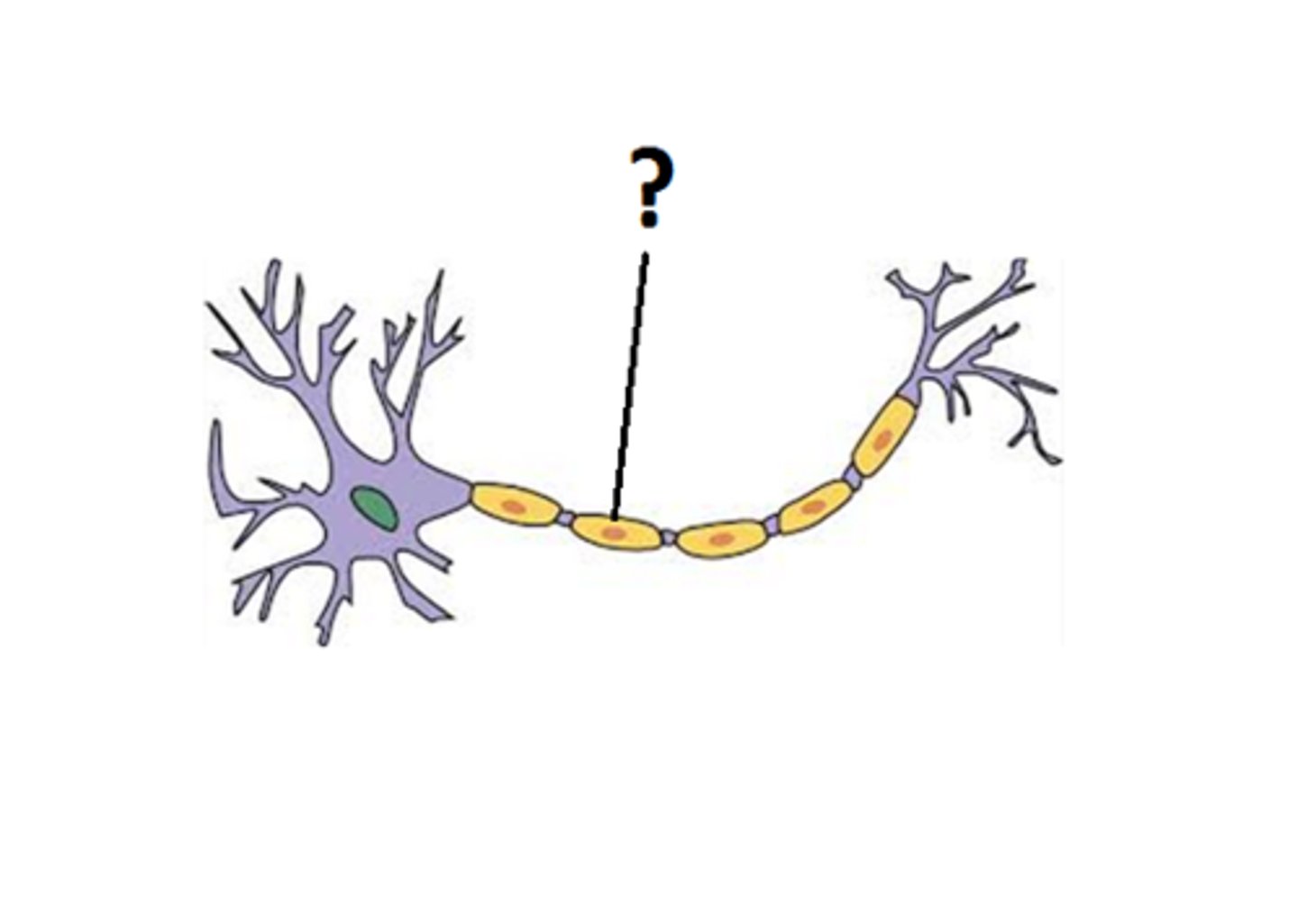
oligodendrocytes
a type of glial cell that forms insulating myelin sheaths around the axons of neurons in the central nervous system (CNS)
schwann cells
a type of glial cell that forms insulating myelin sheaths around the axons of neurons in the peripheral nervous system (PNS)
nodes of ranvier
gap in the myelin sheath of certain axons where an action potential may be generated
excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP)
depolarization in the membrane of a postsynaptic cell caused by the binding of an excitatory neurotransmitter from a presynaptic cell to a postsynaptic receptor; increases likelihood of an action potential
inhibitory postsynaptic potential (IPSP)
hyperpolarization in the membrane of a postsynaptic neuron caused by the binding of an inhibitory neurotransmitter from a presynaptic cell to a postsynaptic receptor; action potential less likely
