AP Psych Unit 1: Brain Parts and Functions
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Brainstem
The brain’s oldest region that controls automatic survival functions and links the brain with the spinal cord.
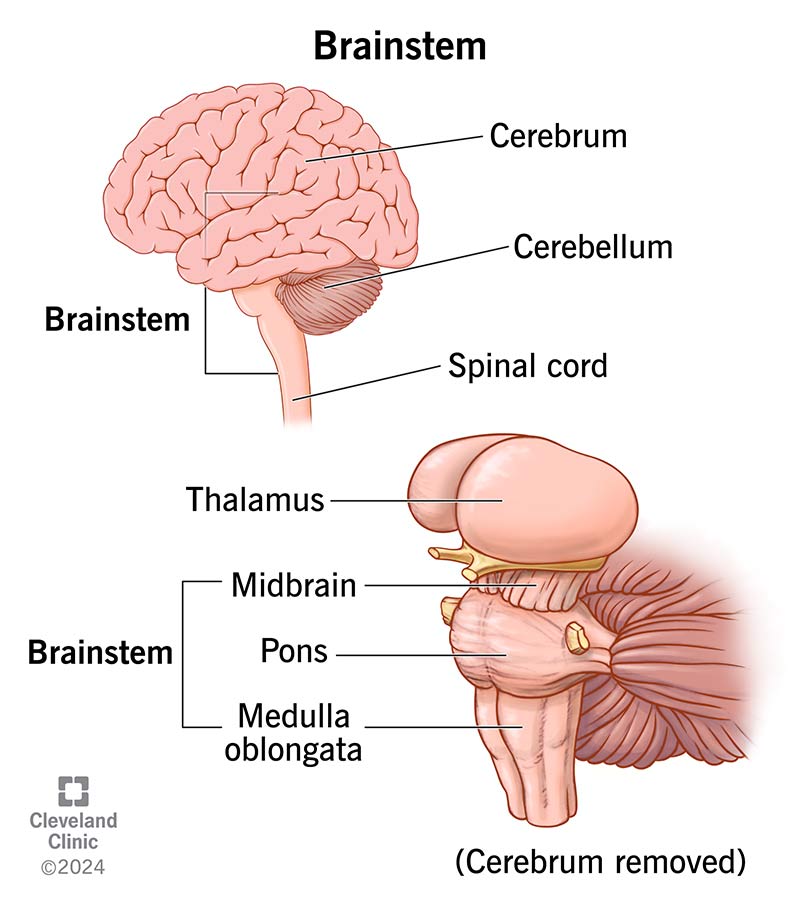
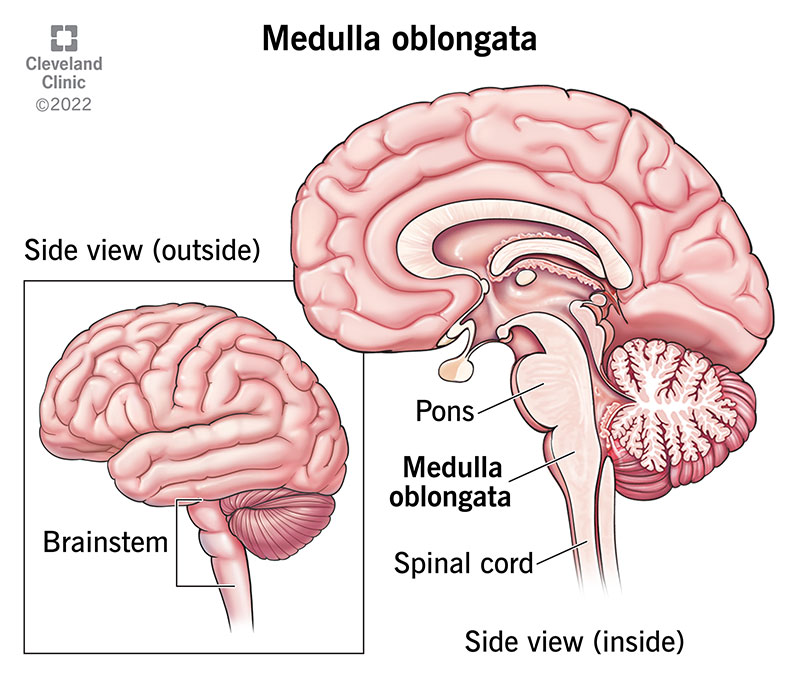
Medulla
The base of the Brain stem that controls heartbeat and breathing
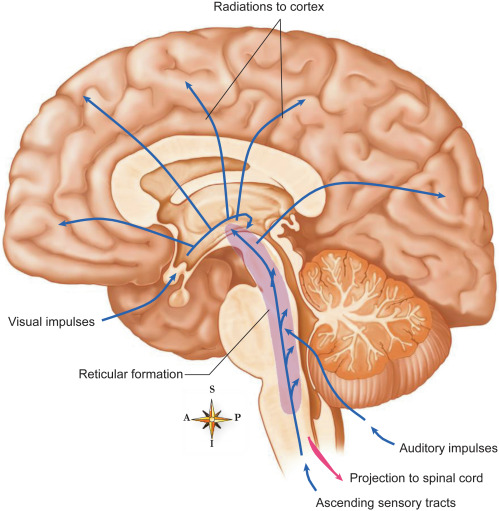
Reticular activating system
a network in the Brain stem that controls arousal and alertness by filtering incoming stimuli.
