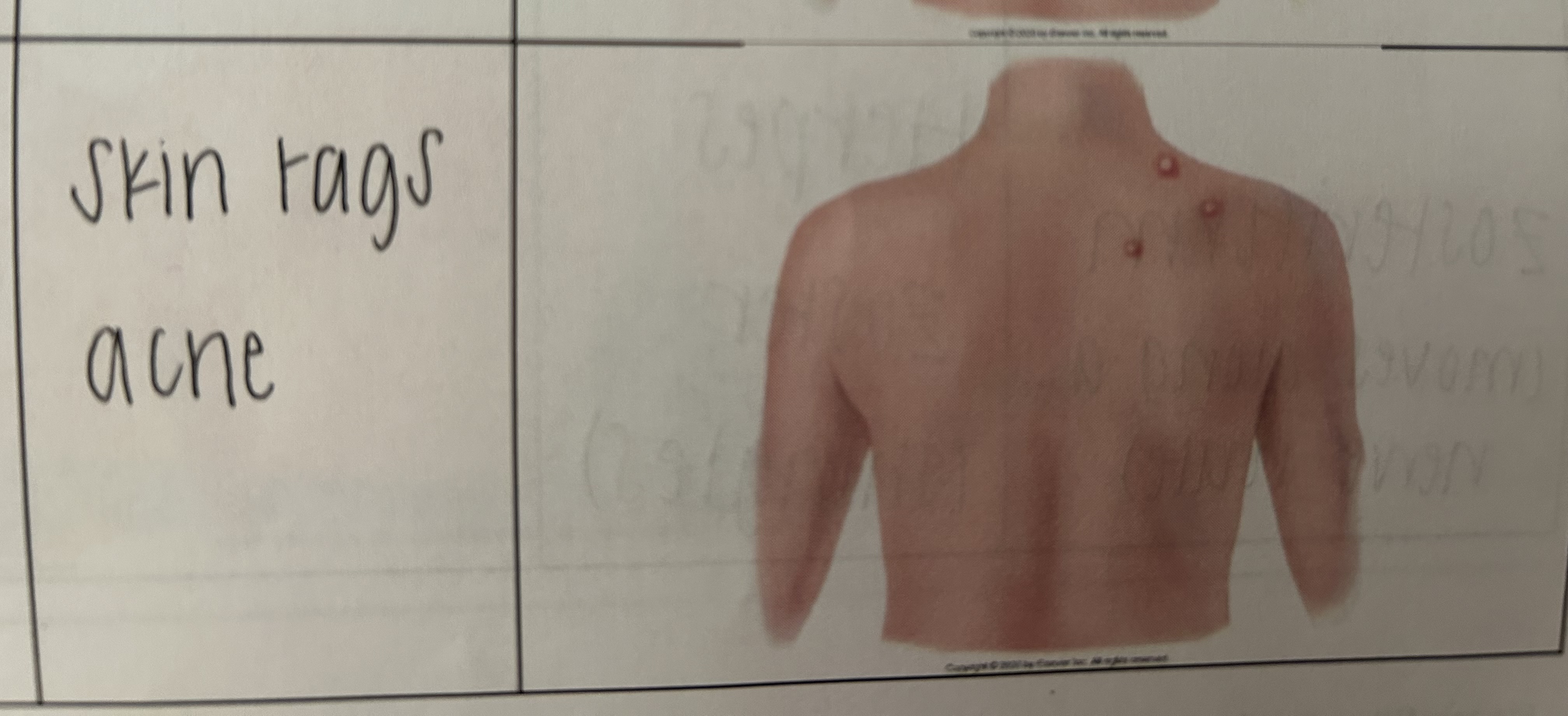
1 - skin, hair, nails vocab
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
epidermis
outer layer, thin but tough
dermis
inner supportive layer
hair shaft
visible projecting part of hair
root
embedded below follicle
bulb matrix
where new cells are produced at high rate
vellus
fine hair that covers most of the body
terminal
darker, thick hair
sebaceous glands
secrete sebum, lubricates skin
forms emulsion
everywhere except palm and soles of feet
sweat gland
eccrine and apocrine glands
eccrine glands
directly on skin surface
produced diluted saline called sweat
reduces body temp via evaporation
apocrine glands
