(BIO 223) Anatomy & Physiology I Lab Collection
1/321
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
322 Terms
what is connective tissue used for?
these cells are used for binding, support, protection, insulation, and transportation (usually blood)
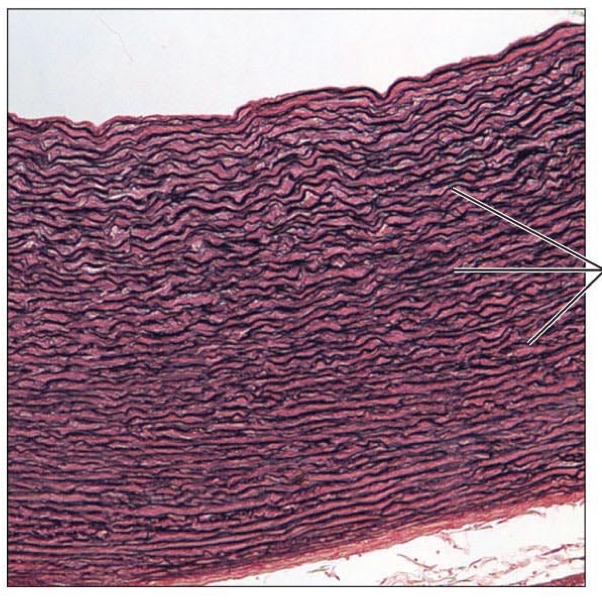
Connective Tissue Proper: Dense Regular
Connective Tissue Proper: Dense Irregular
