Ch 2: The Chemistry of Life
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
What is an Atom?
Basic unit of matter; they make up all matter in the universe
The smallest particle into which a substance can be divided and still retain all of its chemical properties
Key words:
particle
basic units of
matter
divided and retain
chemical properties
What are the 3 main subatomic particles?
Protons
Neutrons
Electrons
What is an atom made up of?
Protons, Neutrons and Electrons
Explain the structure of an atom.
At the center of every atom is a small, very dense nucleus
Whizzing around the nucleus is an orbital cloud of subatomic particles.
Which subatomic particles is the nucleus of an atom made up of?
Protons
Neutrons
Which subatomic particles orbit around the nucleus of an atom?
Electrons
What kind of electrical charge do neutrons have?
no electrical charge; are neutral (/)
neutron neutral no
What kind of electrical charge do Protons have?
Positive charge (+)
Proton: P for Positive and P for Plus (+)
What kind of electrical charge do Electrons have?
Negative charge (-)
The only one without a mnemonic so its negative
Which subatomic particle orbits?
Electrons
electron orbit
electron fence
T or F: (in a typical atom) for every proton in the nucleus, there is an orbiting electron
True
(in an atom) The ____________’s negative charge balances out the ____________’s positive charge so that the atom remains electrically ______________
The Electron’s negative charge balances the Proton’s positive charge so that the atom remains electrically neutral
The chemical nature of an atom is determined by two things:
# of electrons
mass
The mass of an atom refers to what?
The amount of a substance.
On the other hand, weight refers to the force gravity exerts on a substance
Atomic number
# of protons (and technically, neutrons)
ex: atomic number of carbon (C) is 6 because it has 6 protons
T or F: The atomic number is equivalent to the # of electrons
True!
Remember that for every proton there is an orbiting electron! (card 12)
Remember this chart:
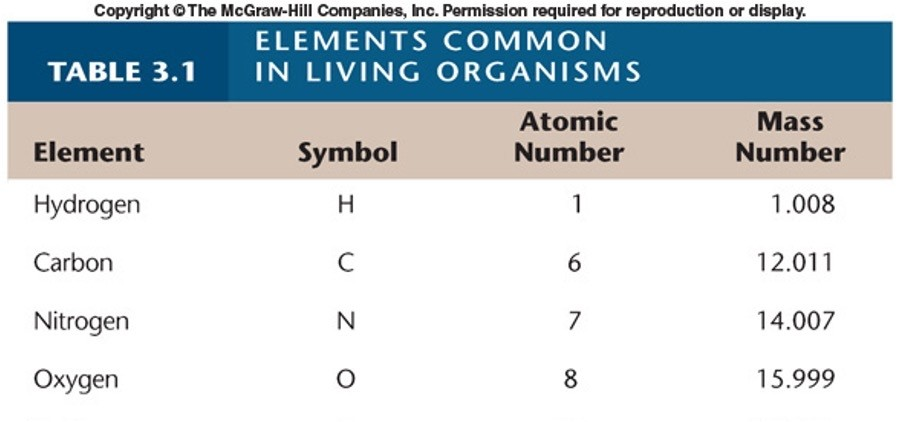
List the symbol and atomic number for Hydrogen
Symbol: H
Atomic #: 1
(1 prot and elect)
List the symbol and atomic number for Oxygen
Symbol: O
Atomic #: 8
List the symbol and atomic number for Nitrogen
Symbol: N
Atomic #: 7
List the symbol and atomic number for Carbon
Symbol: C
Atomic #: 6
List the 4 elements (H, O, N, C) in order from least to greatest in terms of their atomic number
Hydrogen (1) → Carbon (6) → Nitrogen (7) → Oxygen (8)
Electrons orbit the (atom’s) nucleus in something called a
Electron Shell
The orbital plane of electrons
An electron shell is what electrons orbit on; consider it an orbital plane
The electron shell farthest away from the nucleus (the last one) is called the
Valence shell
What is considered the strongest electron shell— the one closest to the nucleus, or the one farthest from the nucleus?
The shell furthest away from the nucleus, aka the valence shell, is the strongest.
what is an orbital in an electron shell?
Orbital refers to the placement/pairs of electrons in a shell.

