Microtubules
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Micro-tubules are polymers of the protein _______. The ______ subunit is a _______ formed from two closely related globular proteins called ______ and ______
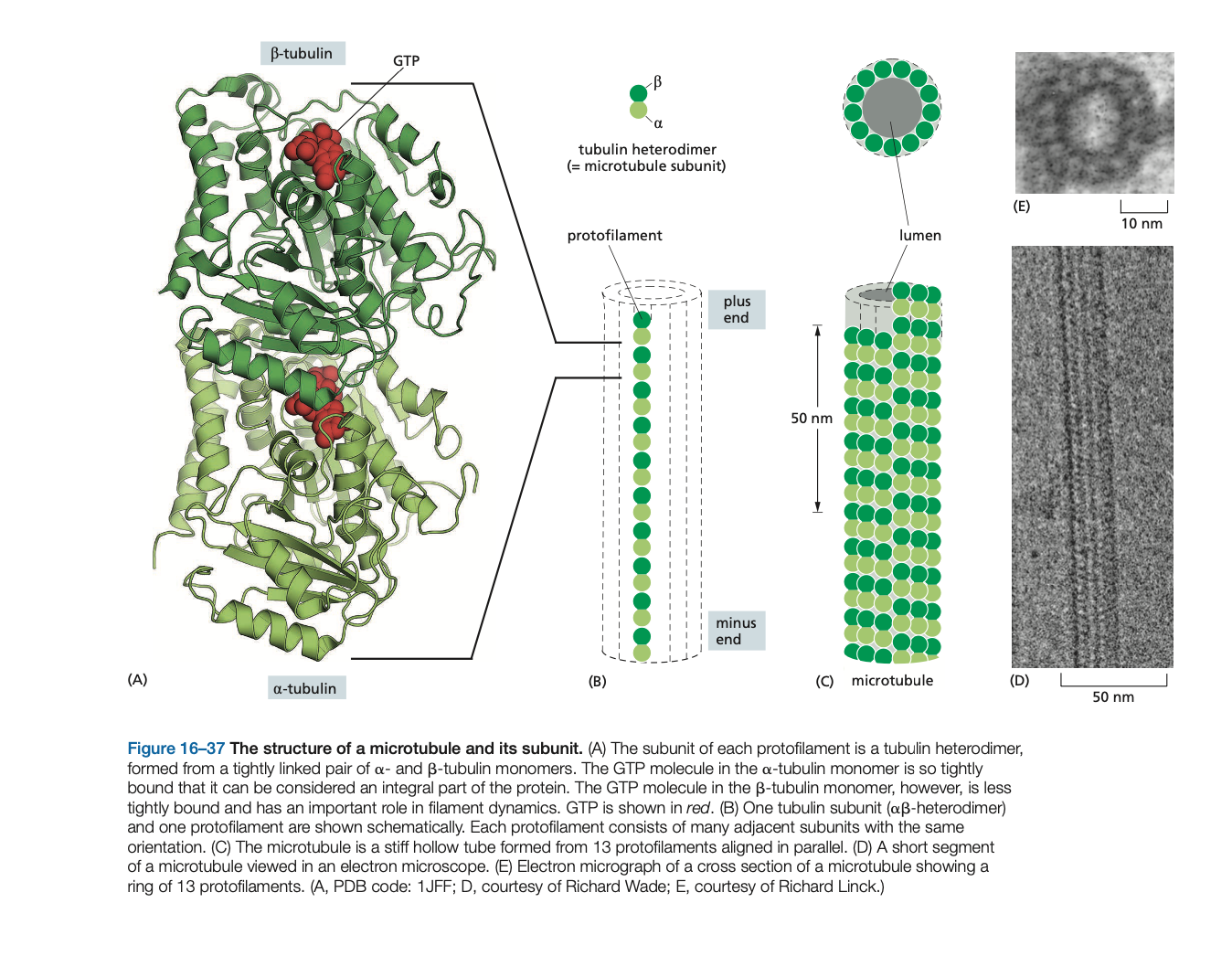
Micro-tubules are polymers of the protein tubulin. The tubulin subunit is a heterodimer formed from two closely related globular proteins called a-tubulin and b-tubulin
microtubules have a inherent _____
microtubules have a inherent polarity
While α- and β-tubulins are the regular building blocks of microtubules, another type of tubulin, called________, is present in much smaller amounts than α- and β-tubulin and is involved in the ______ of microtubule growth in organisms ranging from yeasts to humans.
While α- and β-tubulins are the regular building blocks of microtubules, another type of tubulin, called y-tubulin, is present in much smaller amounts than α- and β-tubulin and is involved in the nucleation of microtubule growth in organisms ranging from yeasts to humans.