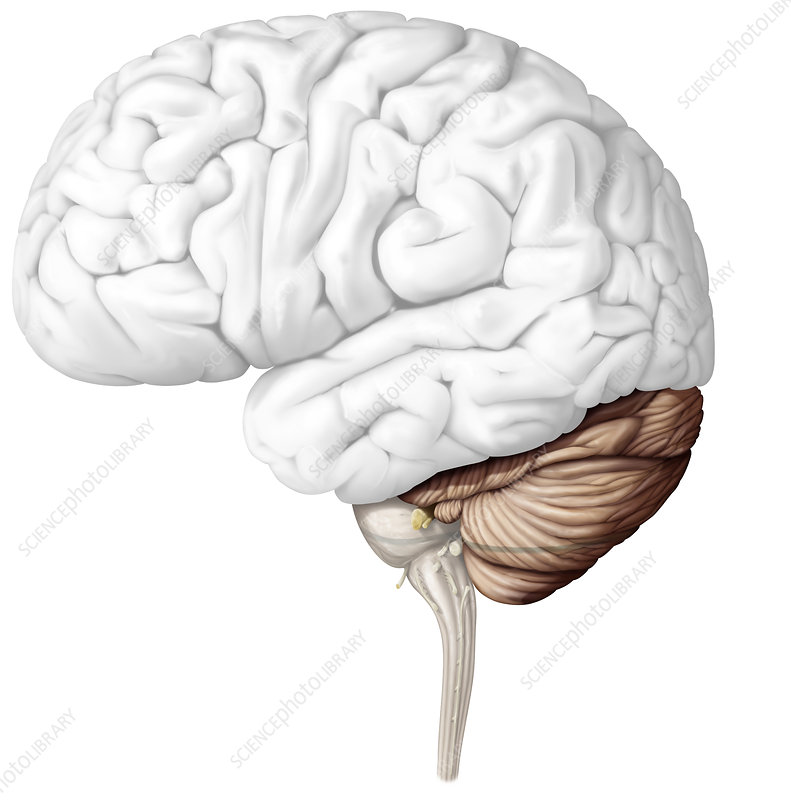
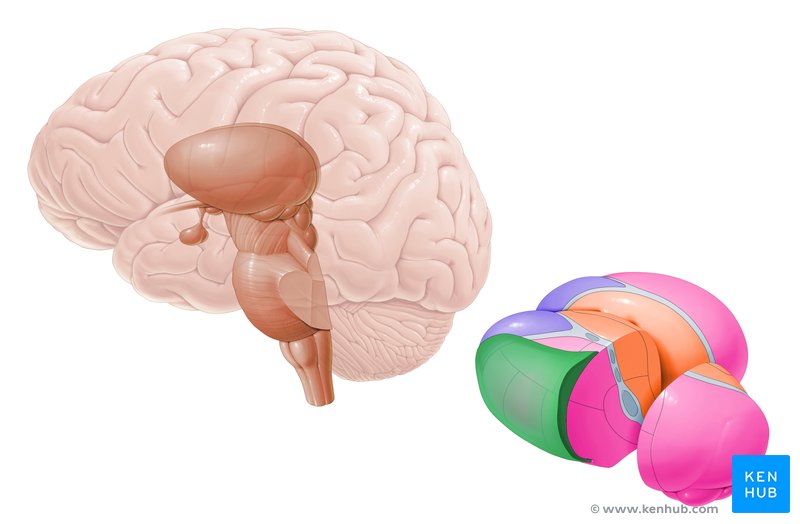
Cerebellum
coordinates balance, movement, and fine motor skills.