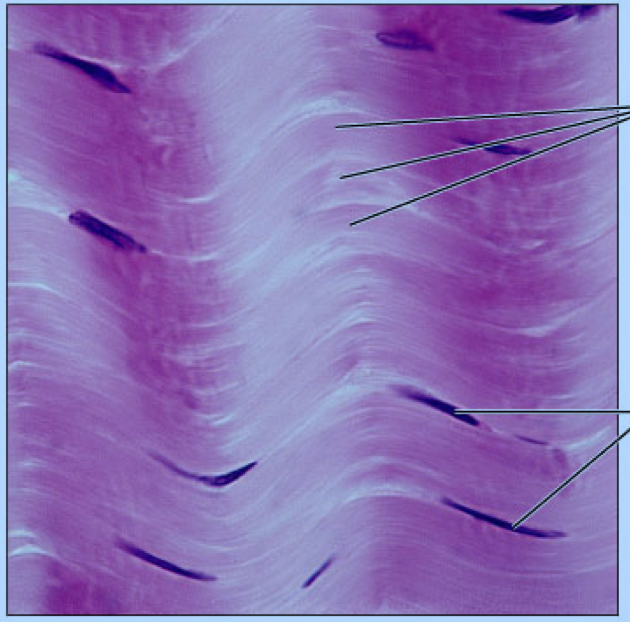
Connective Tissue Proper: Elastic
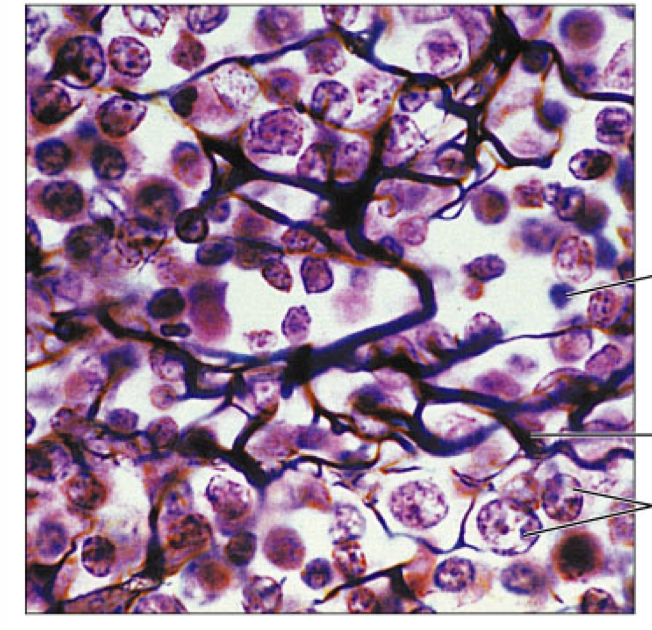
Connective Tissue Proper: Loose, reticular
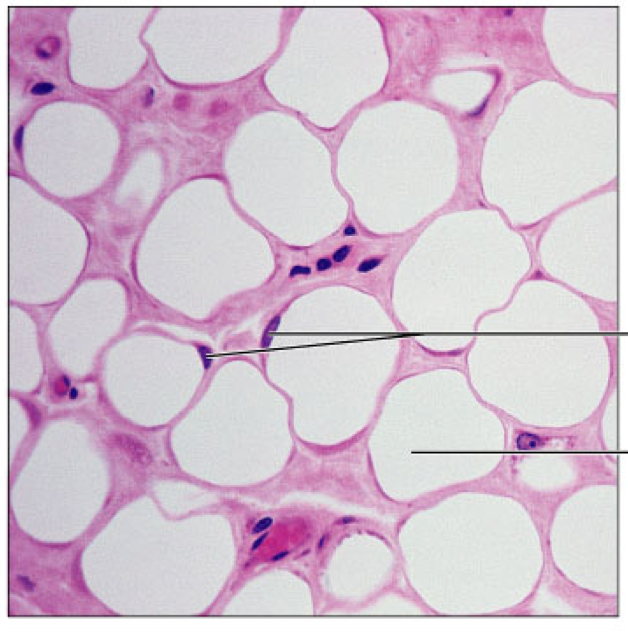
Connective Tissue Proper: Loose, adipose
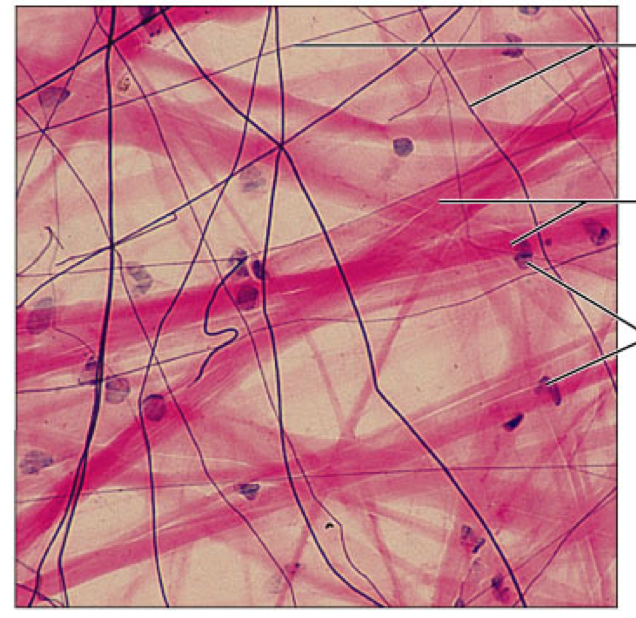
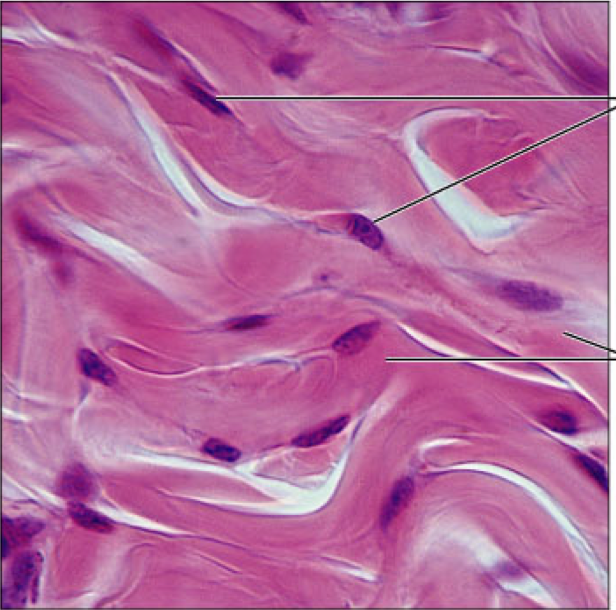
Connective Tissue Proper: Loose, areolar
What are epithelial cells used for?