Microtubules are generally nucleated from a specific intracellular location known as a ____ ____ ____ _____where γ-tubulin is most enriched. Nucleation in many cases depends on the __________. Within this complex, two accessory proteins bind directly to the γ-tubulin, along with several other proteins that help create a spiral ring of γ-tubulin molecules, which serves as a template that creates a microtubule with 13 _______
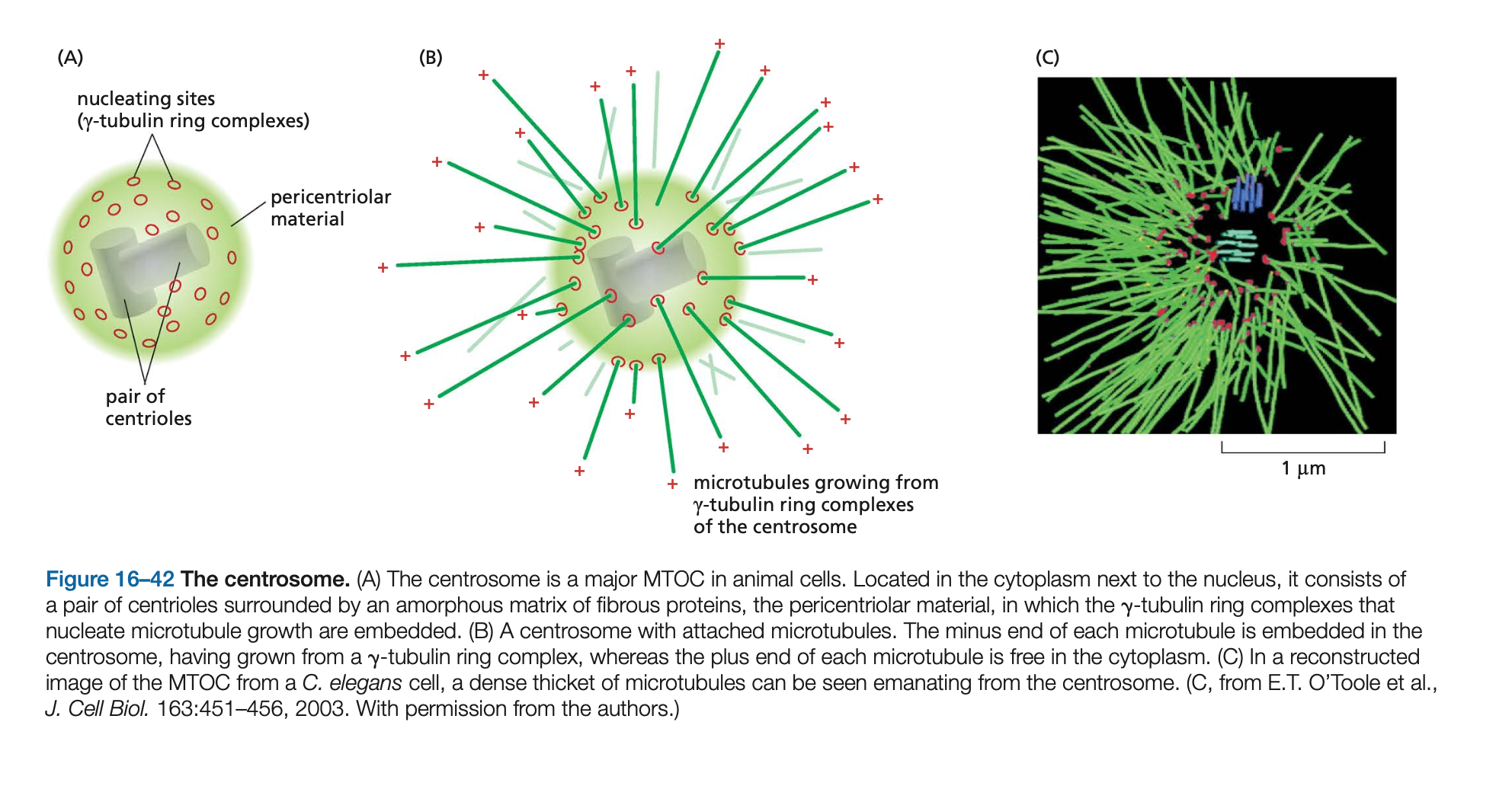
Microtubules are generally nucleated from a specific intracellular location known as a microtubule-organizing center (MTOC) where γ-tubulin is most enriched. Nucleation in many cases depends on the g-tubulin ring complex (g-TuRC). Within this complex, two accessory proteins bind directly to the γ-tubulin, along with several other proteins that help create a spiral ring of γ-tubulin molecules, which serves as a template that creates a microtubule with 13 protofilaments
microtubules are organized by the ______
microtubules are organized by the centrosome
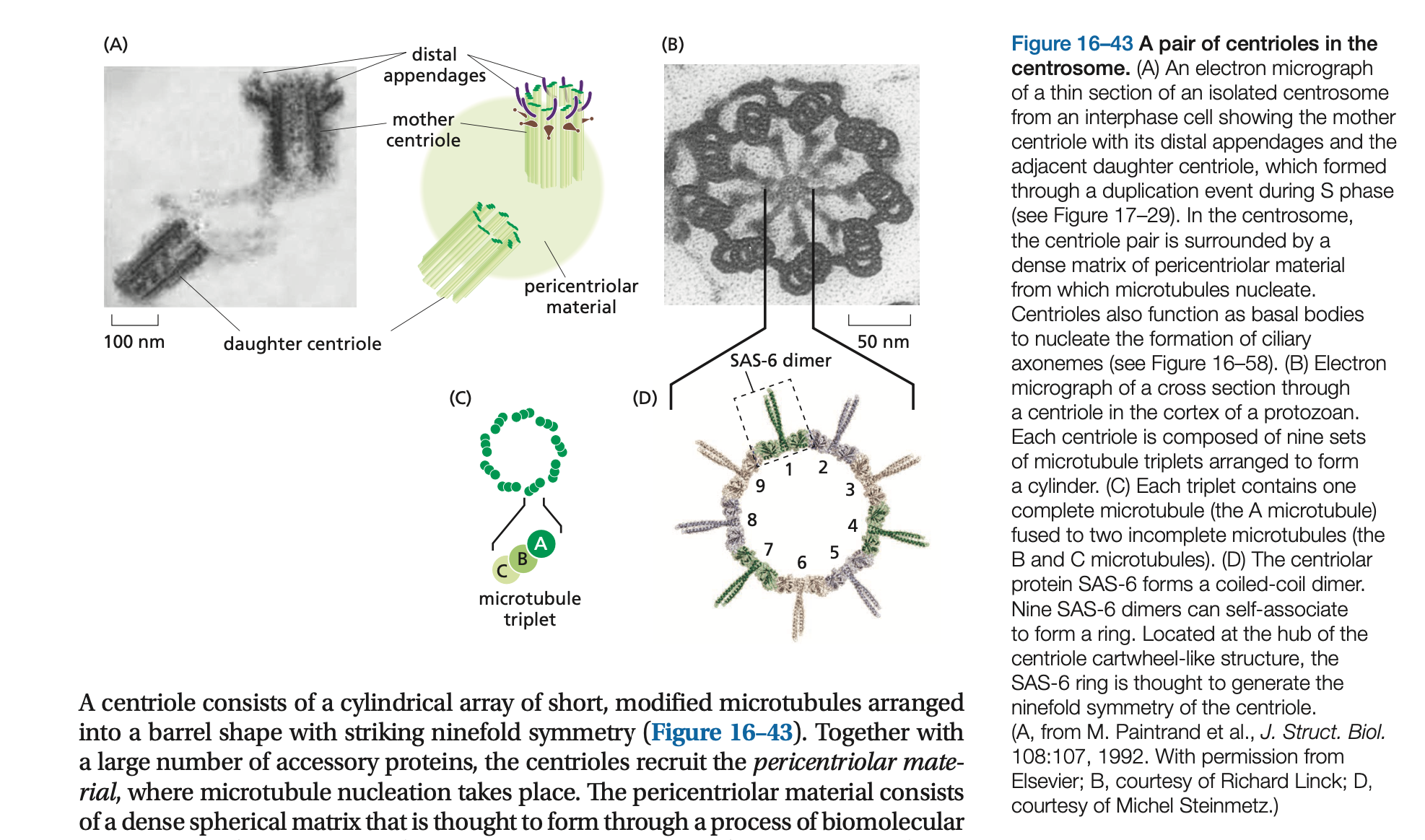
Embedded in the centrosome are the ______, a pair of cylindrical structures arranged at right angles to each other in an L-shaped configuration
Embedded in the centrosome are the centrioles, a pair of cylindrical structures arranged at right angles to each other in an L-shaped configuration
