L8: Amino acid synthesis
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Are amino acids stored in the body?
No
Is there a protein that has a sole function as a supply of amino acids for future use?
No
How is nitrogen obtained for human body?
Nitrogen enters the body mostly as amino acids in dietary proteins
How does nitrogen leave the body?
Nitrogoen leaves the body as Urea, Ammonia, and other products
Explain the concept of amino acid pool
It refers to the very small amount of free amino acids in body (90-100g). Whatever is removed has to be replaced (steady state).
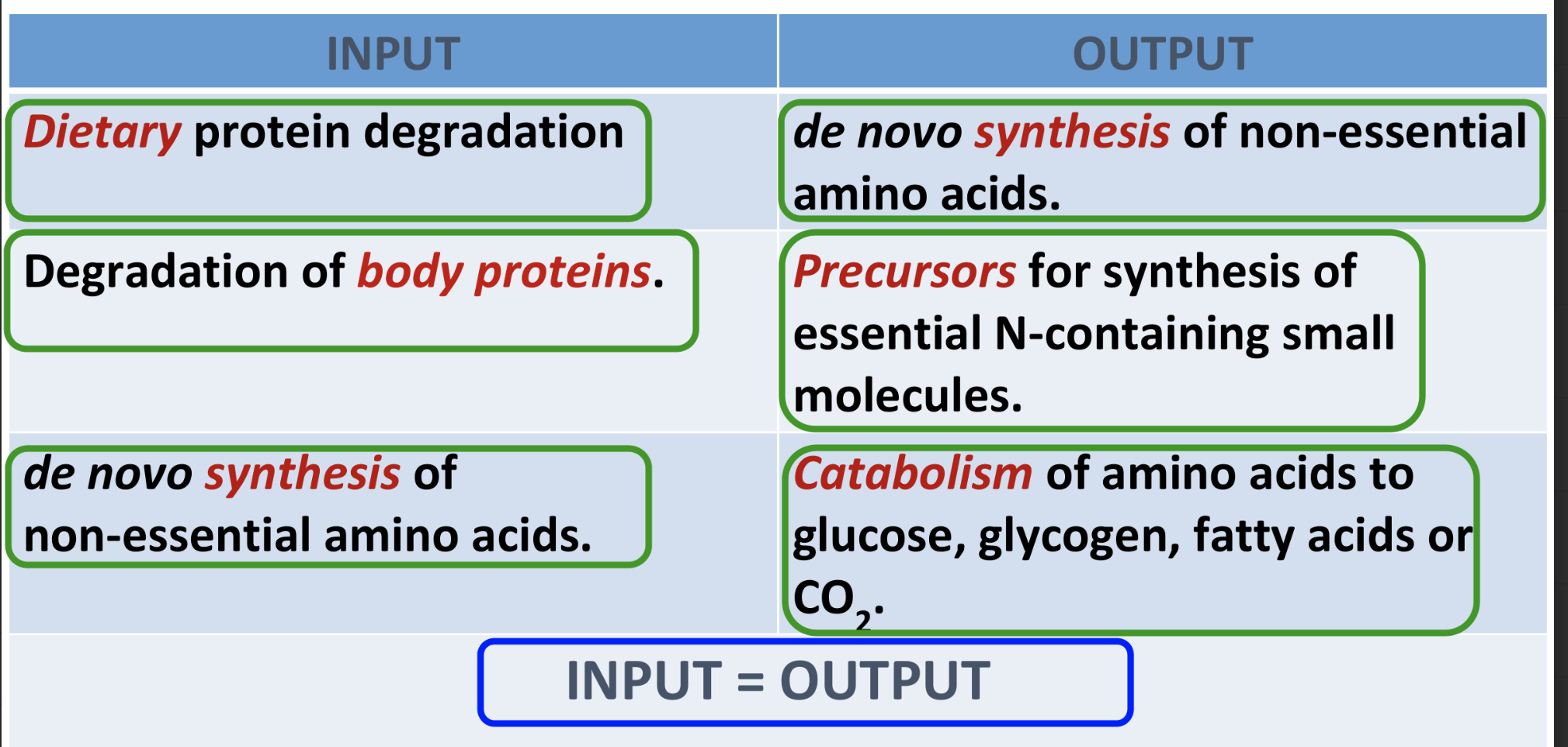
Explain the concept of protein turnover
A constant synthesis and degradation of proteins in the body
Why: To remove abnormal and unwanted proteins
Total amount of proteins in the body should remain constant
Why: There is a need to replace short-lived proteins
What is the function of absorbed amino acids?
Energy source
Used for protein synthesis in the liver and other tissues
Excess a.a. are converted to glycogen and triacylglycerols for storage
Is amino acid metabolism more complex than carbohydrate and lipid metabolism?
Yes.
Describe the general pathways for amino acid catabolism for C atoms and N atoms.
Amino acid is split into carbon rich and nitrogen rich molecules
Carbon atoms → Krebs cycle and acetyl CoA → CO2 + H2O → generate energy
Nitrogen atoms → Synthesis of proteins in liver and other tissues
Amino acid synthesis has ______ pathways for different amino acids.
Amino acid synthesis has different pathways for different amino acids.