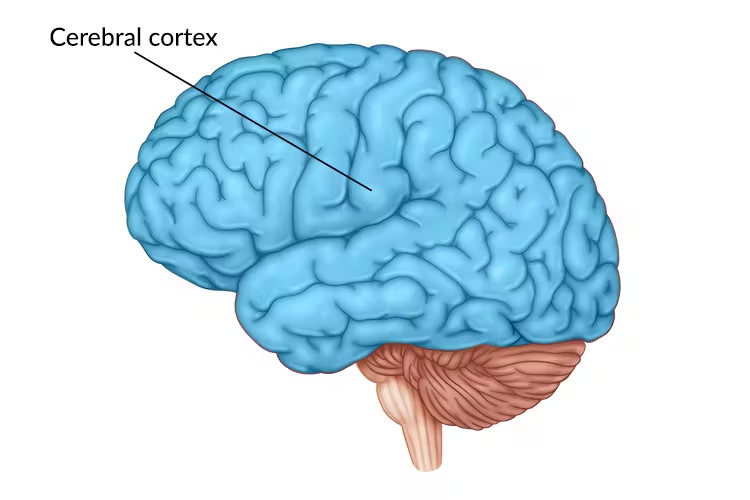
Cerebral Cortex
the brains outer layer of neural tissue that controls higher level thinking, perception, and decision making.
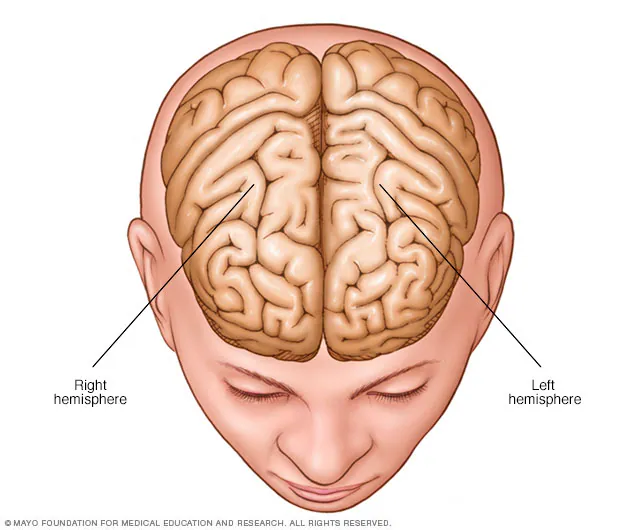
Hemispheres
the 2 halves of the brain- left and right- that control opposite sides of the body and specialize in different functions.
Limbic System
neural system located mostly in the fore brain that includes a group of brain structures involved in emotion and drives.
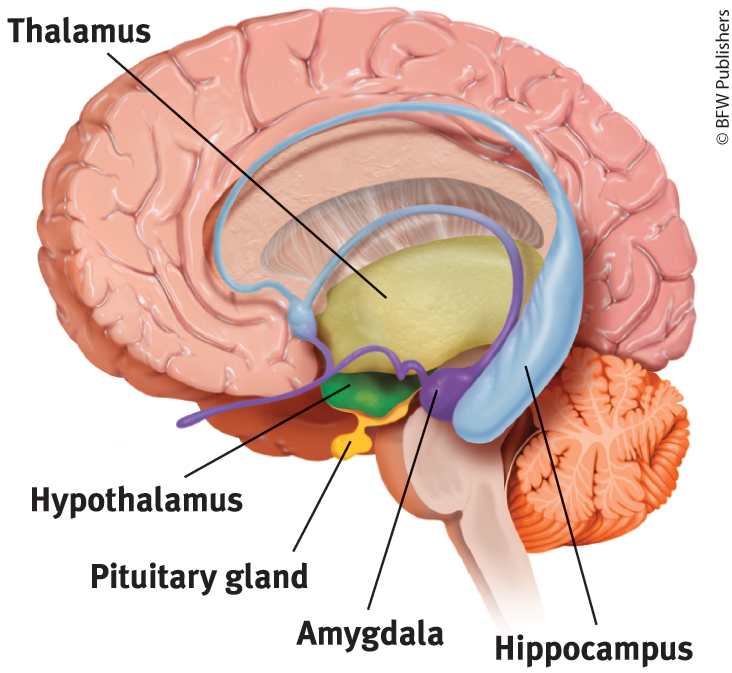
Brain structures in Limbic system
amygdala, hypothalamus, hippocampus, thalamus, and pituitary gland
Thalamus
the brain’s sensory relay system, directs incoming sensory messages to the correct areas in the brain.