summation
individual postsynaptic potentials combine to produce a larger postsynaptic potential
acetylcholine (ACh)
a neurotransmitter for muscle stim, memory, learning. binds to receptors and alters the permeability of the postsynaptic membrane to specific ions, either depolarizing or hyperpolarizing the membrane
neuropeptides
a relatively short chain of amino acids that serves as a neurotransmitter
endorphins
any of several hormones produced in the brain and anterior pituitary that inhibit pain perception, acting as natural pain relievers
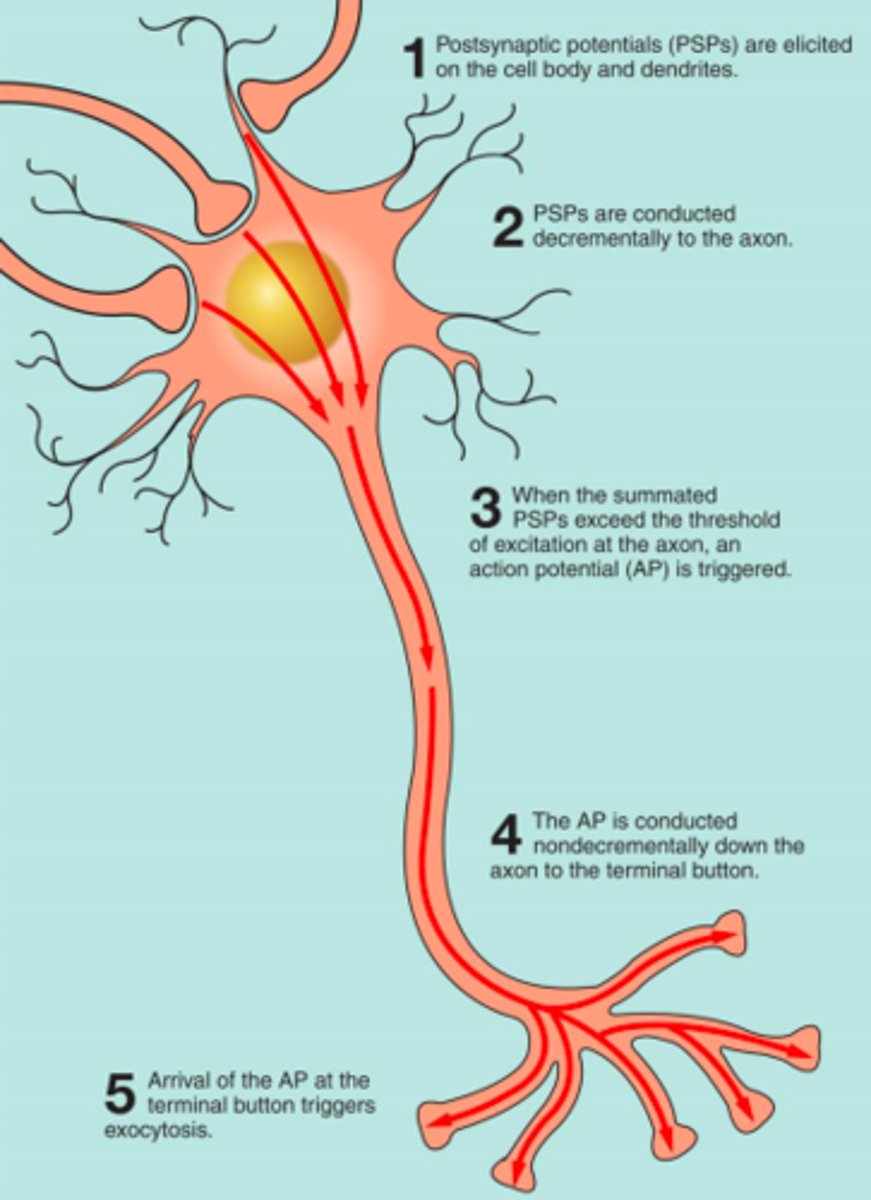
direction of signals through a neuron
1. signal received by dendrites
2. passes through cell body
3. action potential in axon hillock
4. signal transmitted through axon
5. reaches synaptic terminal
what types of glial cells are there?
