Module 3: Anatomy of the X-Ray Unit
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
What are the requirements for X-ray production?
- A source of electrons
- A method to accelerate electrons
- A clear path for moving electrons
- A vacuum
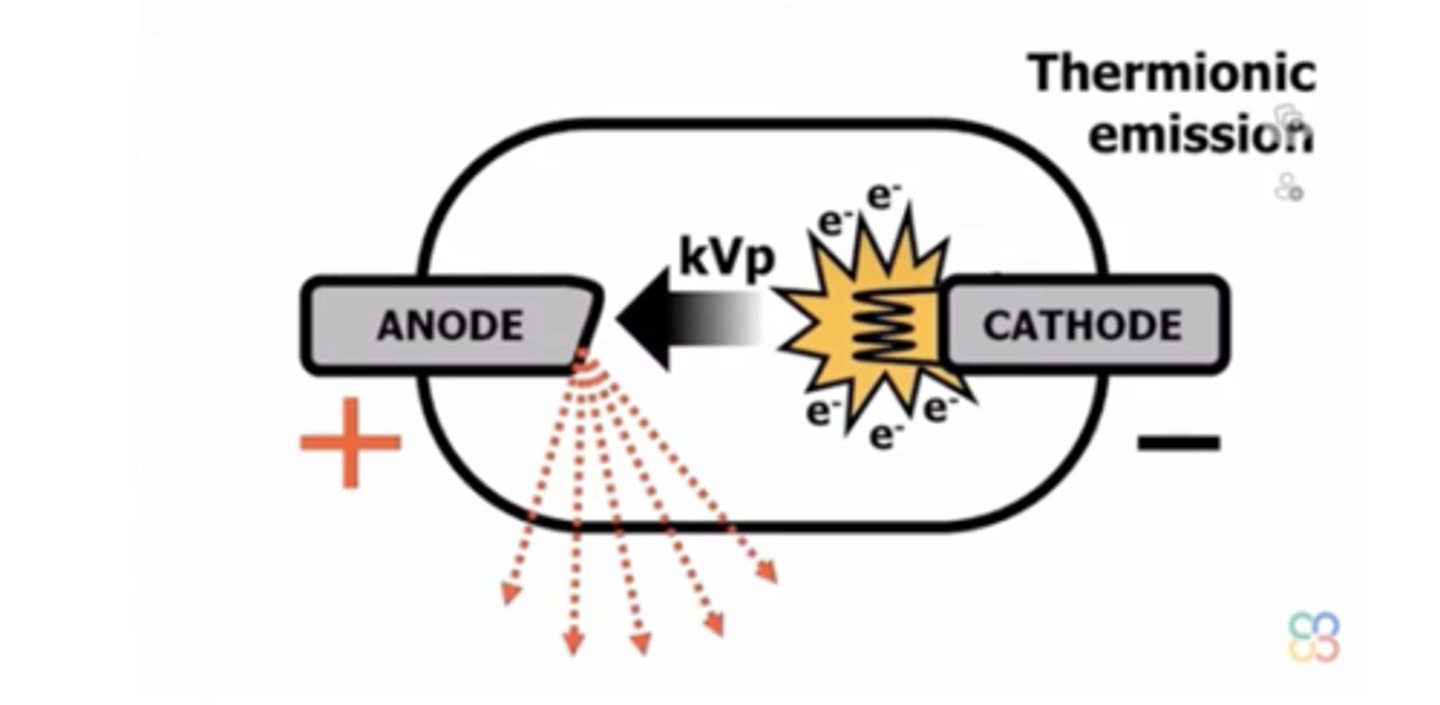
What are the electrical components of the X-Ray machine?
- Wall switch
- Transformers
- Rectifiers
Where is the wall switch located? Why?
Within arms reach of the x-ray machine to quickly shut down the machine in the event of malfunction
What is the function of a transformer?
Increases voltage from power lines to amount sufficient to produce x-rays
What is the function of rectifiers?
Converts alternating current into direct current (“one way street”)
Transformers in the high voltage circuit
- Autotransformer
- High-tension transformer
What is the autotransformer?
Small transformer (size of 5gal pail) that acts as a kV selector
What is the high tension transformer?
“Step-up” transformer
Boosts voltage to quantity sufficient to produce x-ray image
Transformers in the low voltage circuit
- Filament transformer
- mA selector
What is the filament transformer?
“Step-down” transformer
Decreases amount of energy supplied to filament to prevent destruction
Filament current controls _______
tube current (mA)
What is tube current?
Amount of x-ray photons being created
What is the function of the mA selector?
Determines the amount of energy supplied to cathode filament
What is rectification?
Process of converting alternating electrical current to a direct current
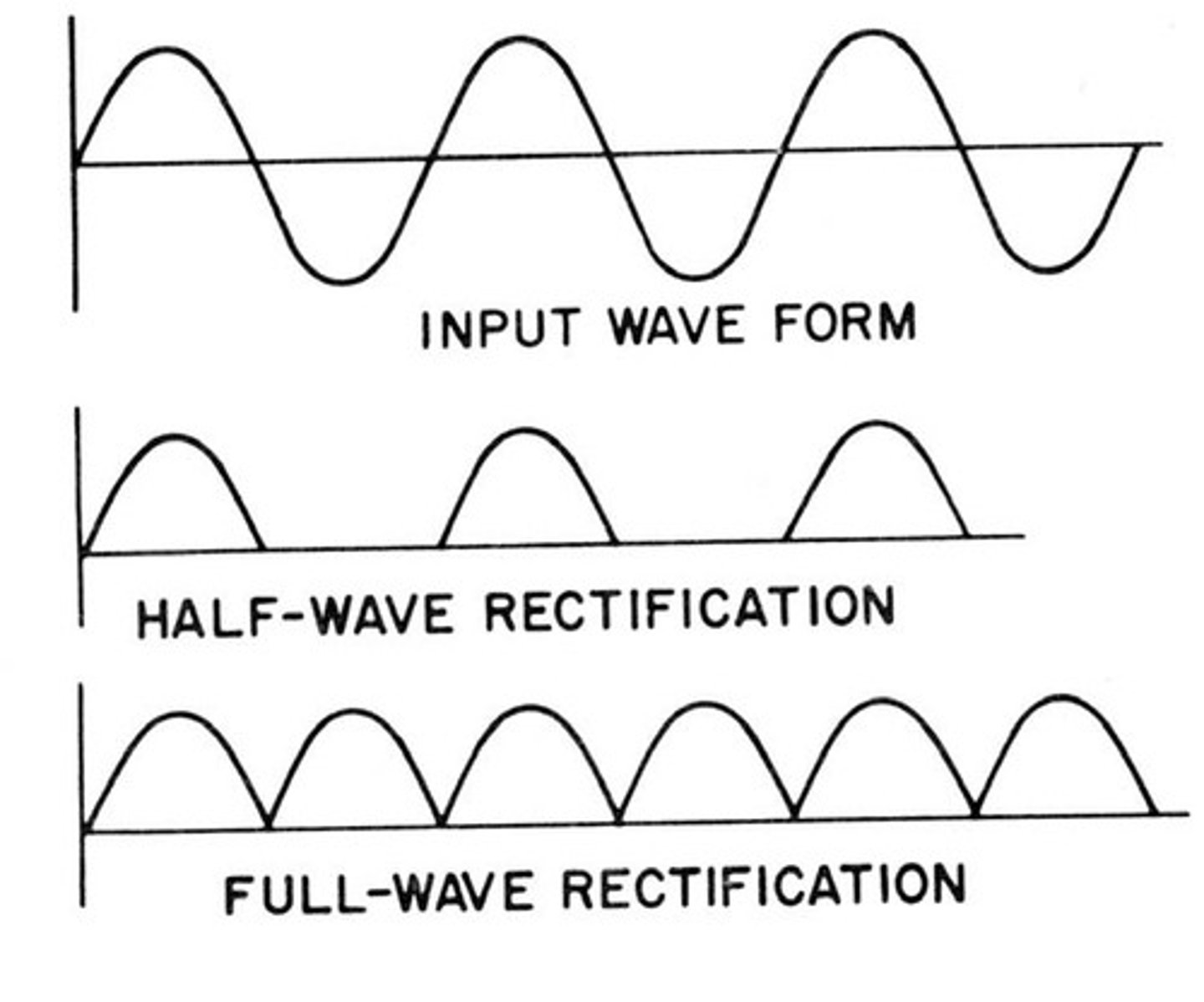
What is the benefit of rectifiers?
More efficient use of electricity (redirects negative current flow into positive)
Allows for decreased exposure time
What are the physical components of the x-ray machine?
