20) isotopes and radioactive decay
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
stable vs unstable isotopes, and applications
stable: don’t change over time, isotope thermometry, tracers
unstable: change into diff elemetn over time through radioactive decay, geochronology, tracer
elemental fractionation
controlled by size and charge
controlled by partitioning into diff minerals, meaning controlled by compatibility
compatibility is controlled by size and charge
isotopic fractionation
controlled by difference in mass
ionic radius is the same, same number of electrons, diff neutrons.
much smaller influence than elemental fractionation. during natural process, there is sometimes a slight preference for a material to incorporate a heavier isotope than a lighter one
relative mass difference between 16-17 and 16-18, twice difference
fractionates the isotopes by twice the amount
if we change 18/16 ratio by 2 units, the 17/16 ratio will change by 1 unit
slope is 0.5 = mass dependent fractionation line
relative mass difference of heavy elements is smaller, so isotopic fractionation will be smaller to (1/87 vs 1/86)
temperature influence of isotope fracitonation
increasing temperature means mass difference matter less due to flexibility of sites
at a certain temp they will have the same isotopic composition
low temp = larger fractionation
3 important points about isotope fractionation
mass dependent
effects are larger for bigger relative mass differences between isotopes
effects are stronger at lower temperatures
why does radioactive decay occur? extra info
unstable nuclides are in a higher energy state
band of stability is at the bottom of an energy valley
its an attempt of unstable nuclide to become more stable by getting rid of extra energy
radiogenic: generated by a radioactive isotope, daughter of parent isotope
decay rate is dependent on the energy state of the nuclide
independent of pressure, temp, and chem composition
types of radioactive decay
beta, positron, electron capture, alpha, nuclear fission
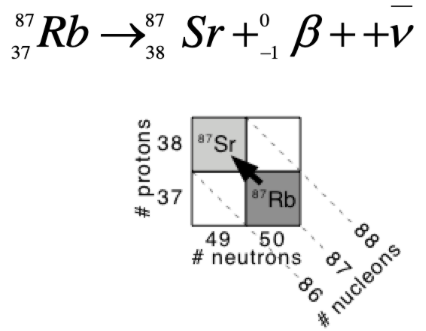
details on beta decay
neutron converted to a proton and beta- particle (negatron)
1 less neutron, 1 more proton
diagonally up-left
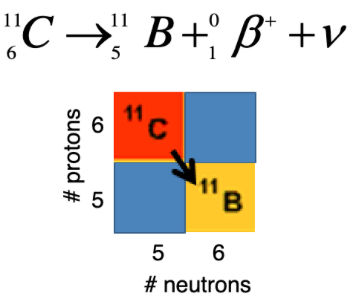
details on positron decay
proton converted to neutron and beta+ particle (positron)
1 less proton, 1 more neutron
diagonally down-right
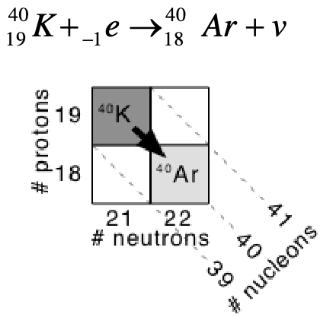
details on electron capture decay
proton capturing an electron from orbital changes into neutron
1 less proton, 1 more neutron
diagonally down-right
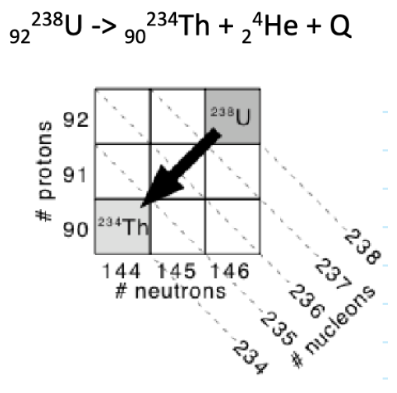
details on alpha decay
alpha particle ejected from nucleus
mass number decreases by 4, number of protons decreases by 2
diagonally down-left skipping a box
Q is total alpha decay energy
