6.3.1, 6.3.2 Bacteria structure, physiology and replication
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Name of arrangement of pairs of circles
Diplococci
Name of arrangement of chains of circles
Streptococci
Name of arrangement of clusters of circles
Staphylococci
Name of rod arrangement
Bacilli
Name of oval rod arrangement
Coccobacilli
Which 2 parts of the bacteria are useful for antigenic typing?
Outer membrane (in gram -ve bacteria only, via O polysaccharide) and flagellum protein
Use of fimbriae
Attachment to other cells
Use of pili
Attachment to fellow bacterial cells for conjugation (DNA exchange)
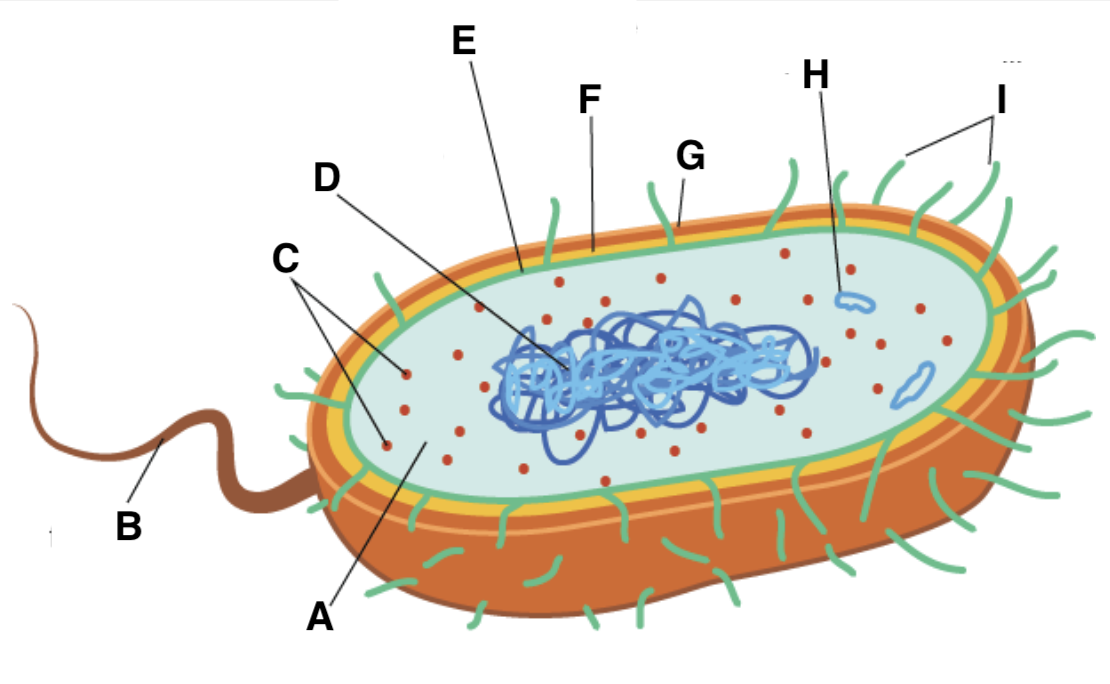
A
cytoplasm
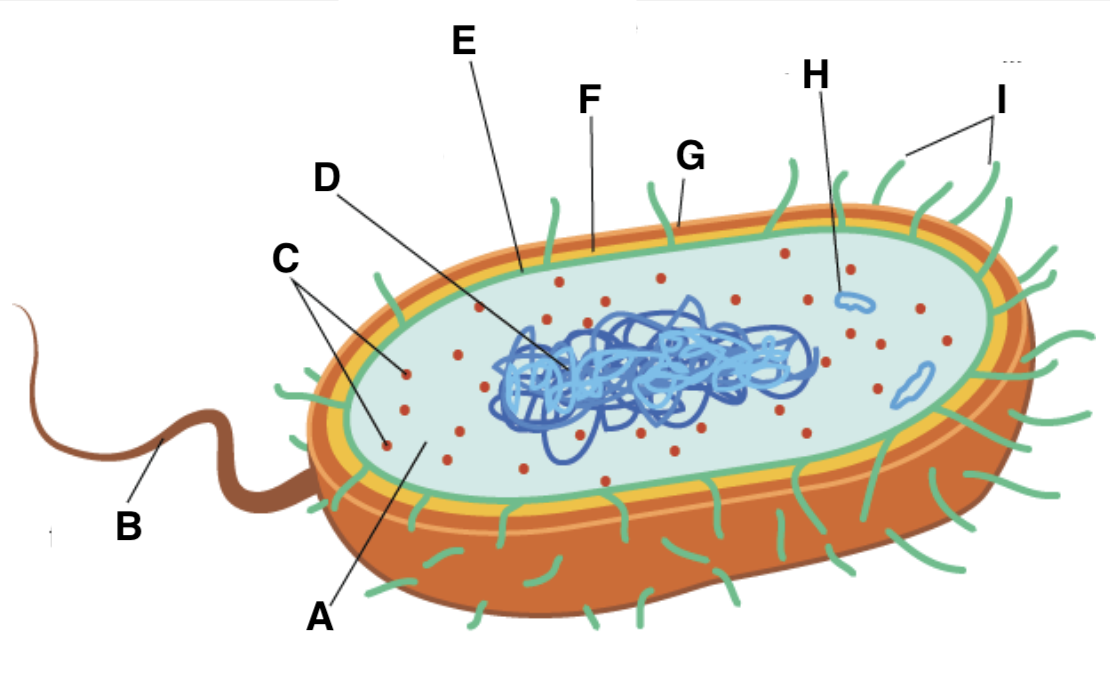
B
flagellum
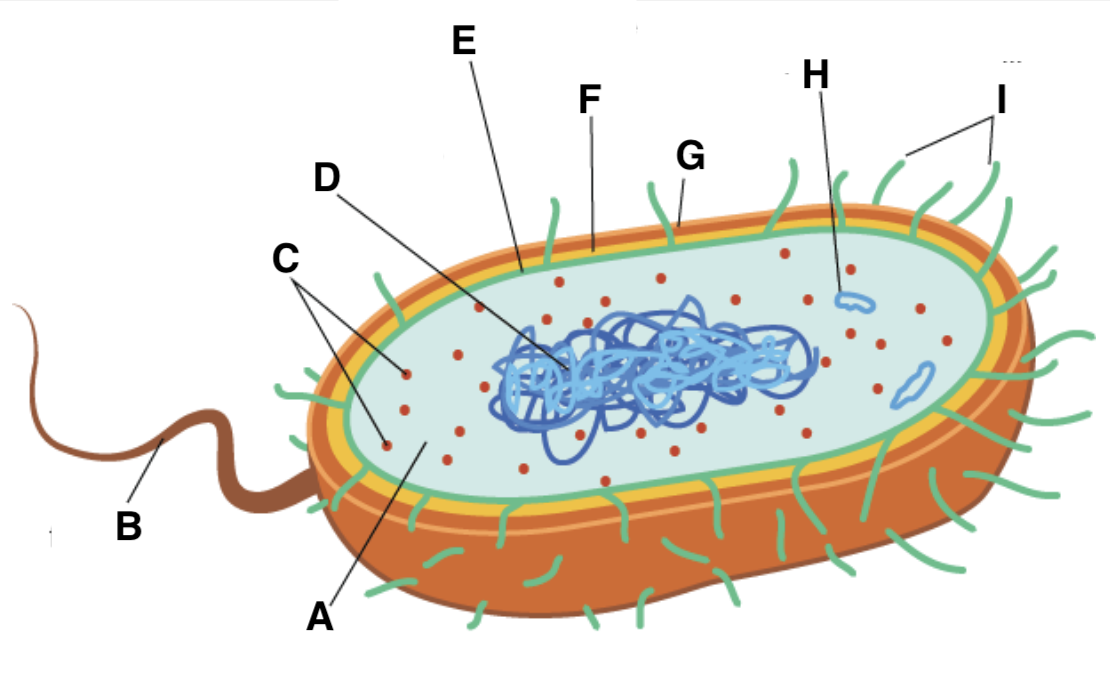
C and type
ribosomes (70S- 50S + 30S)
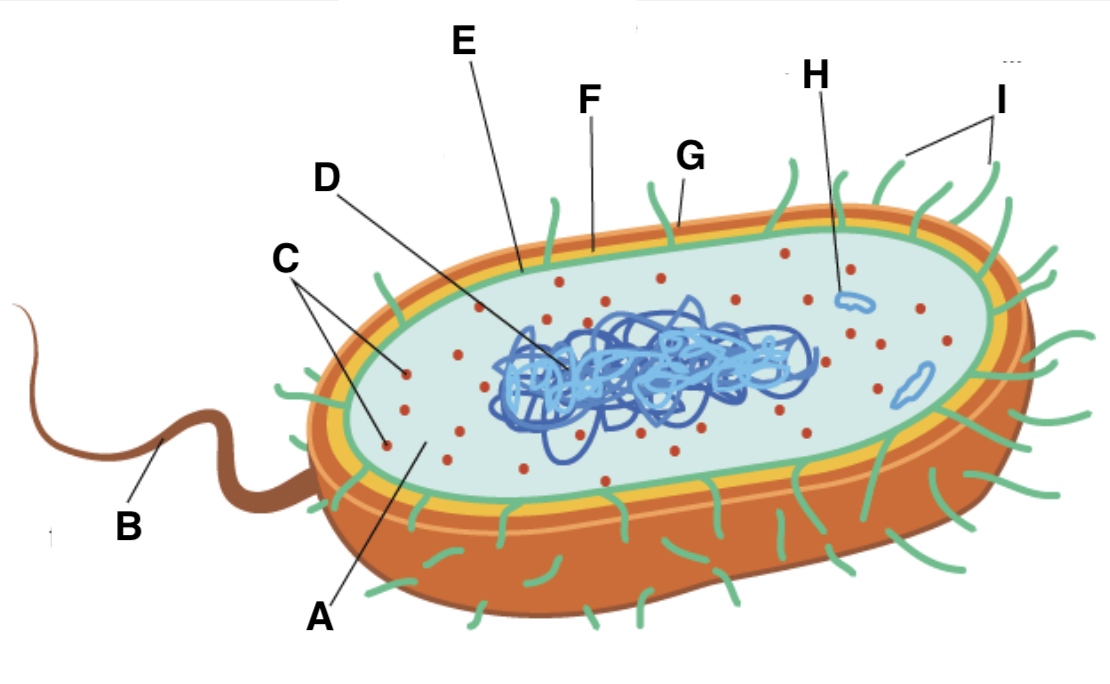
D
nucleoid
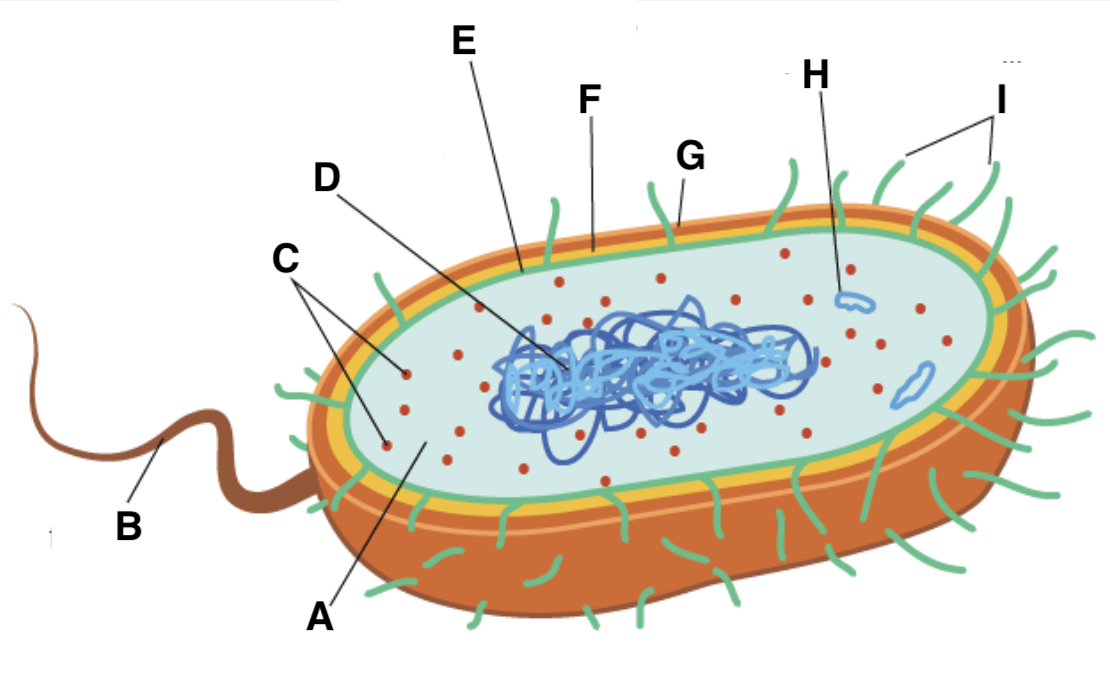
E
plasma (cell surface) membrane
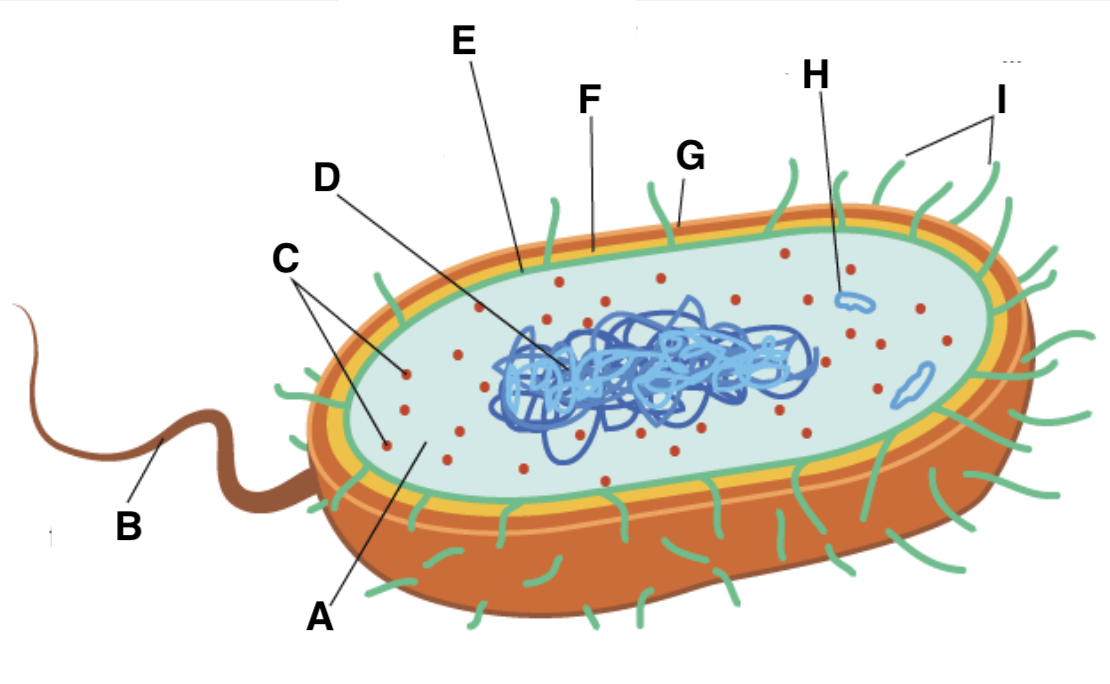
F
cell wall
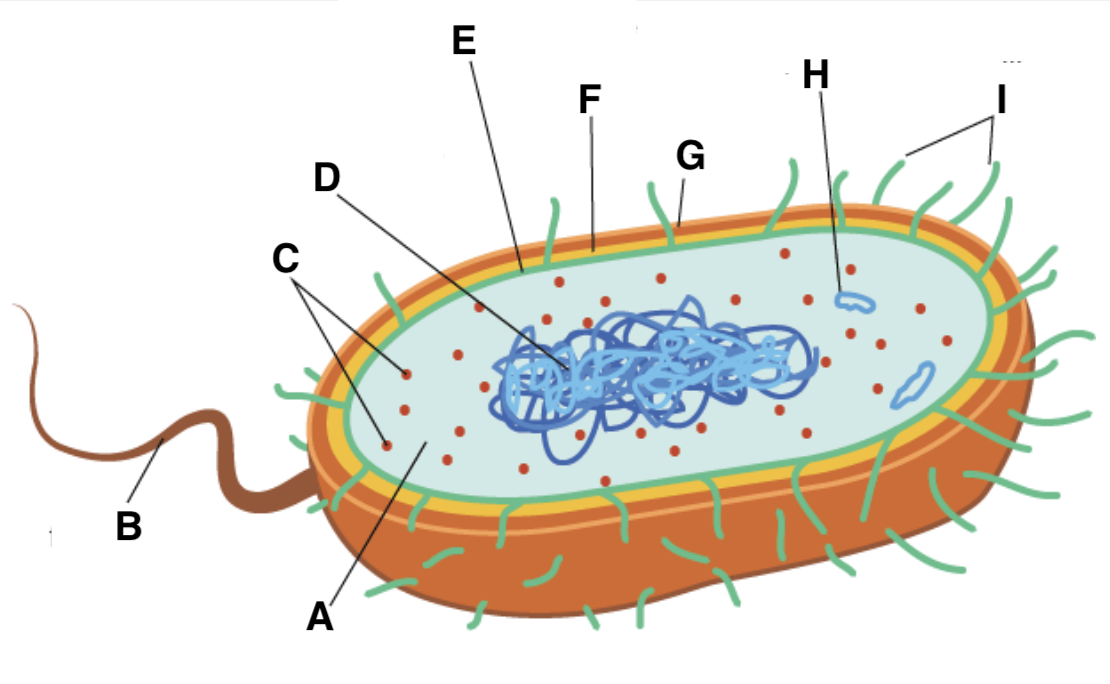
G
capsule
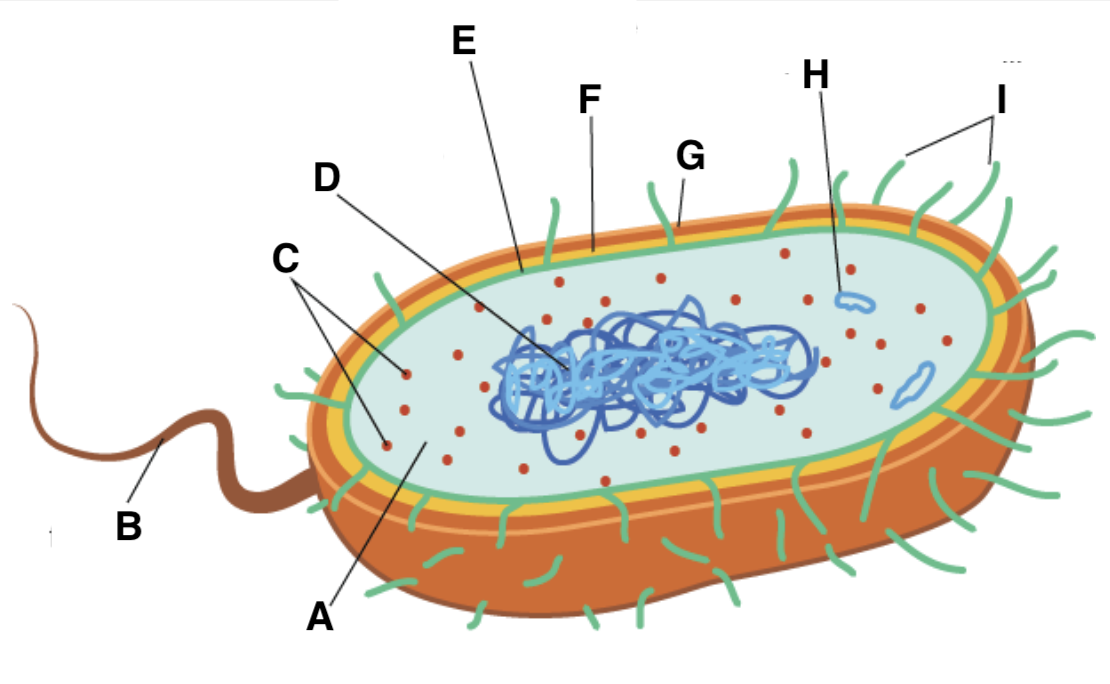
H
plasmid
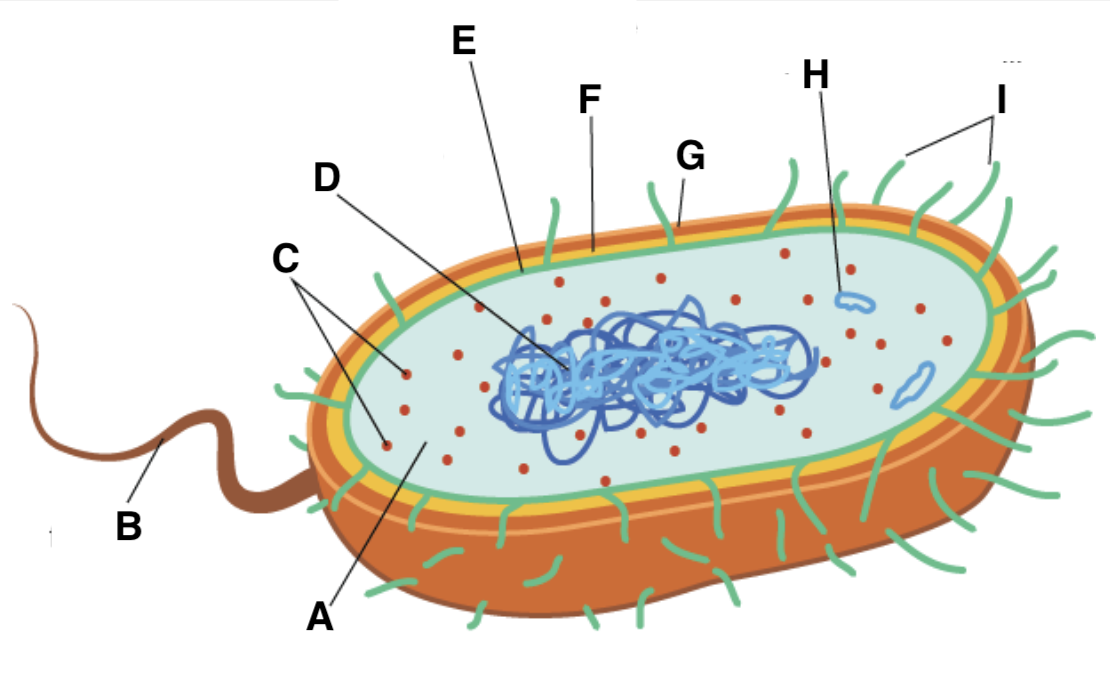
I
pili