- X-ray tube
- Cathode
- Anode
- Collimator
- Control panel

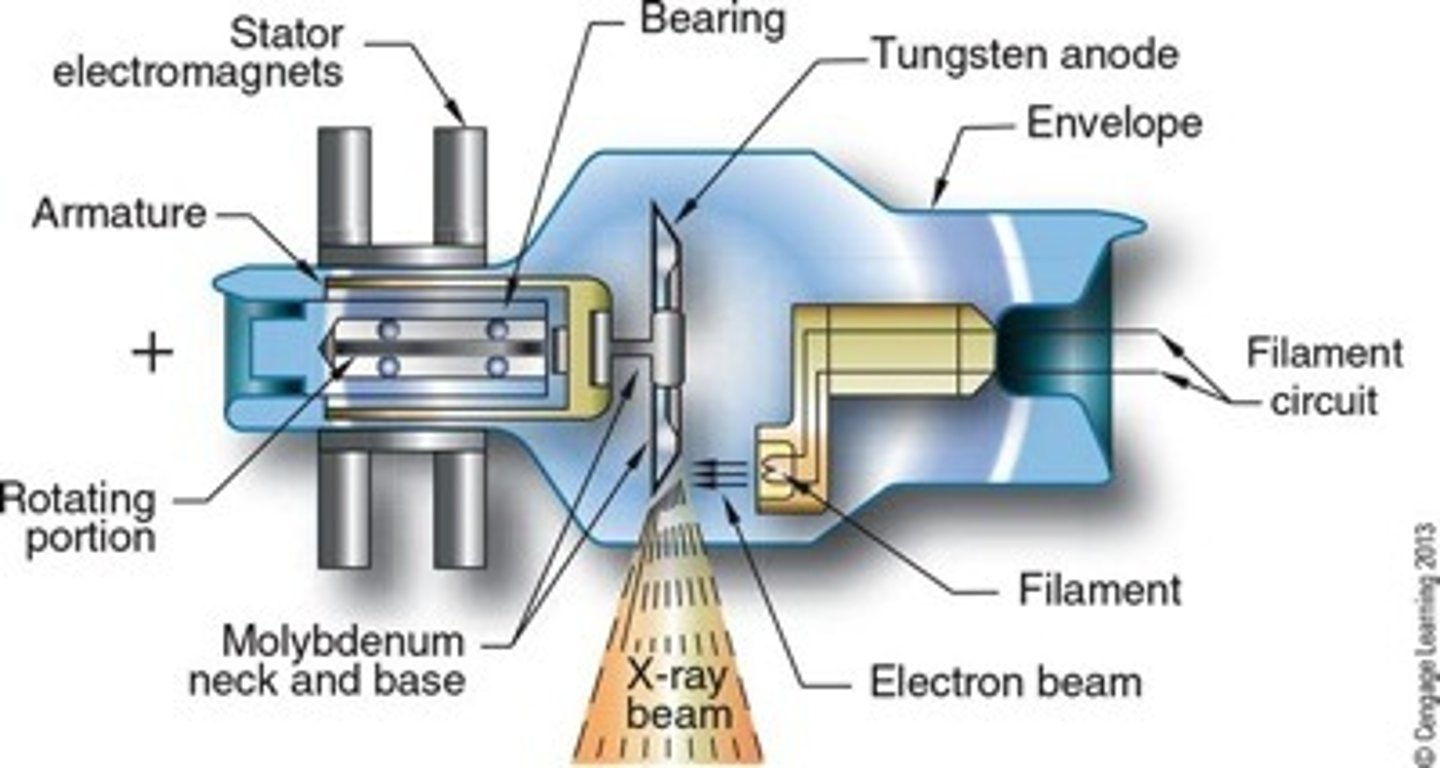
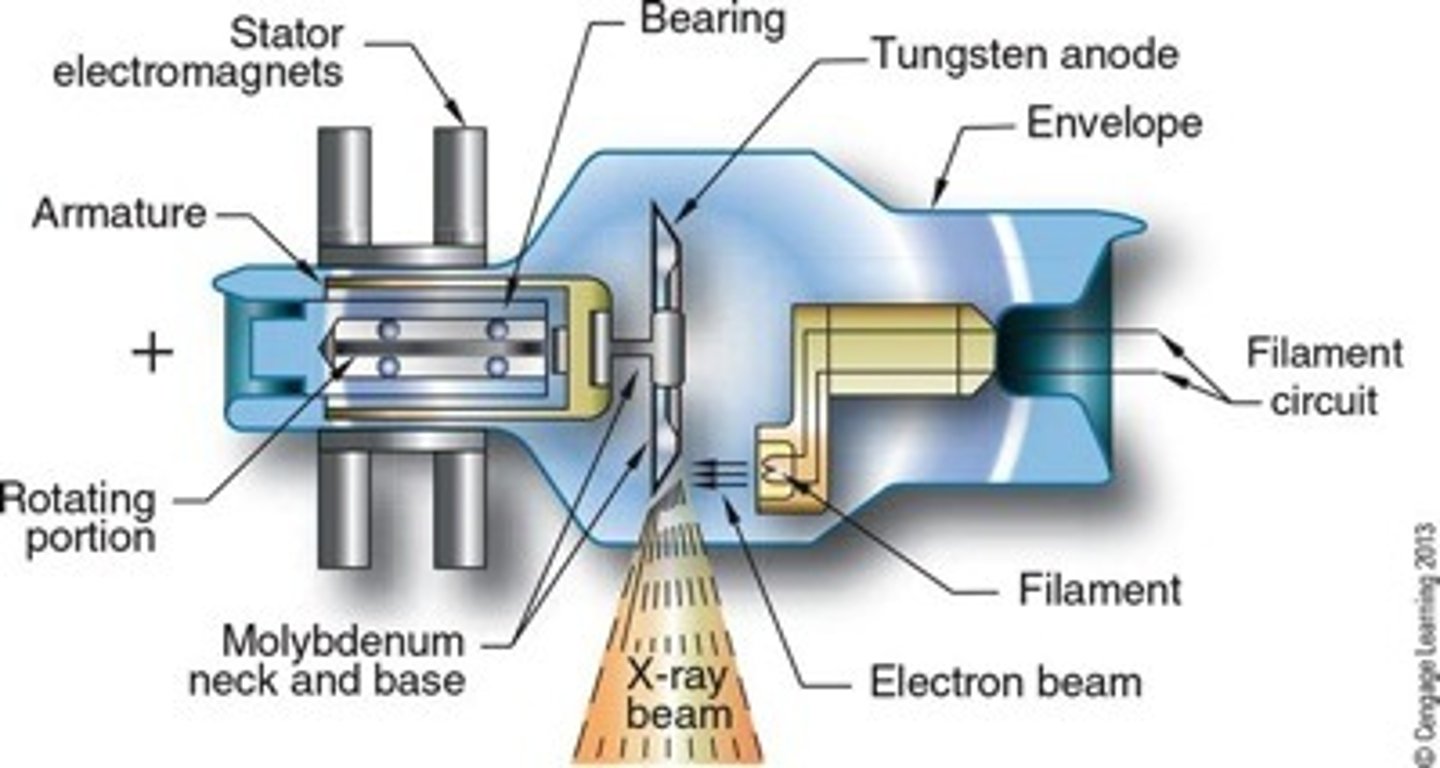
What does the x-ray tube consist of?
Cathode and anode inside a vacuum sealed glass housing
The cathode is the ______ side of the x-ray tube
Negative
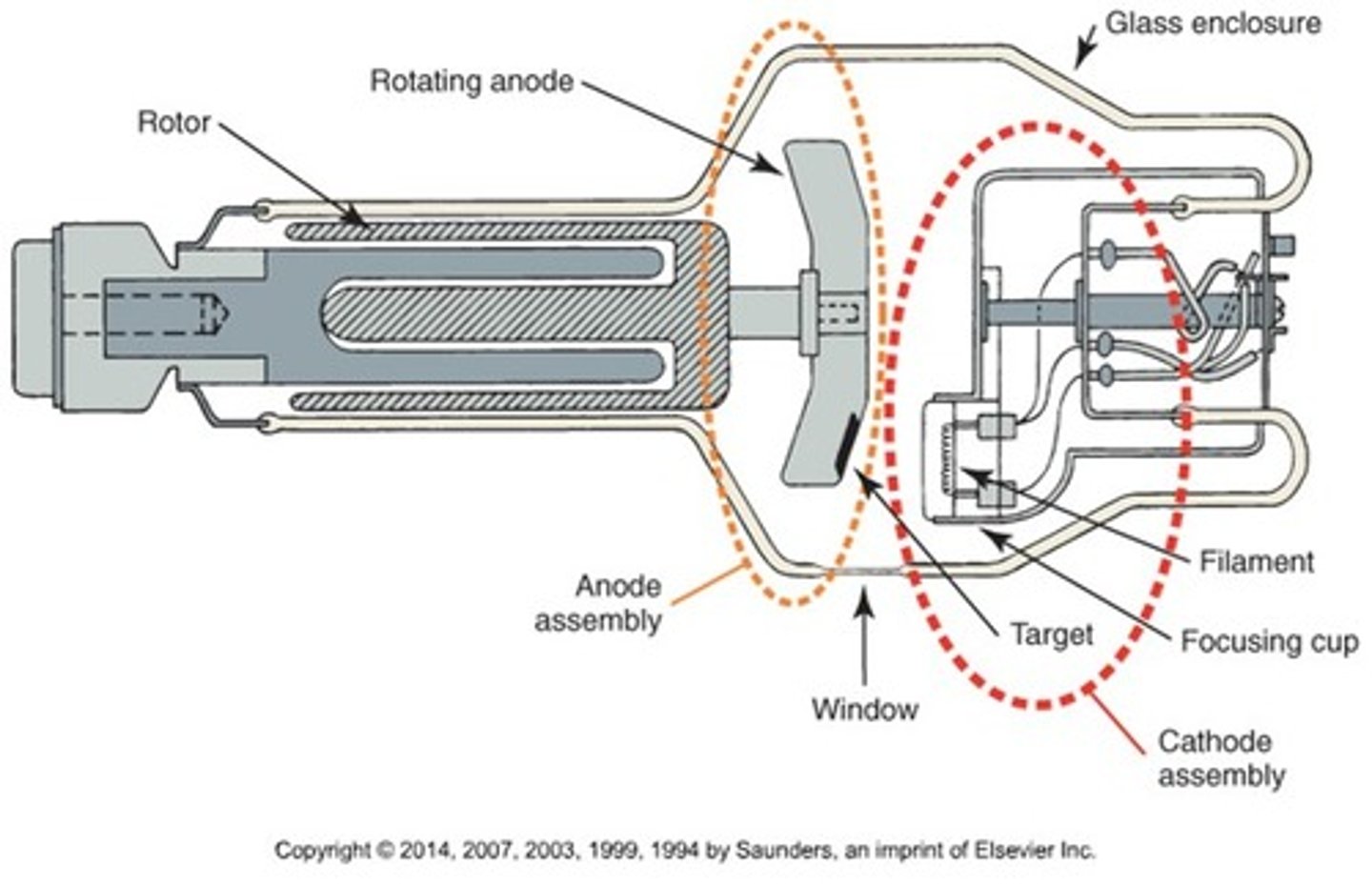
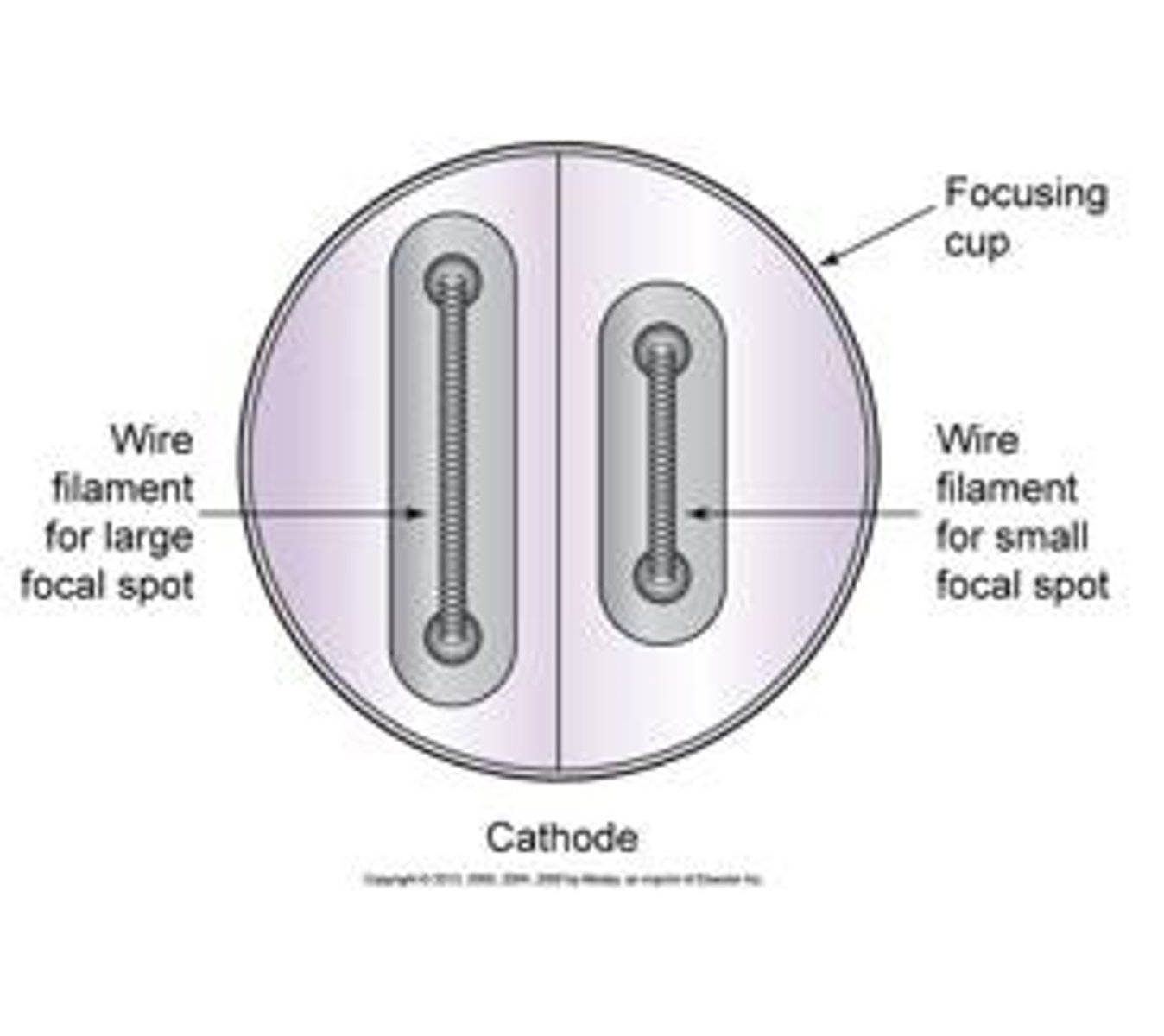
What are the components of the cathode?