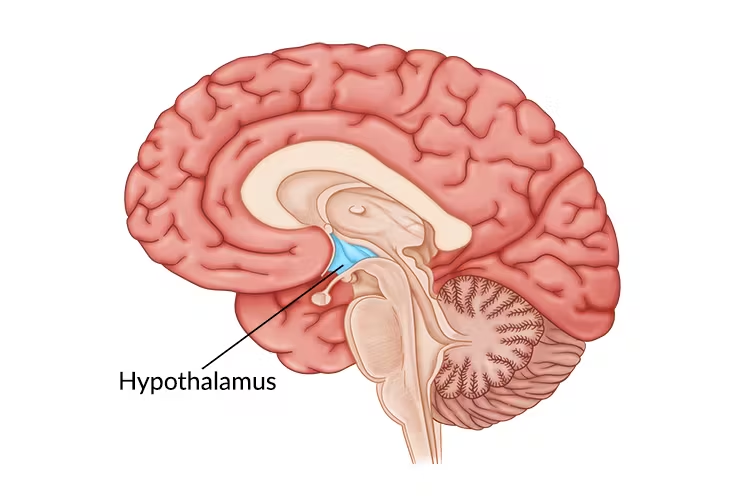
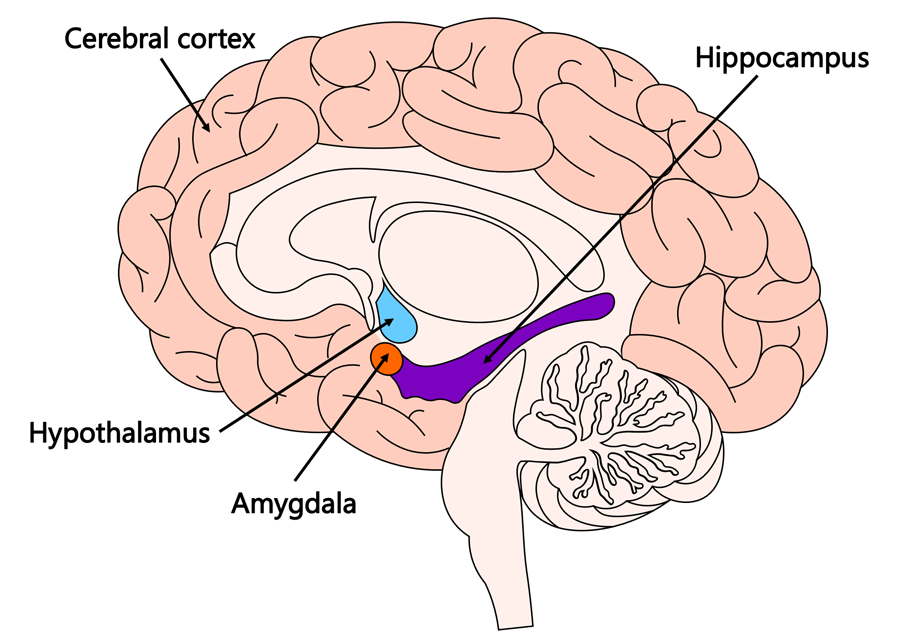
Hypothalamus
directs several maintenance activities and helps govern the endocrine system; linked to emotion and reward.