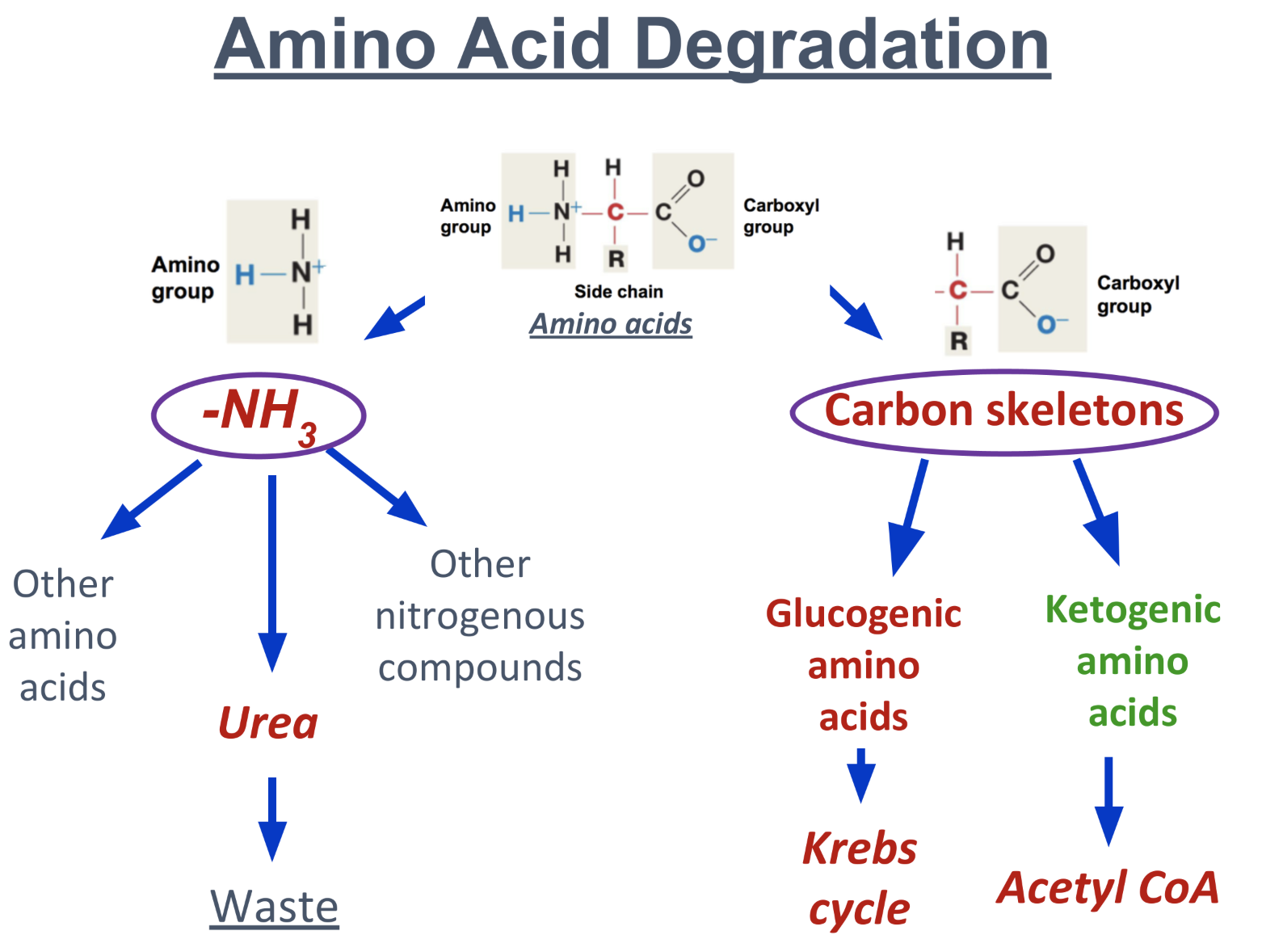
What does amino acid form when broken down?
Broken down into 2 parts
Amino group NH3
used for synthesis of other a.a.
forms urea, excreted as waste
forms other nitrogenous compounds like nitrogenous base of nucleotides
Carbon skeleton
of Glucogenic a.a: enters kreb cycle for ATP synthesis
of Ketogenic a.a: broken down into acetyl CoA
How are ketone bodies detoxified?
Urea cycle
What happens to amino group during break down of a.a.?
