Exam 5: feline Hyperthyroidism
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
how is feline hyperthyroidism generally defined
excessive production and secretion of T4 and T3 by the thyroid gland
most common endocrine disorder in cats
one of the most common geriatric disorders in cats
what is the pathology of hyperthyroidism
primary disease
adenmtous hyperplasia
human - Plummer’s dx
benign
bilateral usually
rarely carcinoma
what is the signalment typically associated with hyperthyroidism
older cats
females
decreased risk in siamese and himalayans
what are the clinical signs of hyperthyroidism
weight loss
polyphagia
PU/PD
hyperactivity
vomiting
apathetic
may not be noticable early in disease
how might hyperthyroidism present on physical exam
thin
palpable thyroid aka thyroid slip
hyperactive
poor hair coat
dehydration
attitude
cervical ventroflexion
tachycardia
murmur
gallop rhythm
what is thyroxic cardiomyopathy
similar to HCM
can cause murmur
usually resolves with therapy
how is blood pressure affected by hyperthyroidism
often hypertensive
older cats with hyperthyroidism, cardiac disease, renal disease, hyperaldosteronism
fundic exam
neurologic
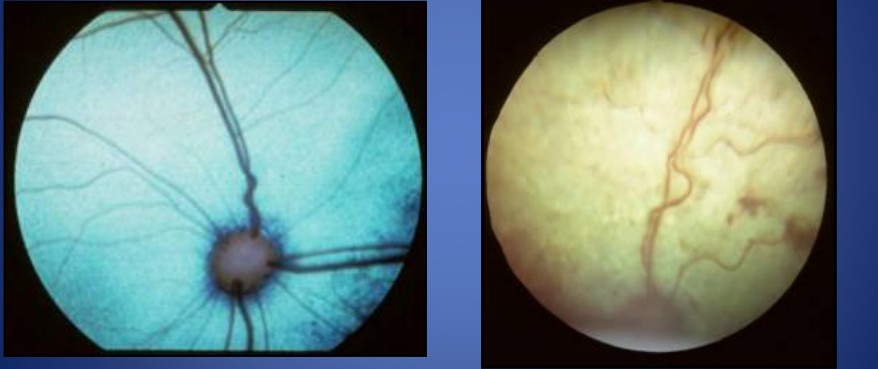
which fundic exam is hypertensive
right
what is the diagnostic process of hyperthyroidism
clinical signs
CBC/chem/UA
concentrations of total T4, free T4, TSH
suppression testing
how will hyperthyroidism present on minimum database
dehydration
azotemia either from dehydration or concurrent renal disease
increased ALT
usosthenuria common
what is the screening test of choice for diagnosing hyperthyroidism
tT4
how is normal T4 in hyperT4 cats described
daily fuctuation
euthyroid sick syndrome
hyper T4 cats may have normal in top ½ of range
if everything else fits with hyperthyroidism, but total T4 is still within normal limits, what do you do?
repeat total T4
free T4 and TSH
T3 suppression
utimately scintigraphy
describe free T4 by equilibrium dialysis
$$
more sensitive than total T4
more false positives (different from dogs)
may be increased in sick patients
most useful in strong suspects with normal T4
describe TSH testing
expected to be very low with hyperthyroidism
canine TSH is not feline TSH is not human TSH
feline closer to canine
what is the theory of the T3 suppression test
T3 should inhibit TSH production and should decrease T4
following T3 administration, T4 should be <50% baseline in normal cats, minimal suppression in hyperthyroid cats
how is nuclear scintigraphy performed
radioactive isotope administered I-123 (half life 8.1 days) or Pertechnetate (HL 6 hrs )
gamma emission then quantified
what is the use of nuclear scintigraphy in diagnosing hyperthyroidism
confirms
unilateral vs biateral
identifies ectopic tissue (surgery is not an option)
helps differentiate adenoma from carcinoma
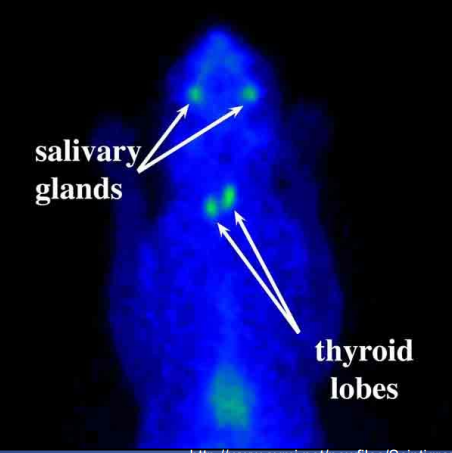
describe the scintigraphy
normal
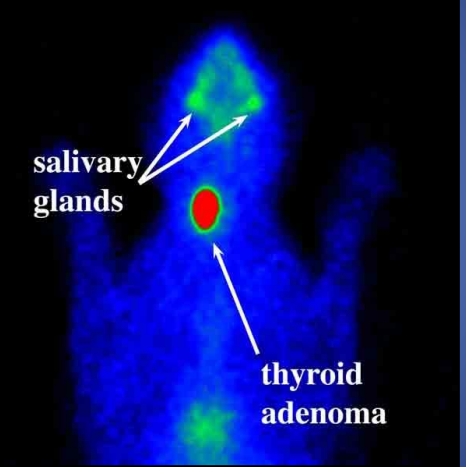
describe the scintigraphy
unilateral adenoma
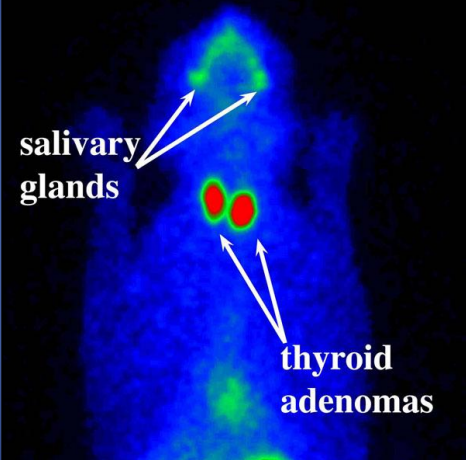
describe the scintigraphy
bilateral adenomas
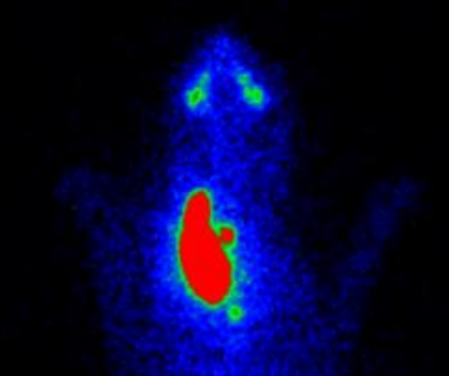
describe the scintigraphy
thyroid carcinoma
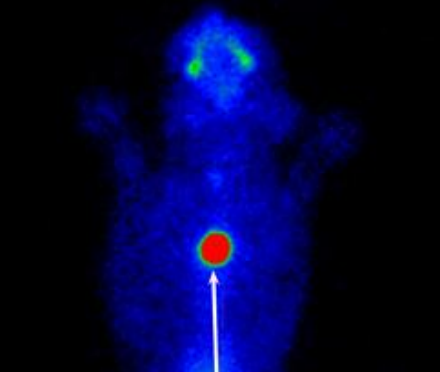
describe the scintingraphy
ectopic thyroid adenoma