- Filament
- Focusing cup
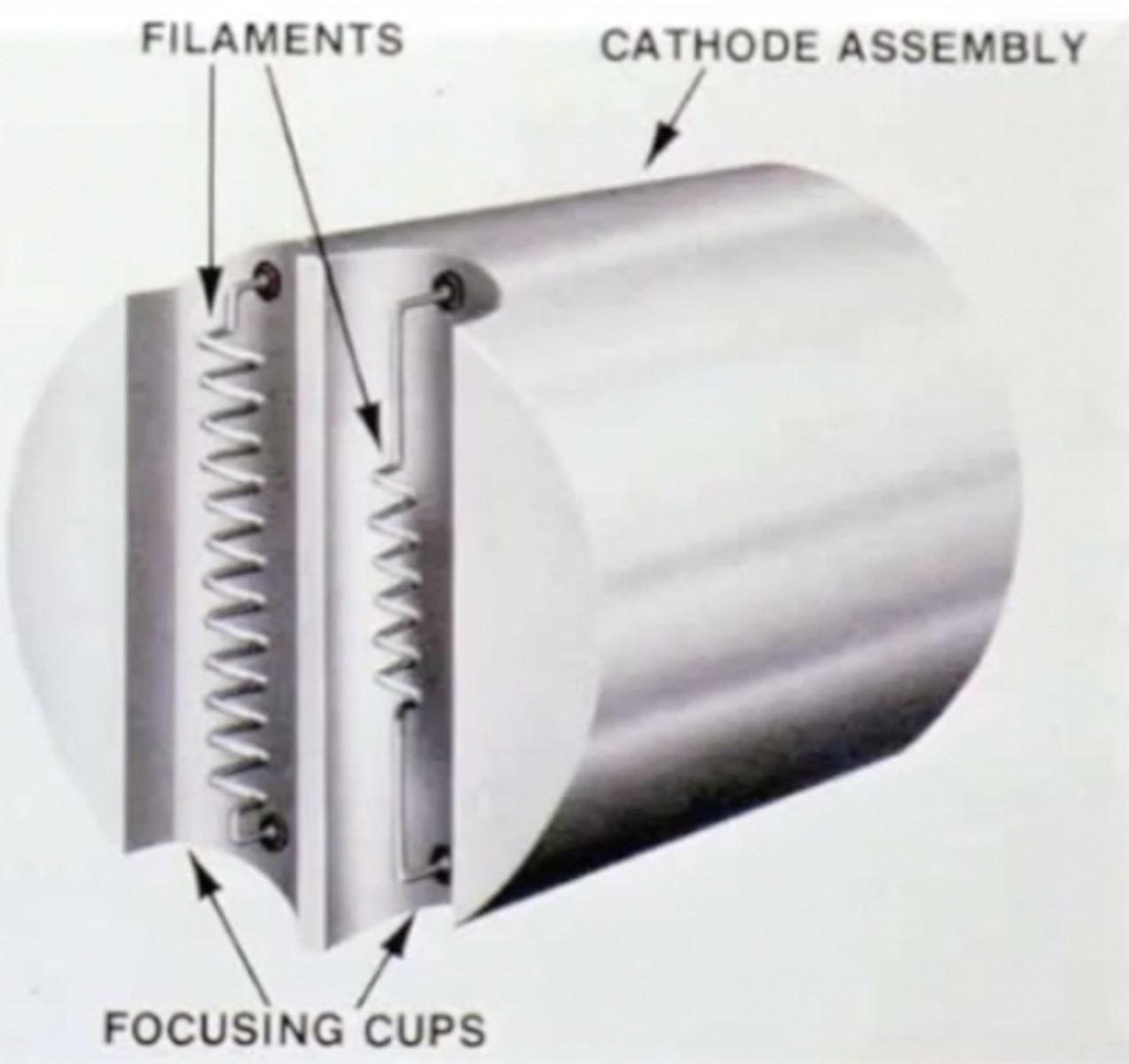
What is the structure of the filament?
2 small coiled wires composed of
Thoriated tungsten
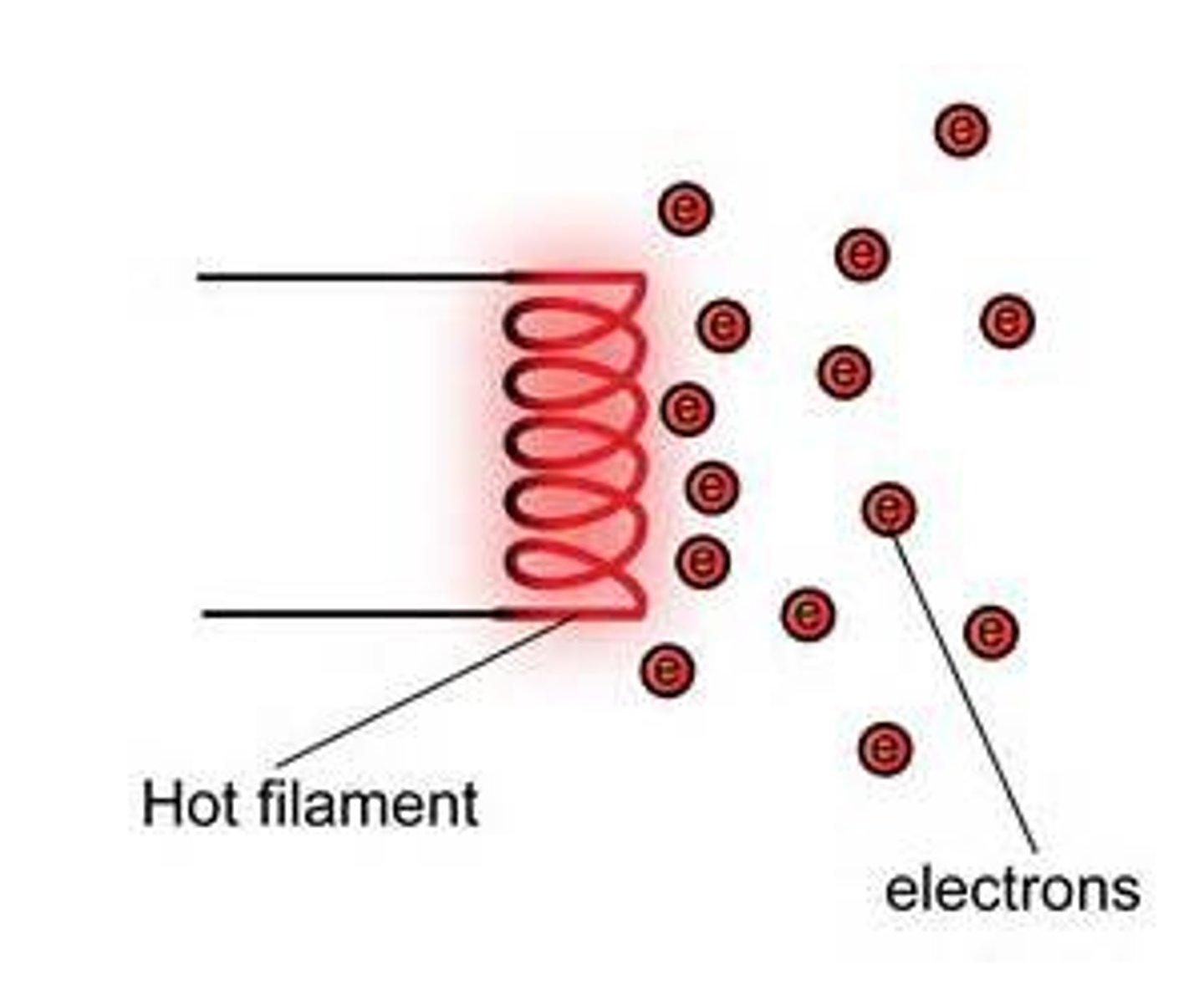
How does the filament work?
