ECON 330 Exam 2
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
Adjustable Rate Mortgages
Flexible Interest Rates keep profits high when rates rise
Lower initial interest rates make them attractive to home buys
Financial Derivatives
Ability to hedge interest rate risk
Payoffs are linked to previously issued securities
Supply Side Changes (Technology)
Improved computer technology lowers transaction costs & makes the computations/information needed to price new products possible (ATM, Junk Bonds)
Securitization
To transform otherwise illiquid financial assets into marketable capital market securities
Mortgage Market in Mid 2000s
Globalization
deregulation as well as a general movie towards globalization and international trade
Growth in international trade and multinational corporations
The monetary base is comprised of:
a. currency and reserves.
b. reserves and government securities.
c. currency and government securities.
d. currency and Federal Reserve notes.
currency and reserves.
If the Japanese price level rises relative to the price level in the United States, what will happen to the value of the Japanese yen in terms of dollars? The value of the yen will
a. Appreciate
b. remain unchanged
c. depreciate
Depreciate
Financial instruments with returns tied to previously issued securities are called:
a. derivatives
b. bonds
c. stocks
Derivates
Which did not help prevent the financial crisis of 2007-2009 from becoming a depression?
The purchase of stock and ownership takeovers of troubled banks by the Federal Reserve.
A rise in the expected future exchange rate shifts the demand for domestic assets to the ________ and causes the domestic currency to_________.
a. right; appreciate
b. left; appreciate
right; appreciate
A rise in the domestic interest rate shifts the demand for domestic assets to the ________ and causes the domestic currency to_________.
a. right; appreciate
b. right; depreciate
c. left; appreciate
d. left; depreciate
right; appreciate
The federal funds interest rate is determined by the:
a. FOMC.
b. supply & demand in the money market.
c. supply & demand in the bond market.
d. supply & demand of reserves.
supply & demand of reserves.
Predict what will happen to the money supply if there is a sharp rise in the currency ratio.
The money supply falls
Open market operations as a monetary policy tool have the advantage that:
a. they occur at the initiative of the Fed.
b. they are flexible and precise.
c. they are easily reversed.
All the above
The players in the money supply process include all of the following except:
a. depositors.
b. banks.
c. Treasury.
d. central bank.
Treasury
Currency in circulation that cannot be redeemed for gold is called:
a. gold bills
b. junk bonds
c. fiat money
d. state money
Fiat Money
The Fed's most commonly used means of changing the money supply is:
OMO (Open Market Operations)
According to the quantity theory, changes in the:
a. quantity of money lead to proportional changes in the growth rate of aggregate output.
b. velocity of money lead to proportional changes in the growth rate of aggregate output.
c. quantity of money lead to proportional changes in the price level.
d. price level lead to proportional changes in the quantity of money.
quantity of money lead to proportional changes in the price level.
The Fed buys $100 million of bonds from the public and also lowers the reserve requirement rate. What will happen to the money supply?
The money supply will increase
The presence of so many commercial banks in the United States is most likely the result of:
previous restrictions on branch banking
A well-functioning financial system:
solves asymmetric information problems.
The Fed is the most independent of all US government agencies. What is the main difference between it and other government agencies that explains the Fed's greater independence?
The Fed's source of revenue is free from the appropriations process
What role do weak financial regulation and supervision play in causing financial crises?
It allows financial institutions a better opportunity to engage in excessive risk-taking behavior.
As financial intermediaries, banks:
Accept deposits and make loans
Why is the originate-to-distribute business model subject to the principal-agent problem?
a. Once the mortgage broker earns their fee, they don’t care if the borrower makes his payment
b. The mortgage broker has little incentive to ensure the borrower is credit-worthy, since loans willbe sold as mortgage-backed securities
c. The more volume the broker originates, the more he or she makes
Uncertainty about future interest-rate volatility and returns is known as:
Interest Rate Risk
As a result of strict banking regulations, the United States has:
many more smaller banks when compared to other industrialized countries
The ratio of the money supply to the monetary base is called:
The money multiplier
Financial Crisis:
particularly large disruption to information flows in financial markets, with the result that financial frictions increase sharply and financial markets stop functioning.
Bank RUN
Everyone wants their deposits at the same time
Dynamics of Financial Crisis:
1) Initiation of Financial Crisis (Credit Boom and Bust); (Asset Price Boom and Bust)
2) Banking Crisis
3) Debt Deflation: Banks hate trying to raise money to pay depositors so
they start selling assets.
Federal Reserve Act
diffuse power along regional lines, between the private sector and the government, and among bankers, business people, and the public —> FOMC, Federal Reserve Banks
District Banks
Quasi-public institution owned by private commercial banks in the district that are members of the Fed system
Member banks elect six directors for each district; three more are appointed by the Board of Governors
Board of Governors
follow the incoming economic data from government agencies and private sector organizations and provide guidance to the policy-makers on the direction in which
the economy might be headed and the potential impact of monetary policy actions on the economy. (federal reserve system)
When the euro appreciates (holding everything else constant), then
European chocolate sold in the United States becomes more expensive.