Components of bacterial capsule
Polysaccharides
Describe the 2 components of peptidoglycan.
Disaccharide backbone (N-acetylglucosamine and N-acetylmuramic acid)
Polypeptide chain
What enzymes make bacterial cell wall crosslinks?
Transpeptidase
Describe the structure of a gram +ve bacterial envelope. (2)
Many peptidoglycan layers
Techoic acid- maintains rigidity
Describe the structure of a gram -ve bacterial envelope. (1)
Thin peptidoglycan layer
Presence of outer membrane
Describe the resulting colours of a gram staining test for and where the 2 results come from.
+ve purple- crystal violet trapped in peptidoglycan cell wall
-ve pink- safranin stains left because crystal violet escapes
Which structure is used for the electron transporters on bacteria?
Plasma (cell surface) membrane
Which 2 structures are often targeted by antimicrobials?
DNA (nucleoid)- easy to get to once inside cell
70s ribosomes- different from eukaryotic
List the 4 phases of a bacterial growth curve.
Lag- bacterial adjustment to surroundings, no growth
Log- exponential growth
Stationary- growth plateaus due to environmental limitations
Decline- bacteria use up available nutrients and start dying off
Which 2 bacteria have endospores?
Clostridium, bacillus
Process of forming endospore
Sporulation
Role of endospore
Highly resistant body to enable dormancy for a long time
Process of reversing endospore to vegetative cycle
Germination
List the 4 types of culture media.
Complete- grows everything
Selective- selects against specific bacteria
Differential- different bacteria show differently
Enrichment- enhances specific bacterial species
Describe how MacConkey medium is both selective and differential. (2)
Fermentable carbohydrate- only bacteria that can process it survives
Acid produced via fermentation changes colour of medium
Appearance of strict aerobe bacteria in culture
Remains at surface of medium
List the 4 types of oxygen requirement.
Strict aerobe
Obligate anaerobe
Facultative anaerobe (can do both)
Microaerophil (requires only a bit of oxygen)
Appearance of obligate anaerobe bacteria in culture
Sinks to bottom of medium
Appearance of facultative anaerobe bacteria in culture
Remains in all depths of culture
Appearance of microaerophil bacteria in culture
Sit in middle of medium