IB Economics HL - 2.8 - 2.10
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Rivalry
A characteristic of a good that states that one person's consumption reduces its availability for someone else.
Excludability
A characteristic of a good that states that it is possible to exclude people from using the good by charging a price for it.
Common Pool resources
Goods that are rivalrous but non-excludable.
Examples include clean air, water bodies, fish in the seas, wildlife, forests, etc.
Why can some common pool resources be a threat to the environment
Common Pool Resources can be depleted, and can be used abundantly without restrictions. Therefore, they might be overused.
Tragedy of the commons
A situation in which people acting individually and in their own interest use up commonly available but limited resources, creating disaster for the entire community in the long term.
Market Failure
The failure of the market to allocate resources efficiently.
Due to allocative inefficiency in over-provision or under-provision.
Externality
A positive or negative impact on a third party as a result of the consumption or production of a product.
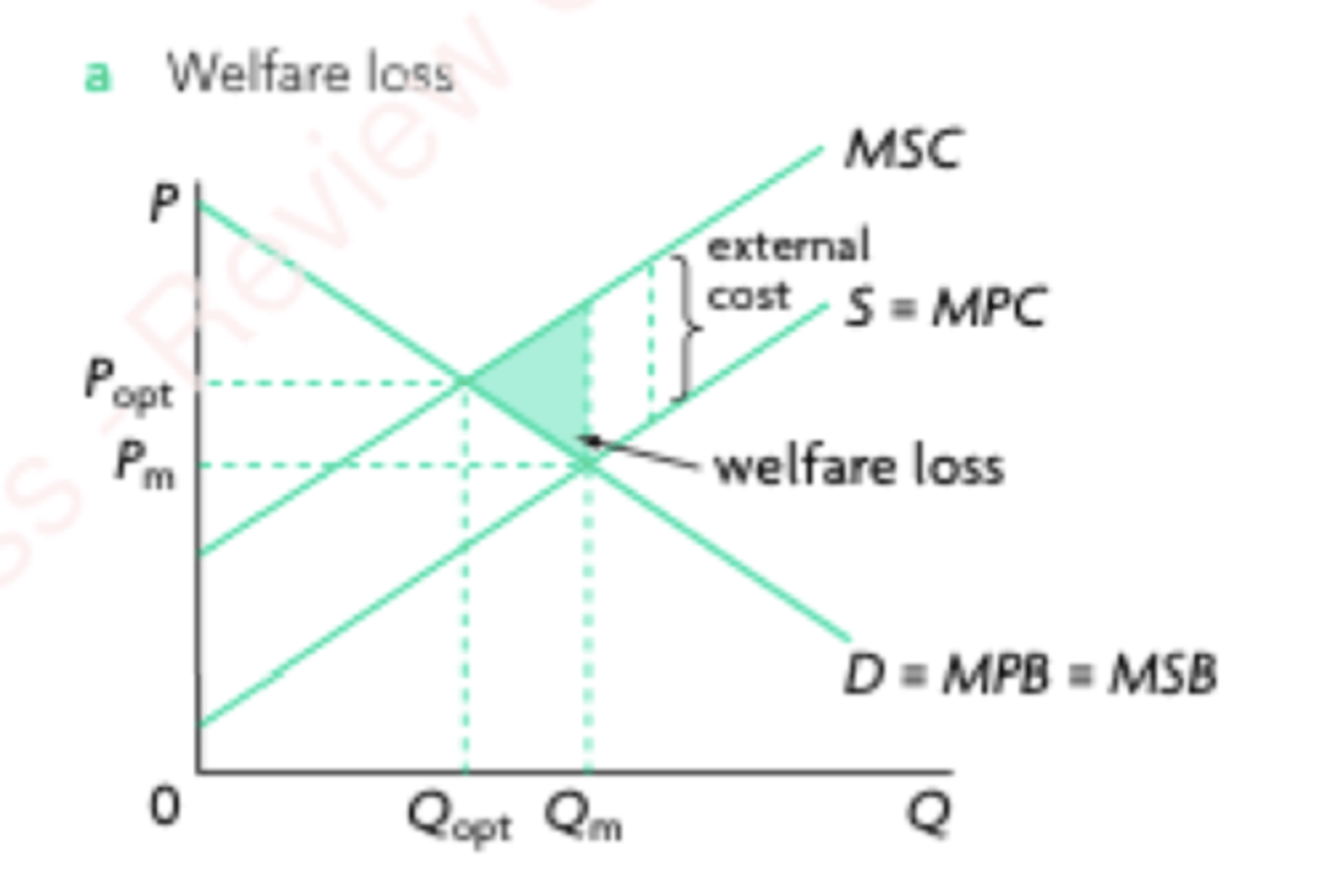
Negative Production Externalities
External costs created by producers that have negative impact on third parties.