details on nuclear fission
heavy nuclide breaking into smaller nuclides and energy
what’s important about K40
can decay to 2 different daughters
using positron decay (Ca40), or electron capture decay (Ar40)
know this a little bit
blue is beta+ or electron capture
red is beta–
yellow is alpha decay
green is spontaneous fission
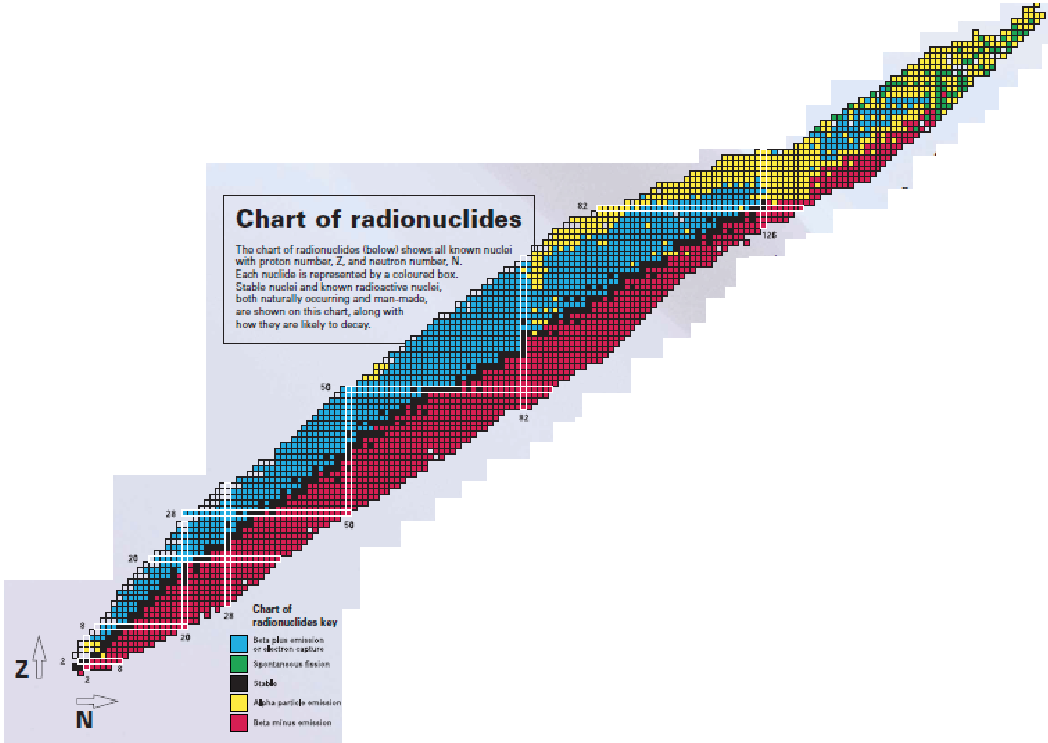
details on gamma ray
gamma rays aren’t a radioactive decay mechanism, but they are released when decay occurs in any mechanism
what is a decay chain
when a parent decays to a stable daughter product through intermediate daughter nuclides that are also radioactive
U238 all the way to Pb206: first is alpha, then beta-, then again beta-, then a bunch of alpha decays to Po or Pb206
explain the basic radioactive decay eqtn
D: amount of daughter isotope you measure in a mineral today
D0: initial daughter, amount of daughter that was originally present in teh mineral or rock at the time of formation
N0: number of parent atoms (radioactive)
N((e^lam*t-1) daughter produced by radioactive decay, N: number of parent isotopes, lam: decay constant, T: time of formation of mineral/rock
reference isotope info
want one with reasonable abundance, semi-close to the one you are looking at
not too abundant
explain methods of radiometric dating using the equation
assume D0 is zero, assume no daughter isotope was taken in at formation
K40→40Ar Ar is noble gas, typically minerals don’t take it in, we can assume any Ar formed was from radiogenic decay
isochron method
explain isochron method
equation in linear form
take multiple samples that formed at the same time, take daughter isotope ratio as y and parent to daughter ratio as x
must form at same time
use this to find slope, then slope = e^lam*t-1, we know the time of formation
line is called isochron
extrapolating the line gives the y intercept, which is the original daughter to isotope ratio
explain isochron example
plag, kspar, biotite
when they crystallized from the magma, they have different parent to daughter ratio
biotite prefers to take Rb into its structure than Sr, so the Rb/Sr ratio is higher
Plag likes to take Sr into system more than Rb, so low Rb/Sr ratio
all minerals have same initial daughter isotope ratio
equal proportion of Sr ratios (mass diff between Sr isotopes is low)
over time, Rb/Sr ratio will decrease, because 86Rb will decay to Sr86
Sr87/Sr86 ratio will increase because Rb87 decays to Sr87
biotite had lots of Rb to start, so a larger change. plag had less Rb to start, so a lesser change
relationship will stay linear
over time the isochron gets steeper (slope increases)
assumptions / conditions in age dating
the number of parent and daughter atoms have changes only by decay of parent to daughter (isotopic system is closed)