Presence of α-amino group prevents amino acids from oxidative breakdown
Removal of α-amino group involves 3 steps:
Transamination
Oxidative deamination
Urea cycle
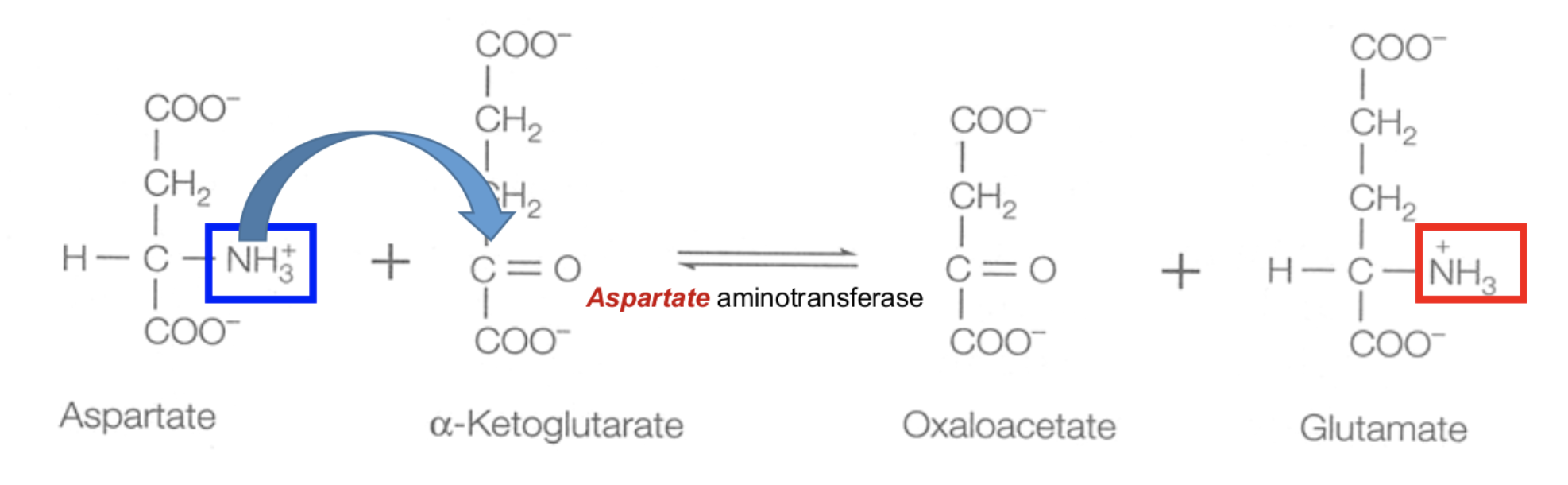
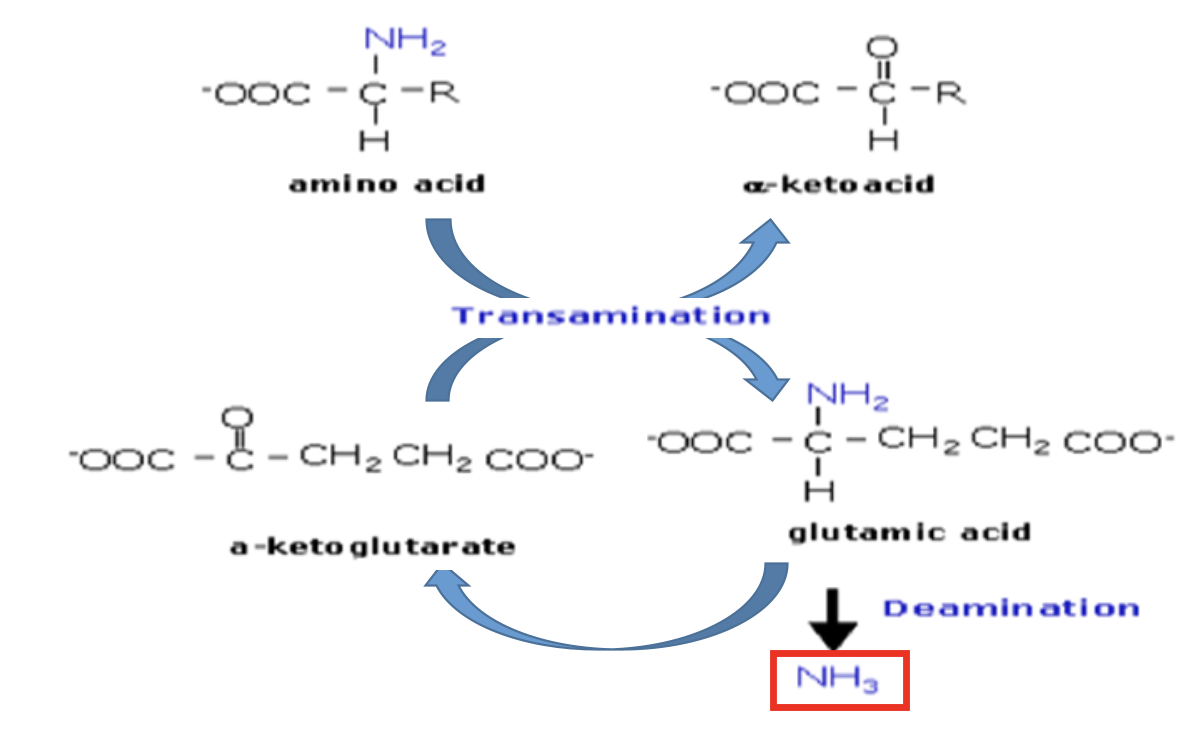
Explain Step 1 of removal α-Amino Group: Transamination
Transamination
For most amino acids, the α-amino (–NH2) group is transferred to α-ketoglutarate.
amino acid + α-ketoglutarate (via aminotransferase) → glutamate + α-keto acid
This is a reversible rxn
Write the reaction equation for transamination of aspartate.