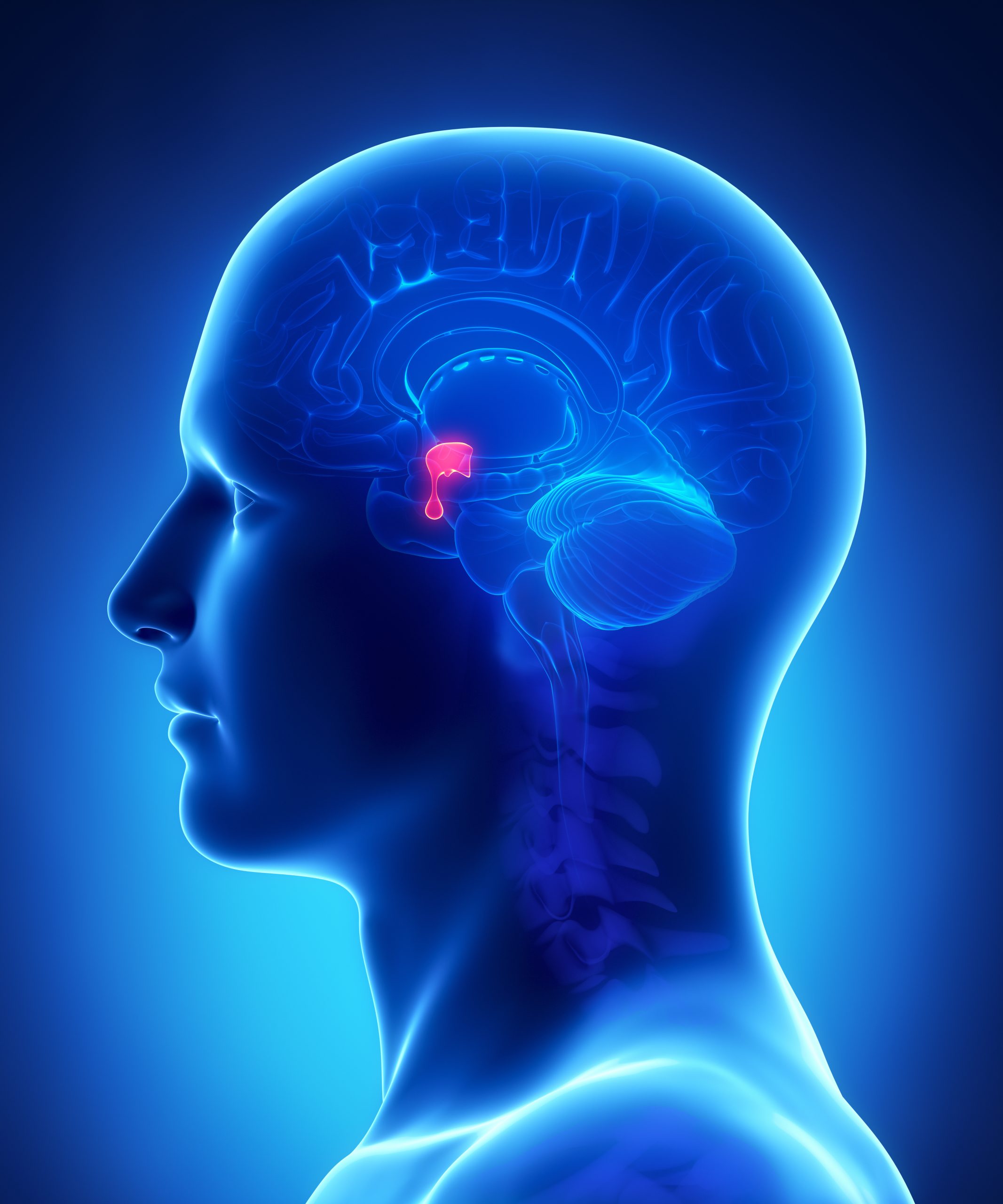
Pituitary gland
the master gland of the endocrine system that controls hormone release and regulates other glands.
Hippocampus
located in the limbic system, helps process explicit memories for storage.
