fnr soils test 2
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
90 Terms
Bulk density
Mass of soil/vol of soil(solids and pores)
Cation Exchange Formula
Sum of all exchangeable cations
What is available water capacity
the range of available water that can be stored in the soil
What is formula for soil porosity
1-(bulk density/ particle density) times 100
Available water capacity formula meaning
field capacity minus wilting point. used for irrigation
What are the units for soil porosity
percentage
Particle density
Mass of soil/ vol of solids
\psi T=\psi M+\psi S+\psi G+\psi P
Water potential formula
Alfisols
(Alfs) moderately weathered soils
Types of horizons in Alfisols
Fragipan, plaic, Duripan
Fragipans
Dense brittle pan
Duripan
Dense, strong silica cemented Pan
Placic
very hard pan, Fe, Mn, cemented
lowercase t
Clay illuviation
Lowercase x meaning
Fragipan
Available water capacity formula
Inches of H2O/inches of soils =AWC (in/in)
Cohesion
Water molecules bonding with itself
What is soil conversion factor
SOM= SOC * 1.72
saturated hydraulic conductivity formula
Ksat=(q/A) * (L/Delta H)
Mollisols define
(olls) meaning soft moderately weathered
Parent material of mollisol
calcareous loess
What does loess mean?
Transported by wind
What effects rate of decay
Temperature
Organic matter (wood vs grass)
Water (moist soil)
Stage of decay
immbolization of nitrogen
nitrogen not used, woods
Categories of organic soil
Hummus (collid which means glue)
fresh residue(litter)
living organisms
decomposing orgo matter
mobilization of nitrogen
release of nitrogen, greens, high nitrogen content
percolation test
time it takes water to drop 1 inch in a pre-wetted hole= time/drop in water level = min/inch
Agrillic horizon in mollisols
accumulation of clay
What are the units for bulk density
g/cm3 and g/cc
What are the units for particle density
g/cm3
What are the units for Ksat
in/h or cm/h
What does particle density help determine
soil porosity
What is base saturation formula
BS=(Ca + Mg + K + Na)
What is Ksat used for
the perc test
What are the units for cation exchange capacity
meq/100g
What is cation exchange capacity used for
soil fertility
Are earthworms beneficial or parasites
Major decomposers and use bacteria for nutrition
What kind of organisms are earthworms
hermaphrodites
What are surface species of earthworms called
Epideic species
What are the upper soil species of earthworm called
Endogeic species
What are the deep borrowing species of earthworms called
Anemic species
What are nematodes
Non segmented worms
Where do nematodes live
Maximum in A horizon and around roots
Are nematodes beneficial or parasitic
Beneficial nematodes control diseases and cycle nutrients. Mineralizing nutrients for the plants
Do nematodes provide symbiotic or parasitic
Parasitic because they damage plant cell walls
What kind or organisms are Protozoa
Single celled organisms and larger than bacteria
Where do Protozoa live
Maximum in A horizon. Around root and in humus
Are Protozoa beneficial or parasitic
Beneficial because they release nitrogen
Do protozoa form symbiotic or parasitic relationships?
They form both because not only do they feed on bacteria but also other protozoa
What kind of organisms are soil algae
Single celled, autotrophic, cyanobacteria
Where does soil algae live
Maximum in the A-
hor.; Around roots; On humus;
On the surface of
soil aggregates;
In spaces between
soil aggregates
Are soil algae beneficial or parasitic
??
Do soil algae form symbiotic or parasitic relationships?
It forms symbiotic relationships by providing protection to algal cells and then host gets energy
What type of organisms are fungi
small cells that grow hyphae to push through soil particles
Where do fungi live?
between soil particles, roots, and rocks
Are fungi beneficial or parasitic
They can be both. There root pathogenic fungi like Rhizoctina. But there is mycorrhizal fungi that solubilize phosphorus
Do fungi form symbiotic or parasitic relationships
in exchange for carbon from the plant, mycorrhizal fungi help solubilize phosphorus and bring soil nutrients so symbiotic
What kind of organism is bacteria
one celled organism
Where are bacteria found?
In A horizon around roots, humus, on and between soil aggregates
Are bacteria beneficial or parasitic
beneficial because it can cycle nutrients and suppress diseases
Do bacteria form symbiotic or parasitic relationships
Nitrogen fixing bacteria form symbiotic relationships with the roots of trees and legumes
What kind of organisms are actinomycetes
large group of bacteria that grow hyphae like fungi
Where are actinomycetes found
A horizon around roots, in humus, on top and in between soil aggregates
Are actinomycetes beneficial or parasitic
beneficial because they decompose hard substances like cellulose and chitin
Do actinomycetes form symbiotic or parasitic relationships
The Frankia Family forms symbiotic with non legume plants the same way nitrogen fixing bacteria do
Sodium Absorption ratio formula
..
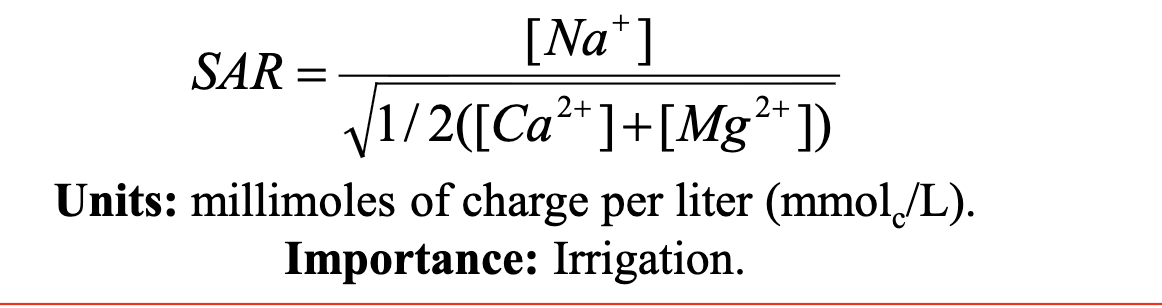
SAR units
mmol/L
What is SAR formula used for
irrigation
Aridisols
(id) meaning dry
What does the lowercase letter "z" mean?
soluble salts
What is the least decomposable compound?
ligin
Which cation predominates in the sodic soils?
sodium
What is the name of the sphere in the soil dominated by soil microorganisms?
rhizosphere
"Loss on ignition" method is used to determine what soil property?
soil organic matter
What does the lowercase letter “s” mean
illuvial accumulation of OM and Fe and Al oxides
What does lowercase “o” mean?
Accumulation of Fe and Al oxides
What does lowercase letter “h” mean?
Illuvial accumulation of organic matter
What value of sodium adsorption ratio would classify soil as sodic?
Above 13
What rule of cation exchange is used during fertilizer application?
Mass action rule
What are units of avalible water. capacity
in/in or cm/cm
What does lowercase k mean
accumulation of carbonates