C=O and H-C-NH3+ swap places
Write the reaction equation for transamination of alanine
C=O and H-C-NH3+ swap places
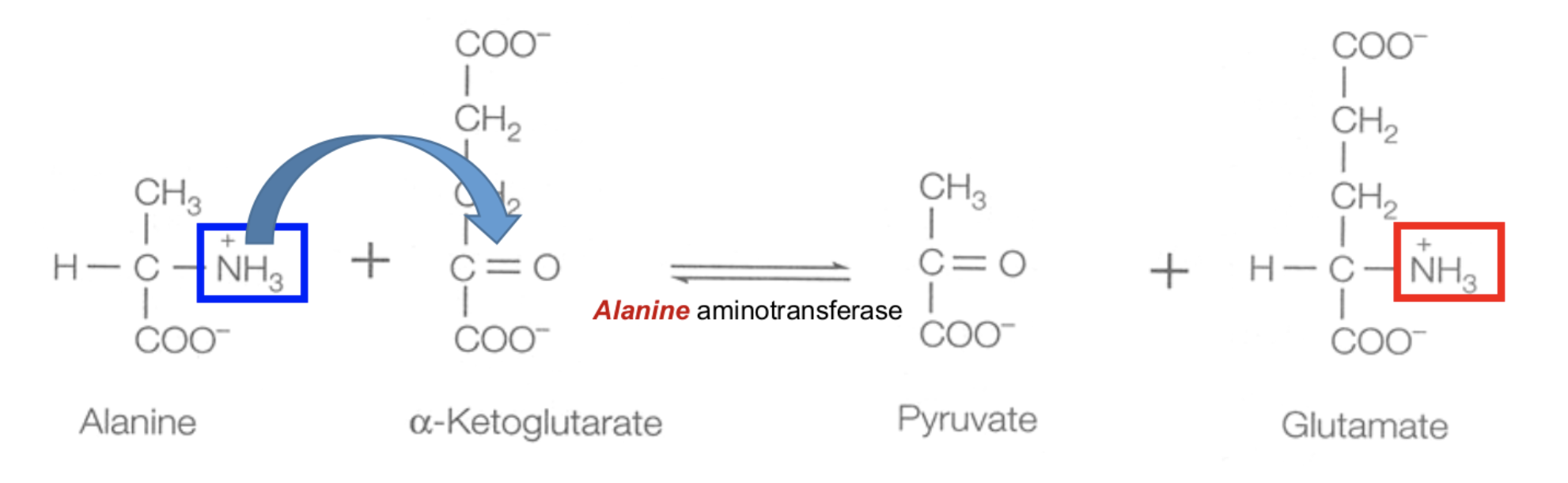
What is the enzyme used for transamination?
Amino acid name + aminotransferase e.g. alanine aminotransferase
What are aminotransferases?
Intracellular liver enzymes
Substrate specific: Specific only for one amino acid
Named after amino acid it works on (the amino acid group donor)
e.g. Alanine aminotransferase (ALT), Aspartate aminotransferase (AST)
