Bis 2c Lab Practical UC Davis
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
which are not cephalized
mussels, clams,
Hemimetabolous
(of an insect with aquatic young) undergoing incomplete metamorphosis in which the young does not resemble the adult
holometabolus
dramatic change
Cnidaria
cnidocytes, radial symetry, incomplete gut, sting, anemonies, jellies,
monophyletic
ALL descendants came from one common ancestor
paraphyletic
Pertaining to a group of taxa that consists of a common ancestor and some, but not all, of its descendants.
polyphyletic
pertaining to a group of taxa that includes distantly related organisms but does not include their most recent common ancestor
Clade
evolutionary branch of a cladogram that includes a single ancestor and all its descendants
Cladogram
Diagram that shows the evolutionary relationships among a group of organisms
chronogram
branch length is proportional to time
Phylogram
A phylogenetic tree in which the lengths of the branches reflect the number of genetic changes that have taken place in a particular DNA or RNA sequence in the various lineages
Homology
similarity resulting from common ancestry
Homoplasy
A similar (analogous) structure or molecular sequence that has evolved independently in two species.
convergent evolution
Process by which unrelated organisms independently evolve similarities when adapting to similar environments
polytomy
a branch point from which more than two descendant groups emerge
Cogruence
common branching pattern
Coccus
round
Bascillus
rod shaped
helical
spiral
Lateral Gene Transfer (LGT)
The transfer of genetic material to unrelated organisms
LUCA
Last Universal Common Ancestor. The shared ancestor that multiple organisms diverged from
Microbiome
all of the microorganisms that live in a particular environment, such as a human body
Amoeboid form
