neurons
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
neurons have
unidirectional flow of information
the nervous system
is the main controlling and communicating centre of the body
coordinates and controls all bodily functions
processes information from environment and enables body to respond accordingly
3 parts of axon
axon hillock
axolemma
axoplasm
nucleolus is post mitotic → diffused chromatin in neurons allows for
transcription
neuronal cytoskeleton composed of
microtubules
neurofilaments
microfilaments
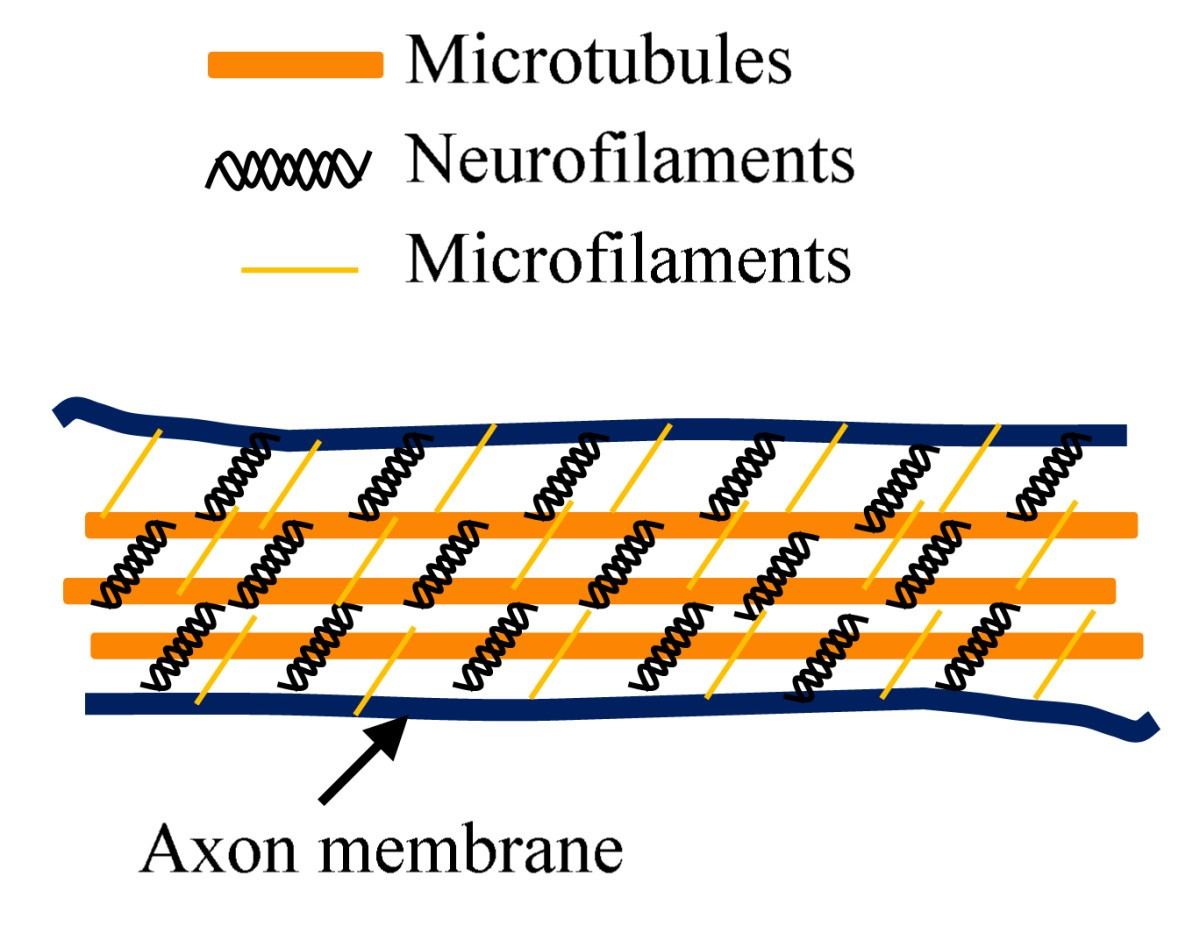
microtubules have
alpha and beta tubulin dimers → transport within the neuron
neurofilaments have
coiled-coil fibres → structural maintenance
microfilaments have
actin dimers → structural movement of cargo
kinesins are
slower than dyneins
many axons are myelinated by
glial cells
multiple sclerosis
when immune system attacks myelin sheath of nerves in brain and spinal cord
myelination speeds up
nerve conduction
saltatory conduction
coverings of peripheral nerves
endoneurium
perineurium
epineurium
endoneurium
delicate connective tissue layer surrounding axon and schwann cells
perineurium
connective tissue layer surrounding groups of axons forming fascicles
epineurium
robust connective tissue layer surrounding individual fascicles, contains blood vessels
nissl staining
basic dyes i.e. cresyl violet → stains cell body
nissl substance
rER
chromatolysis
dissolution of nissl substance
functional classification of neurons
sensory/afferent neurons
motor/efferent neurons
interneurons
structural classification of neurons
multipolar
bipolar
(pseudo)unipolar
example of multipolar neuron
motor neuron in spinal cord
example of bipolar neuron
cells in retina
example of pseudo unipolar
primary somatosensory neuron in the dorsal root ganglion
neurons connect via
synapses
two types of synapses
electrical
chemical
synapses can be
axo-dendritic
axo-somatic
axo-axonic
axo-dendritic
terminal synapses onto dendrites
axo-somatic
terminal synapses onto cell body
axo-axonic
terminal synapses onto axon
neurons can only make a binary decision
to fire an action potential or not (all or nothing)
convergence
when one neuron receives multiple inputs from many other neurons
divergence
when one neuron sends out and synapses with many other neurons
5 types of nervous system disorders
vascular disorders e.g. stroke
infections e.g. meningitis
structural disorders e.g. bell’s palsy, brain and spinal cord tumors
functional disorders e.g. epilepsy
degeneration e.g. Parkinson’s, Huntington’s, Alzheimer’s
treatment for parkinson’s symptoms
Levodopa - precursor to dopamine
Carbidopa - given with levodopa so cells outside brain do not use levodopa and more gets to the brain
MAO-B inhibitors - less dopamine breakdown