Heated to create thermionic emission
What is thermionic emission
Heat induced movement of electrons
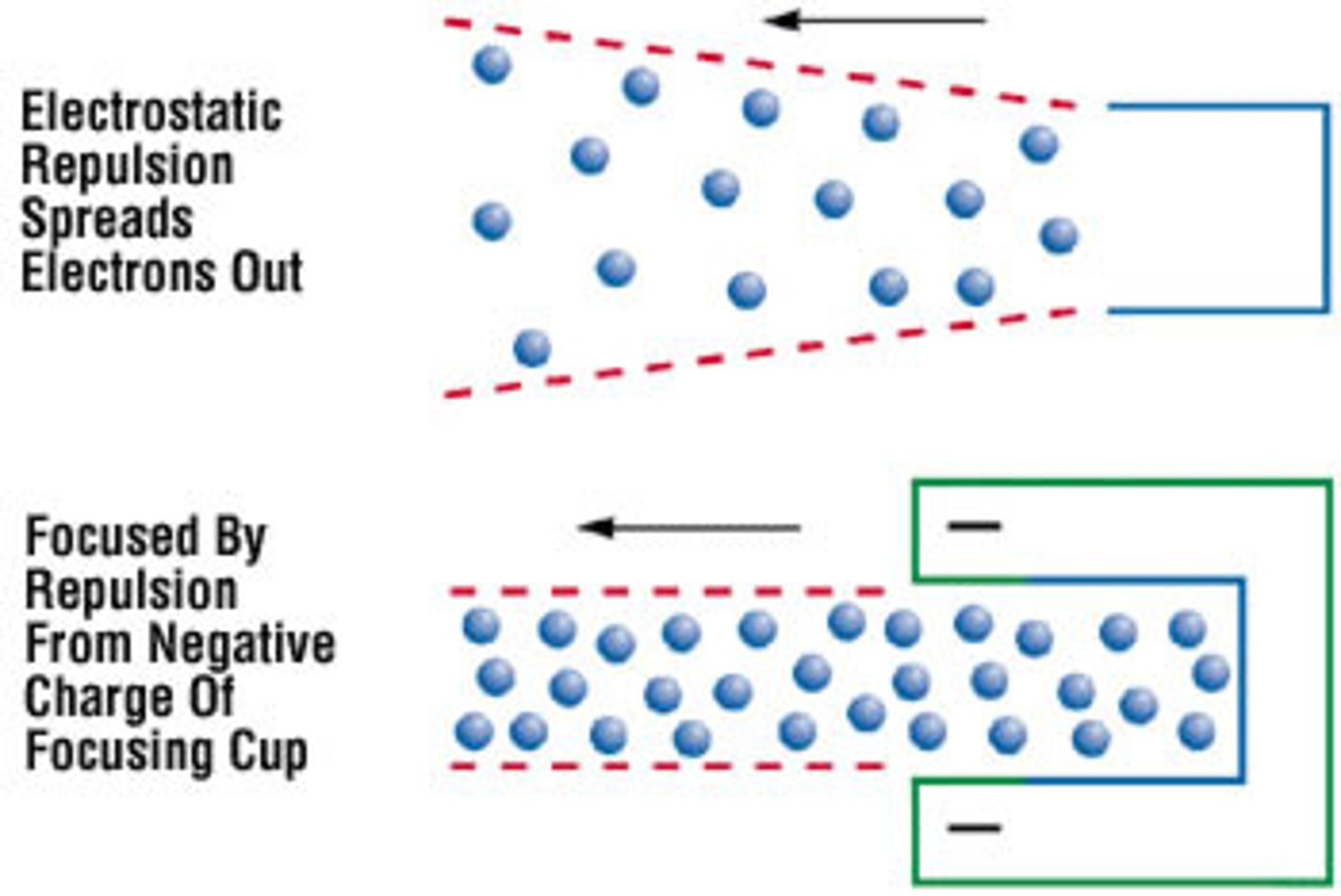
What is the function of the focusing cup?
Directs electrons towards anode target
The anode is the _________ side of the x-ray tube
Positive
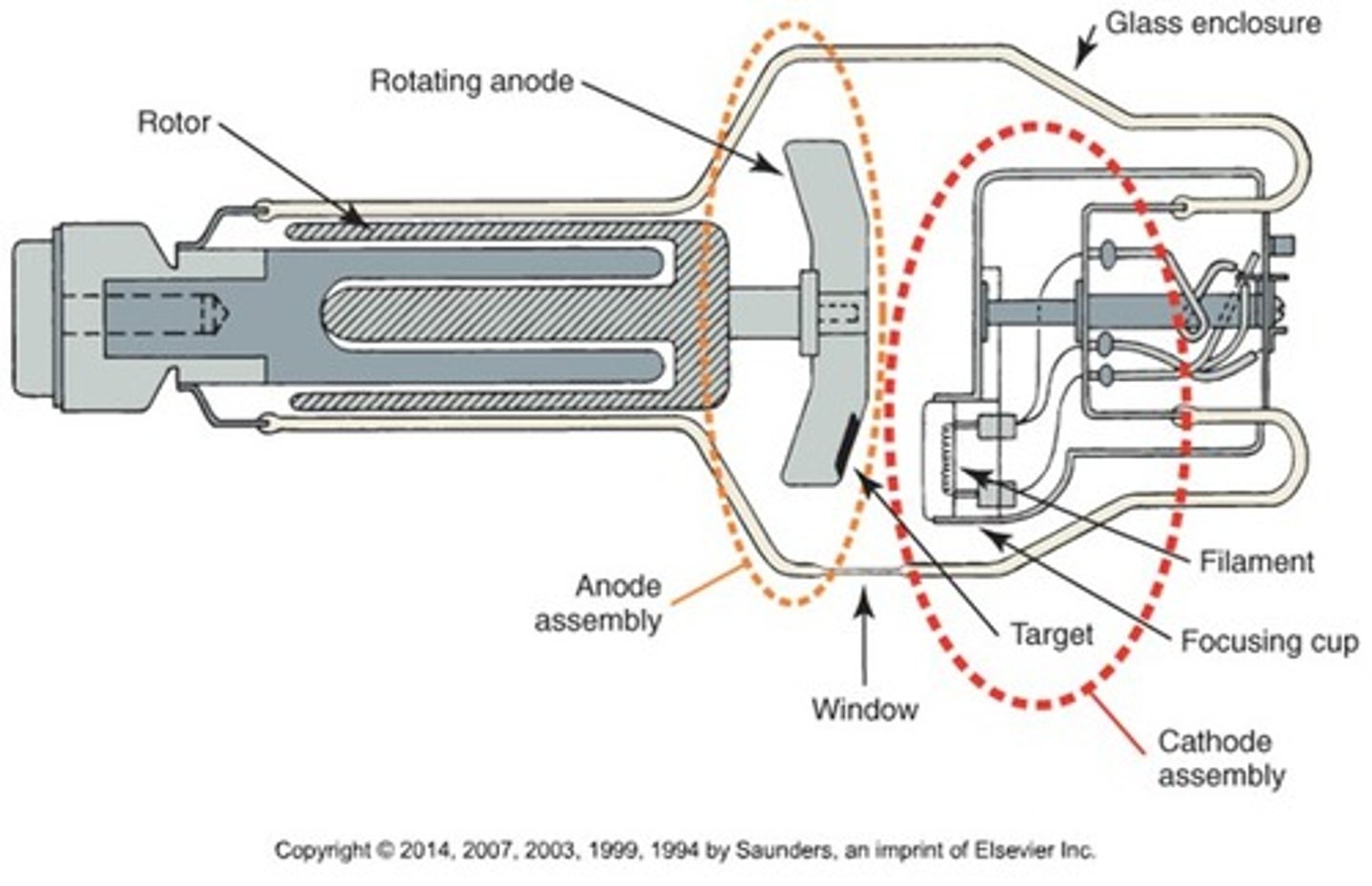
What are the components of the anode assembly?
- Anode disc
- Rotor
Stationary anodes are used most frequently in ________________
Portable equine units, dentistry
What is the structure of the stationary anode?
Rhenium alloyed tungsten target embedded in end of copper rod
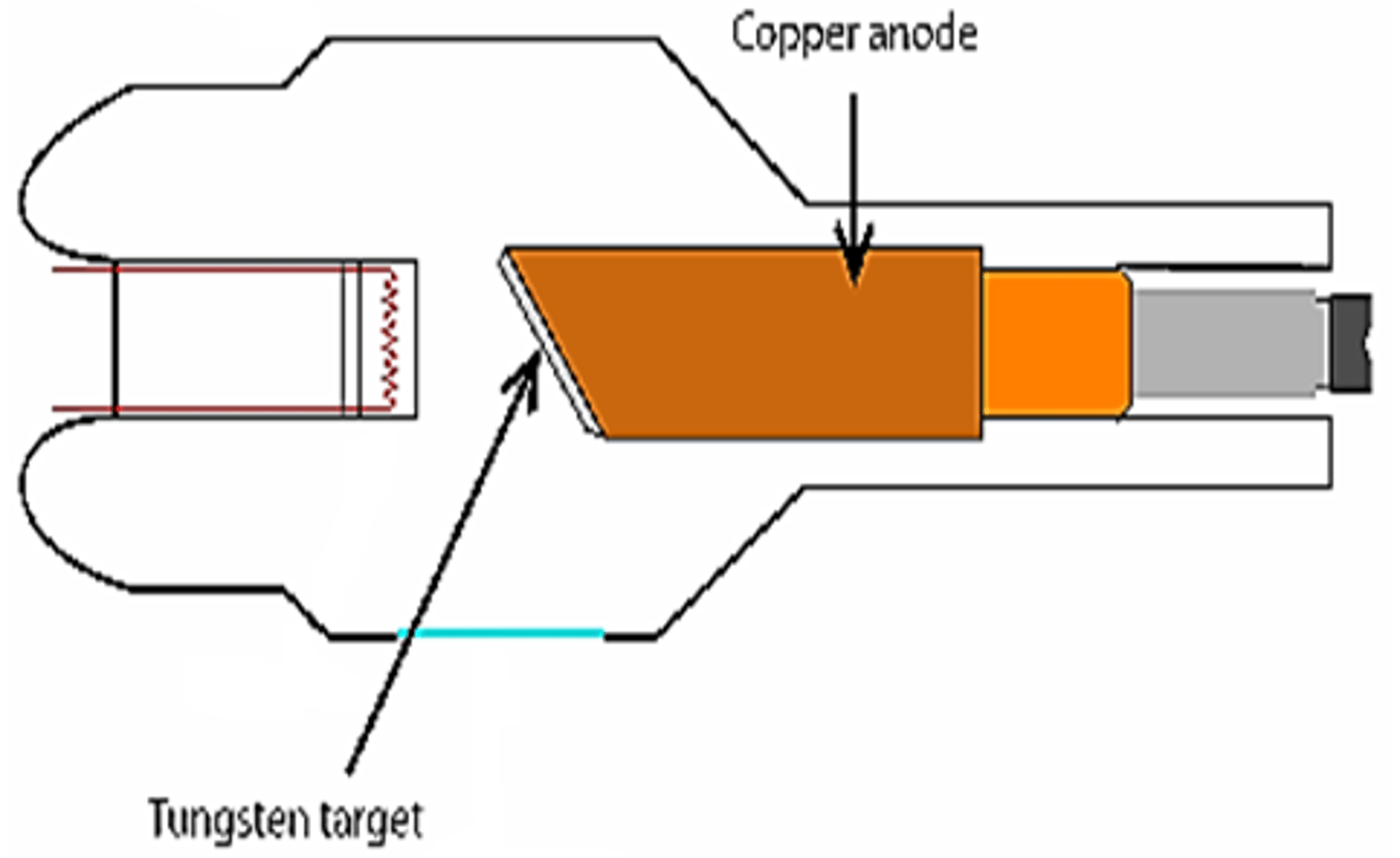
Target angle of the stationary anode is _______ degrees
45
What is the most common type of anode?