Negative Production Externalities Graph
Since it relates to PRODUCTION, the supply will shift.
Since there is a negative impact on society, MSC > MPC.
The welfare loss is due to the misallocation of resources, as MSC > MSB.
Policies to correct negative externalities of production
1. Pigouvian Taxes - Indirect tax based on output.
Indirect Tax = External Cost, so supply shifts upwards. This results in allocative efficiency.
2. Carbon Tax - Tax per unit of carbon emissions of fossil fuels to reduce pollution and innovate.
3. Tradable Permits - Allow for a system of internal trade by trading pollution permits. Overall less emission.
4. Legislation & Regulation - Laws passed which firms have to obey
5. Education and awareness creation - Educating the public regarding problems.
6. International Agreements
Regulation for negative externalities of production
Setting a max level of pollutants emitted
Banning the use of harmful substances
Issuing licenses / permits for certain activities
Prohibiting construction or agriculture in certain areas
Restrictions on the quantity of logging
Restrictions in the form of quotas for fishing
Protecting certain areas
Advantages of policies to correct negative externalities of production
Taxes on emissions are better than on output, because taxes on emissions force producers to reduce pollution or use less polluting resources, whereas on output, they are forced to reduce output.
Legislation is easier to implement and can be very effective.
Education results in firms being influenced by consumer opinions and making changes, else they will face sales drops.