produce milky secretion and open into follicles
axillae, genital area, nipples and navel
emotional and sexual stimulation
when mixed w bacteria, creates body odor
lanugo
newborn baby hair all over body (vellus)
vernix
cheesy substance on newborn for immunity
melasma
grey/brown patch on elder/pregnant women
senile purpura
when old people get purple (bruises)
keloids
abnormal type of scarring
puritis
itching
hypopigmentation
lighter than expected areas
hyperpigmentation
darker than expected areas
seborrhea
excessive oil production
xerosis
dry skin
alopecia
hair loss
hirsutism
too much hair growth (lady beards)
pseudo folliculitis
ingrown hair
edema
fluid accumulating in interstitial space
mobility
ease of skin to rise
turgor
ability to return promptly when released
poor turgor = dehydration, extreme weight loss
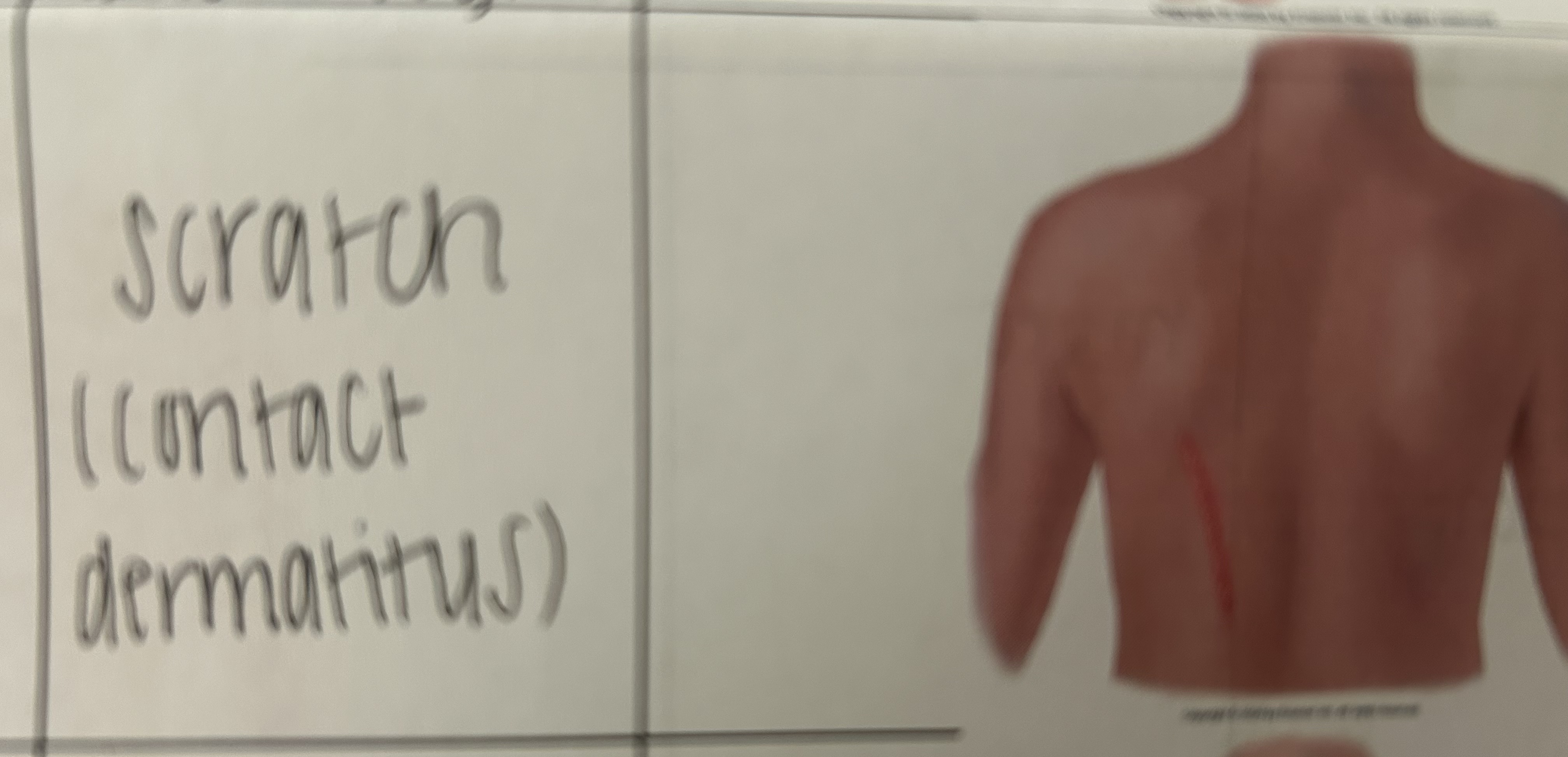
linear lesion
gyrate lesion

confluent lesion
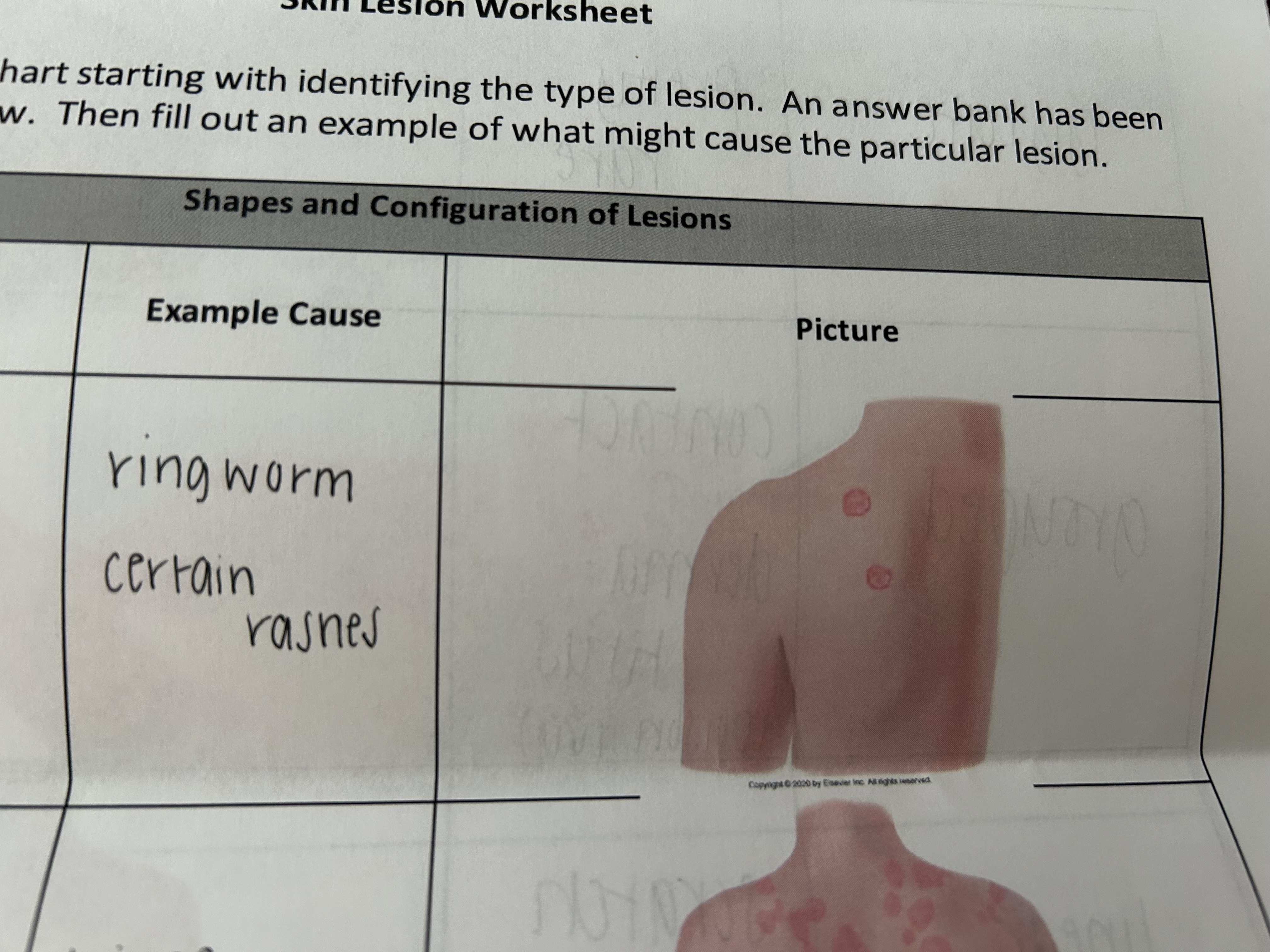
grouped lesion

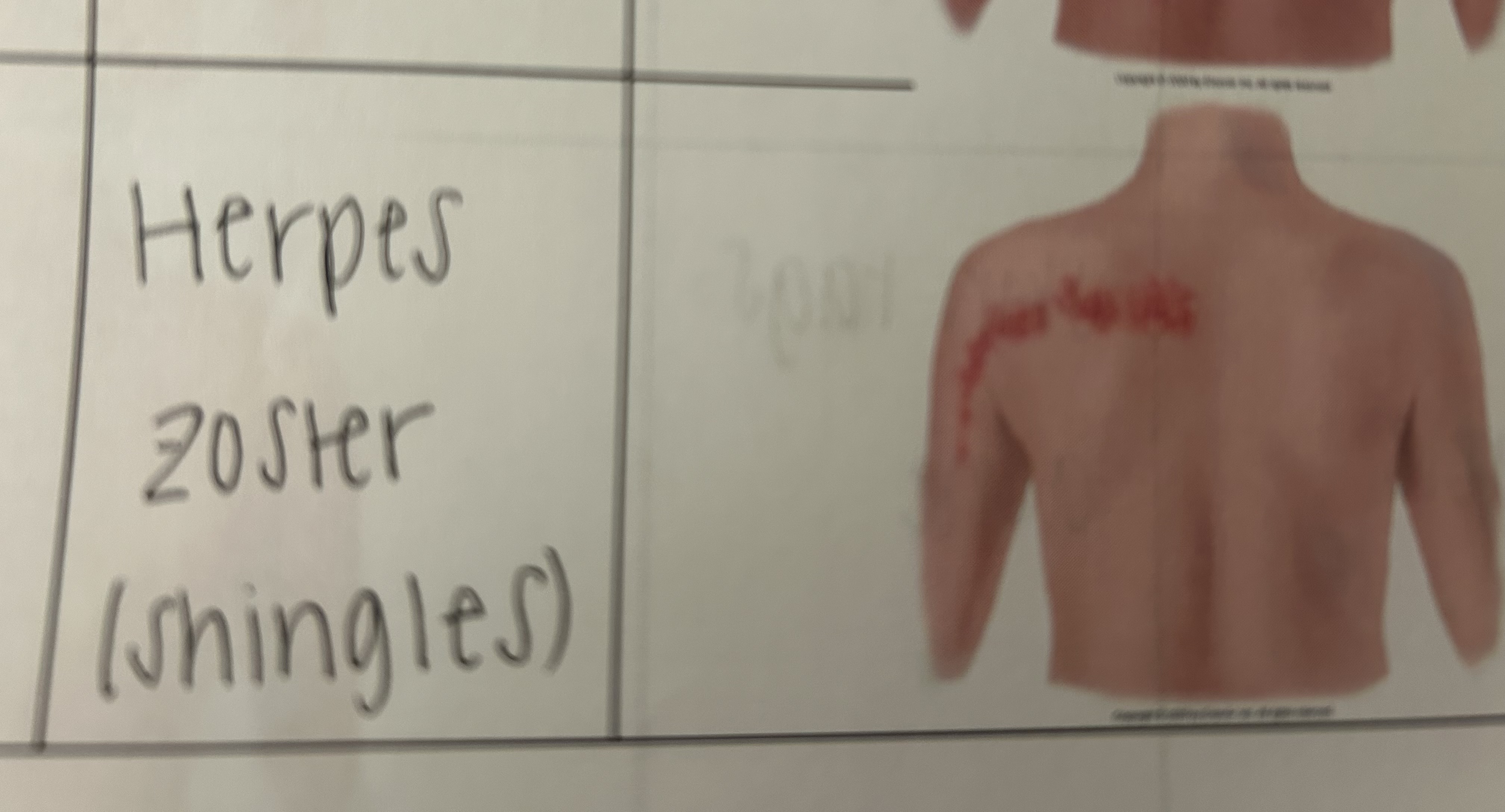
zosteriform lesion
annular lesion
discrete lesion
stage 1 - non blanchable erythema
Intact skin is red but unbroken. Localized redness in lightly pigmented skin does not blanch (turn light with fingertip pressure). Dark skin appears darker but does not blanch. May have changes in sensation, temperature, or firmness.
stage 2 - partial thickness skin loss
Loss of epidermis and exposed dermis. Superficial ulcer looks shallow like an abrasion or open blister with a red-pink wound bed. No visible fat or deeper tissue.
stage 3 - full thickness skin loss
PI extends into subcutaneous tissue and resembles a crater. See subcutaneous fat, granulation tissue, and rolled edges, but not muscle, bone, or tendon.
stage 4 - full thickness skin/tissue loss
PI involves all skin layers and extends into supporting tissue. Exposes muscle, tendon, or bone, and may show slough (stringy matter attached to wound bed) or eschar (black or brown necrotic tissue), rolled edges, and tunneling.