Rotating
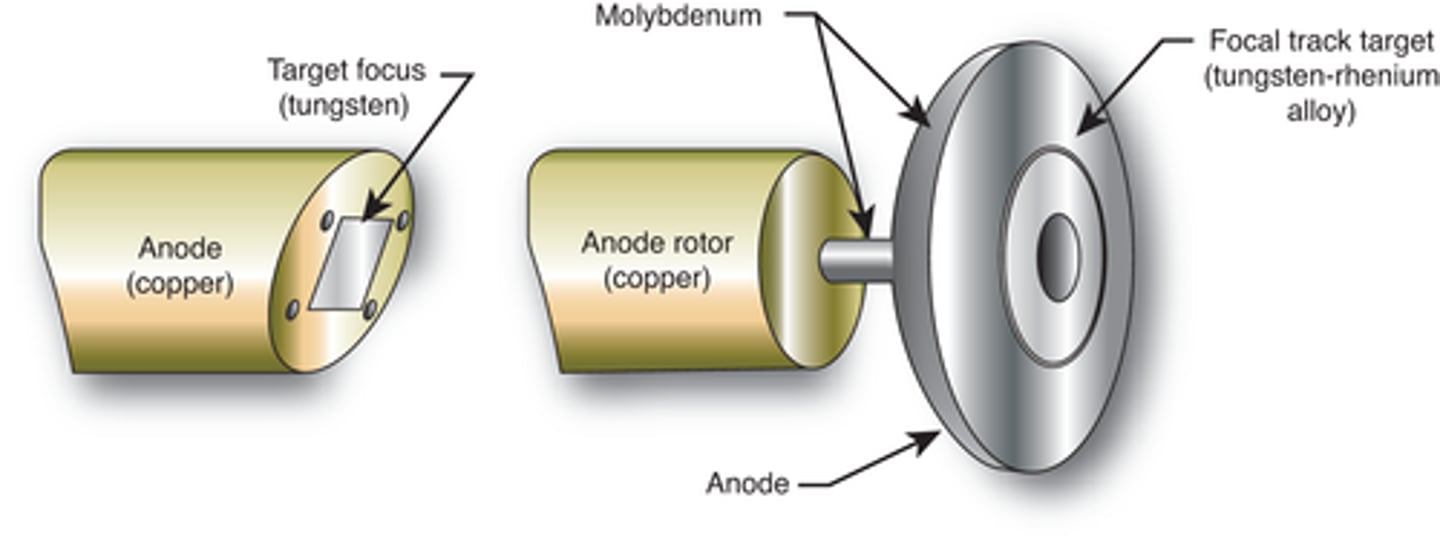
What is the structure of the rotating anode?
Rotating discs (5-13cm in diameter) composed of molybdenum with graphite backing
Rhenium alloyed tungsten as target
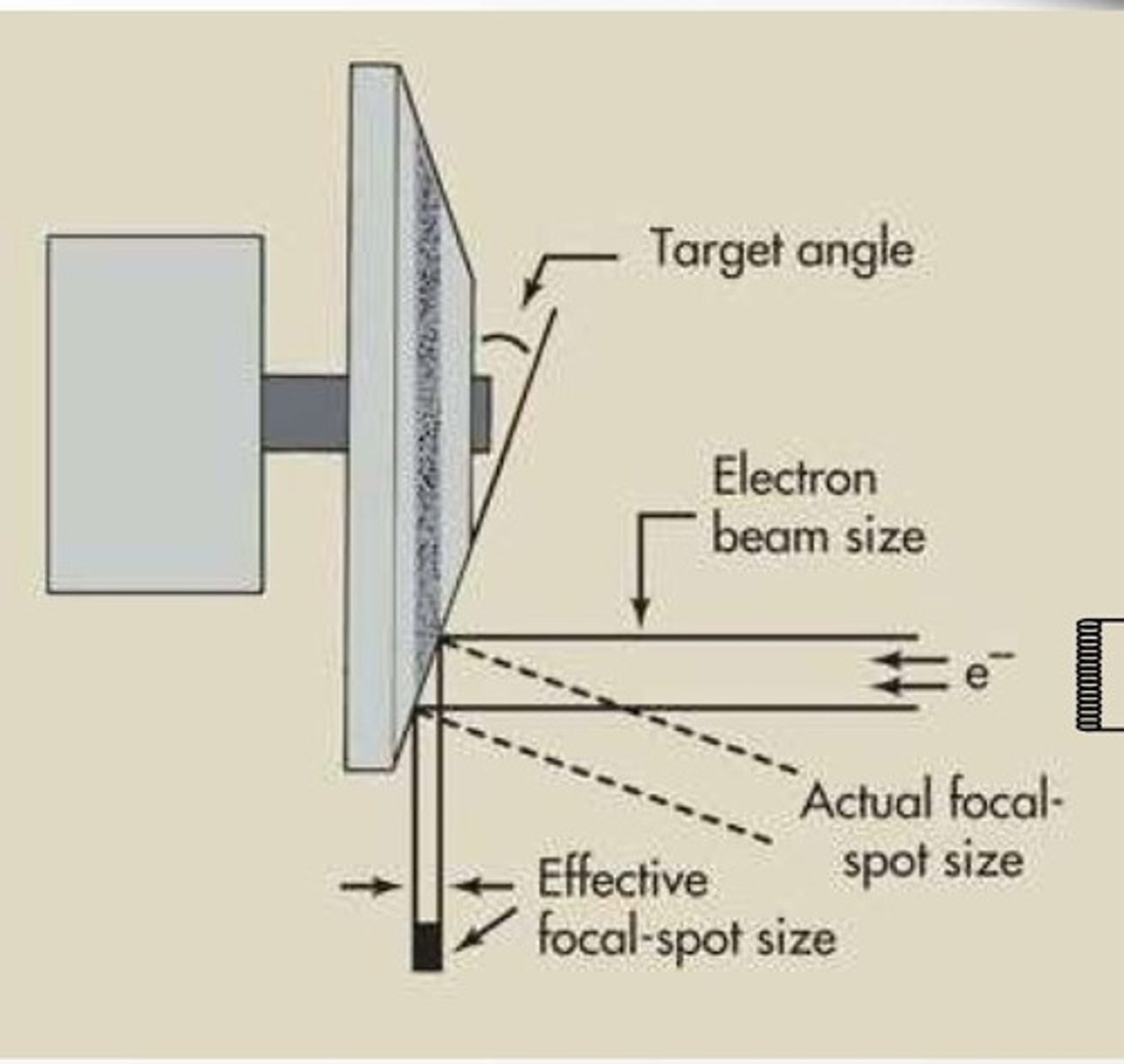
What is the anode focal spot? What is it's function?
- Portion of anode where electrons impact
- Where x-ray photons are created
- Point SID is measured from
Rotating anodes have a ______ target area
Larger
What is the line focus principle?