If the Mexican peso depreciates against the dollar, then
the dollar has appreciated against the peso.
A decrease in government budget deficits will _________ of bonds.
DECREASE the SUPPLY
A decrease in liquidity will ___________ of bonds.
DECREASE the DEMAND
A decrease in wealth of people will ___________ of bonds.
DECREASE the DEMAND
A decrease in expectations for economic growth will ______________ of bonds.
DECREASE; SUPPLY
You pay for a 150 euro dinner in Paris with your credit card. When you get home you see a charge of $75 on your credit card bill. What was the spot exchange rate for this purchase?
2 Euros Per dollar
What are the three major parts of the Federal Reserve System
Board of Governors; Federal Reserve Banks; Federal Open Markets Committee
What is the advantage in securitizing mortgages to savers?
diversify/spread risk
When the Federal Reserve buys bond from the public…
How does that affect the Money Demand?
No Change
When the Federal Reserve buys bond from the public…
How does that affect the Money Supply?
INCREASE
When the Federal Government sells bonds to the public…
How does that affect the Money Supply?
No Change
When the Federal Government sells bonds to the public…
How does that affect the money demand
No Change
What happens to Money Demand if
Real interest Rates rise
DECREASE
What happens to Money Demand if
RGDP Rises
Increases
What happens to Money Demand if
Transaction Cost Rises
INCREASE
What happens to Money Demand if
Price Level Rises
DECREASE
What happens to Money Demand if
Money Supply Rises
no change
If MB = 100. The reserve requirement ratio (r) is 10%. Total reserves = 90 and currency ratio = 5%.
(MB = Currency + Bank Reserves)
Total Currency
MB = TC + Total Reserves
100 = TC + 90
10
If MB = 100. The reserve requirement ratio (r) is 10%. Total reserves = 90 and currency ratio = 5%.
What are Total Deposits?
CR = RR / X
.05 = 10/ X
200
If MB = 100. The reserve requirement ratio (r) is 10%. Total reserves = 90 and currency ratio = 5%.
What are total Excess reserves?
Reserve Requirement Rate / Total Deposits (.10 * 200 = 20)
ER = 90 – 20 == 70 (total reserves – Required Reserves)
If MB = 100. The reserve requirement ratio (r) is 10%. Total reserves = 90 and currency ratio = 5%.
What is excess reserve ratio?
Excess Reserves / Total Deposits
(70 / 200)
.35
If MB = 100. The reserve requirement ratio (r) is 10%. Total reserves = 90 and currency ratio = 5%.
What is the money multiplier?
1 + Currency Ratio/ (Currency Ratio + Reserve Requirement Ratio + Excess Reserve Ratio)
1 / (.05 + .35 + .10) = 2
If MB = 100. The reserve requirement ratio (r) is 10%. Total reserves = 90 and currency ratio = 5%.
What is Total Money Supply?
MB * MM = 200
100 × 2
A coupon bond has a face value of 2000 and a coupon rate of 5%. Its current Yield to Maturity is 10%. It matures in 3 years. What is the current price. (assume annual payments end of the year) (Show your work)
100 / (1 + .1) + (100 / 1 + .1) ^2 +(100 / 1 + .1)^3 + (2000 / 1 + .1)^3 = 1751.31
5% * 2000 = 100
You bought a 3-year coupon bond for 7,000 today. It has a coupon rate of 10% and a Face Value of 10,000.(assume annual payments end of the year)
7000 = 1000 / ((1+YTM)^1)+ (1000 / (1+YTM)^2)+ (1000 / (1+YTM)^3) + (10000 / (1+YTM)^3)
Draw the Money Market of the United States Before and after a large increase in the currency ratio.
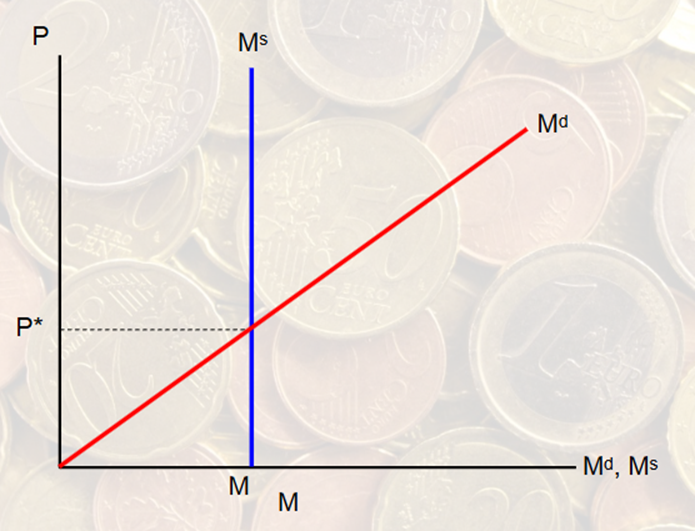
Supply moves to the left more
the FED did nothing —> Increase
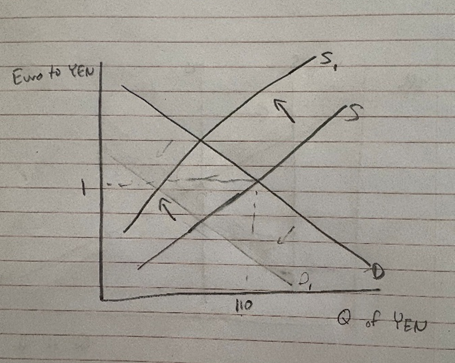
Draw the foreign exchange market for Yen with an equilibrium exchange rate of 1 Euro to 110 Yen. Show what happens if Europe prohibits the export of goods to Japan.