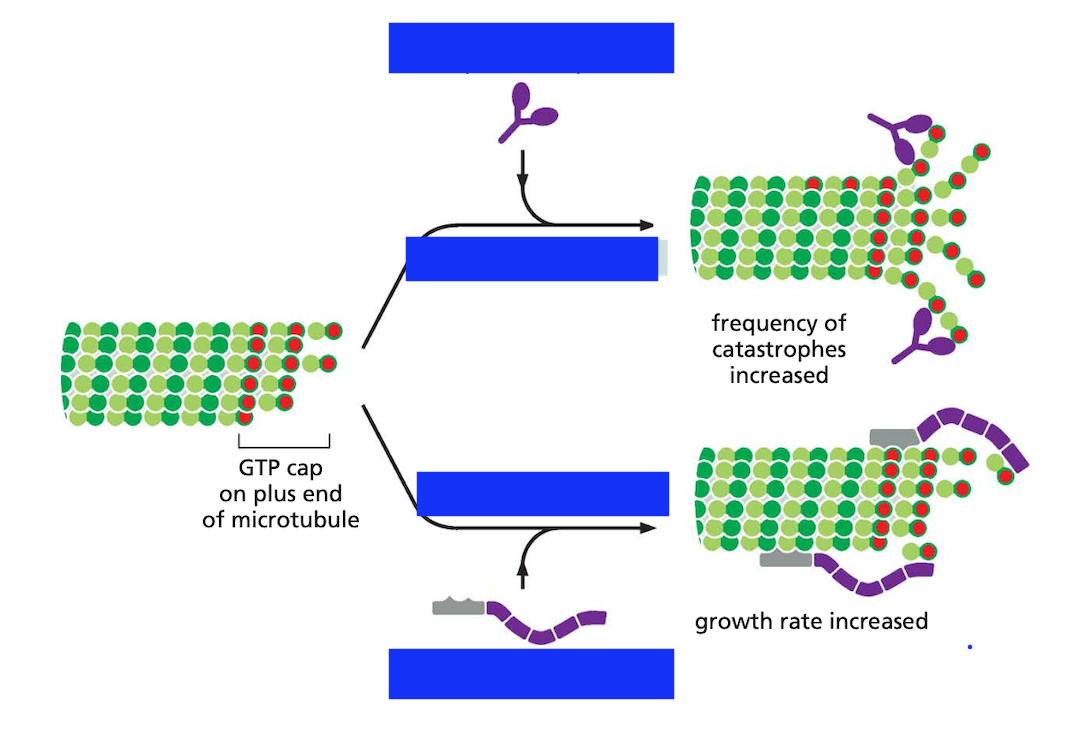
Microtubules are dynamic rapidly growing and shrinking called ____ _____
Microtubules are dynamic rapidly growing and shrinking called dynamic instability
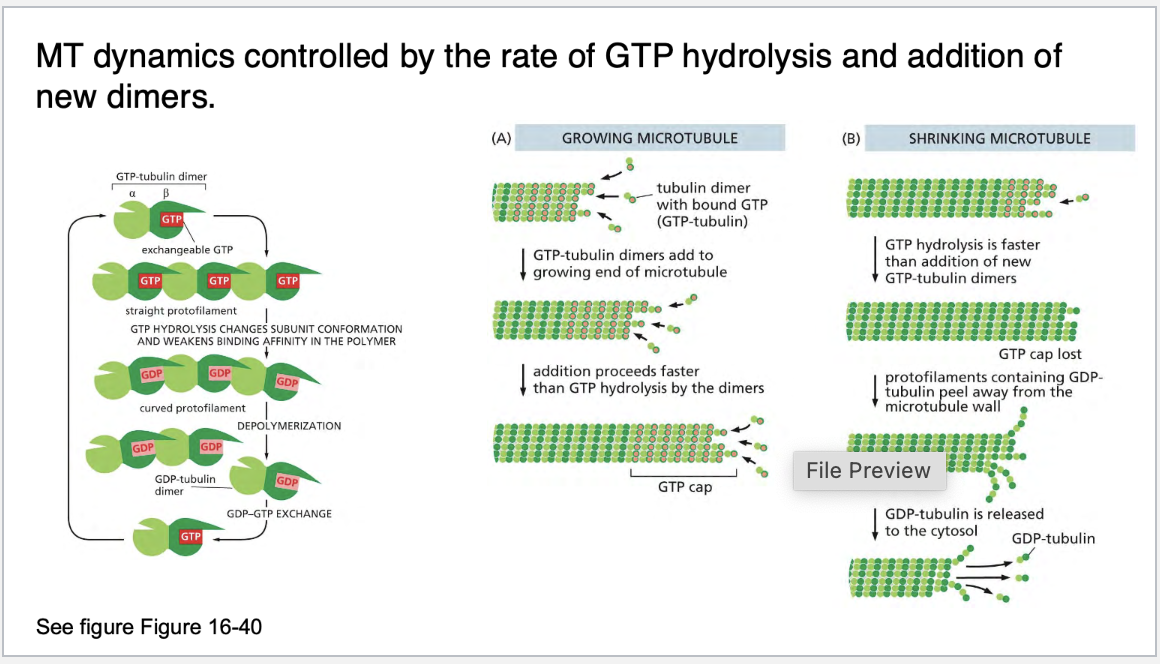
explain dynamic instabiility and what its rate is controlled by
Thus, as in the case of actin filaments, two different types of microtubule structures can exist, one in the T form bound to GTP and one in the D form bound to GDP. But this T form may not persist. Often GTP-tubulin subunits will assemble at the end of the microtubule at a rate similar to the rate of GTP hydrolysis, and in this case hydrolysis will sometimes “catch up” with the rate of subunit addition and transform the end to a D form. This transformation will be sudden and random, with a certain probability per unit time that depends on the concentration of free GTP-tubulin subunits, and it produces the microtubule’s dynamic instability.
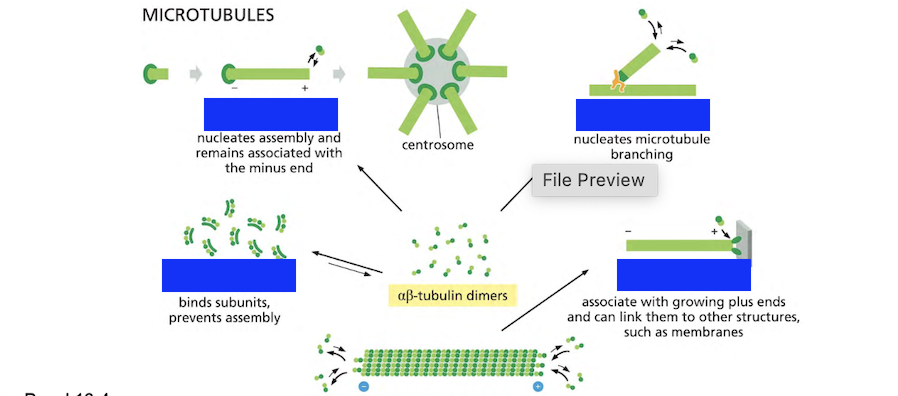
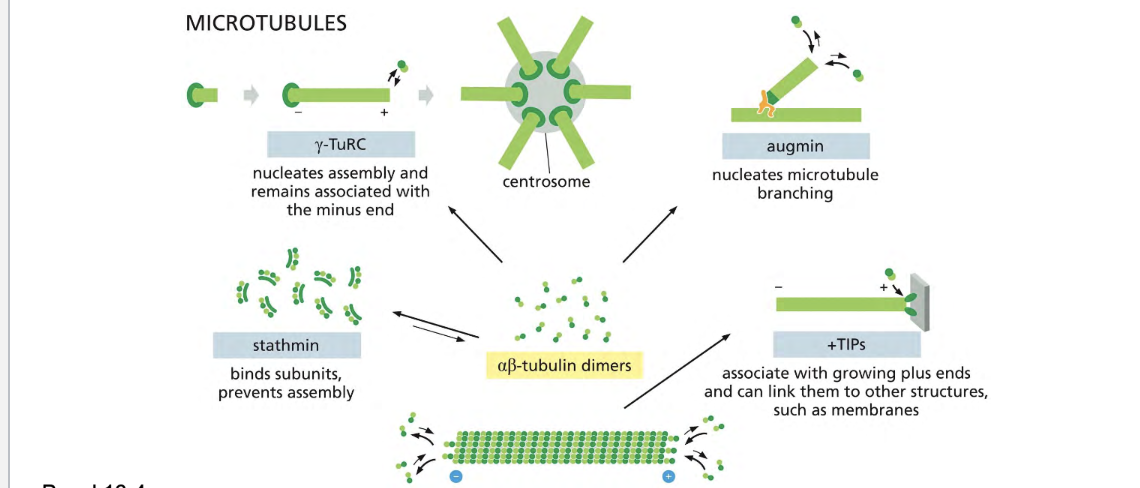
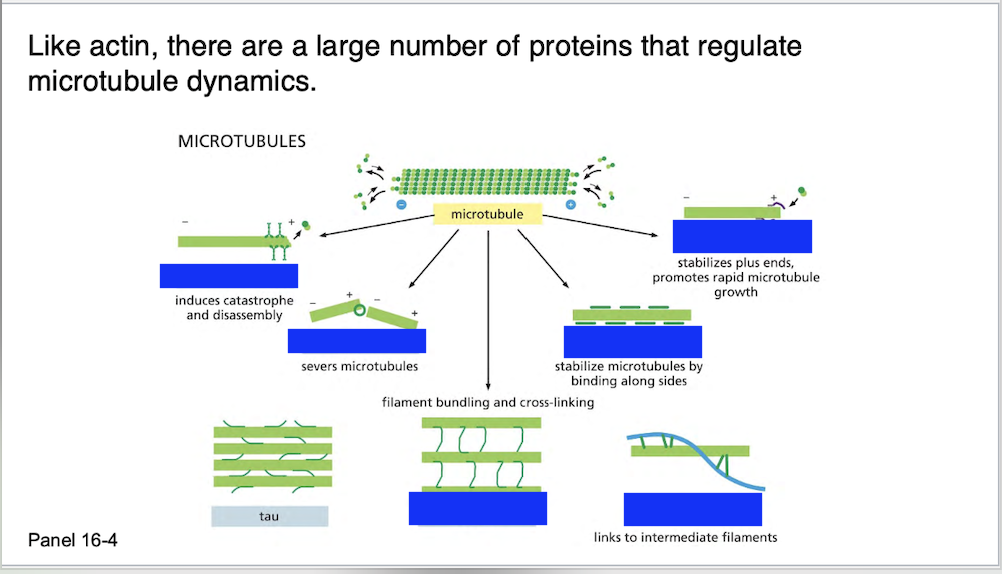
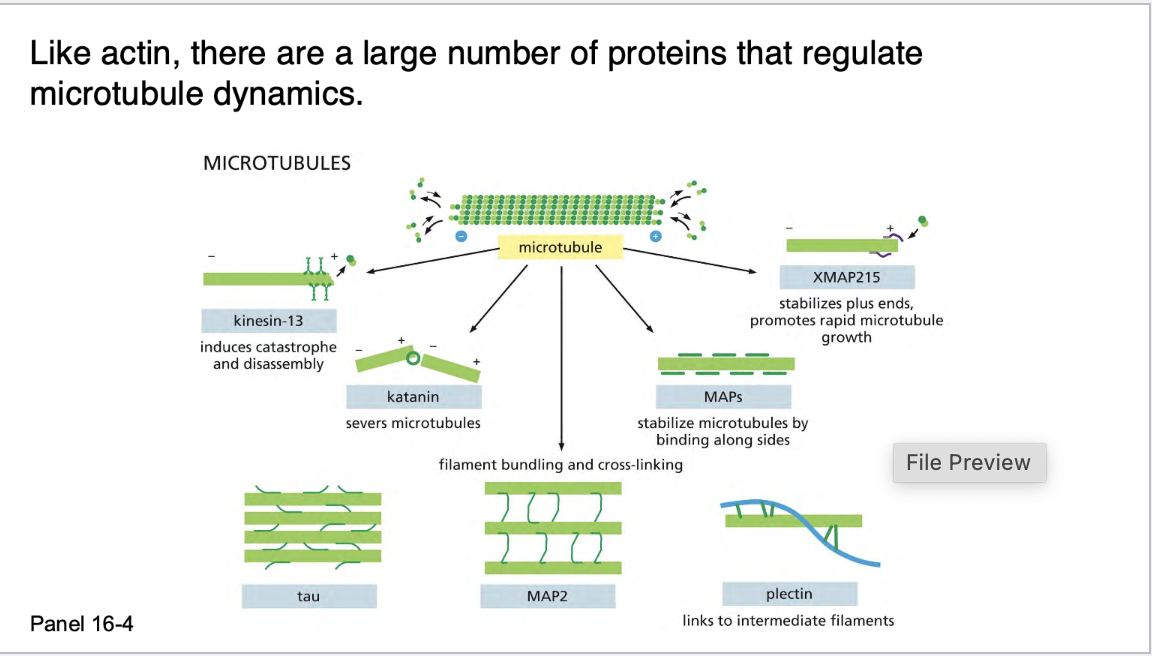
Proteins that bind to microtubules are collectively called ________, or _____.