Change of direction of the electron cloud as a result of the target angle
Electrons strike target and are directed down towards patient
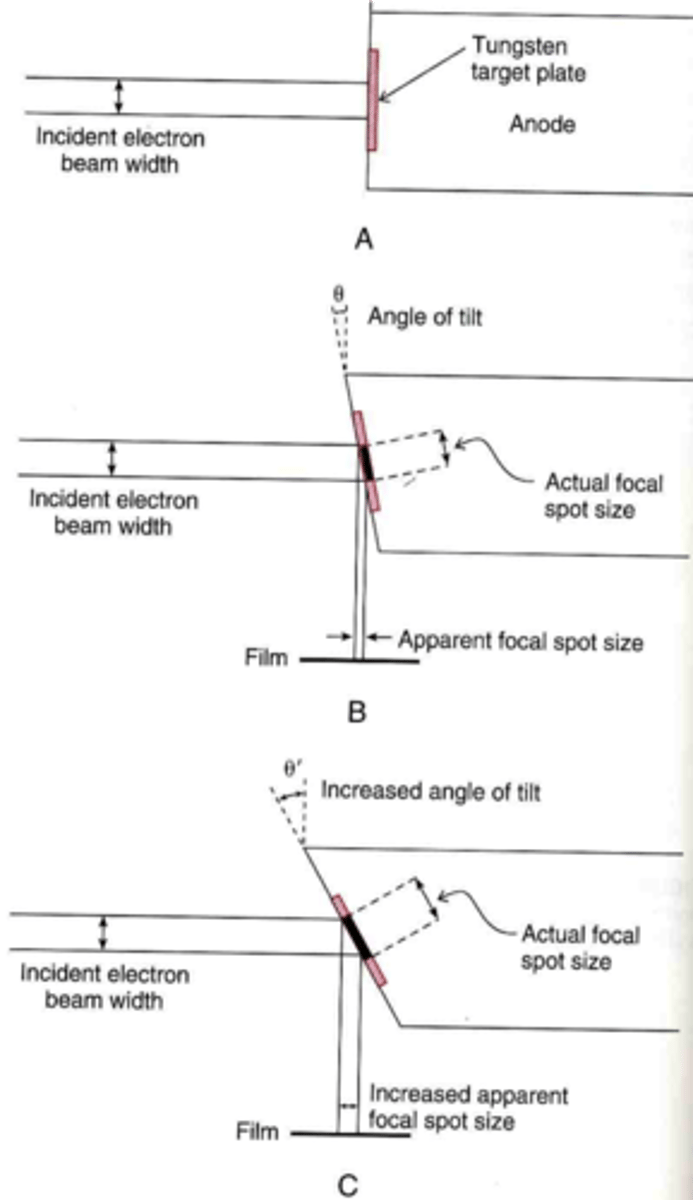
Degree of angle of the anode affects ________________________
size of useful x-ray beam
The effective focal spot size is controlled by ______________________
actual focal spot (AF) size
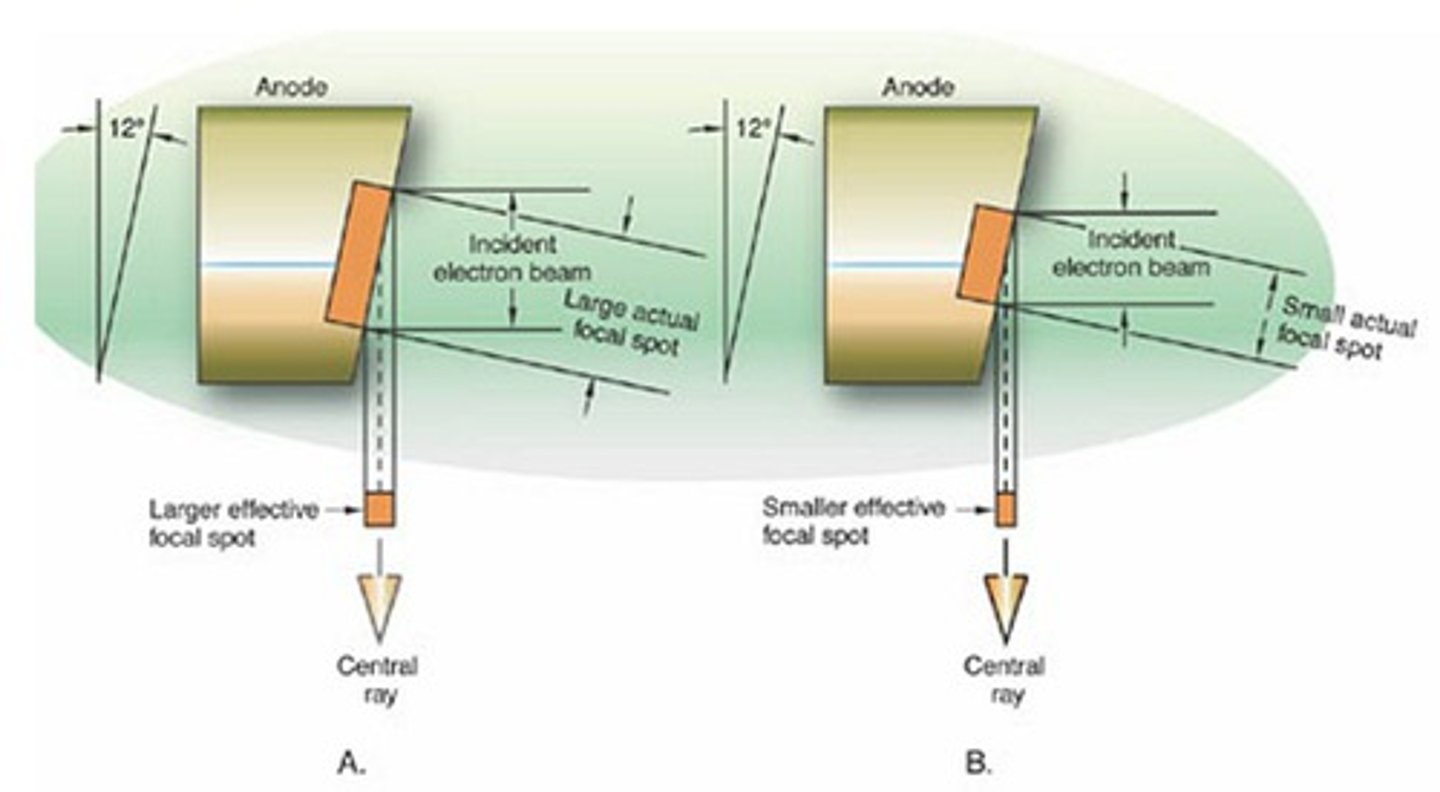
What is the actual focal spot?
Stream of electrons hitting anode target (does not change)
What is the effective focal spot?
Stream of electrons directed towards patient after striking anode target (changes depending on the angle of the anode target)
What is focal spot bloom?
Region of reduced resolution at edges of radiographic image
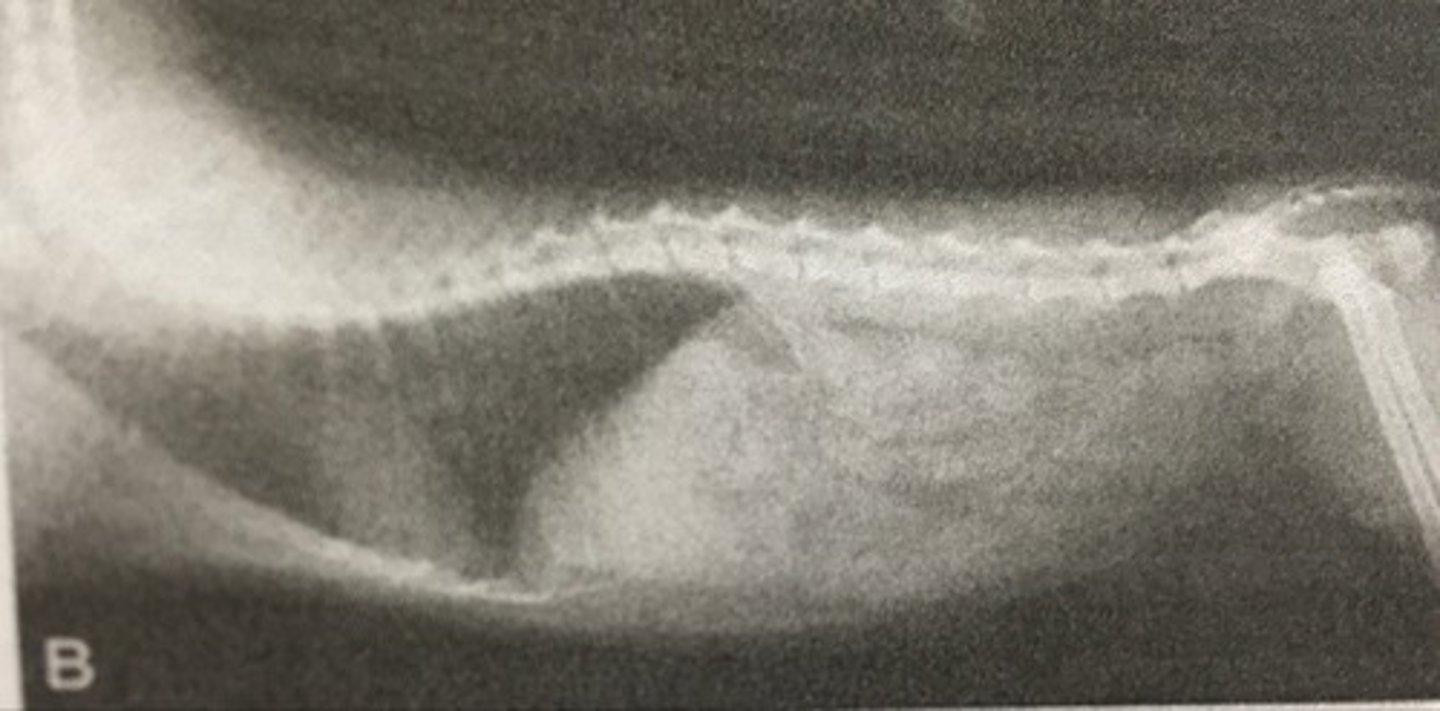
What causes focal spot bloom?