You can see in the second shell, there are 4 orbitals.
Orbitals can hold up to how many electrons?
2
remember: orbital refers to a pair of electrons
The first shells in any atom contains how may electrons? That means how many orbitals?
Two electrons— that means one orbital.
After the first shell, how many electrons can the rest contain? That is how many orbitals?
8 electrons— that means 4 orbitals.
During chemical reactions, electrons can be …. when the shells (orbitals) are not full
shared, lost, or gained
Why: Because they’re trying to fill their outermost electron shell. This causes them to be more reactive.
What are ions?
Atoms that have gained or lost at least one electron.
All ions have …. charge
electrical/net charge
What are the two types of ions?
Cations
Anions
What is a Cation?
A positively charged ion
caTion posiTive
CaTion has a ‘t’, so does word “posiTive”
ex: Sodium (Na) looks like (Na+) when it becomes a cation
How does an ion become positively charged? Or, in other words, become a cation?
Positive when it loses electron(s)
Take away the electron (-) to create a positive
What is an Anion?
A negatively charged ion
aNion Negative
aNion has a ‘n’, so does word “Negative”
ex: Sodium (Na) looks like (Na-) when it becomes an anion
How does an ion become negatively charged? Or, in other words, become an anion?
Negative when it gains electron(s)
What is an Isotope?
Atoms that have equivalent protons and electrons BUT different # neutrons
protons = electrons
≠ neutrons
related to radioactive decay
What is Radioactive Decay?
When an atom’s nucleus breaks up into particles with lower atomic numbers
radioactive isotopes are used in dating fossils
What are the atoms of Molecules held together by?
by energy, or chemical bonds
same atoms
What is chemical bond?
The energy within a molecule that holds the atoms together— kind of like the glue of molecules
What are the 3 kinds of chemical bonds you can find in molecules?
Ionic
Covalent
Hydrogen
Describe “Ionic bonds”
Holds atoms (in molecule) together when ions of opposite charge are attracted to each other
Moderate strength bond
The glue here is attraction between oppositely charged ions
Hetero

Describe “Covalent bonds”
Hold atoms (in molecule) together by sharing electrons
strongest type of bond
The glue here is sharing electrons
Covalent
co means together
valare means to be strong

Describe “Hydrogen bonds”
Helps stabilize atoms in a molecule when the partially positive charge of a hydrogen atom in one water molecule → attracted to → partially negative charge of an oxygen atom in another water molecule.
So basically, you have two water molecules. One of them has a partially ‘+’ Hydrogen atom, the other has a partially ‘-’ oxygen atom. Those two are attracted to each other because of that, forming a weak bond which shouldn’t even be considered a bond because it’s too weak to do that, BUT, it does help stabilize a bond between the two atoms.
What is the word for a partial charge between atoms within a molecule called— when a molecule has positively and negatively charged ends, causing electron rich or poor regions?
Polar molecules
One portion of a polar molecule attracts electrons more strongly than another portion, with the result that the molecule has electron-rich (–) and electron-poor (+) regions, giving it magnetlike positive and negative poles. Water is one of the most polar molecules known.
What are compounds?
Molecules made of more than one type of atom
Molecules are made of the same atom. A compound is like a molecule, but is made of two different atom kinds.
What are the 5 properties of Water that make it important to life?
Heat storage
Ice formation
High heat of vaporization
Cohesion
High Polarity
What does the “heat storage” property of water state?
Because there are so many hydrogen bonds in water, a lot of energy is needed to change water’s temperature
takes a long time for water to heat up → minimizes temp. changes
What does the “high heat of vaporization” property of water state?
A lot of energy is required to turn liquid into vapor
What does the “Ice formation” property of water state?
IN ICE….
water molecules are spaced farther apart.
As temp drops, less molecule movement → H bonds stabilize and hold individual molecules farther apart.
Structure of a solid is less dense than liquid, which is why it floats

What does the “cohesion” property of water state?
Hydrogens bond to one another and attract to other polar molecules— when water molecules bind with each other, the attraction is called cohesion
cohesion creates surface tension of water → the tension is what causes water to bead or supports weight of insect.

What does the “high polarity” property of water state?
Ions and polar molecules dissolve in water (are water soluble)
polar molecules are hydrophilic → love water
What is ionization?
when an atom "turns into" an ion by either adding or removing electrons, giving it a positive or negative charge.
Water can ionize into either of these ions…
H+ or OH-
What is a Hydrogen ion (H+)
A single proton that dissociates from a hydrogen atom nucleus as a positively charged ion.
What is pH?
a measure of H+ in a solution
What is the pH scale?
A method of measuring hydrogen ion (H+) concentration of a solution

What is a solution?
A liquid or something
Describe the range on the pH scale
Scale ranges from 0 to 14
0 → (highest hydrogen ion concentration→ acidic)
14 → (lowest hydrogen ion concentration→ basic)
Pure water has a pH of what? (Aka, what is the neutral pH lvl)
7
What do Acids do to a solution (pH scale)
add H+
What do Bases do to a solution (pH scale)
remove H+
or add OH-
OH is more base related
Are solutions with a pH less than 7 more acidic or basic?
acidic
Are solutions with a pH greater than 7 more acidic or basic?
basic
What are buffers?
Chemicals that can add or remove H+ within a certain pH range