no daughter isotope was present in the system to start with
decay constant is known accurately
analytical data are accurate (from mass spectrometry)
choosing an appropriate decay scheme for geochronology
isotopic decay must be active to determine absolute time
clock has to be running
if all parent has decayed to daughter, no way of knowing time
which type of disturbance is most likely
loss of daughter
parent is something the mineral usually likes to take into the structure, but if the daughter is something the mineral reall doesn’t like to have in its strucutre, the system is strained, and daughter will leave
weathering can cause parent to leave, mineral structure likes parent, causing it to gain
isotopic disturbance is a funciton of what
closure temperature
temp below which a mineral/rock becomes closed to diffusional exchange of isotopes with the surroundings

explain this
if you use A for dating, you get the time at which it became closed to diffusion
A mineral with a lower closure temp will give you a younger age
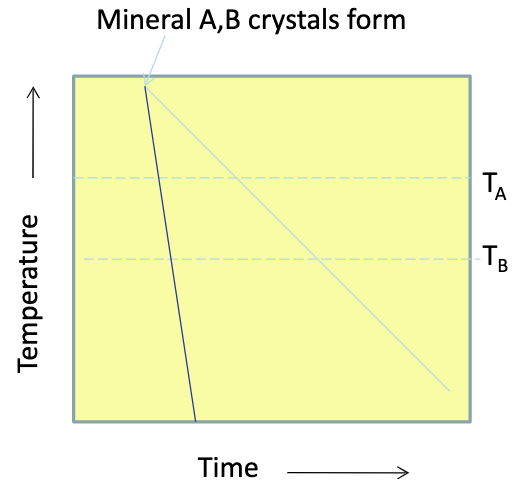
what is the effect of cooling rate on closure temp
a fast cooling rock will have less difference in age using different minerals for dating (steeper slope)
a slow cooling rock will have much more difference in age using diff minerals for dating
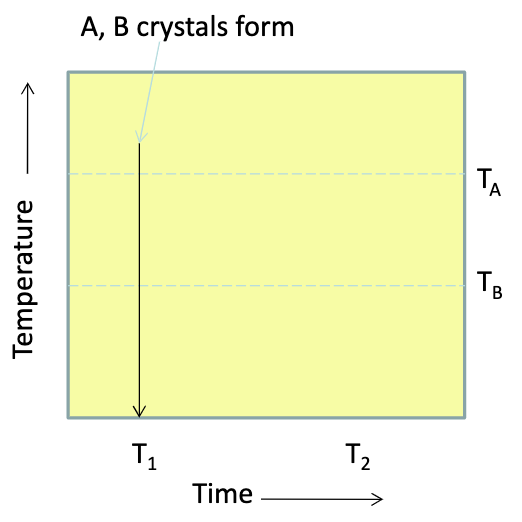
what is the effect of metamorphism on closure temp
using A, you’d get the original T1 crystalizing temp because closure T of A is higher than the meta temp
using B, you’d get the age of meta if all the daughter that was accumulated between T1 and T2 leaks out
meta resets the time, you start at time zero
if only some daughter is lost, you get an age between original and meta (but that’s not significant)
partial metamorphism has no geological significance, gives you a date where nothing happened
details on summary
losing daughter is as if decay hasn’t occured as much, you get a younger age, same as if you gain parent. daughter/parent ratio decreases
losing parent or gain of daughter results in apparent older age. daughter/parent ratio increases
discordance
if the dates disagree from multiple methods
causes of discordance: isotopic system did not remain closed
commonly loss of Pb or intermediate daughter products
secular equilibrium
established if parent isotope has significantly longer half-llife compared to intermediate daughters
once all bowls are full, one drop from top bowl will correspond to a drop out of the last bowl, no overall change
details on zircon
common accessory mineral in igneous and meta rocks
harder than quartz, doesn’t get destroyed easily, survives multiple sedimentation cycles
when it forms, takes in uranium
Zr4+ cation and U4+ is a simple substition
Pb2+ is not easily substituted, so zircon has neglible initial daughter levels