Disadvantage of policies to correct negative externalities of production
Imposing tax policies can be difficult to impose, as the methods of production, pollutants, value of damage, and amount of must be decided.
Tradable permits also face similar issues, but deciding the maximum limit can be difficult.
Legislation/Regulation also require information to be implemented. There
are also monitoring costs.
Educational campaigns may only be partially effective and content be interpreted wrongly.
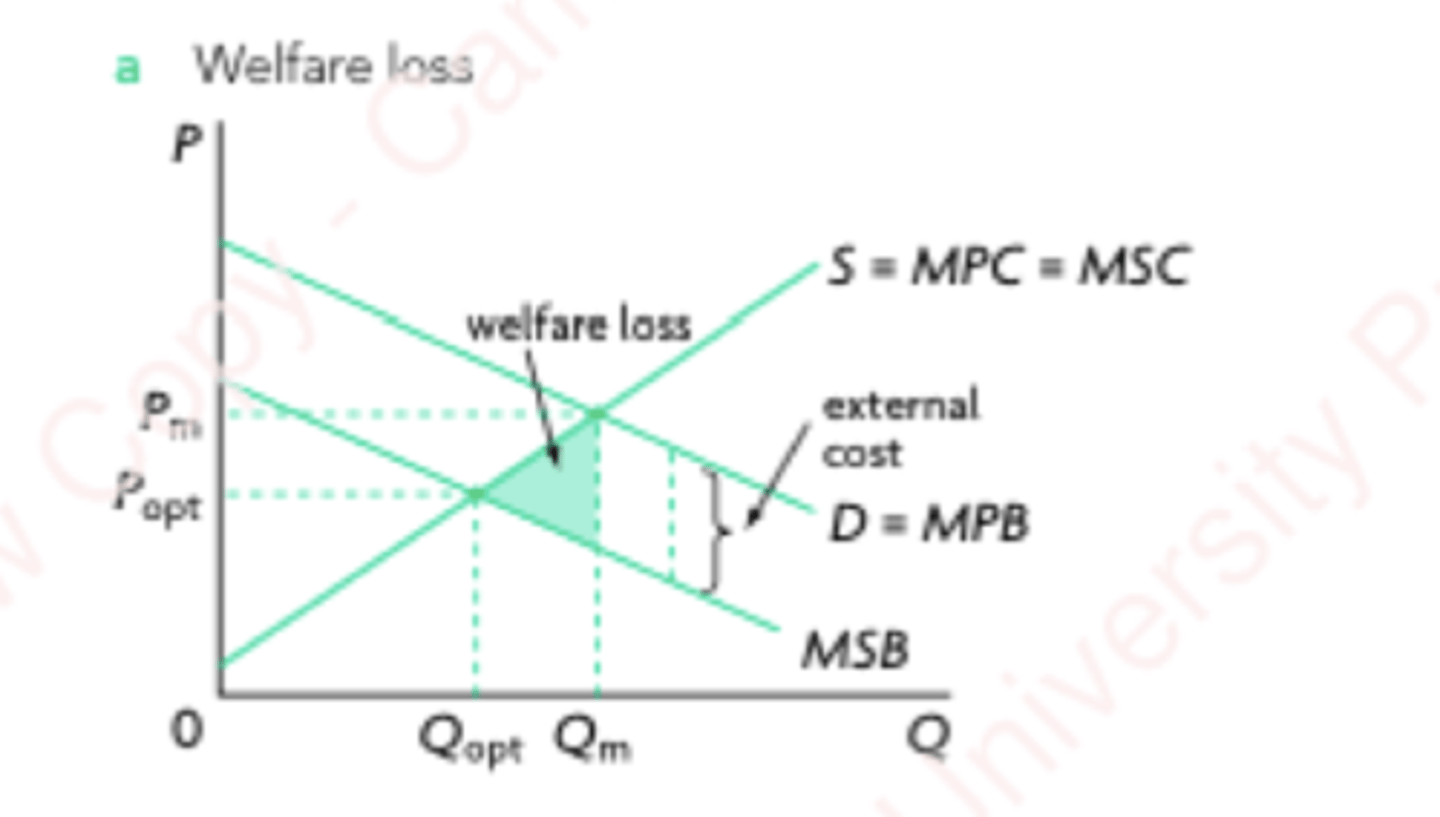
Negative Consumption Externalities
External costs created by consumers that have negative impact on third parties.
Negative Consumption Externalities graph
Since it relates to CONSUMPTION, the demand will shift.
Since there is a negative impact on society and personal comfort is prioritised, MPB > MSB.
The welfare loss is due to the misallocation of resources, as MSC > MSB.
Demerit Goods
Goods that are to be undesirable for consumers and are over-provided.
Policies to correct negative consumption externalities
Pigouvian Taxes - Indirect tax based on output.
Indirect Tax = External Cost, so supply shifts upwards. This results in allocative efficiency.
Legislation/Regulation to limit certain activities.
Education and Awareness
Nudges
Advantages of policies to correct negative consumption externalities
Incentivise or force consumers to alter their consumption.
Education is simpler than other methods.
Disadvantages of policies to correct negative consumption externalities
It is difficult to design an accurate tax level.
Some demerit goods have an inelastic demand, so Qty Dmd might not decrease by a lot.
