Groundwater Midterm
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
What process moves water from the surface to the subsurface?
Infiltration
What process moves water within the subsurface?
Percolation
What process moves water from ground water to the atmosphere?
Evapotranspiration
What process moves water from glaciers to the atmosphere?
Sublimation
What process moves water from the biosphere to the atmosphere?
Transpiration
What process moves water from ground water to streams?
Seepage
Weight
Mass x gravity(9.81 m/s²)
Porosity
Proportion of a rock or sediment that is open space, not necessarily connected
Permeability
Ability of a rock to allow the passage of fluid through material
Measure of the rate at which water can flow through a rock.
Which has a greater effect on porosity, grain size or packing?
Packing, the more packed the less space is between particles.
Which has a greater effect on porosity, grain size or sorting?
Sorting because larger grain sizes can be sorted in such a way to eliminate pores.
Transmissivity
the ability of a medium to allow the passage of water, radiation, or light, and the ease with which groundwater flows through an aquifer
Transmissivity Equation
T = Kb
K= the coefficient of permeability
b= thickness of the aquifer
Units= length² / time
Transmissivity (Theim Equation)
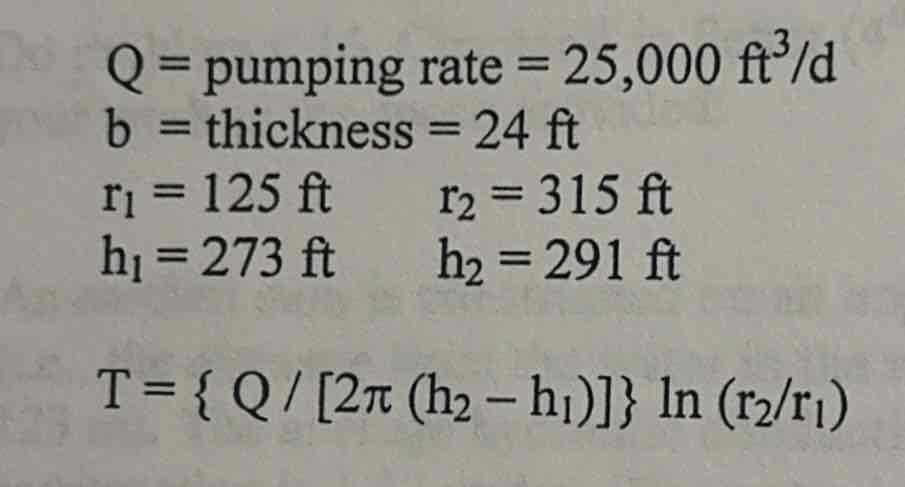
Hydraulic Conductivity
a measure of how easily water or other fluids can pass through porous materials, soils, or rocks. It's also known as the coefficient of permeability.
= K
Volume
ft³ or m³
Hydrologic Budget Equation
P = Et + RO + GWS
Darcy’s Law
Flow of fluid through a porous medium
Q= discharge
K= hydraulic conductivity

Specific yield
the ratio of the volume of water that a saturated rock or soil will yield by gravity to the total volume of the rock or soft.
Specific discharge
the volume of water that flows through a unit cross-sectional area of porous media per unit time.
Isotropic
Have the same index of refraction in all directions
ISO=equal
Uniformitarianism
The present is key to the past
Population
Growth is the biggest problem facing humanity
Pleistocene
2 m years ago - 10,000 years ago
Homogeneous
All the same
Holocene
the name given to the last 11,700 years* of the Earth's history
Pathways
Flow from high to low in broad looping curves from recharge areas to discharge areas in unconfined aquifers
In confined aquifers movement is controlled by the geometry of rock units
Speed of groundwater
Few cm to m per day
Fluid potential
Water flows through arc and soil under the influence of…
Varies from one area/ spot to another
Flow nets
Are used to show ground water flow
Exponential lines
Are roughly perpendicular to flow lines
Will never intersect
They get closer together closer to the surface or in a river were water flows faster
Artesian pressure
Allows groundwater to flow upward
Chicot Aquifer System
Largest Aquifer in Louisiana
Very thick, 500 m (1500 ft)
Lower half filled with salt water
Rocks: massive sandstone interceded with clay layers tilted south so we get water North of us
Age: Pleistocene
Problems with the Chicot Aquifer
Over 19,000 “non-hazardous” waste pits
Over-pumping
Hydrology
The study of waters of the earth; rivers, lakes, groundwater
Hydrogeology
Interaction of water with geological materials
Geohydrology
An engineering term
Where is the water?
Salt water- 96%
Fresh water- 4%
Glaciers- 3%
Groundwater- 1%
Lakes and rivers- 0.009%
Atmosphere- 0.001%
Biosphere- 0.0001%
Finding Evaporation
1) Use standard pan-evaporation data
2) Use a soil psychrometer
3) Use model estimates
4) Use a “nomograph”
5) Use a Thornthwaite Method w/T
Aquifer
Porous and permeable layer that contains and produces groundwater
Aquiclude
Or aquitard
Impermeable layer that blocks flow
Unconfined Aquifer
The permeable layer extends to the surface.
It consists of an unsaturated zone separated from the saturated zone by the groundwater table.
Confined aquifer
The permeable layer is overlain and underlain by a less permeable layer (aquitard or aquiclude)
Water Table
Is a subdued reflection of the topography
Pressure Surface
The level to which water will rise in wells in confined aquifers.