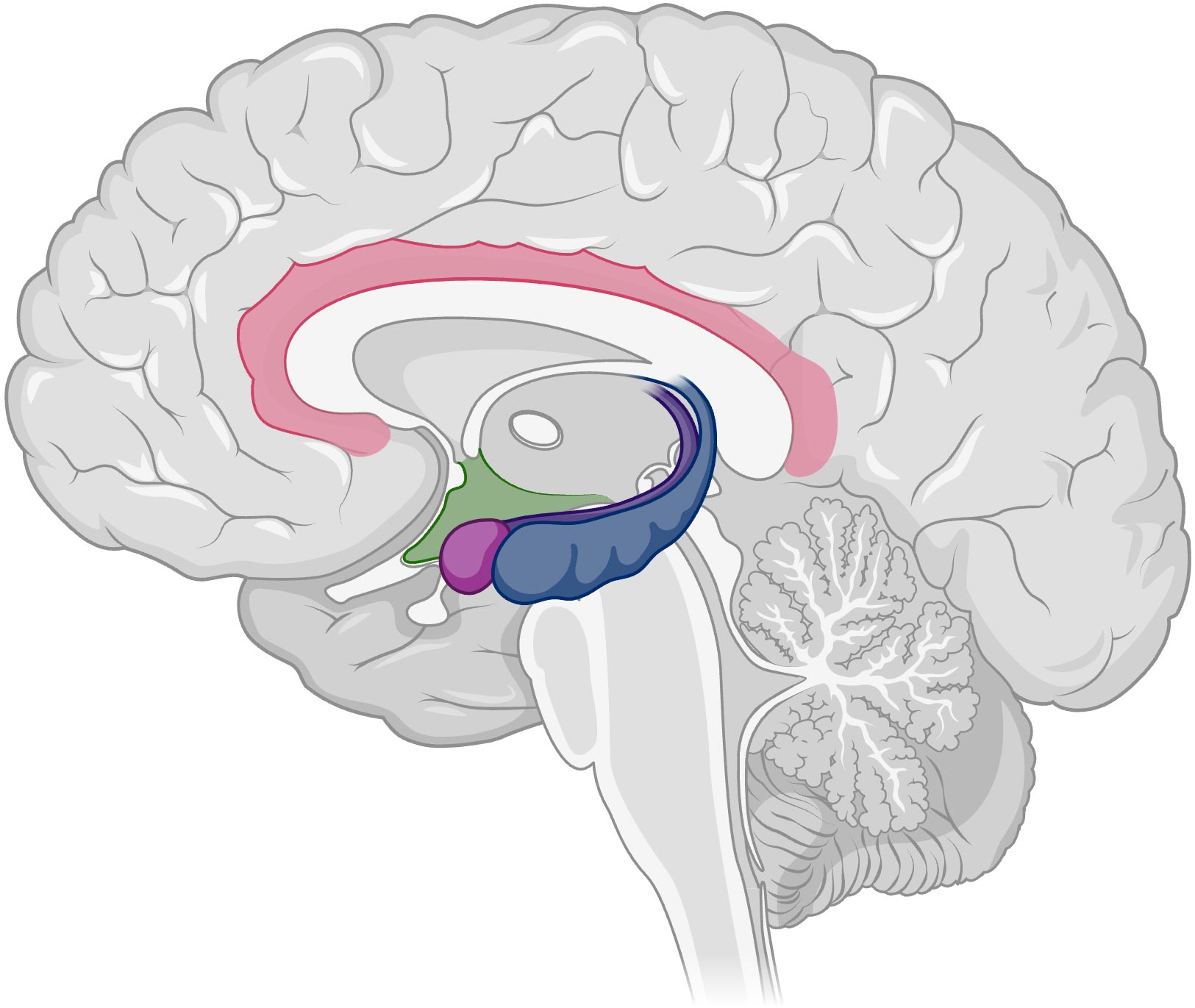
Amygdala
2 Lima bean size neural structures in the limbic system; linked to emotion
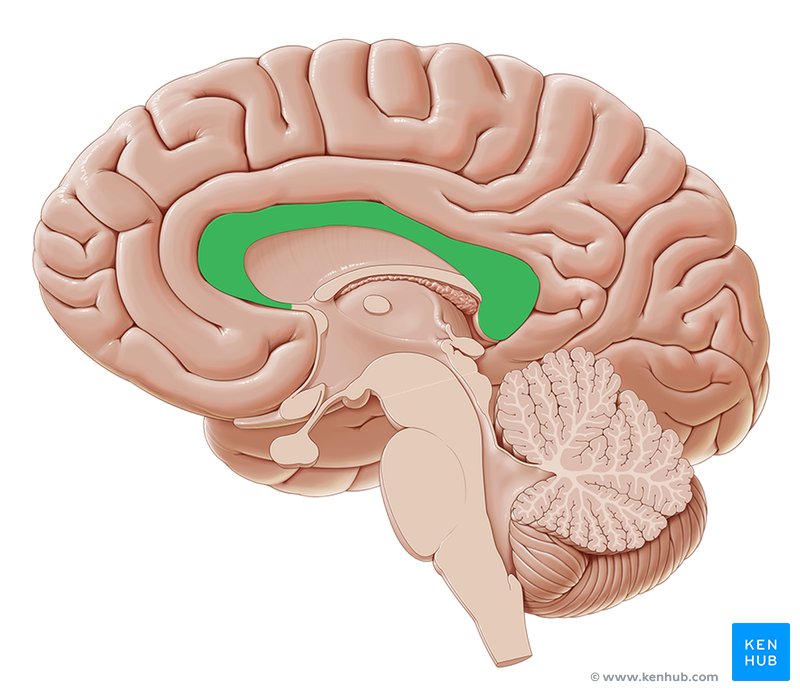
Corpus Callosum
thick band of neural fibers that connect the left and right hemispheres of the brain, allowing them to communicate and share info
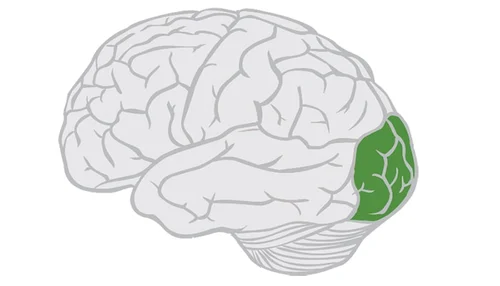
Occipital lobes
portion of cerebral cortex lying at the back of the head, includes areas that receive info from visual fields
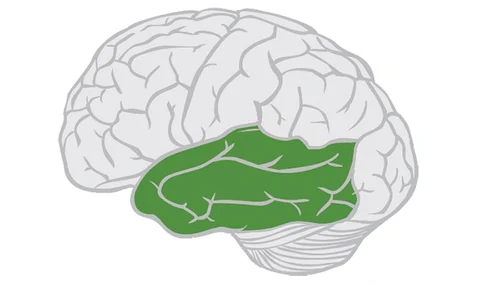
Temporal lobes
part of celebral cortex located on sides of the Brain that processes auditory info and language composition
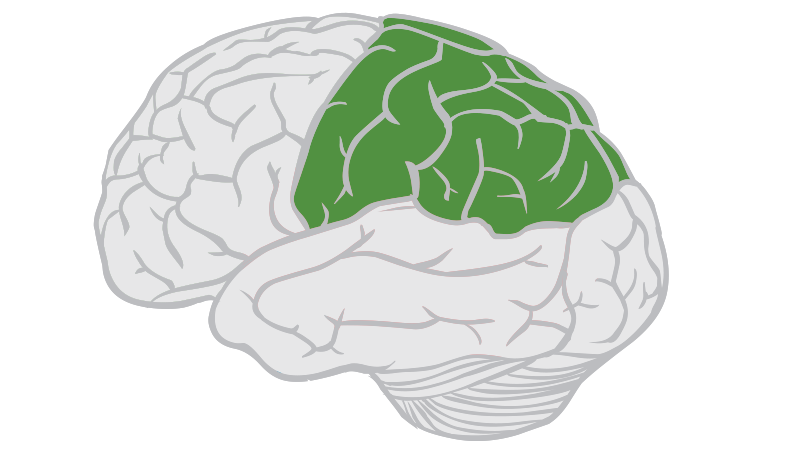
Parietal lobes