Proteins that bind to microtubules are collectively called microtubule associated proteins, or MAPs.
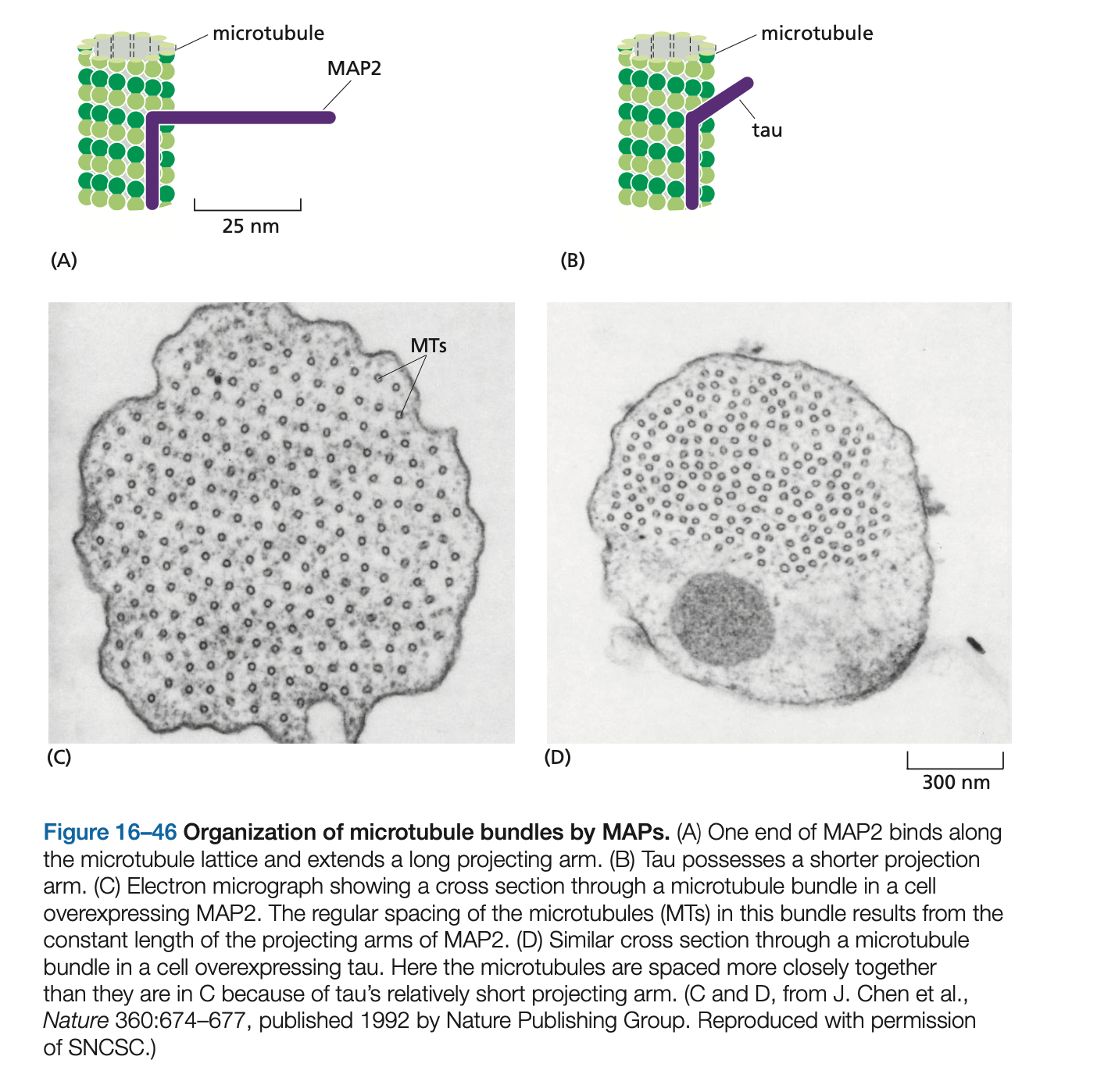
Cells overexpressing ____, which has a long projecting domain, form bundles of stable microtubules that are kept widely spaced, while cells overexpressing ____, a MAP with a much shorter projecting domain, form bundles of more closely packed microtubules
Cells overexpressing MAP2, which has a long projecting domain, form bundles of stable microtubules that are kept widely spaced, while cells overexpressing tau, a MAP with a much shorter projecting domain, form bundles of more closely packed microtubules
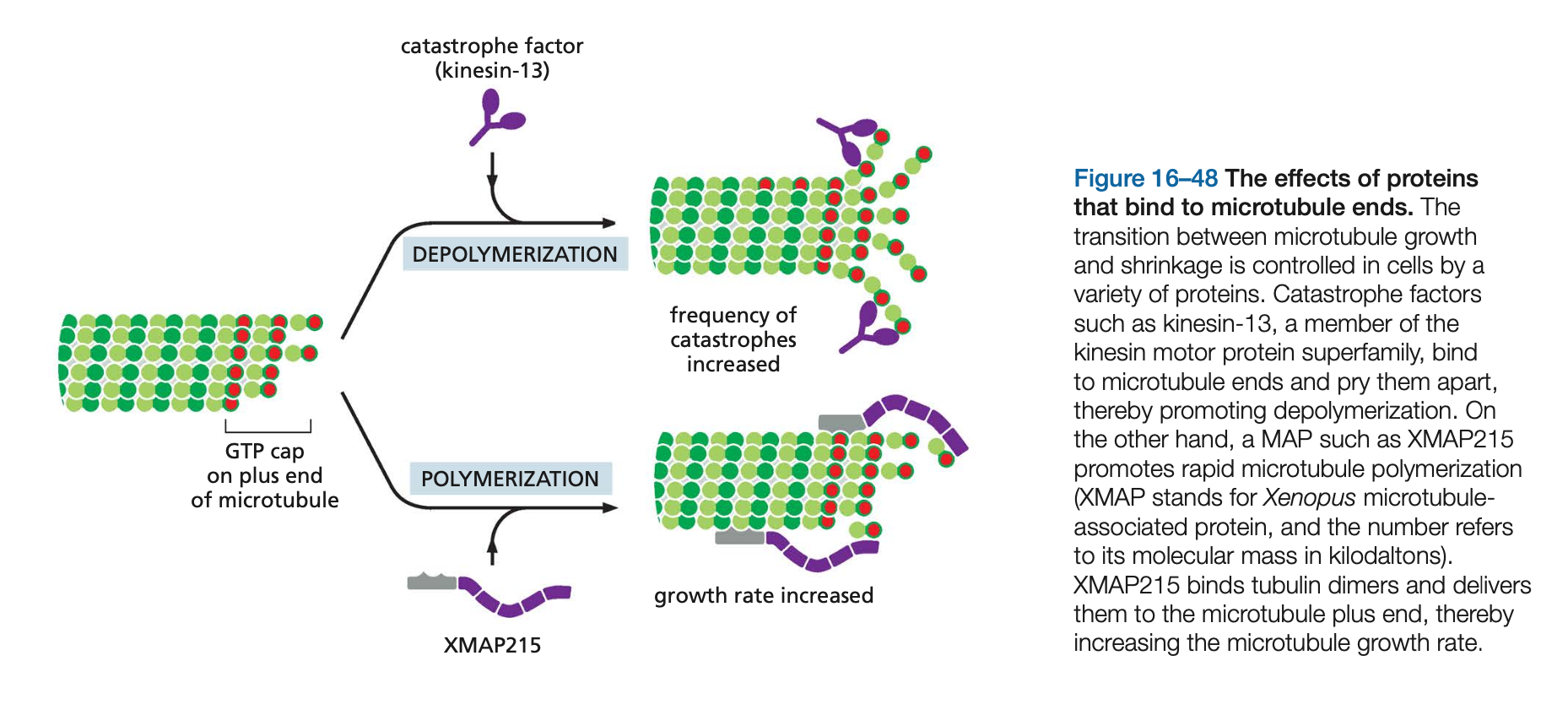
Stabilized MT can be used as a track to move ______ and _____.