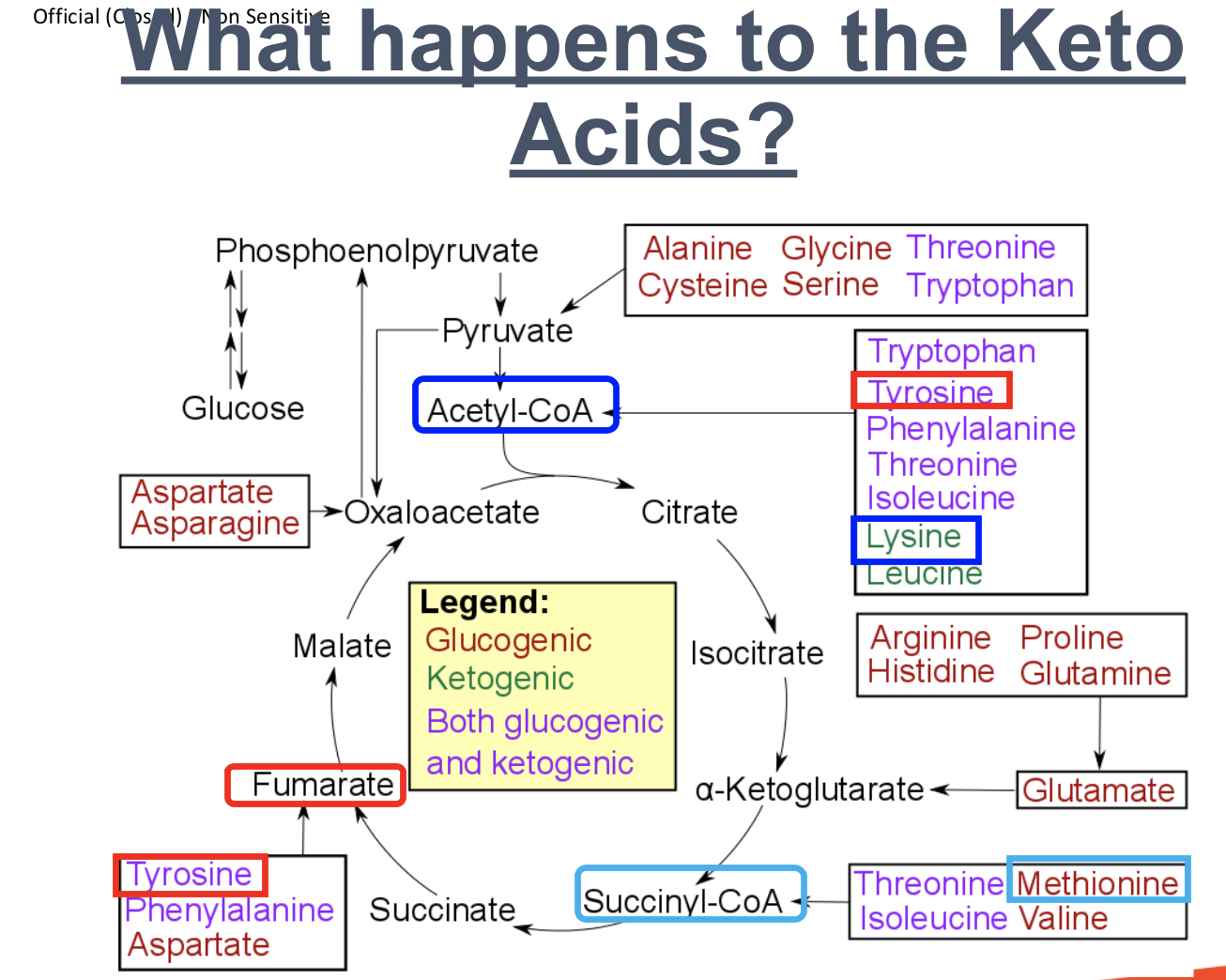
What keto acids can be formed from transamination and what happens to them after?
The remaining carbon skeleton will eventually be
converted into one of the following seven keto
acids:
Pyruvate
Acetyl CoA
Acetoacetyl CoA
α-Ketoglutarate
Succinyl CoA
Fumarate
Oxaloacetate
These keto acids are subsequently converted to glucose or ketone bodies
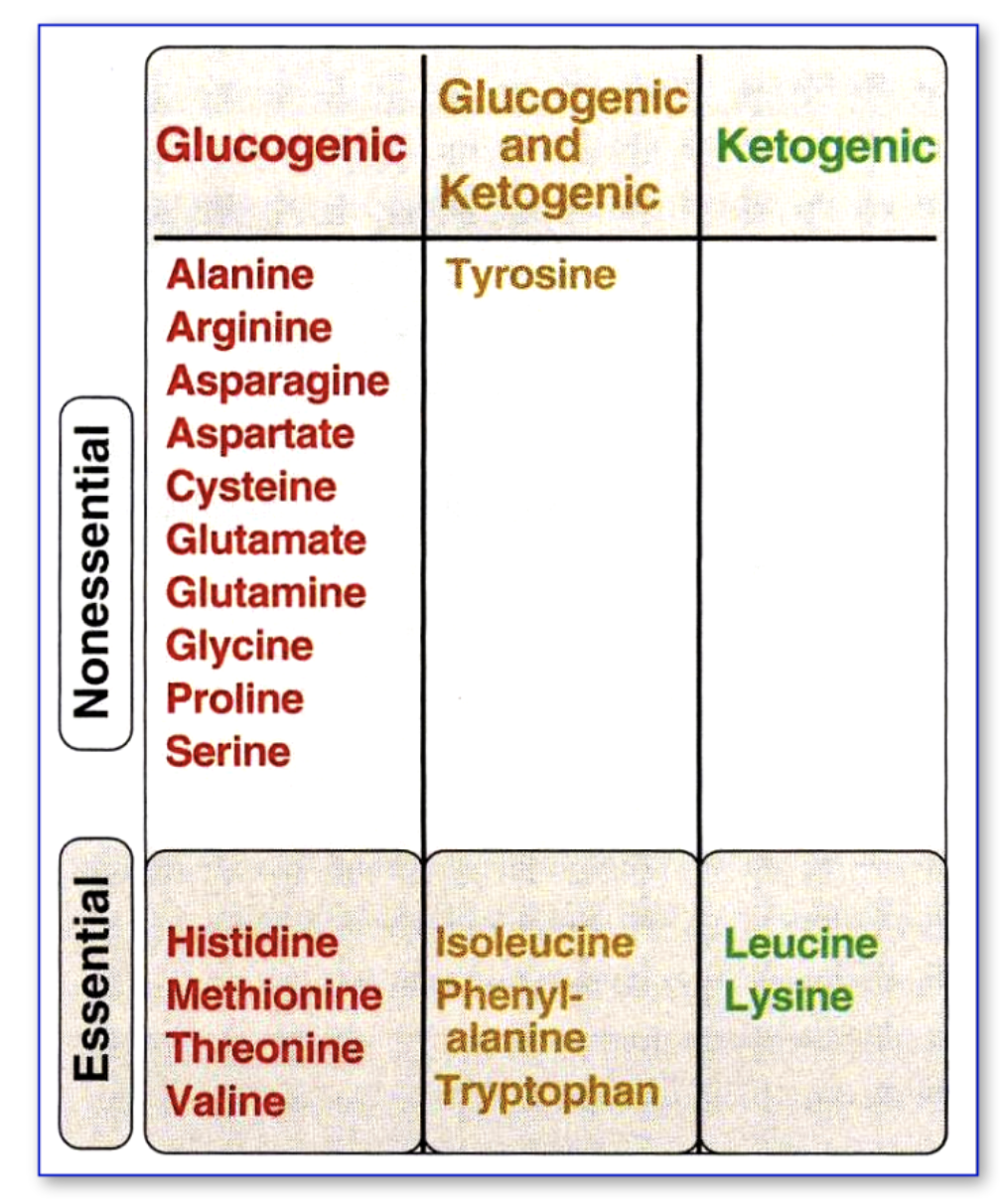
What are the 3 categories of amino acids in terms of breakdown?