microglia, ependymal cells, astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, and schwann cells
sensory neurons
a nerve cell that receives information from the internal or external environment and transmits signals to the central nervous system
interneurons
an association neuron; a nerve cell with in the central nervous system that forms synapses with sensory and/or motor neurons and integrates sensory input and motor output
motor neurons
nerve cell that transmits signals from the brain or spinal cord to muscles or glands
order of action potentials
1. resting potential & voltage-sodium channels are closed
2. depolarization, opening the channels
3. rising phase of the action potential activating a positive feedback cycle
4. falling phase of the action potential, opening voltage-potassium channels
5. undershoot, where there's a high permability for K+ but it eventually returns to resting potential after a refractory period
evolutionary adaptations of axon structure
1. wider axon that provides less resistance to the current associated with an action potential than does a narrow axon
2. electrical insulation (in vertebrates, the myelin sheath) that causes the depolarization current associated with an action potential to spread farther along the axon interior, bringing more distant regions to the threshold sooner
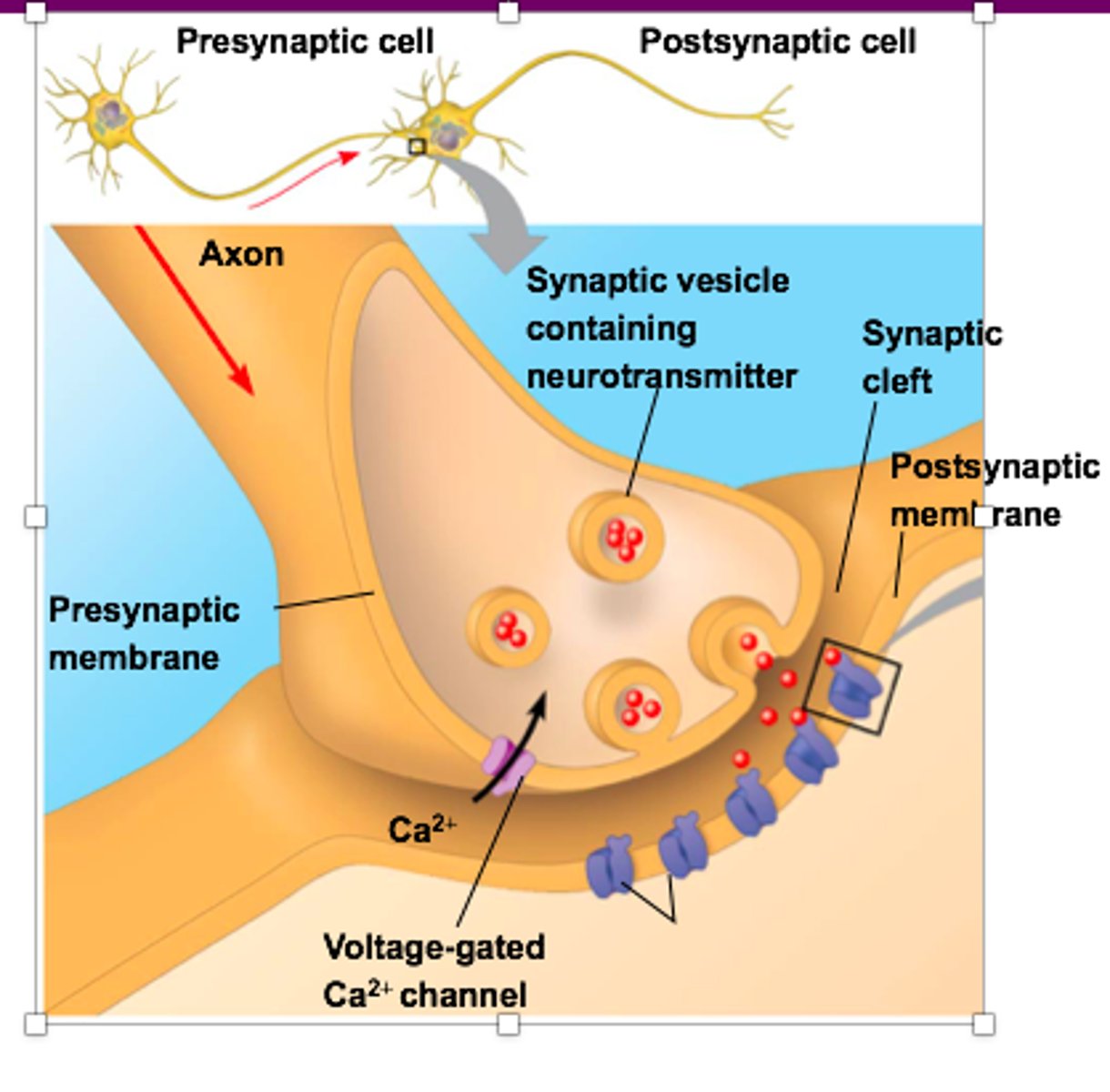
order of neurotransmitter signals
1. action potential arrives, depolarizing presynaptic membrane
2. opening of voltage-gated channels; influx of Ca2+
3. elevated concentration causes synaptic vesicles to fuse with presynaptic membrnae, releasing neurotransmitter into the synaptic cleft
4. neurotransmitter binds to ligand-gated ion channels in postsynaptic membrane
spatial summation
when several synapses occur at the same time, an additive effect
