chemical energetics
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Energy
Neither created nor destroyed , can be changed from one form to another , involve chemical change
Calorimeter
Used to measure the change in thermodynamic quantity thermochemical equations
Enthalpy (H)
Refers to energy content that is stored in a substance
Smaller =more stable system
Only possible to measure enthalpy change not enthalpy itself
enthalpy change (triangle H)
amount of energy involved in a chemical reaction
Represents the difference in energy content of the reactants and products
Usually measured in kilojoules (kJ)
Formula of Enthalpy change
Total energy of reactants - total energy of products
Exothermic reaction
A reaction in which heat is lost to the surroundings causing an increase in temperature of the surroundings
Release heat + rise in temp of the surroundings = exothermic
Negative sign
Means lose heat , always for exothermic reactions
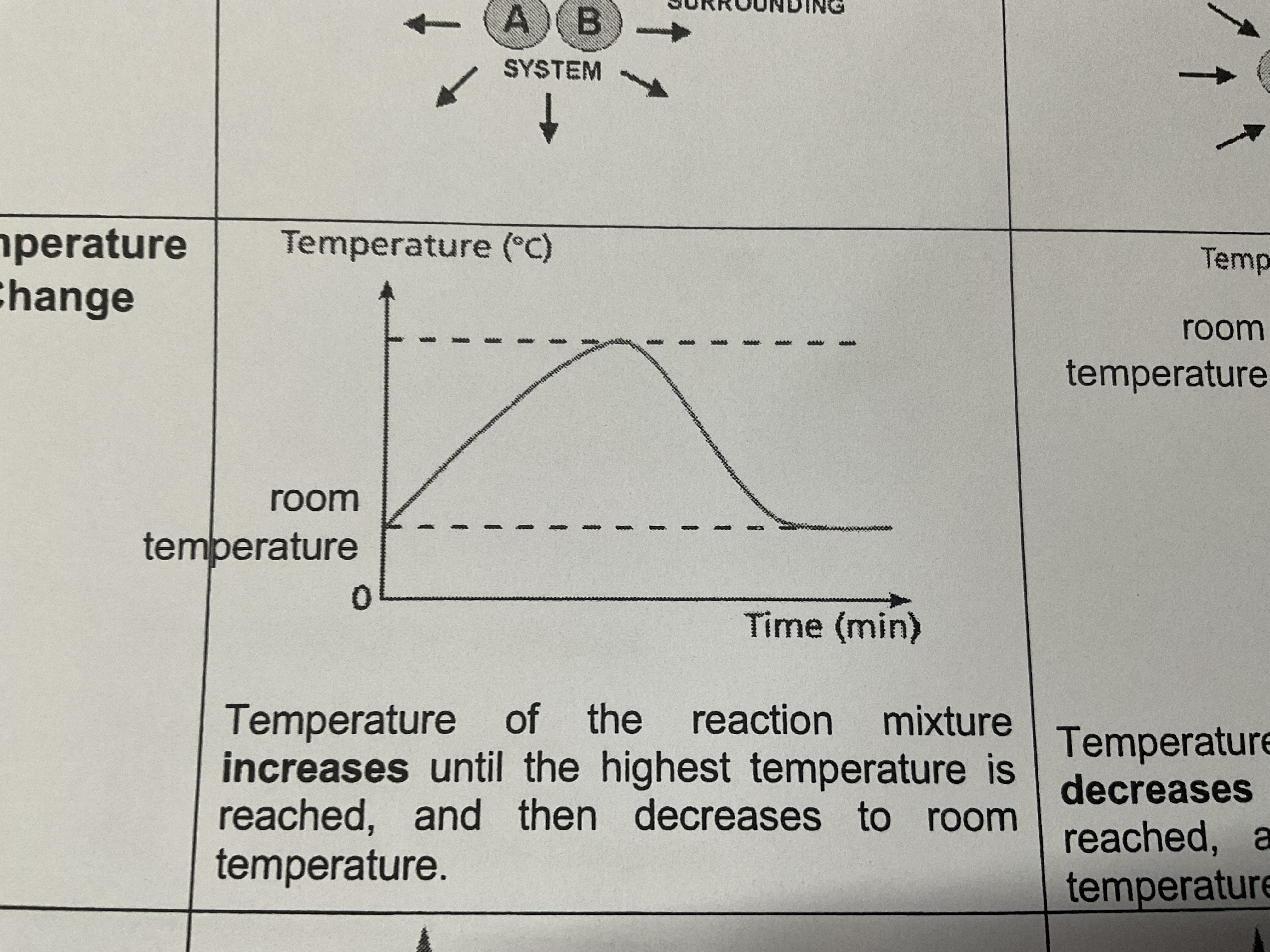
Temperature change for exothermic reactions