Draw the foreign exchange market for Pounds with an equilibrium exchange rate of 150 Yen to 1 Pound. Show what happens if the Japanese economy’s productivity grows faster than Britain’s.
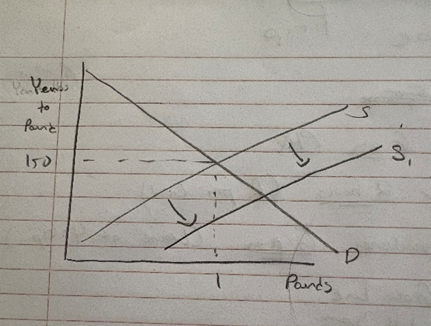
Demand shifts to the left too
List 3 factors that determine exchange rates in the long run?
Productivity; Trade Barriers; Relative Price Level
Why would a local bank lend money to people with poor credit records and low income to buy a house?
Just sell the loan
List one factor that determine exchange rates in the short run?
interest rate differentials between countries.
What is the most important factor that gives the Federal Reserve the Ability to be so independent?
The ability to make decisions without requiring approval from the executive or legislative branches of government. (have its own funding)
UNDER EXPECTATION THEORY OF INTEREST RATES. If this year a 1-year bond has a return of 1%, and people believe next year a one-year bond will have return of 2%, and the year after people believe a 1- year bond will have a return of 3%. What should interest rates on a 3-year bond be today?
1% + 2% + 3% / 3 = 2%
If the 3-year bond rate is 5% what is the liquidity premium
3
What is the Global Pool of money
total amount of capital (money) available worldwide for investment and lending
Draw the Bond market. Be sure to label everything. Show what happens before and after China becomes more wealthy.
Borrowing?
Interest Rates?
Lending?
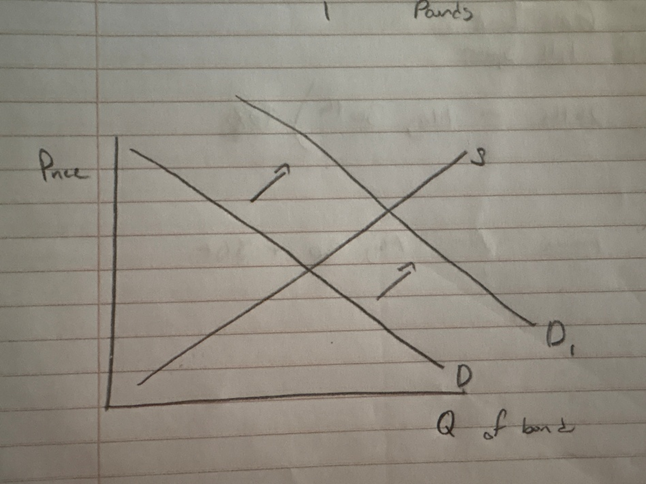
INCREASE
DECREASE
INCREASE
The Federal Reserve has set the discount rate at 2%. It pays 1% on Reserves. The current Federal Funds Rate is 1.5%. Draw the Federal Funds Market
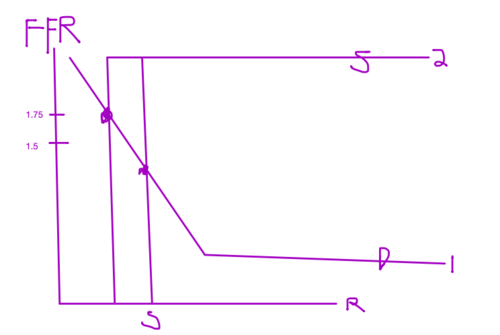
Show above what happens when the Fed uses open market operations to raise the Federal Funds rate to 1.75%
line moves to the left since supply is moving only
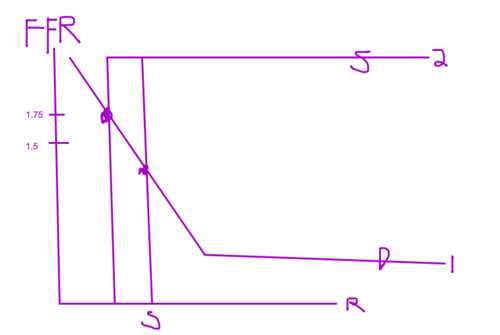
How do they raise the rate?
FOMC, OMO, Adjusting Reserves