Green Plants Vocab Long
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Gametophyte
Sporophyte
Spore
Seed
haploid generation produces gametes
diploid generation, produces spores
meiotically produced haploid cell, divides mitotically to produce a plant
embryo packaged with resources inside a protective coat
Cuticle
Stomata
Guard cells
Waxy layer coating plant, reduces water loss
small pore found in the epidermis (outer layer) of plant leaves, stems, and other organs used in gas exchange and water regulation
opens and closes the stoma to regulate water and gas
4 Main walls in plants
simple water conducting cell: elongated but lack much structural support, meaning they don’t have strong walls. (Mosses)
First Vascular Tissue: have cellulose in their primary cell wall, but some of them start to add lignin, which is a tough material that adds strength and support, allowing the plant to grow taller. (seedless vascular plants)
Tracheids: primary cell wall (with cellulose) and a secondary cell wall (with lignin), making them more rigid and able to support taller plants. Have pits for water flow (all vascular plants)
Vessel Elements: have primary and secondary walls like the tracheids, but the ends of these cells are open, creating continuous tubes through which water can move much more efficiently. (Flowering plants)
– Alkaloids, terpenes, tannins
Flavonoids
Pollen
Bade taste to deter herbivores
absorbs harmful UV lights
Allows sperm cells to travel to egg cells without water
Flowers
– Sporophyte structure which contain tiny gametophytes
Microspore
Stamen
anther
Pollen
haploid spore that develops into a male gametophyte in plants.
Male reproductive organs of a flower
Part of the stamen that produces pollen
contains sperm cells
Megaspore
Capel
Ovule
haploid spore produced in the ovule
female reproductive organ of a flower.
Contains the megaspore that develops into the female gametophyte (embryo sac)
Fruit
• Structure derived from the ovary
• Encloses one or more seeds
• Not all are sweet
Saprophyte anatomy
– Foot: absorbs nutrients from gametophyte
– Seta: stalk, conducts nutrients to sporangia
– Sporangium: capsule, produces spores
• 1 capsule can produce 50+ million spores
Xylem
Phloem
typically moves roots to leaves, carries water, cells called tracheids- dead when functional, lignified for support
moves source to sink, sugar and nutrient conduction
Sporophyll
Sori
Strobili
Modified leaves used adapted for producing sporangia
sporophylls in Pterophyta (Fern)
Strobili: sporophylls in Lycophyta (club mosses)
Homosporous
Heterosporous
Producing one type of spore that develops into a bisexual gametophyte, common in many ferns.
plants produce two distinct types of spores: megaspores and microspores. (common in flowering plants)
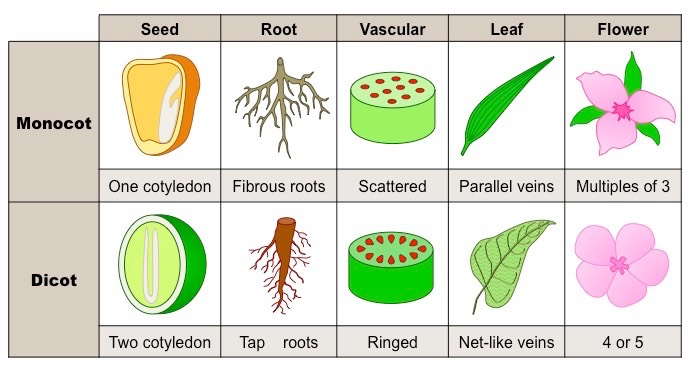
Monocot vs dicot
Monocots are monophyletic
Dicots are not