macules
solely a color change, flat and circumscribed, less than 1cm
ex; freckles, flat nevi, hypopig, petechlae
patches
macules that are larger than 1cm
ex; mongolian spot, vitiligo, cafe au lait spot
papules
something you can feel, caused by superficial thickening of the epidermis ,1cm
ex; moles warts
plaques
papules coalescing to form surface elevation wider than 1cm
ex; psoriasis
nodules
solid, elevated, hard, soft, greater than 1cm, may extend deeper into dermis than papule
tumors
larger in diameter, firm or soft, deeper into dermis, may be benign or malignant
wheals
superficial, raised, transient and erythematous, irregular in shape due to edema
ex; mosquito bite, allergic reaction
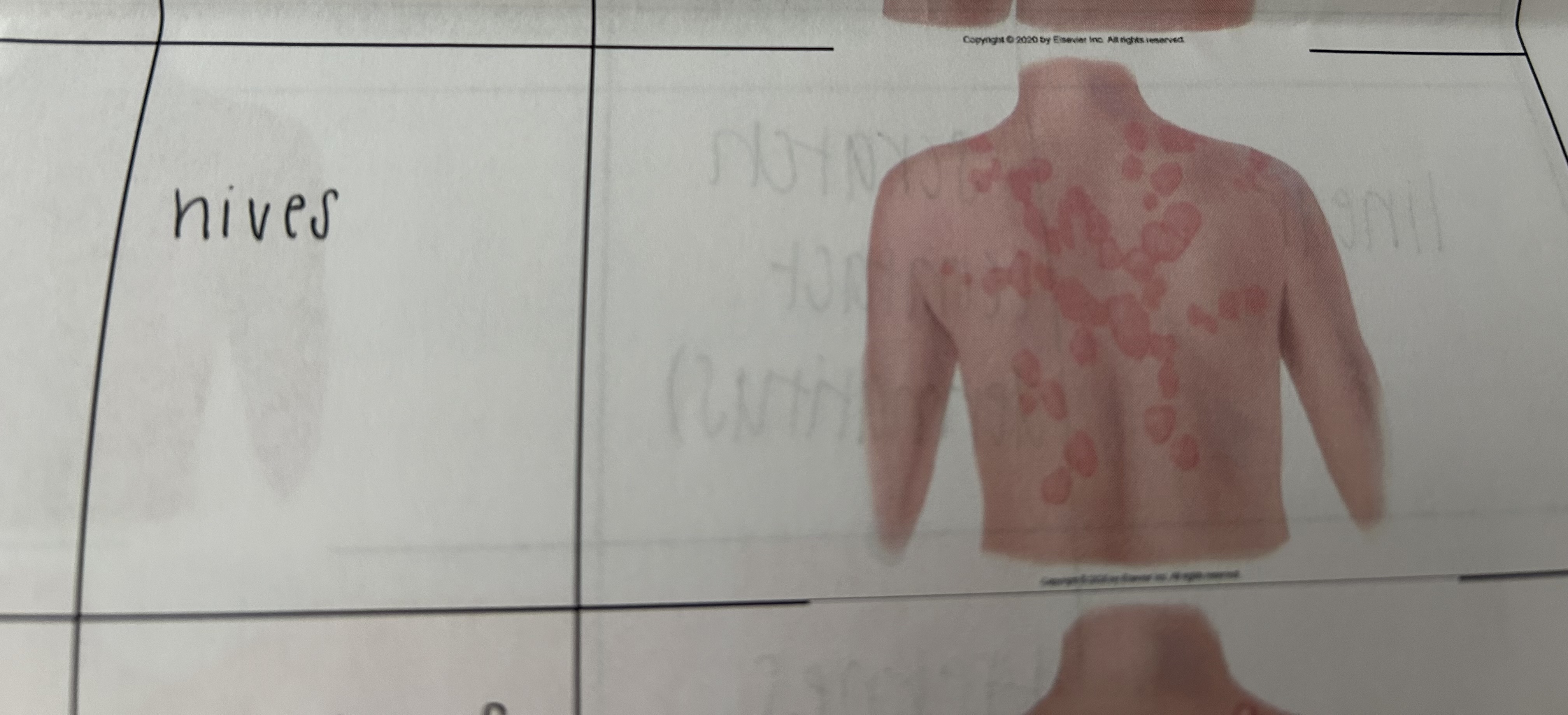
urticaria
wheals coalesce to form extensive pruritic reaction
ex; hives
vesicles
elevated cavity containing fluid up to 1cm
ex; blisters, herpes, chicken pox, shingles
bullas
larger than 1cm, usually single chamber, superficial in dermis, ruptures easily
ex; burns, friction blister
cysts
encapsulated fluid filled cavity
pustules
pus in cavity that is circumscribed and elevated
ex; acne, impetigo