After transamination, amino acids formed can be classified as:
Glucogenic: converted to glucose
Ketogenic: converted to ketone bodies
Both glucogenic and ketogenic: converted to either glucose or ketone bodies
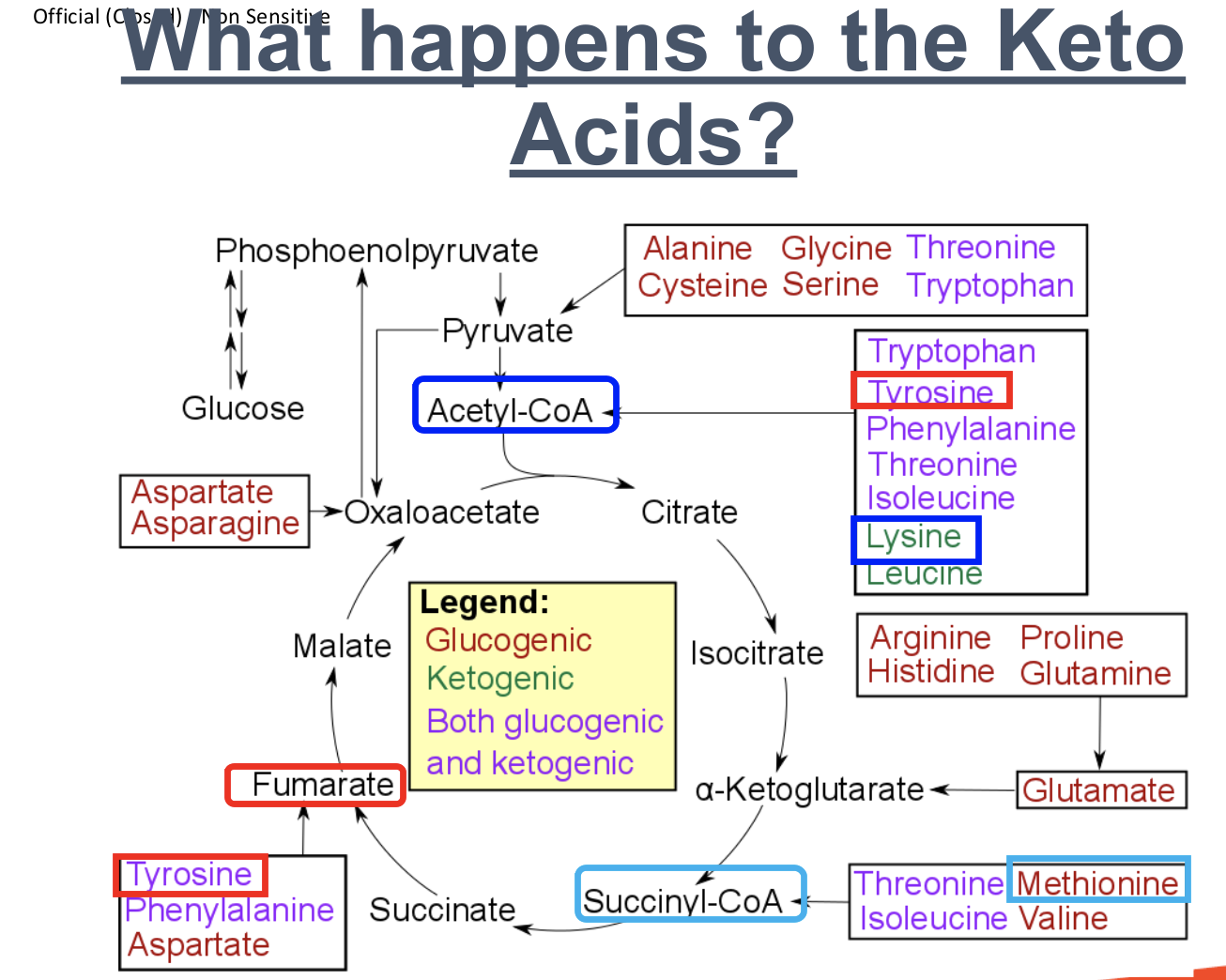
What happens to the Keto acid Methionine (Glucogenic)?