1m=
3.28 feet
1 acre =
43,560 ft
1 cm =
0.0328 feet
1 foot=
30.48 cm
Area
Pie*r²
Difference between transmissivity and hydraulic conductivity
transmissivity is the total flow of water through an aquifer, while hydraulic conductivity is the rate of flow through a unit cross-sectional area
1 mile=
5,280 feet
Four types of groundwater contamination
Salt water intrusion, agricultural products,
Two basic processes that operate to transport solutes. How do they relate to dispersion and retardation?
Recharge areas
Topography: high
Water table depth: deep
Vadose zone size: thick
GW movement: down
Flow line configuration: diverge
Discharge area
Topography: lows
Water table depth: shallow
GW movement: up
Flow line configuration: converge
Other clues: wet, vegetated
Regional
Recharge area size: small
Depth:width (ratio): 1:2
Water volume: bigger
Temperature: hotter
Composition (TDS): High
Local
Recharge area size: big
Depth:width (ratio): 1:5-1:10
Water volume: smaller
Rate of water movement: quick
Temperature: cooler
Composition (TDS): fresh
Chico aquifer
Southwest Louisiana
Sandstone with clay layers
Pleistocene
Faults
500 meters
Flows south a few cm a day
Flow systems
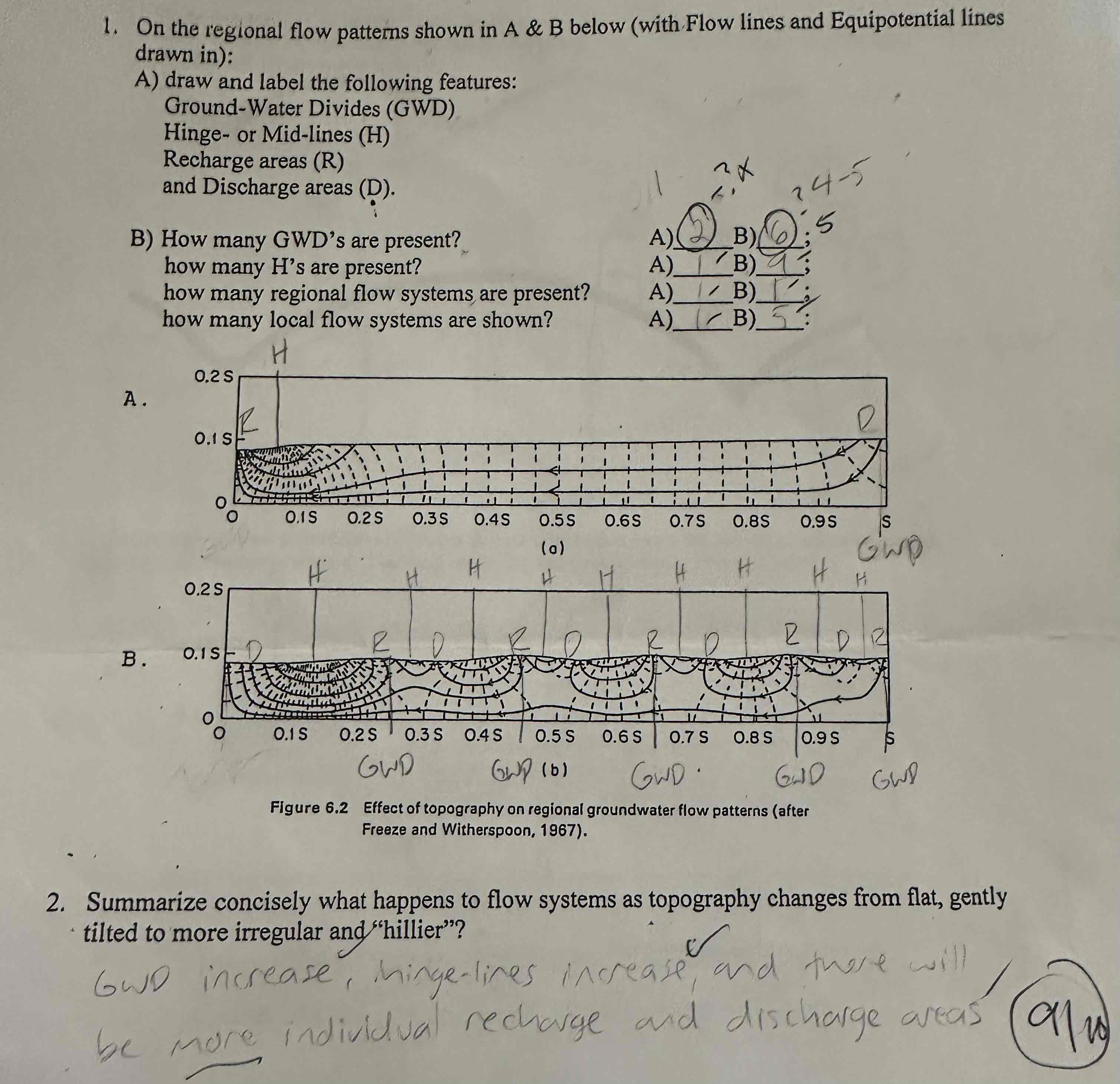
What happens to flow systems as topography changes from flat, gently tilted to more irregular and “hillier”?
GWD increase, hinge-lines increase, and there will be more individual recharge and discharge area.
Reductive desorption
a process where arsenic, often bound to iron oxides in soil or sediment, is released into water due to a reduction in the oxidation state of the iron, causing the arsenic to detach and become mobile in the water
Hydrologic Gradient
Dh/dl