Legislation cannot deal with all negative externalities
Education has a cost
It is difficult to design effective nudges
Regulation to address negative externalities of consumption
Ban/limit certain goods in places (difficult to track)
Raise awareness to decrease consumption of certain goods
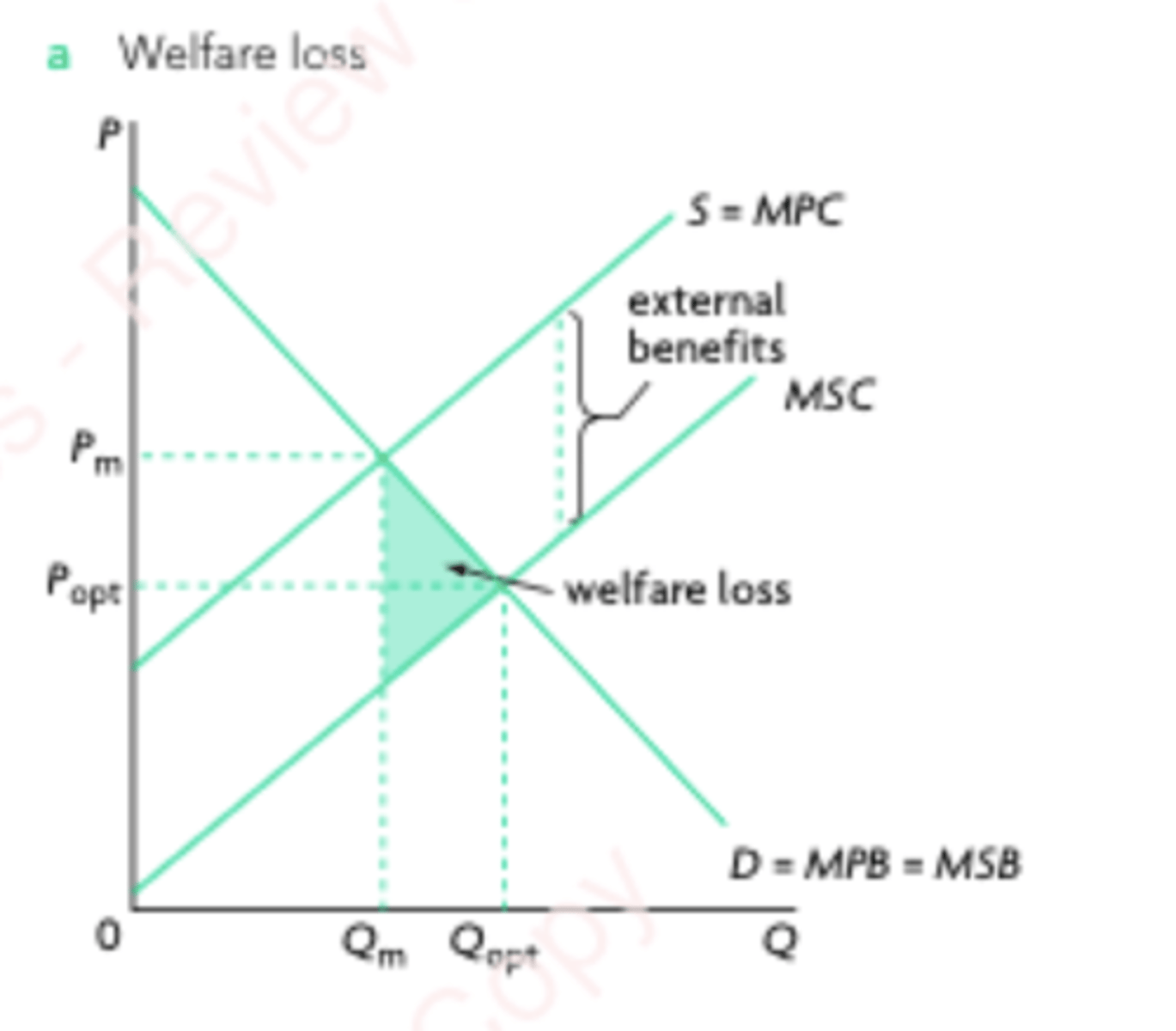
Positive production externalities
External benefits created by producers, when there are positive impacts on third parties as a result of the production of certain products.
Too few resources are allocated towards these goods, so they are underproduced.
Positive Production Externality Graph
MSC > MPC
Qm < Qopt
Policies correcting positive production externalities
Direct government provision
Subsidies
Positive consumption externality
External benefits created by consumers to third parties as a result of the consumption of certain products.
Positive consumption externality graph
MSB > MPB
Qm < Qopt
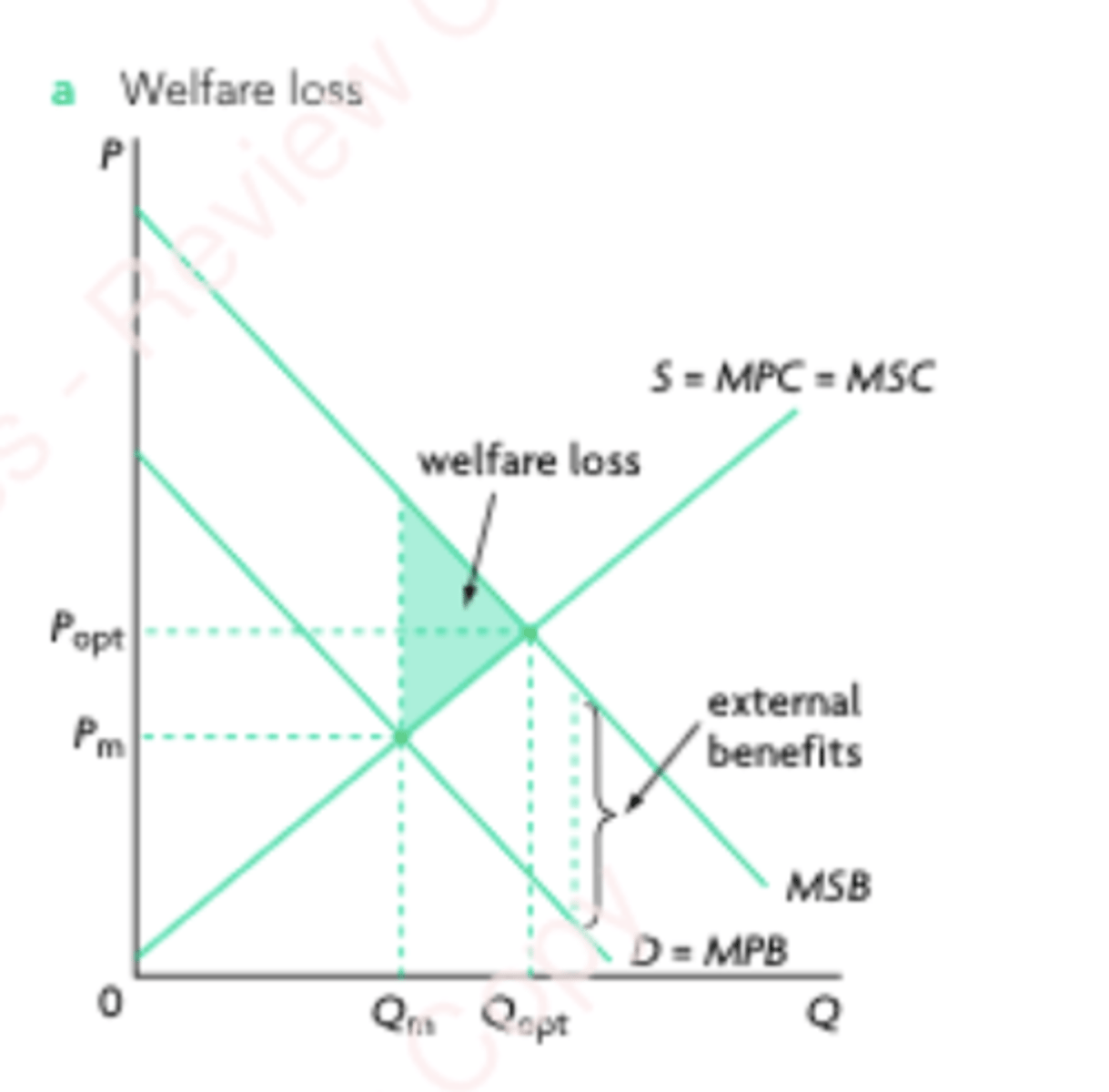
Merit goods
Goods that are desirable for consumers but are under-provided by the market.
Policies to correct positive consumption externalities
Legislation and Regulation
Education and awareness creation
Nudges
Direct government provision
Subsidies
Disadvantages of policies to correct positive externalities
Subsidies and direct provision have an opportunity cost
Calculating external benefits for perfect amount is difficult
Legislation can only be effective in certain cases
Designing nudges can be difficult
Public Good
Non-rivalrous, non-excludable
Free rider problem
People enjoy the use of a good without paying for it.
Government policies to provide public goods
Direct government provision
Contracting out to the private sector
(increased competition, better quality and cheaper due to better capital, but less control for government, costs of contracts, competition may lose quality, and monitoring costs)
Asymmetric Information
Buyers and sellers do not have equal access to information, resulting in allocative inefficiency
Adverse Selection
One party in a transaction has more information about the quality of the product being sold than the other party.
Policies for when sellers have more information than buyers
Regulation - to ensure quality and safety measures are maintained. However, these are bureaucratic procedures that may slow down activity. There are also opportunity costs of monitoring.
Provision of information (by govt itself) - Has costs and is bureaucratic
Licensure of certain professions.
Policies for when buyers have more information than sellers (offering insurance compensations)
Risk-based pricing - Offering customers compensation prices based on their previous history and currently- recurring risks.
Medical underwriting Offering customers compensation based on their medical history.
Moral Hazard
Situations where one party takes risks, but does not face the full cost of these risks because they are borne by the other party.
Impact of moral hazards on market failure
The sellers will under-allocate resources to the production of insurance services, as sellers try to protect themselves against higher costs due to the risky behaviour of the buyers of the insurance.
Circular Flow of Income