- Heat
- Age
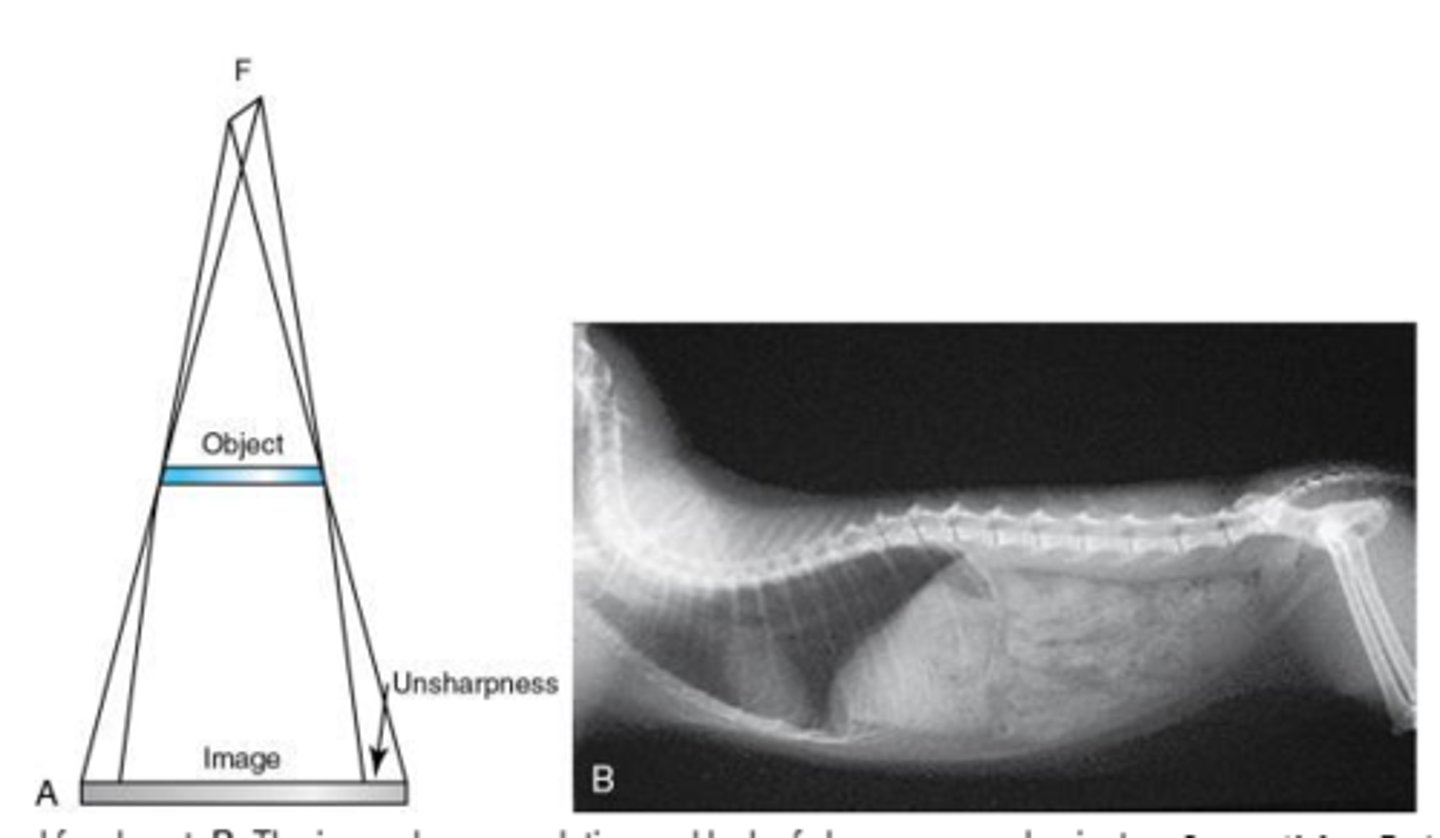
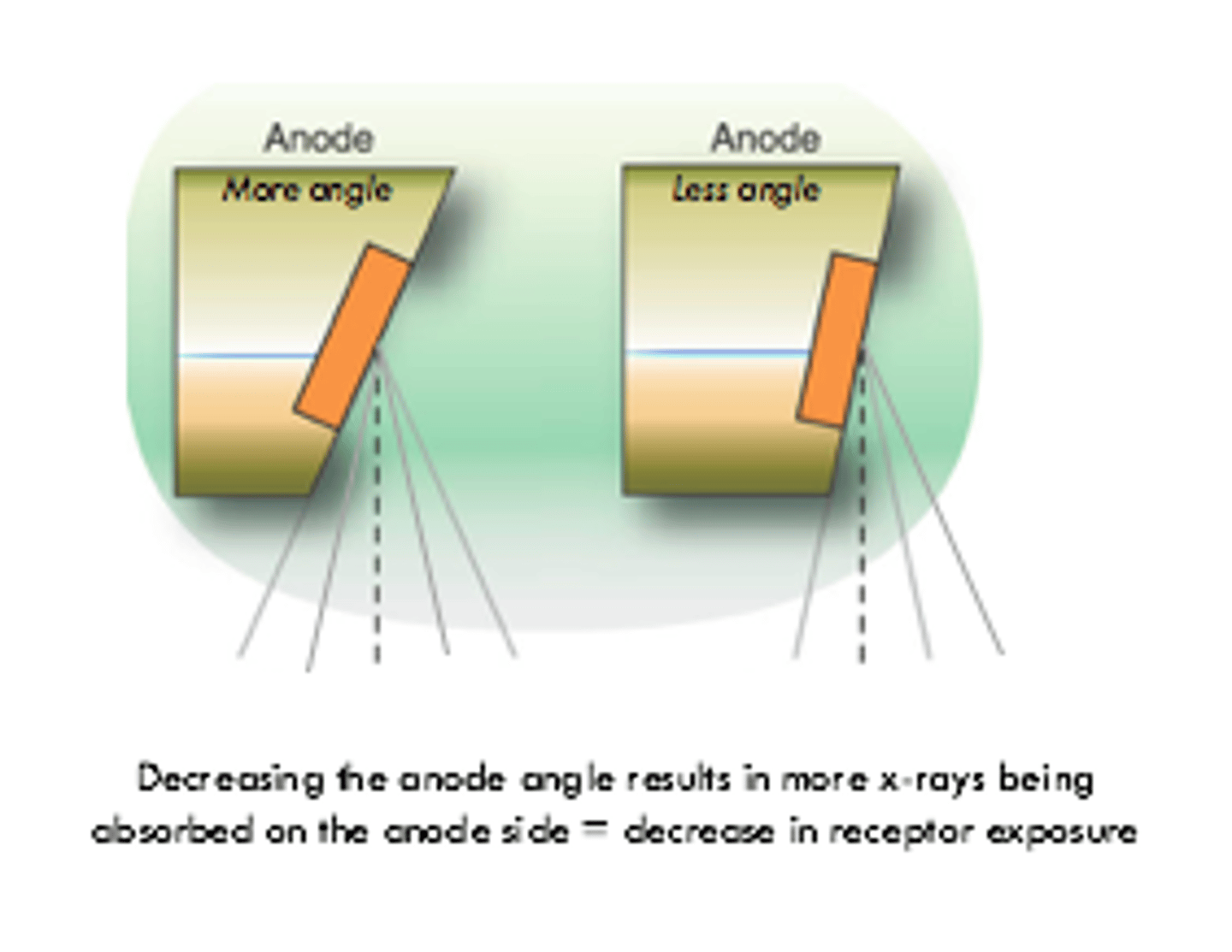
What is the anode heel effect?
Variation in radiation intensity across the length of the radiation field- more rays absorbed at the heel (therefore less intense).
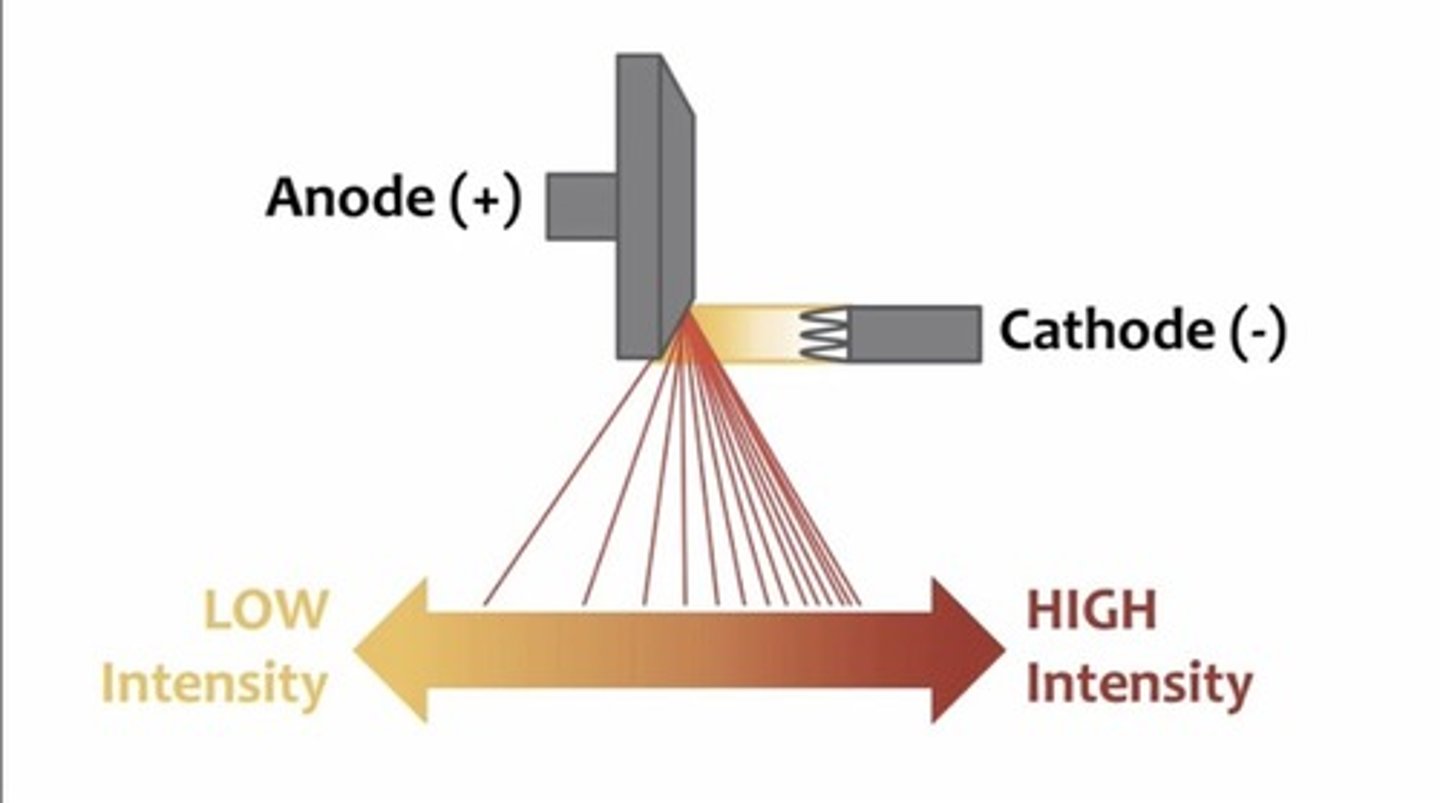
X-ray beam is stronger at the __________ side
Cathode
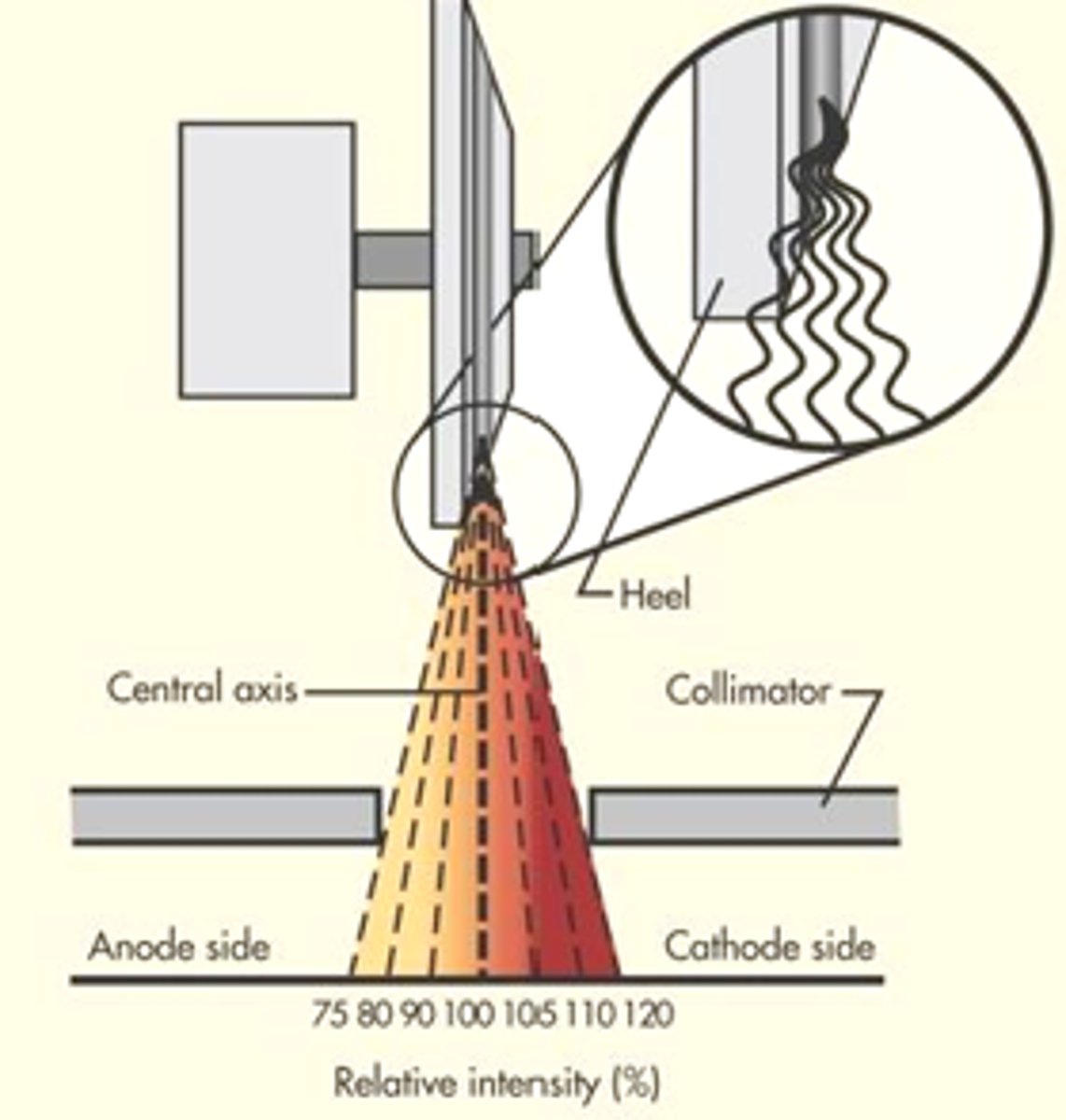
A small anode angle = _________________
Increased anode heel effect
What is the function of the collimator?