wobbly
flagellate form
tail
ciliate form
cilia movement
phase contrast
transforms subtle changes in light waves passing through the specimen into differences in light intensity, best for observing intracellular structures (archea)
plasmodial slime molds
a type of protist that has ameboid cells, flagellated cells, and a plasmodial feeding stage in its life cycle-- looks like net
cellular slime molds
A type of protist that has unicellular amoeboid cells and a multicellular reproductive body in its life cycle-- little bloops
calculate size from microscope (10x)
1.778 mm
calculate size from microscope (40x)
0.55 mm
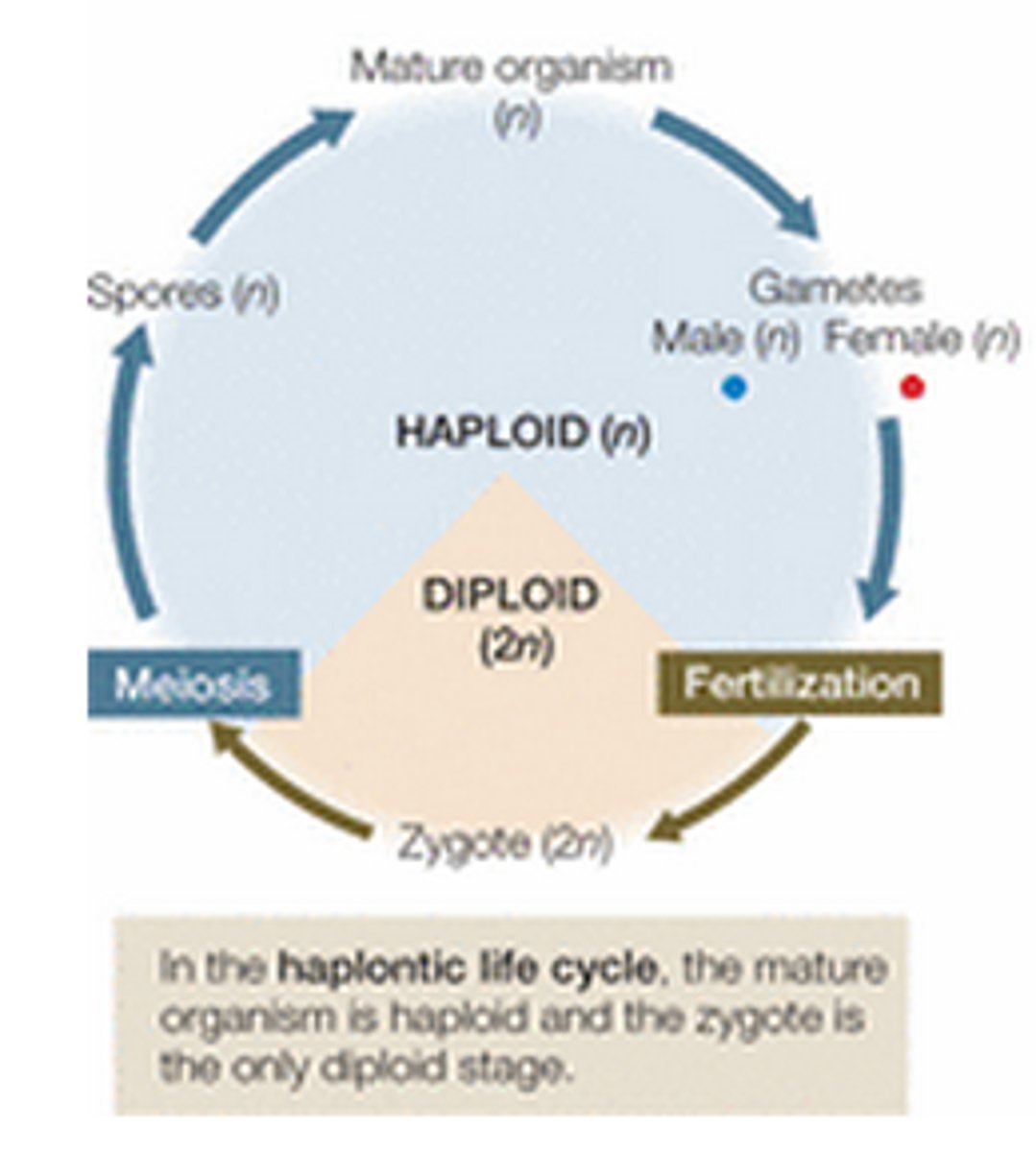
haplontic life cycle
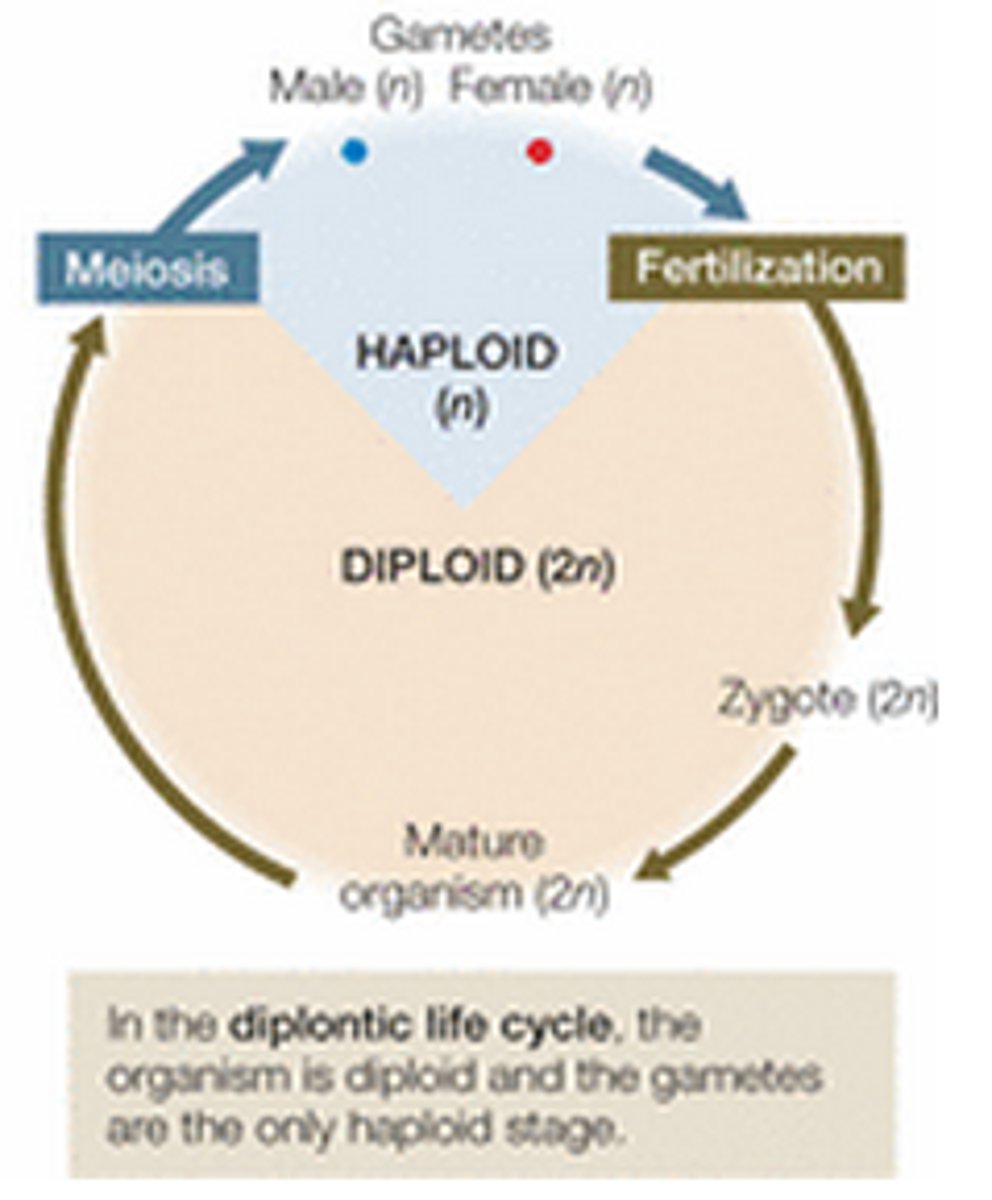
diplontic life cycle
Alternation of generations life cycle
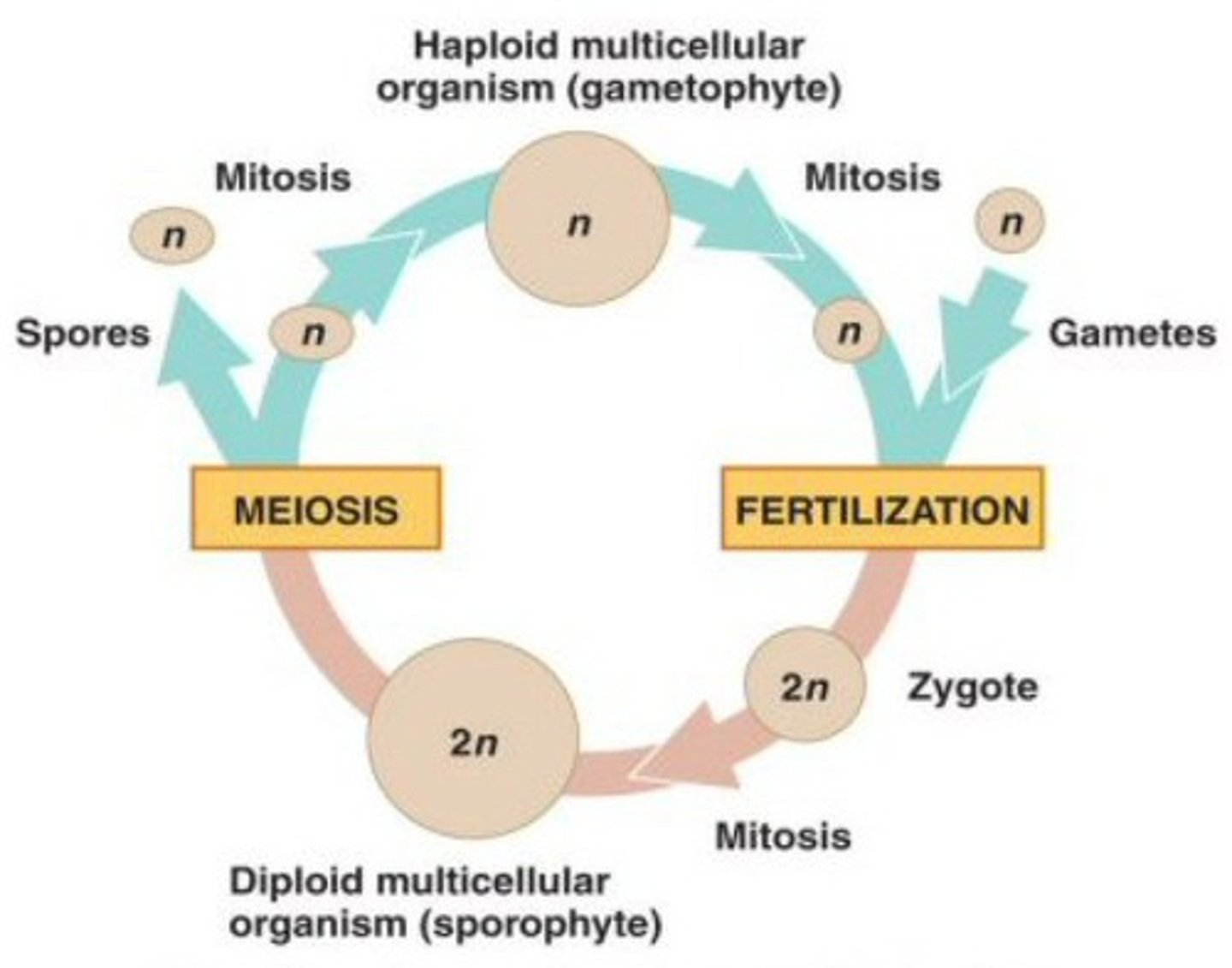
gametophyte
The stage in the life cycle of a plant in which the plant produces gametes, or sex cells.