Stabilized MT can be used as a track to move organelles and cargo.
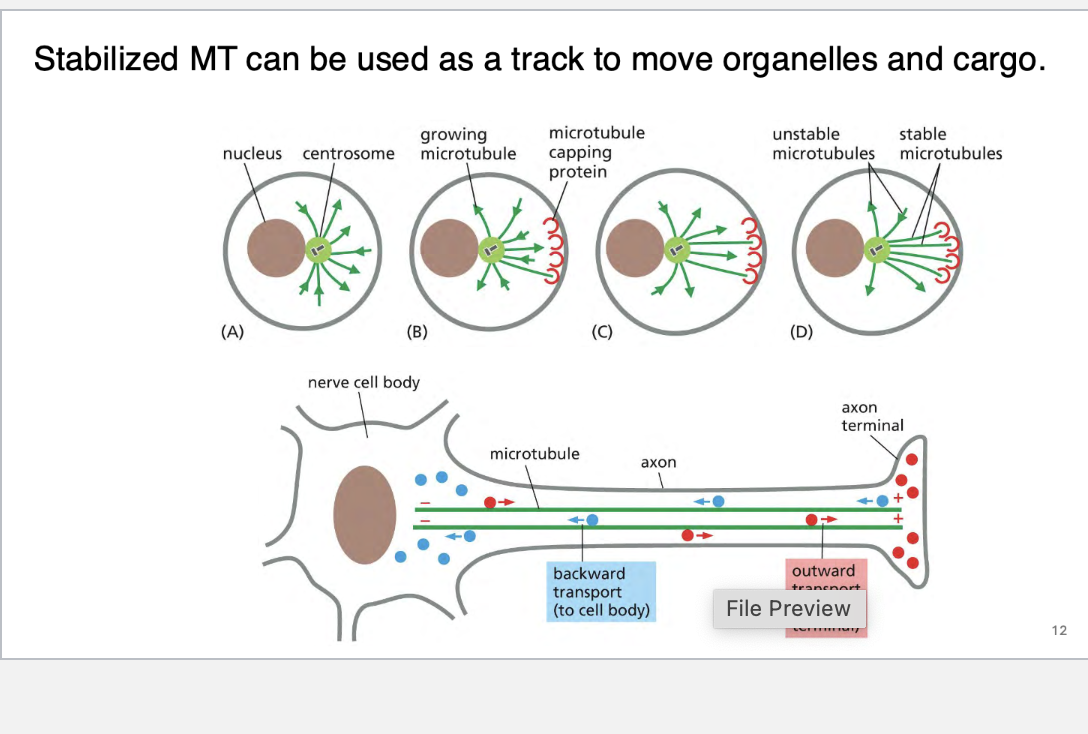
what motor proteins use atp to move cargo on microtubules
kinesins
Most kinesins move toward the plus end of microtubules, which usually points away from the cell center (toward the cell periphery).
This makes them key players in anterograde transport—carrying cargo like vesicles, organelles, and proteins outward from the cell body.
Kinesins use ATP hydrolysis to “walk” along microtubules.
Each step involves one head binding to the microtubule, hydrolyzing ATP, and then the other head swinging forward—like a molecular walking mechanism.
Most kinesins have two globular heads (motor domains) that:
Bind to microtubules
Hydrolyze ATP
The tail region binds to cargo via adaptor proteins.
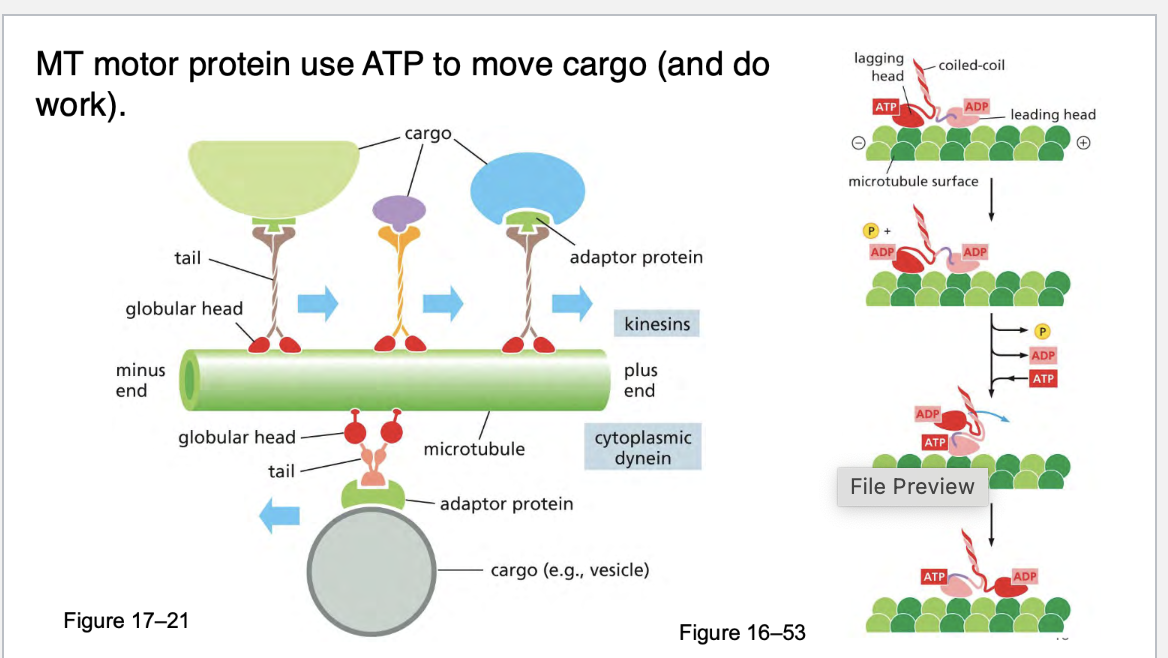
what two organelles does the microtubules regulate the localization of?
ER and GOLGI and mitochondria
what does colchicine do to micrtubule dynamics?
Colchicine is a drug that disrupts microtubule dynamics—it binds to tubulin, the building block of microtubules, and prevents them from functioning properly.
microtubule drugs are used in cancer how?
