inheritance, variation and evolution
1/69
Earn XP
Description and Tags
biology aqa gcse topic 6 SO FAR ONLY 6.1-6.17 INCLUSIVE
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
what is DNA?
a polymer that carries genetic information
describe the structure/shape of DNA
a polymer made of two strands twisted around each other in a double helix
where in the cell is DNA found in prokaryotic cells, and in what form?
loose in the cytoplasm as a single loop or in plasmids
where in the cell is DNA found in eukaryotic cells, and in what form?
stored in the nucleus in chromosomes
what is the function of DNA?
it codes for the production of proteins
what is a chromosome?
a long strand of tightly coiled DNA that usually contains thousands of genes
what is a gene?
a short section of DNA on a chromosome that codes for a specific protein
put these in size order from smallest to largest: DNA, gene, chromosome, cell, nucleus, genome
DNA, gene, chromosome, genome, nucleus, cell
what is the name for a single unit that makes up a DNA molecule?
nucleotide
what are the components of a nucleotide?
phosphate, base and the sugar
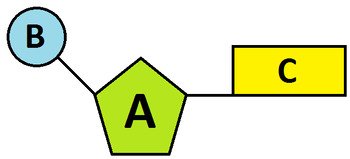
label part A of the nucleotide
the sugar
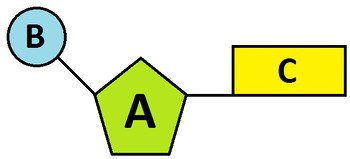
label part B of the nucleotide
the phosphate
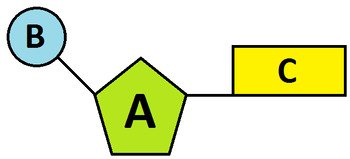
label part C of the nucleotide
the base (A, T, C, or G)
what is the genome?
the entire genetic material of an organism
what was the Human Genome project?
an international research effort to identify all the DNA base pairs that make up a random person
why was the Human Genome project so imporant (3 reasons)?
helped identify genes linked to different diseases for better prevention and treatment, improved understanding and treatment of inherited diseases, helped trace human migration patterns to understand ancient history
what are the 4 different nucleotide units? (different bases)
A, T, C and G
which base does A pair with?
T
which base does C pair with?
G
what word is used to describe different DNA strands (e.g. A and T, C and G)
complementary
how do genes code for proteins?
each sequence of 3 bases codes for a specific amino acid, order of base pairs controls order of assembly for amino acids to make a specific protein with a specific shape
what happens in protein synthesis? (4)
a template molecule (mRNA) is copied from a DNA base sequence of a gene, this leaves the nucleus and attaches to a ribosome, carrier molecules (tRNA) bring specific amino acids in the right order to add to the protein chain, when chain is complete it folds up to form a unique shape
where are proteins synthesised?
on ribosomes
why is the specific shape of a protein so important?
so they can do their job, e.g. enzymes need specific shape so active site complements substrate
what is a mutation?
a random change to DNA base sequence that occurs continuously
what are the 3 types of mutation?
insertion, deletion and substitution
are mutations always harmful?
no, most are neutral and some can be beneficial
what happens in substitution mutations?
a base(s) has been replaced that may or may not affect an amino acid
what happens in insertion mutations?
a base(s) has been added to the sequence, this changes the amino acid’s sequence and the protein’s shape and function
what happens in deletion mutations?
a base(s) has been removed from the sequence, this changes the amino acid’s sequence and the protein’s shape and function
give 2 examples of neutral mutations
heterochromia, polydactyl in cats
give 2 examples of harmful mutations
sickle cell anaemia, cystic fibrosis
give an example of a beneficial mutation
melanism in peppered moths
how do mutations that effect the amino acid’s sequence affect an organism? (explain the sequence, 4)
change in a DNA base sequence causes a change in the base sequence of the template molecule (mRNA), this changes the amino acid sequence of the protein, protein’s shape and function changes, this causes a change in the phenotype of the organism
can be mutations be inherited?
yes, but it must be a mutation in the parent’s gametes
what 4 possible effects could a mutation have on an enzyme?
no effect, lose activity (substrate can’t bind), improve activity (enzyme is more efficient), change activity (catalyses a different reaction)
what is non-coding DNA?