high closure tmep for Pb diffusion, need high grade meta to reset the clock
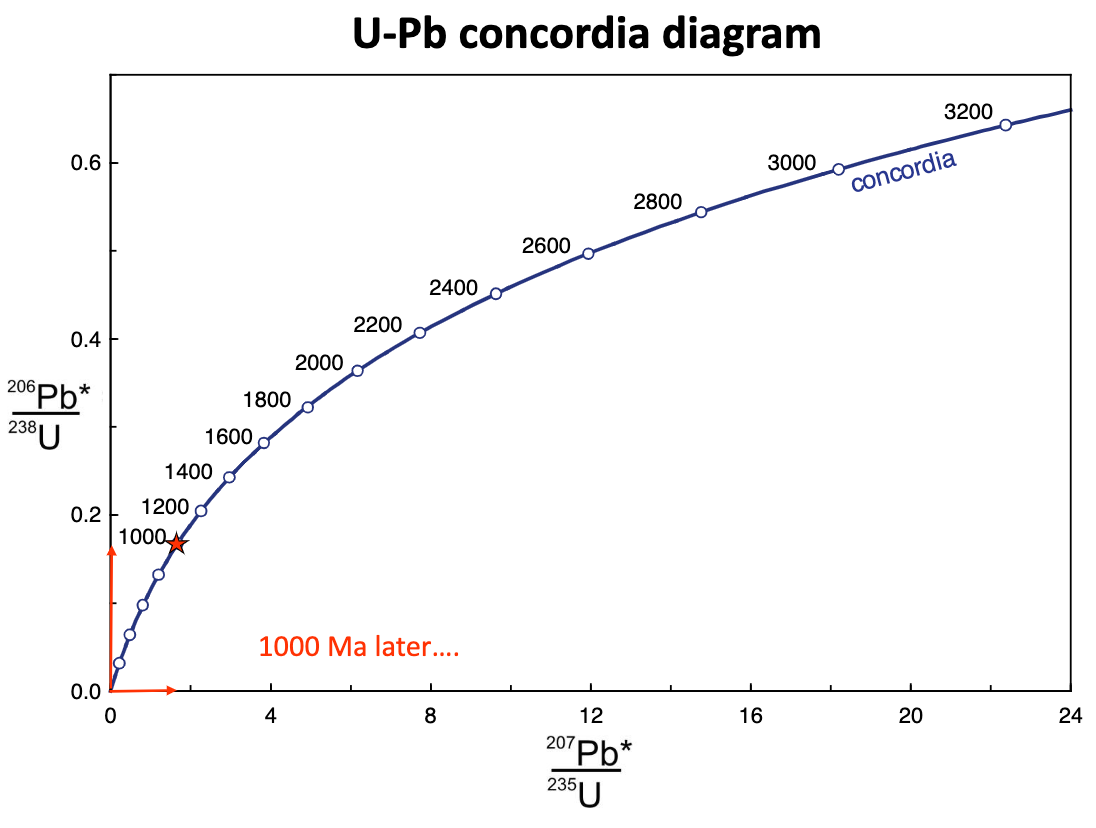
explain U-Pb concordia method
for minerals with no common Pb, it’s a function of time
concordia curve: points in time showing isotopic evolution of Pb with time in a closed system
each number is millions of years
if it plots on the curve, it tells you that 2 methods are giving the same age (concordant)
a sample with lead loss will plot below the concordia
a sampel with uranium loss will plot above the concordia (reversely discordant)
advantages of the U-PB concordia methad
two different isotopic decay systems offer as a check to each other
meaningful geocrhonological info can be dervied even if teh system behaved as an open system
why are isotopes fractionated
difference in bond strength between a molecule with heavy isotopes and one with light isotopes
differences in vibrational energy and bond strength affect the way different isotopes respond to certain physical processes
lighter atoms bonded together will vibrate more than the heavier isotope
potential energy of H-H bond is higher than the D-D bond
details on eqlm isotopic fractionation
reaction at eqlm
due to differences in bond strenght of different isotopes within these phases
heavier isotope forms a stronger bond, so it preferentially partitions into the material with a stronger bonded structure
ex: condensation of water vapour: 18O is preferentially transferred to the precipitation
D is preferentially transfered into the precipitation
liquid has stronger bodning than vapour
liquid will be enriched in heavier isotopes
D/H ratio in rain would be higher than in vapour
what are isotopologues
compoudns that differ only in teh isotope makeup of the elements they contain
H2O, HS16O, Hs18O, D216O, D218O, DH17O
details on kinetic isotopic fracitonation
when one isotope reacts more rapidly than another in an irreversible reaction
kinetically controlled stable isotope fractionation reflects the readiness of a particular isotope to react
lighter isotopes diffuse faster than heavier isotopes in many situation
lighter isotopes react more readily and get preferentially incorporated at noneqlm
Ex: evaporation of water
H2 and 16O molecules escape into vapour preferentially compared to D2 and 18O. water vapour is enriche in 16O and 1H
D/H in water is larger than D/H in vapour
reporting stable isotope compositions
measure heavy/light ratio
ligihter isotope is usually most abudnant one by a lot, so number ends up being very small
why we use delta notation
delta = heavy/light sample - heavy/light standard
/ heavy light standard *1000
in parts per mille %.
positive means sampel is enriched in 18O relatie to standard
negative measn the sample is depleted in 18O relative to standard