sporophyte
Diploid, or spore-producing, phase of an organism
Antheridia
male gametangia
Archegonia
female gametangia
gametangia
A reproductive organ that houses and protects the gametes of a plant
sporangium
spore capsule in which haploid spores are produced by meiosis
sori
clusters of sporangia
Just before Embryophytes
1. waxy cuticle, alt of gen, multicellular gametangia, unbranched sporophyte, multicellular embryo, apical cell w/ 2 of more cutting,
Embryophytes
liverworts, hornworts, moss,
just before tracheophytes
vascular tissue, tracheids, apical meristem, reduced gametophyte, dominate branched sporophyte,
tracheophytes
microphylls, lycopodium and selaginella, s has heterospory
before euphylophytes
chloroplast dna inversion, megaphylls
euphyllophytes
monilophytes: equisetum, psilotum, ferns
before seed plants
integument, ovule, seeds, pollen w pollwn tube, heterospory, bifacial vascualr cambium
Gymnosperms
cycad, gingko, gnetophytes, conifers, gnetophytes have vessel elements, no flowers or fruit in any
before angiosperms
endosperm, double fertilization, carpel, fruit, vessel elements
basal angiosperms
include the flowering plants belonging to the oldest lineages
Monocots
one cotyledon
Eudicots
Member of a clade consisting of the vast majority of flowering plants that have two embryonic seed leaves, or cotyledons.
bryophytes are
non-vascular
liverworts
a nonvascular plant that's shaped like a human liver. found growing as a thick crust on moist rocks or soil along the sides of a stream.
moss
dense carpets leafy gametangia, sporangium once fertilized
hornworts
blue green (cyanobacteria), indeterminate growth,
lycophytes
shift to vascular, so sporophyte dominant, gametophyte lives independently of sporophyte, microphyls, sporangia in strobuli (cones)
monilophytes
chloroplast dna inversion
horsetail
holow upright stems, reduced leaves,
Whisk Ferns (Psilotum)
dichotomous branching, reduced leaves, no roots, epiphytes (grow on other plants)
epiphytes
Photosynthetic plants that grow on other trees rather than supporting themselves
true ferns
sori, microphylls, fiddleheads,
cycads
baby palm trees w cones, dioecious, large compound leaves,
Gingko biloba
heart shaped leaves, fleshy seed coat
gnetophytes
paired, opposite leaves, vessel elements, double fertilization,
conifers
woody, cones,
basal angiosperms
paraphyletic group, like eudicots but w weird flower leaf things
monocot
parallel leaf vein, scattered vascular bundle stems, 1 cotyledon
eudicots
netted leaf veins, ordered vascular bundles, bvc, 2 cotyledons, flower parts in 4 or 5s,
Protostomes vs. Deuterostomes
Protostomes: 1st indentation develops into the mouth, anus develops from 2nd opening
Deuterostomes: 1st indentation becomes the anus, mouth develops from second opening
protostomes
Lophotrochozoa and Ecdysozoa
Arthropods
A group of organisms that have jointed appendages, an exoskeleton, bilateral symmetry, and reproduce sexually; insects, arachnids, millipedes and cenitpedes, and crustaceans
Chordata
notochord, dorsal nerve cord, pharyngeal gill slits, post-anal tail
Echinodermata
radially symmetrical marine invertebrates including e.g. starfish and sea urchins and sea cucumbers, water vascular system, tube feet,
Ecdysozoa
Supergroup of protostomes; characterized by periodic molting of their exoskeleton. Include the nematoda and arthropods.
Annelida
segmented worms, paired setae, segmentation
Mollusca
(snails, clams, squids, octopuses) have a soft body that in many species is protected by a hard shell, mantel, shell, radula
Lophotrochozoa
One of two distinct clades within the protostomes. It includes annelids and mollusks. trochophore larvae, spiral cleavage
Bilateria
bilateral symmetry, triploblastic, complete gut
Ctenophora
Comb jellies; 8 ciliated bands; 2 tentacles; gut with one opening; no body cavity; biradial symmetry
Spicules
small, spike shaped particles of calcium carbonate or silicon dioxide that make up the skeleton of some sponges
porifera
sponges, spicules
metazoa
blastula, multicellularity, collagen
Cephalization
concentration of sense organs and nerve cells at the front of an animal's body