- Regulates the size and shape of the x-ray field
- Reduces the amount of scatter radiation produced in the patient
- Reduces patient dose
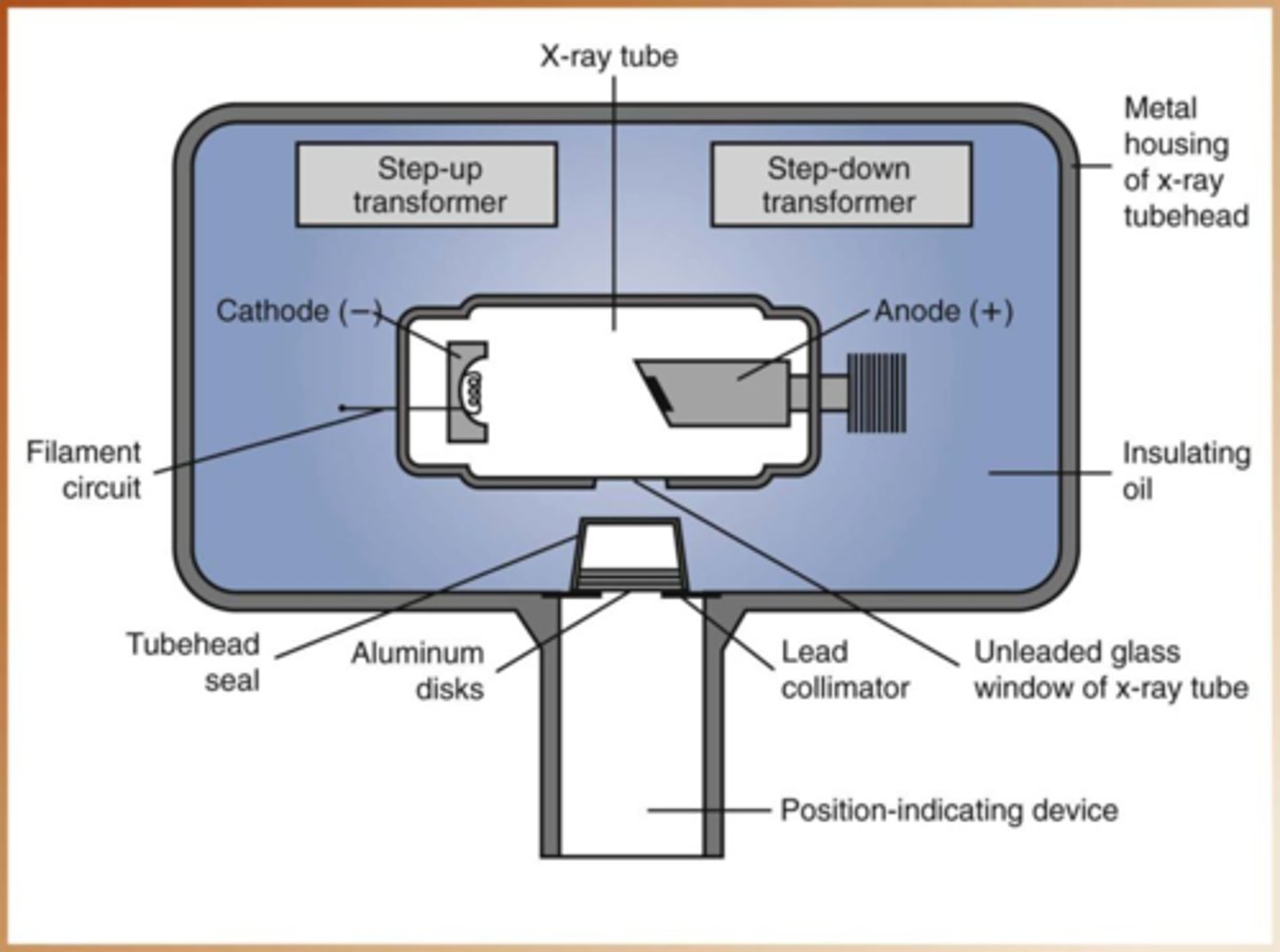
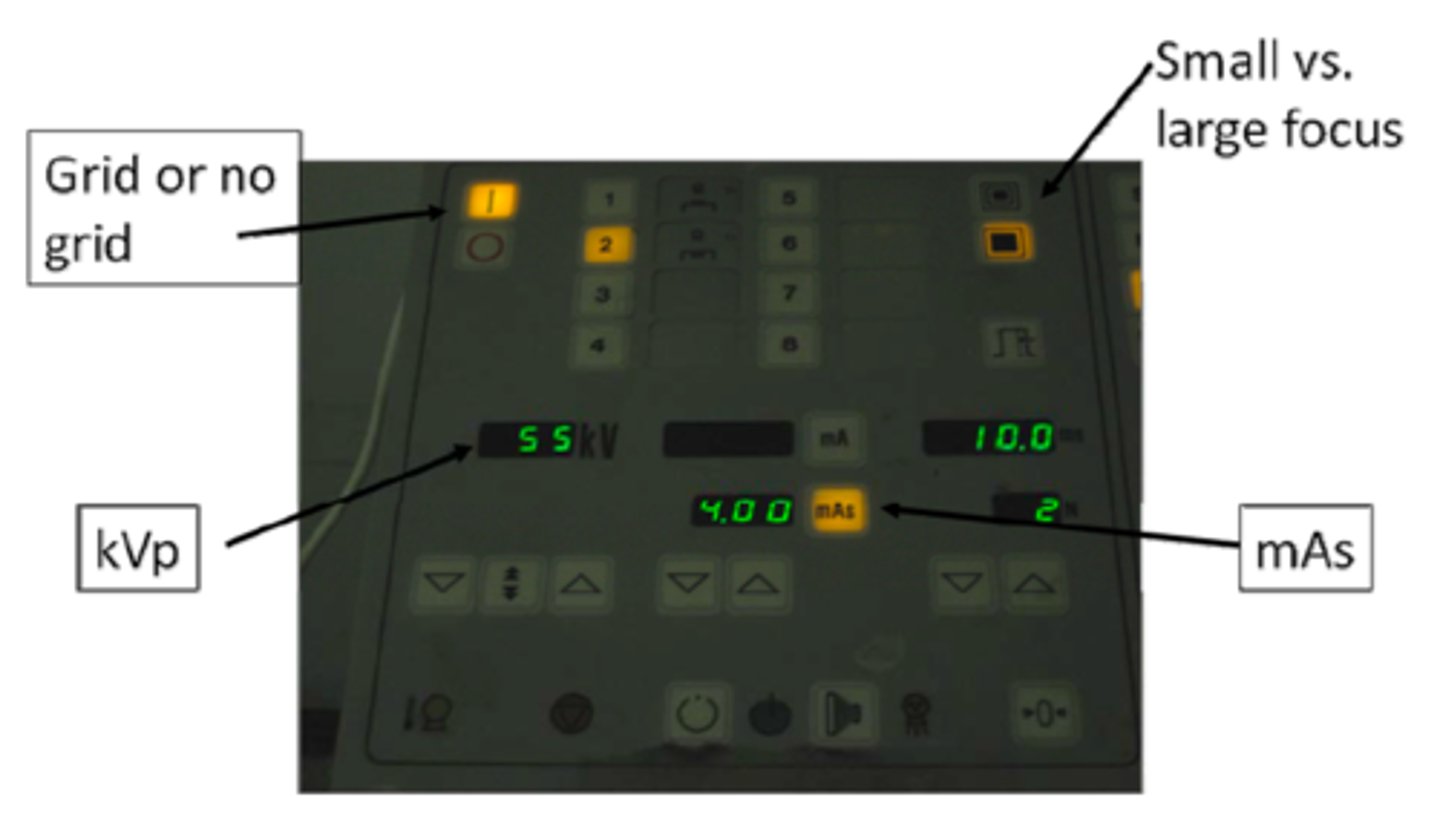
What are the components of the control panel/operating console?
- On/Off switch
- mA (tube current)
- Time (seconds or less)
- kVp (kilovolts peak)
- Exposure button/foot pedal

What are the sources of tube failure?
- Cathode failure
- Anode target failure
- Glass envelope damage
How does cathode failure occur?
Filament evaporation
How is cathode failure prevented?
- Appropriate use of prep switch (heat cathode slowly)
- Shutting down equipment when not in use
How does anode target failure occur?
Damage caused by heat or bearing failure
What happens when the anode target fails?
Tube remains functional, but produces irregular and inconsistent densities
How do you prevent anode target failure?
- Tube warm up
- Appropriate settings
How does glass envelope damage occur?
- Metal deposits on side of tube causing "arcing"
- Presence of air within tube housing