Temperature of the reaction mixture increases until the highest temperature is reached , and then decreases to room temperature
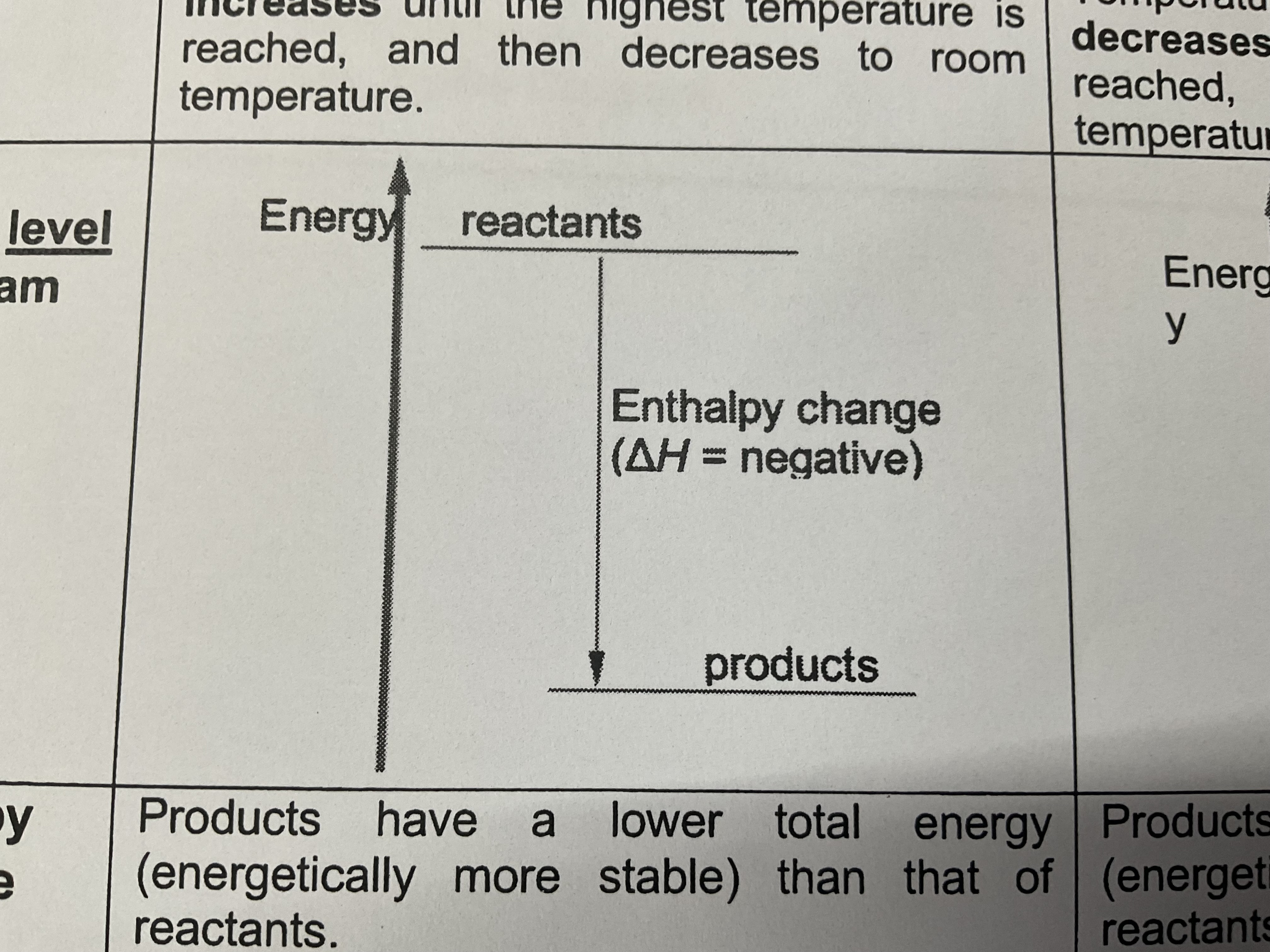
Energy level
Reactants (more energy , less stable ) —(Enthalpy change , energy loss to surroundings , heat is released to the surroundings and temperature of surroundings rises)→products have less energy , more stable
Diff in energy levels of the products and the reactants = the amount of energy released during the reaction
Exothermic reaction example
Physical = condensing steam to water (solid to liquid ) + freezing (liquid to solid )
Chemical = combustion of fuels , respiration and neutralisation
Combustion of fuels example
C + O2 = CO2
2H2 + O2 =2H2O
CH4 +2O2 = CO2 +2H2O
Respiration chemical equation
C6H12O6 + 6O2 = 6CO2 + 6H2O
Neutralisation between acid and alkali formula eg
NaOH + HCL =NaCl +H2O
Endothermic reaction
A reaction in which heat is absorbed from the surroundings causing a decrease in the temperature in the surroundings