Methionine (Glucogenic)
Methionine undergoes transamination to form amino group and carbon skeleton
Carbon skeleton converted to the keto acid, Succinyl-CoA
Succinyl-CoA enters Krebs cycle, is converted to succinate → fumarate → malate → oxaloacetate
Oxaloacetate converted to phosphoenolpyruvate
Phosphoenolpyruvate converted to glucose
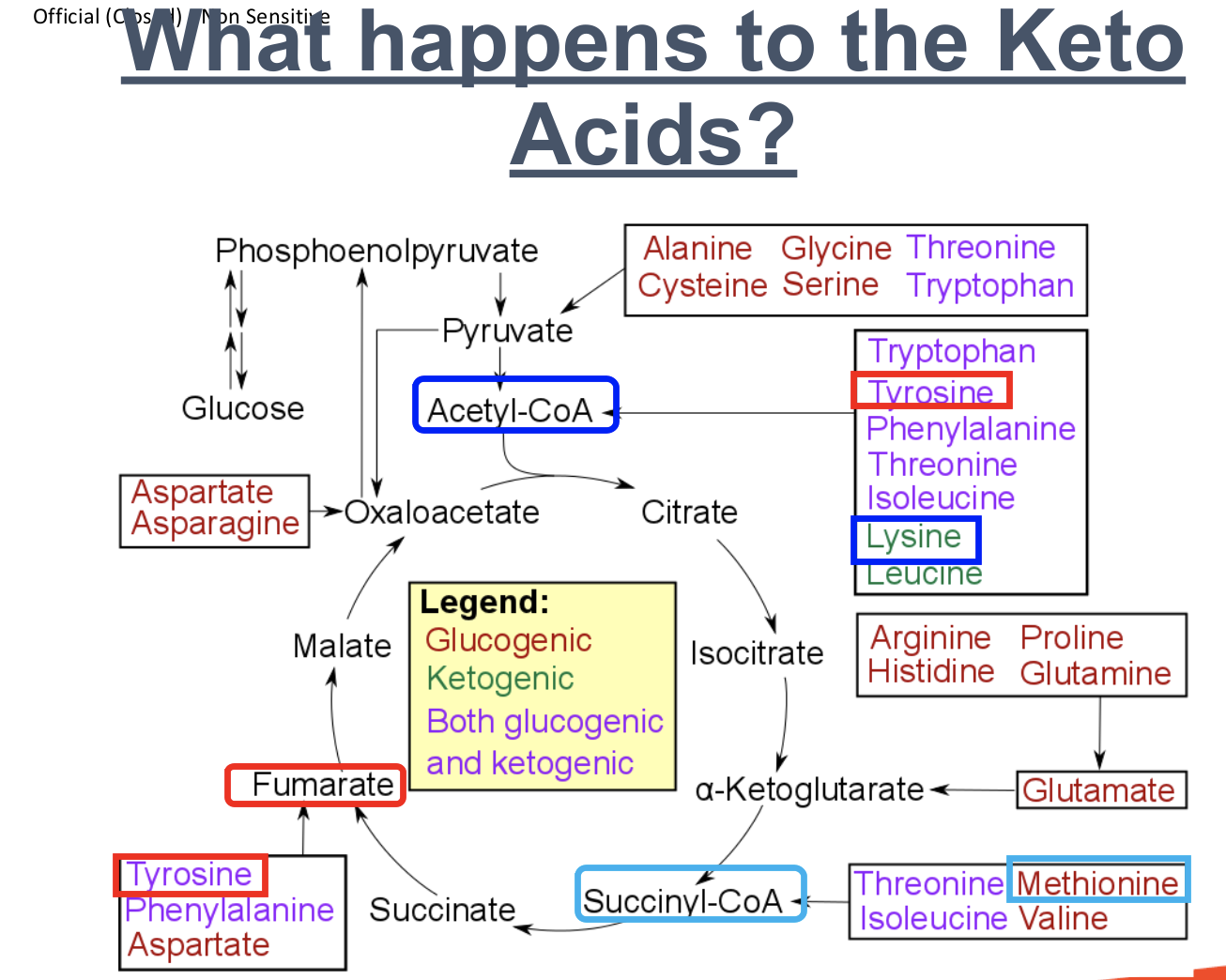
What happens to the Keto acid, Lysine (Ketogenic)?
Lysine (Ketogenic)
Lysine undergoes transamination to form amino group and carbon skeleton
Carbon skeleton is converted to keto acid, acetyl-CoA
acetyl-CoA is converted to ketone body
What happens to the Keto acid, Tyrosine (Both Glucogenic and Ketogenic)?
Tyrosine (Both glucogenic and ketogenic)
1. Tyrosine undergoes transamination to form amino group and carbon skeleton.
Glucogenic pathway:
2a. Carbon skeleton is converted to the keto acid, fumarate → malate → oxaloacetate
3a. Oxaloacetate is converted to phosphoenolpyruvate
4a. Phosphoenolpyruvate is converted to glucose
OR
Ketogenic pathway:
2b. Carbon skeleton is converted to the keto acid, Acetyl-CoA
3b. Acetyl-CoA is converted to ketone body
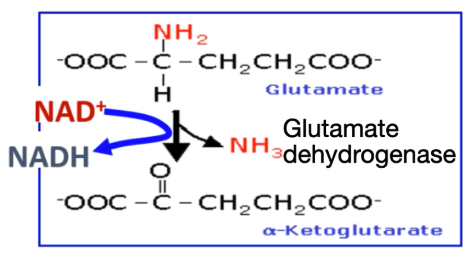
Explain Step 2 of removal of α-Amino Group: Oxidative deamination
Glutamate undergoes oxidative deamination to produce ammonia + α-ketoglutarate.