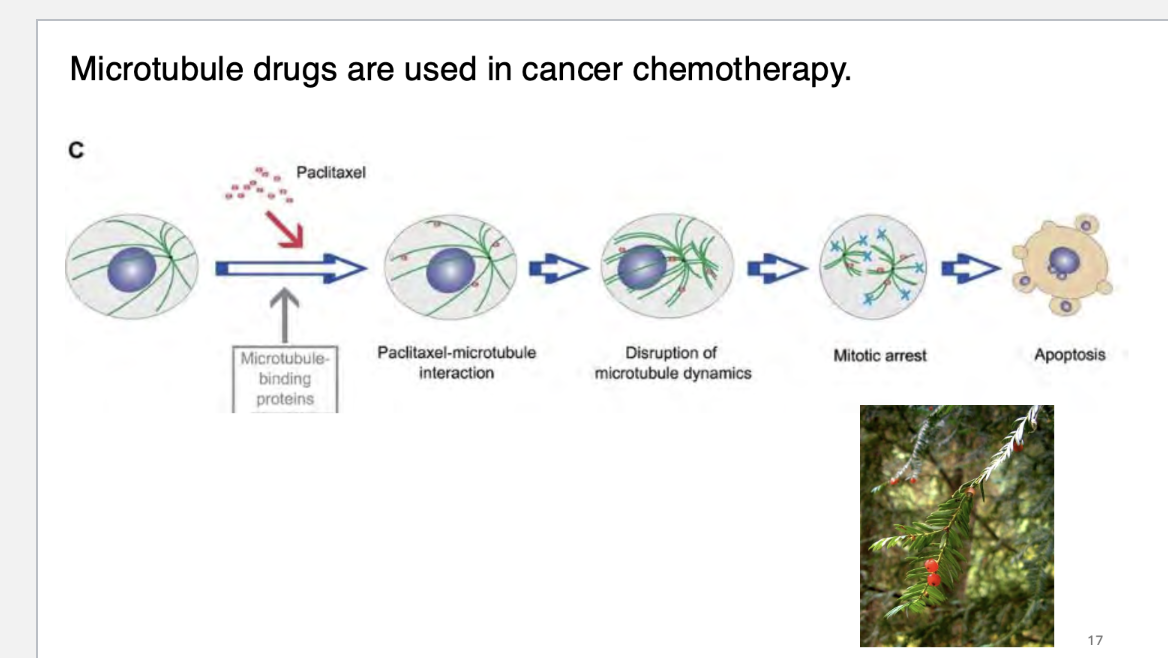
what are cilia?
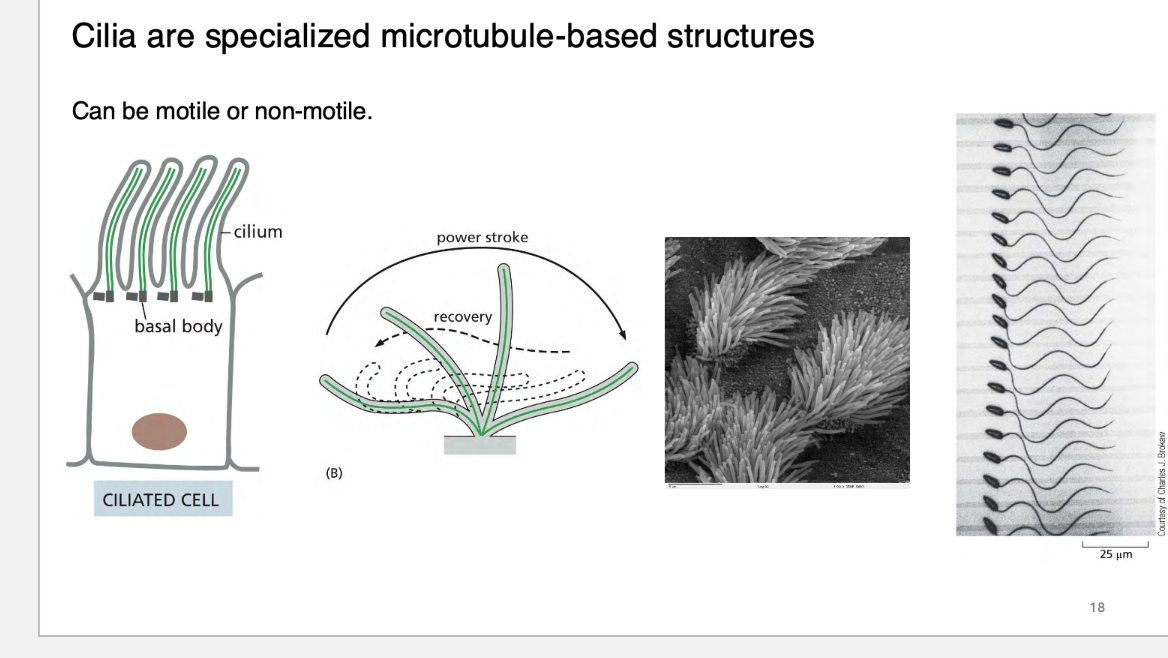
cilia have a defined microtubule orginazation, in a what array?
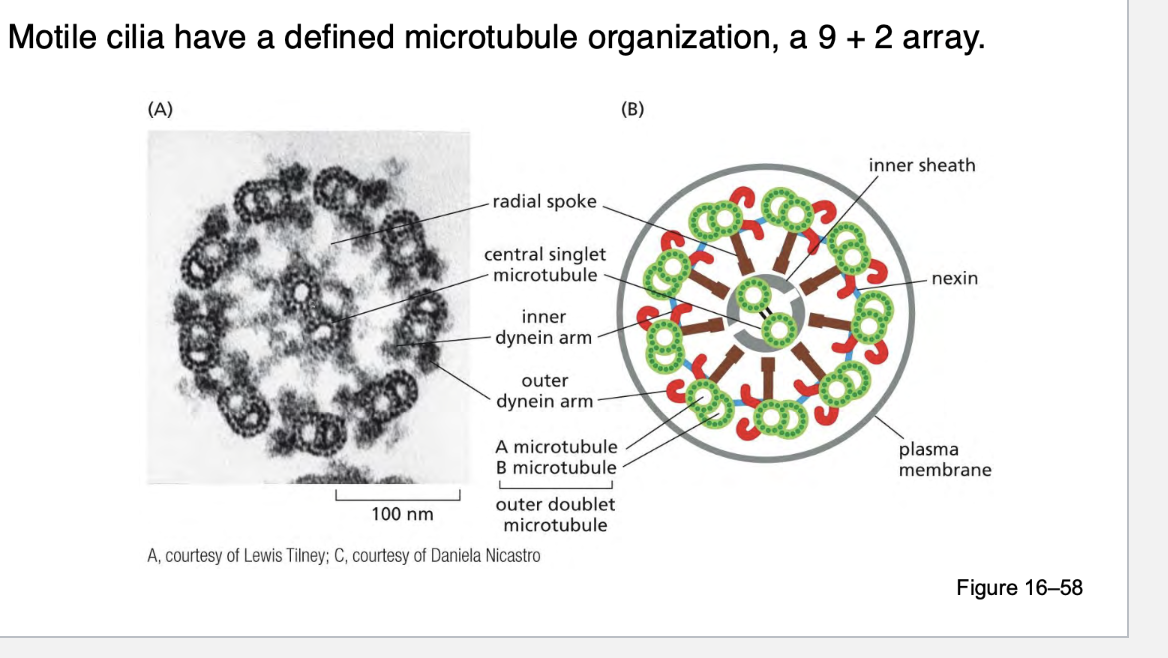
There are 9 pairs of microtubules (called doublets) arranged in a circle around the outside.
In the center, there are 2 single microtubules.