part of celebral cortex at the top and back of the brain that processes sensory info and spatial awareness
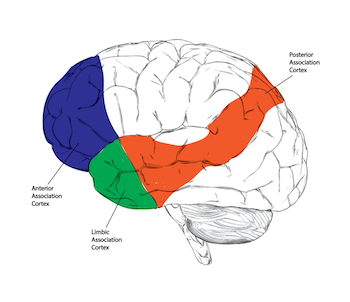
Association areas
areas of the celebral cortex that are involved in higher mental functions
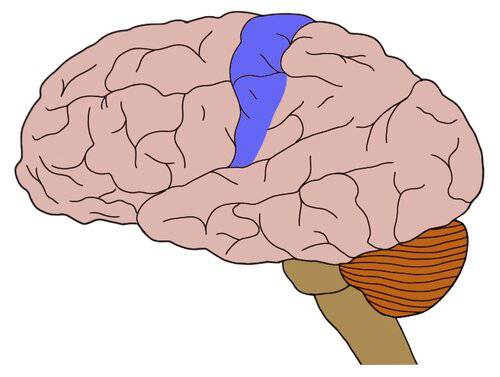
Somatosensory cortex
area of parietal lobe that processes touch, pressure, pain, etc
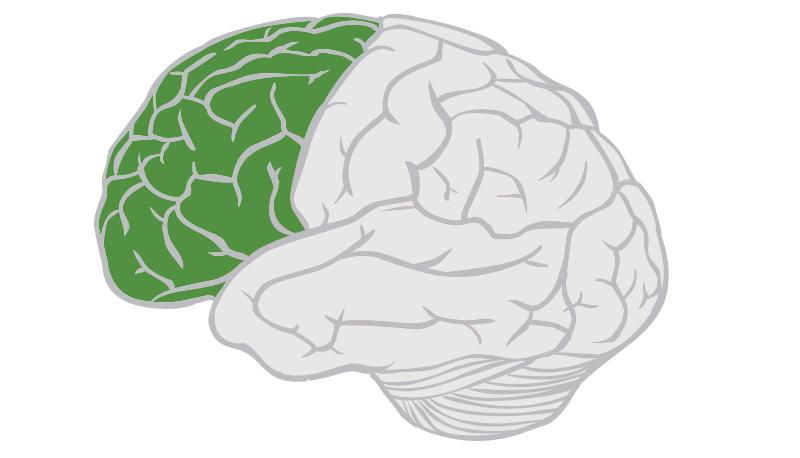
Frontal lobes
portion of celebral cortex lying behind the forehead that controls movement, higher order thinking, and executive functioning
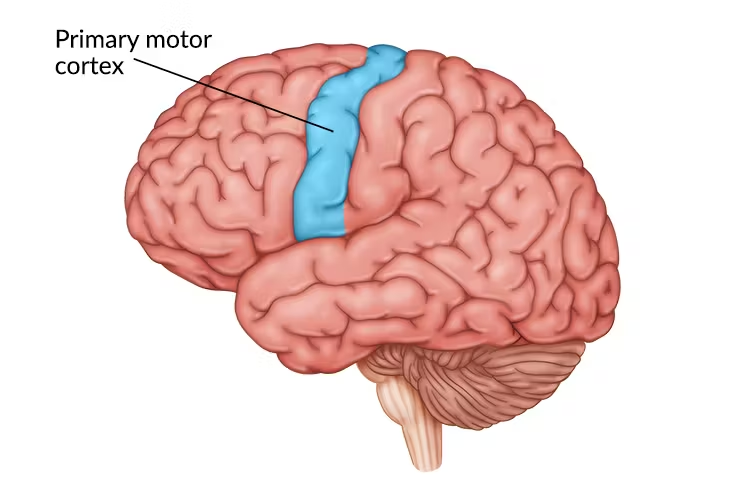
Motor cortex
area of the frontal lobe that controls voluntary movements
Prefrontal cortex