(Heat gain from surroundings , temperature of surroundings drop)
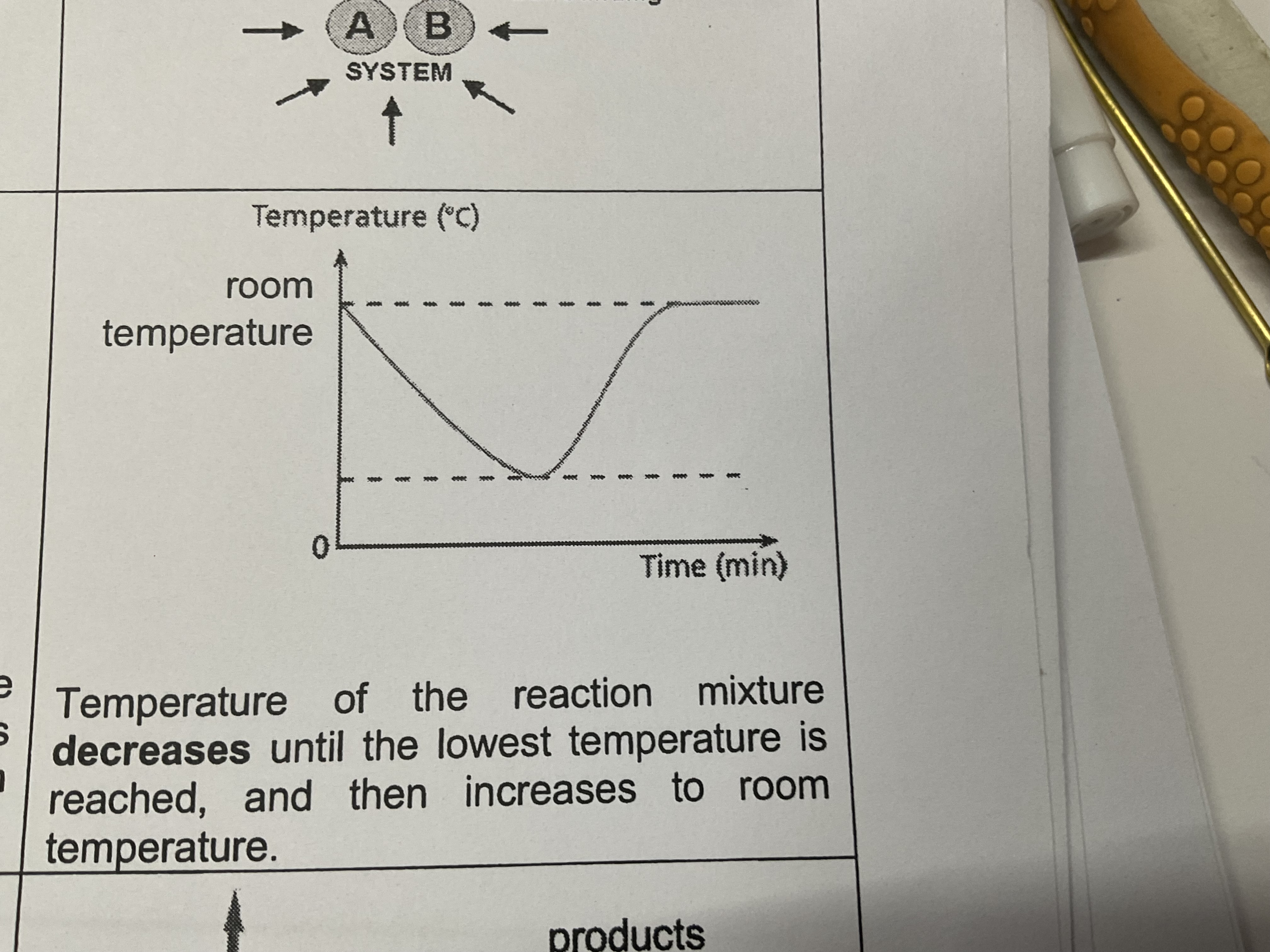
Temperature change in endothermic reaction
Temperature of the reaction mixture decreases until the lowest temperature is reached and then increases to room temperature
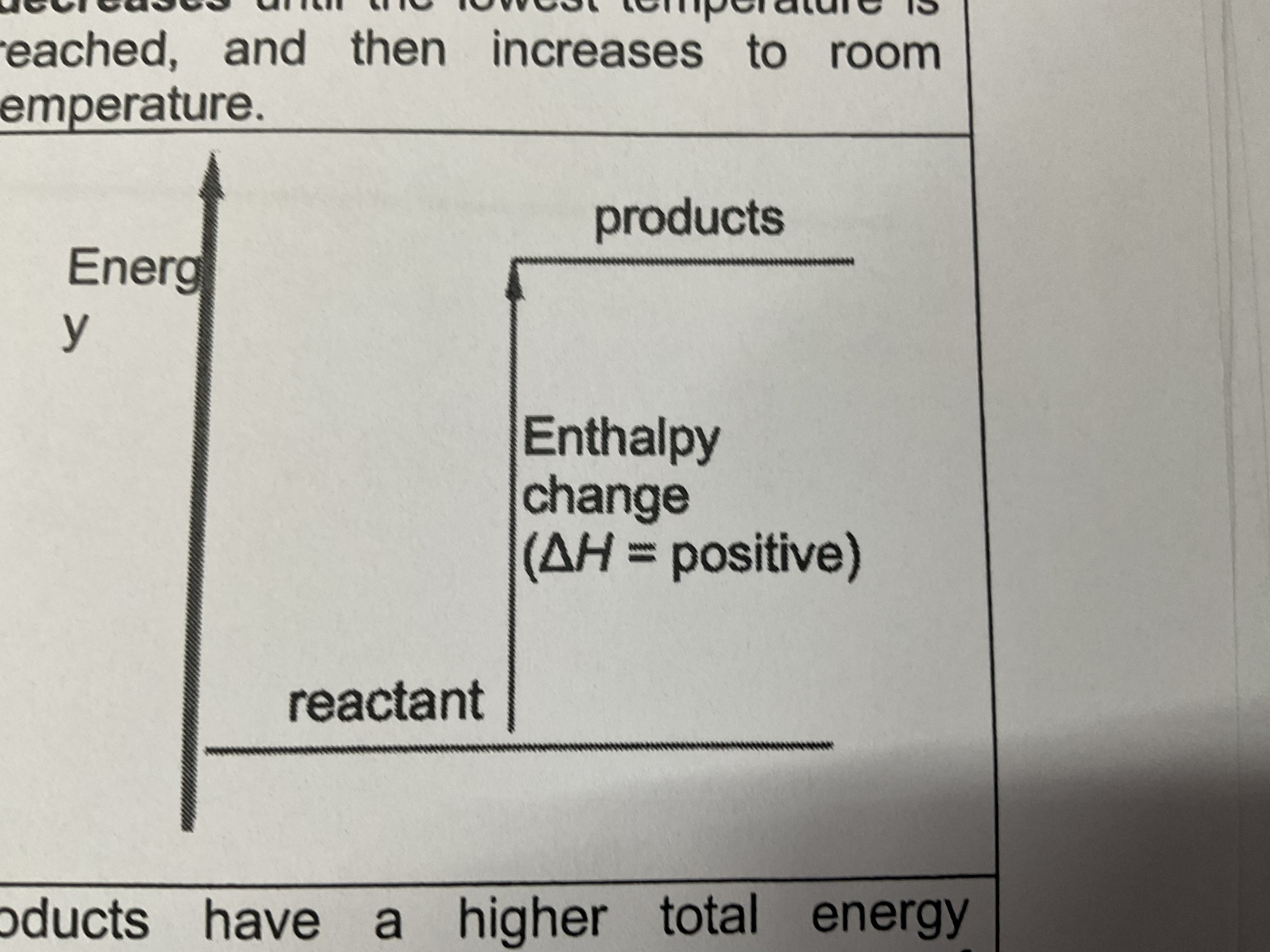
Endothermic energy level reaction
Products have a higher total energy , less stable than the reactants . Heat is absorbed from the surroundings and temperature of the surroundings drops
Difference in the energy levels of the products and the reactants is equal to the amount of energy absorbed during the reaction ( a,ways positive)
Positive sign
Only for endothermic means that energy is gained/ absorbed from the surroundings
Endothermic process
Physical : evaporation (liquid to gas), melting (solid to liquid )
Chemical reactions : photosynthesis , decomposition
Bond breaking
Endothermic
Bond forming
Exothermic
When bonds are broken
Energy is absorbed from the surroundings
When bonds are formed
Energy is released to the surroundings (exo)
Overall enthalphy change formula
Total energy absorbed for bond breaking - total energy released from bond forming
In an exothermic reaction
More energy is released in forming bonds than absorbed in breaking bonds (overall gives out energy)
In an endothermic reaction
More energy is absorbed in breaking bonds than released in forming bonds (more energy taken in than given out)
Bond enthalphy of an X-Y bond
Average amount of heat absorbed to break one mol of that bind in gaseous state
The amount of energy absorbed to break a chemical bond is the same as
The amount of energy released when chemical bond is formed
Stronger bond
More energy is absorbed to break that bond and thus the higher its bond energy (KJmol)
To calculate Enthalpy change of a reaction
Total energy absorbed for bond breaking (endo, reactant)- total energy released from bond forming (exo,product)
Activation energy
Minimum energy required by the reactant particles in order for a chemical reaction to occur