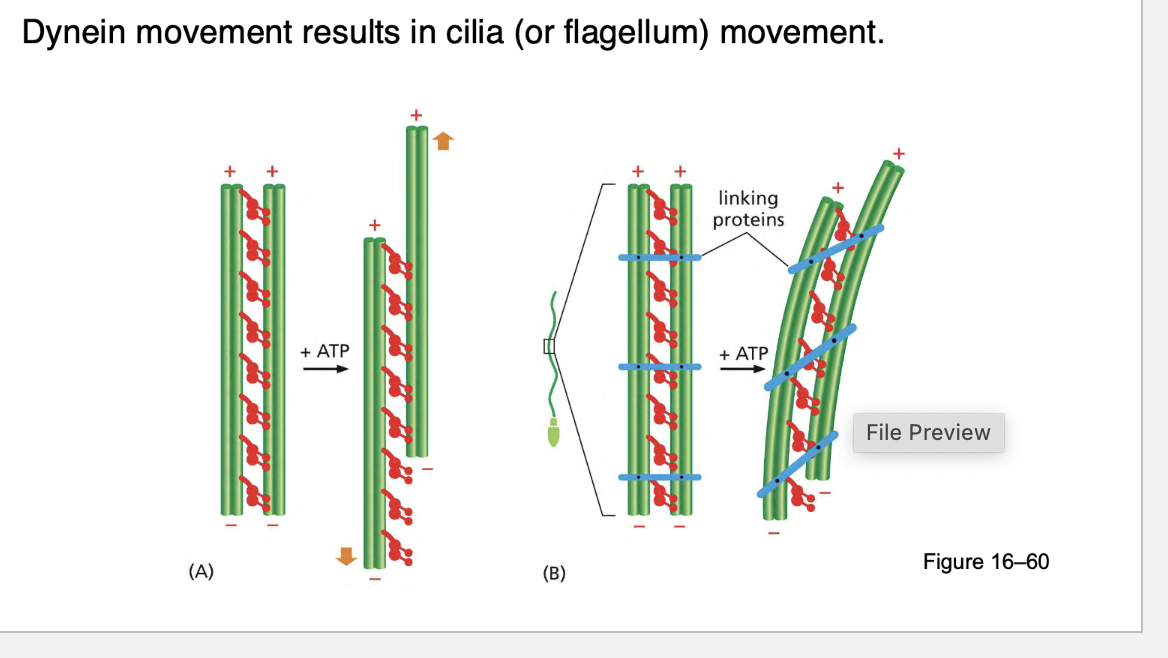
Dynein movement results in cilia (or flagellum) movement. how?
Dynein is a motor protein that walks along microtubules using ATP as energy.
It is attached to the outer microtubule doublets in the 9 + 2 arrangement.
Specifically, axonemal dynein is the type that works in cilia and flagella.
Sliding Microtubules:
Dynein "walks" along the adjacent microtubule doublets, causing them to slide against each other.
When dynein tries to move one doublet relative to the next, the sliding is restricted by crosslinking proteins, so instead of sliding freely, the microtubules bend.
Bending Action:
The sliding force is converted into bending motion by links and dynein arms between adjacent microtubules.
As dynein moves, one side of the structure is pushed in one direction, while the opposite side is pushed in the other direction.
This causes a bending wave that propagates along the cilia or flagellum, producing movement.
what is the differece between motile and primary cilia?
Non-Motile: Unlike motile cilia, primary cilia are stationary and don’t move.
Microtubule Organization: Primary cilia typically have a 9 + 0 arrangement:
9 microtubule doublets form the outer ring (no central pair of microtubules).
This simpler structure means primary cilia lack the central pair of microtubules found in motile cilia and flagella.
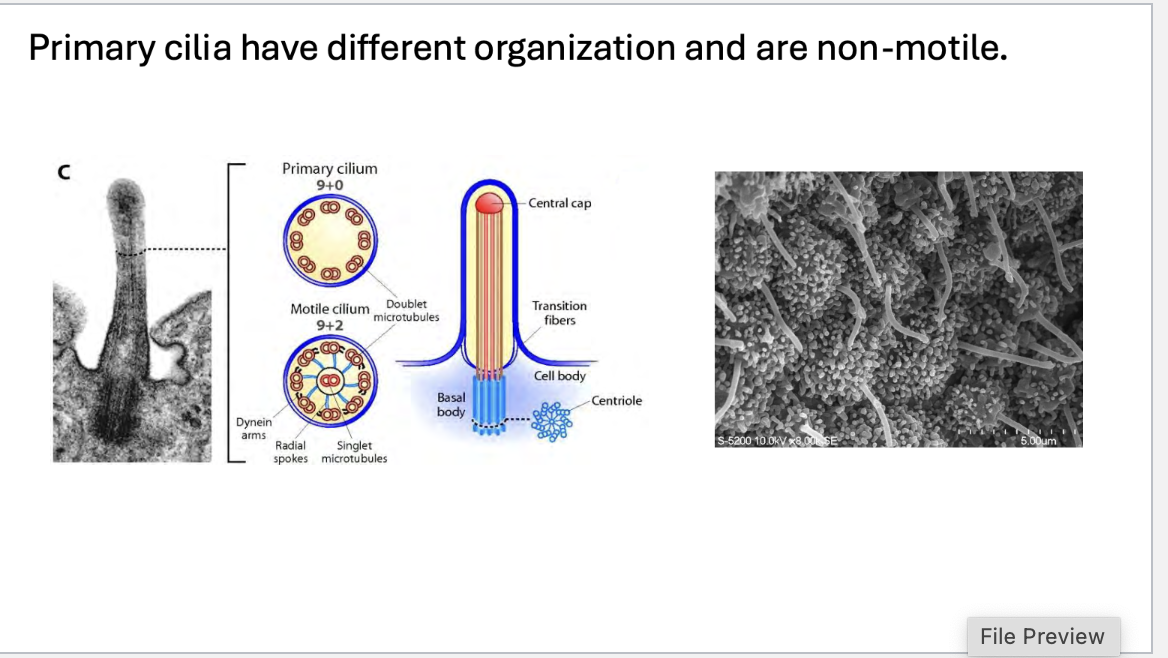
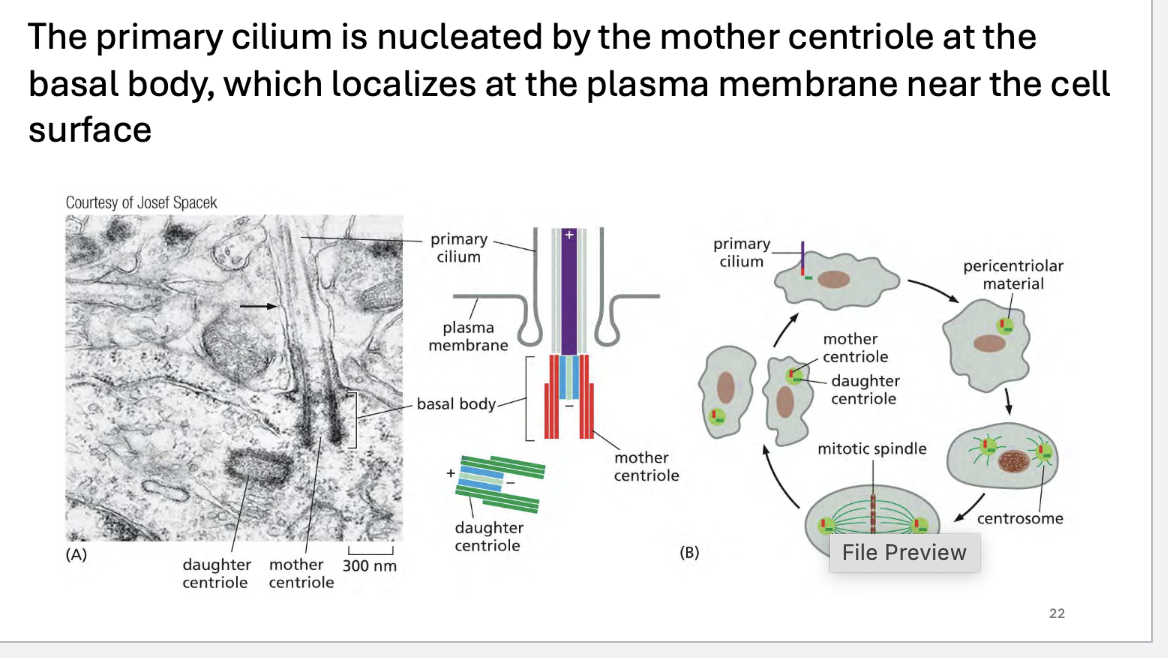
The primary cilium is nucleated by the _____ centriole at the ____ ____, which localizes at the plasma membrane near the cell _____
The primary cilium is nucleated by the mother centriole at the basal body, which localizes at the plasma membrane near the cellsurface
Centrosome and Centrioles:
Every cell has a centrosome, which consists of a pair of centrioles: a mother centriole and a daughter centriole.
The mother centriole is crucial in the formation of the primary cilium.
Basal Body Formation:
The mother centriole acts as the nucleating center for the basal body.
The basal body is a modified centriole that is positioned near the plasma membrane.
It serves as the anchoring point for the primary cilium.
Cilium Extension:
Once the basal body is anchored to the plasma membrane, microtubules extend from the basal body, forming the axoneme of the primary cilium.