front part of the frontal lobes that enables judgement, planning, and social interactions
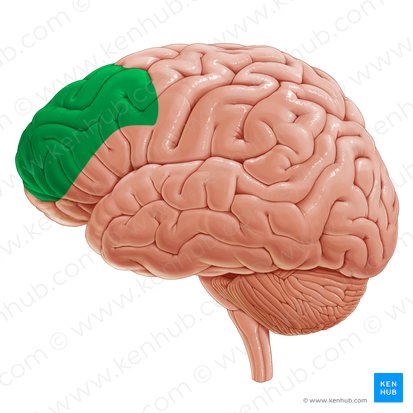
Broca’s area
part of the frontal lobe that controls speech production
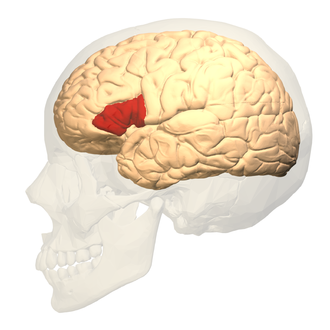
Wernickle’s area
part of the temporal lobe that comprehends and understands language
Split-brain
condition in which the corpus callosum is severed, so the 2 hemispheres of the Brain cannot communicate
Cortex specialization
different parts of the cerebral cortex have specialized functions
Contralateral hemispheric organization
the brains left hemisphere controls the right side of the body, and the right hemisphere controls the left side
Aphasia
loss or impairment of language ability due to brain damage