α-ketoglutarate is then used again for transamination reactions
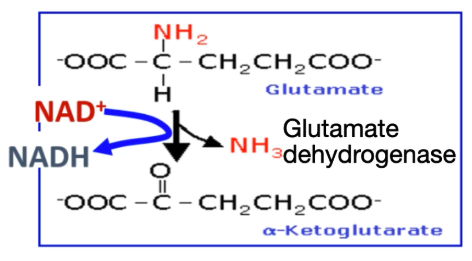
Write the reaction equation for oxidative deamination
Explain Step 3 of removal of α-Amino Group: Urea cycle.
Draw the structures involved and write out the chemical equation.
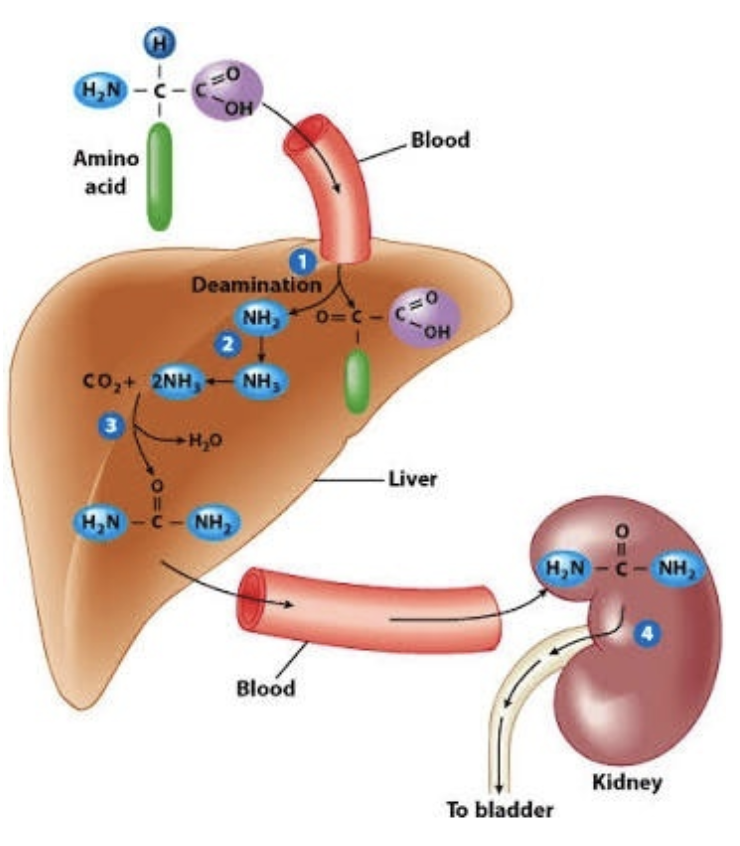
Ammonia enters urea cycle,
Ammonia is converted to urea. Urea is excreted from the body as urine
Urea cycle
Requires CO2, aspartate and 3ATP
Produces urea and fumarate.
Occurs partly in mitochondrial matrix, partly in cytosol
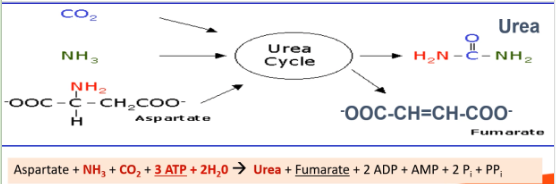
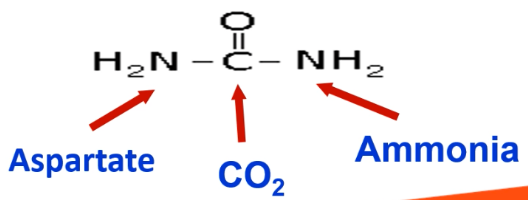
Draw out the structure of urea and state where each component is from
Carbonyl group is from CO2.
One -NH2 group is from ammonia.
Another -NH2 group is from aspartate.
What is the fate of urea?
Diffuses from the liver into bloodstream
Transported in the blood to the kidneys
In kidneys, filtered and excreted in urine
From what are the 10 non-essential amino acids synthesised from?
From intermediates of glycolysis:
Serine, Glycine, Alanine
From intermediates of the Krebs cycle:
From Oxaloacetate:
Asparagine, Aspartate
From α-Ketoglutarate:
Glutamate, Glutamine, Proline, Arginine
From other (essential) amino acids:
From Phenylalanine:
Tyrosine
From Methionine:
Cysteine
Draw the diagram for amino acid degradation (Transamination, Oxidative deamination)
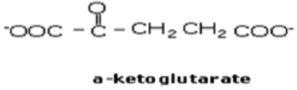
Draw the structure of α-ketoglutarate
Same structure as glutamate, just that H-C-NH3+ is swapped for C=O