The cilium grows outward from the cell surface as the microtubules extend, and it becomes surrounded by the cilia membrane.
Importantly, the primary cilium is non-motile and serves primarily as a sensory structure.
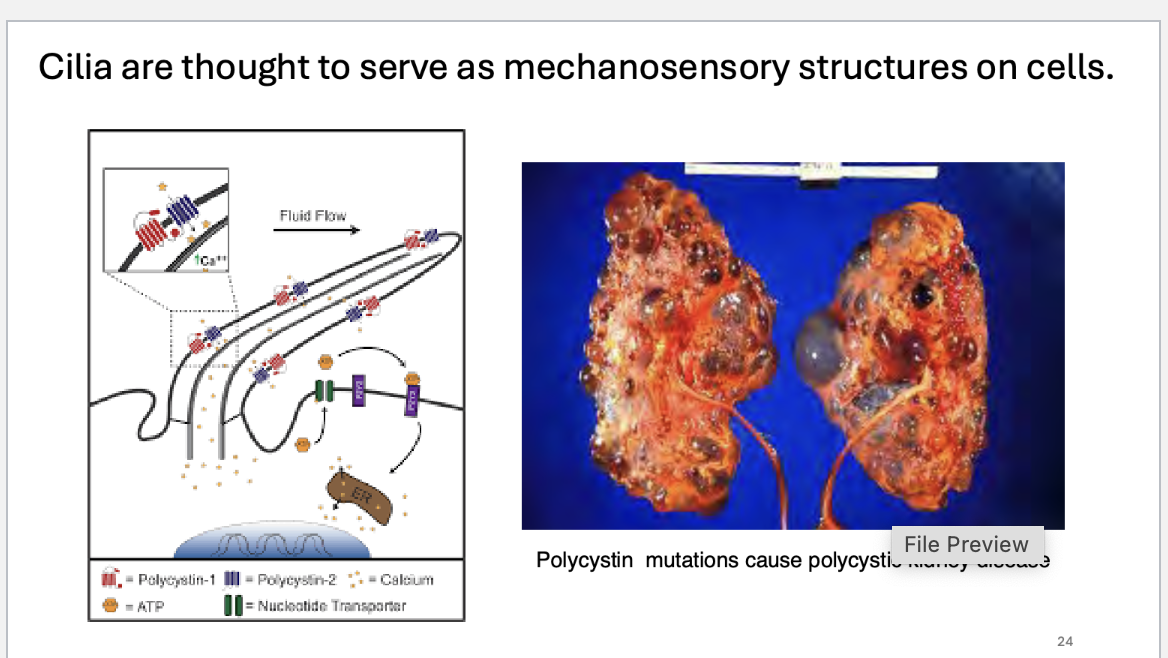
Cilia are thought to serve as _____ structures on cells.
Cilia are thought to serve as mechanosensory structures on cells.
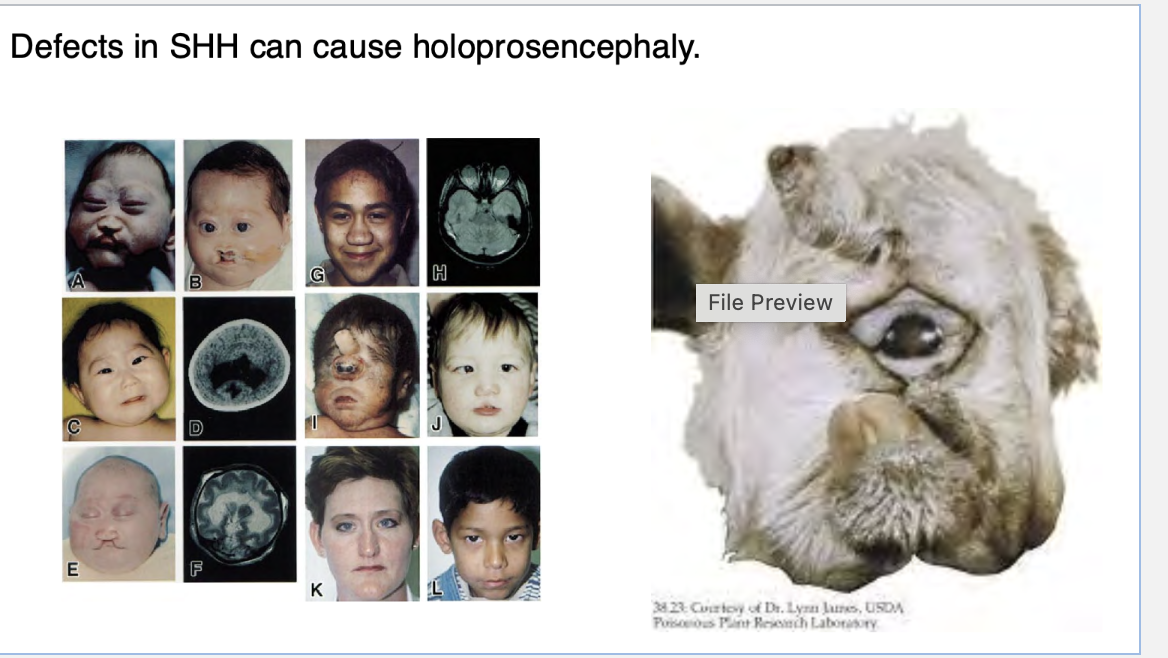
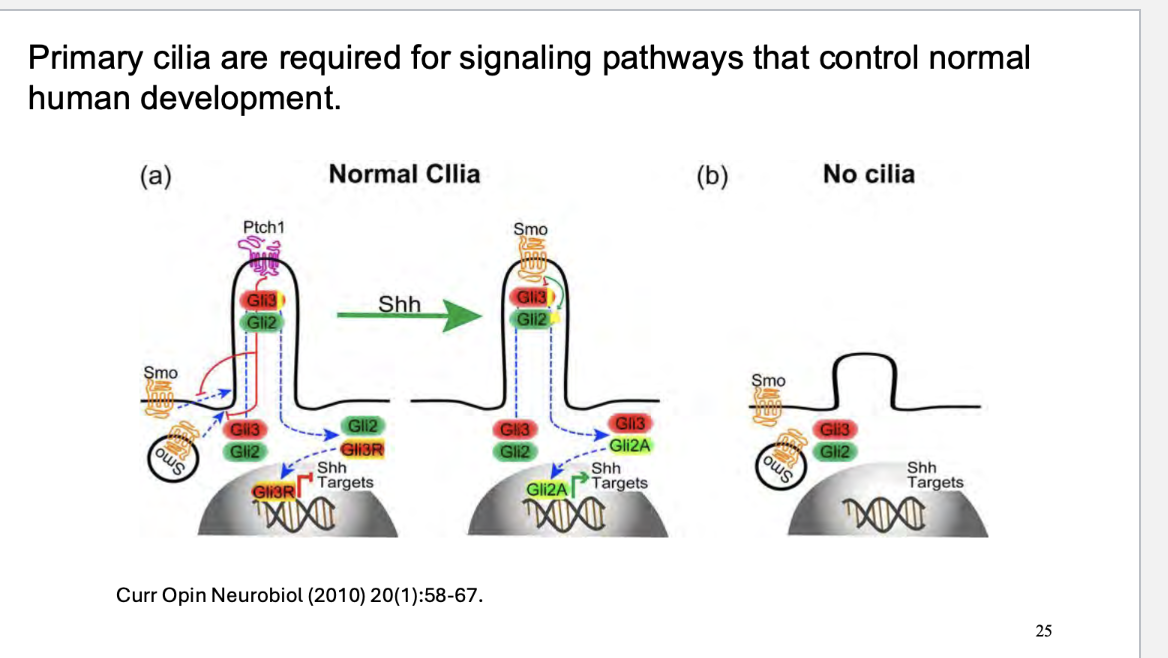
how is shh and cilia related? what a defect of shh cause
The primary cilium is essential for the proper activation of the SHH pathway because SMO and GLI proteins are specifically localized to the cilium. Without this ciliary involvement, SHH signaling cannot function properly.
The cilia facilitate the movement of key signaling molecules within the cell to the axoneme (the microtubule structure of the cilium), where they are activated or inactivated, ensuring proper downstream effects.
Holoprosencephaly (HPE) is caused by disrupted SHH signaling, leading to defects in forebrain patterning during early development.