temporal summation
if single EPSP synapses again before resting membrane potential is fully restored, repeating synapses can show additive effect; this is where frequency modulation for intense stimuli comes into play
glutamate def
primary excitatory neurotransmitter, playing an important role in formation of long-term memory
biogenic amines
synthesized from amino acids
dopamine
a neurotransmitter associated with movement, attention and learning and the brain's pleasure and reward system
serotonin
a neurotransmitter that affects hunger,sleep, arousal, and mood.
norepinephrine
an excitatory neurotransmitter involved in arousal, as well as in learning and mood regulation
neuro communication as a gas
some vertebrates neurons release dissolved gases, like nitric acid (NO) and carbon monoxide, as neurotransmitters
as a college student, studying for this exam what neurotransmitter would be helpful
glutamate
saltatory conduction
rapid transmission of a nerve impulse along an axon, resulting from the action potential jumping from one node of Ranvier to another, skipping the myelin-sheathed regions of membrane
inhibitor drug examples and their effects
crotoxin from american rattlesnake and botulinum toxin (botox) decrease ACh release
inhibitor drugs
most act by inhibiting release of neurotransmitters
blocking agents
most act by blocking various channel proteins (like saxitoxin from red tide algae) & tetrodotoxin from pufferfishand some by blocking neurotransmitter receptor sites (like curare from a s. american tree)
enzyme destroyers example
nerve gas (sarin) kills by spastic paralysis due to its inactivation of ACh
strychnine, aka rat poison
interferes with IPSP's in spinal cord, muscles have difficulty "turning off" leading to spastic paralysis and asphyxiation