DNA that doesn’t code for proteins
what is the function of non-coding DNA?
controls whether genes are on (leads to production of protein) or off (does not lead to production of protein)
what could happen if there is a mutation in non-coding DNA?
can lead to genes being on/off more and producing more/less proteins than normal
what is a gamete?
a sex cell formed by meiosis that has half the number of chromsomes in a body cell
what is sexual reproduction?
the fusion of male and female gametes (fertilisation)
how does sexual reproduction lead to genetically varied offspring?
gamete formation involves cells divided by meiosis and mix of genetic information from two parents
give examples of gametes in humans and plants
humans: male - sperm cells, female - egg cells. plants: male - pollen, female - egg cells
why does asexual reproduction lead to genetically identical offpsring (clones) (3)
cells divided by mitosis so produces genetically identical cells, no fusion of gametes so no mix of genetic material, only one parent
what is mitosis?
division of the nucleus
why is cell division by mitosis important?
for growth and repair of damaged tissues, organs and organisms (by replacing dead/damaged cells)
explain the process of mitosis (4)
cells replicate their sub-cellular structures and DNA (to form 2 copies of each chromosome), mitosis occurs, 2 copies of each chromosome are pulled to the opposite ends of the cell, division of the cytoplasm and cell membrane forms 2 daughter cells that are genetically identical
how many chromosomes are in a human body cell?
46 chromosomes (23 pairs)
how many chromosomes are in a gamete?
23 total
explain the process of meiosis (4)
DNA and sub-cellular structures replicate, 2 copies of each chromosome are pulled to opposite ends of the cell, cell divides twice, forms 4 genetically different gametes with a single cet of chromosomes (half amount of original cell)
what happens after fertilisation?
fertilised cell (zygote) divides repeatedly by mitosis, ball of genetically identical cells is an embryo, cells in embryo differentiate into specialised cells
advantages of sexual reproduction (2)
genetic variation in offspring (helps species adapt using natural selection in an environment change), allows humans to use selective breeding to produce better traits in animals/plants such as faster food production
disadvanatges of sexual reproduction
requires two parents, takes longer and produces fewer offspring than asexual reproduction
advantages of asexual reproduction
only requires one parent, is faster and produces more offpsring than sexual reproduction, more time and energy efficient, genetically identical offspring good for colonisation
disadvantages of asexual reproduction
no selective breeding, no genetic variation and therefore no benefit when adapting to an environment change using natural selection
give 3 examples of organisms that can produce asexually or sexually given the circumstances
fungi (asexually by releasing spores, sexually for variation), malarial parasites (asexually in human host, sexually in mosquito), flowering plants (asexually to produce runners, sexually to produce seeds)
what is a chromosome?
a tightly-coiled thread-like structure of thousands of genes found in the DNA in the nucleus
are chromosomes usally found alone or in pairs?
usually in pairs
what is an allele?
a different form of gene
give 2 examples of a characteristic controlled by a single gene
fur colour in mice and red-green colour blindness in humans
What is a dominant allele?
An allele that is always expressed, even if only one copy is present
What is a recessive allele?
An allele that needs 2 copies to be expressed
What does homozygous mean?
2 of the same alleles of a particular gene, e.g. BB or bb
what does heterozygous?
2 different alleles of a particular gene, e.g. Bb
what is a genotype?
the alleles that an organism has for a particular gene, e.g. BB or Bb
what is a phenotype?
the physical characteristics determined by an organism’s genotype
why does the actual ratio of characteristics not match the ratio of expected characteristics in offspring?
fertilisation is random