used for providing cover for organs and protection, can secrete or absorb
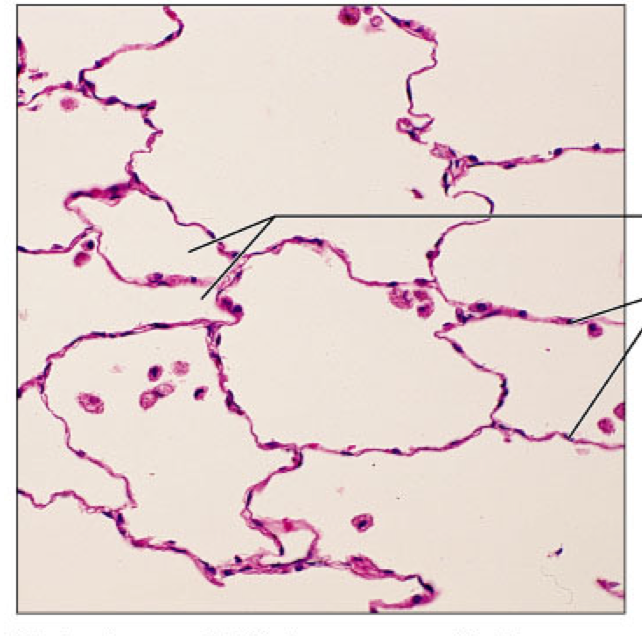
Epithelia: Simple Squamous
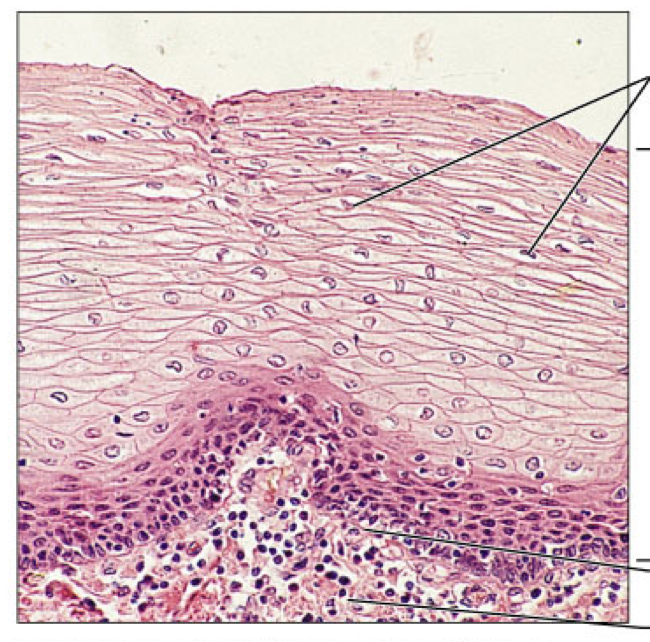
Epithelia: Stratified Squamous
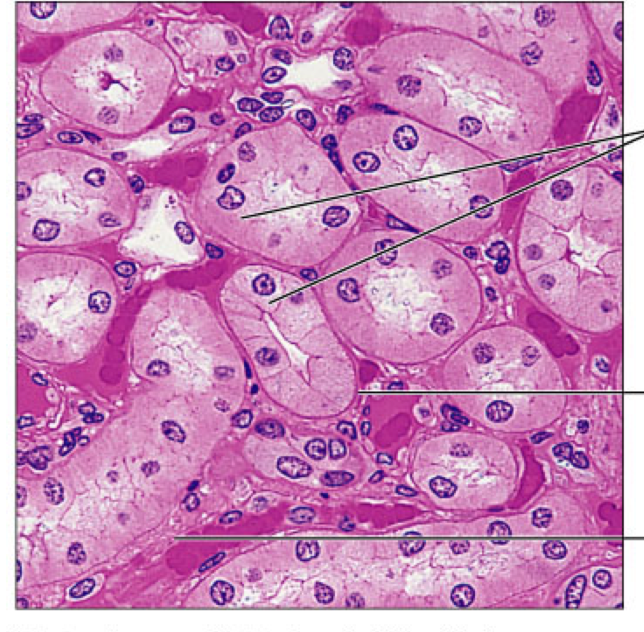
Epithelia: Simple Cuboidal
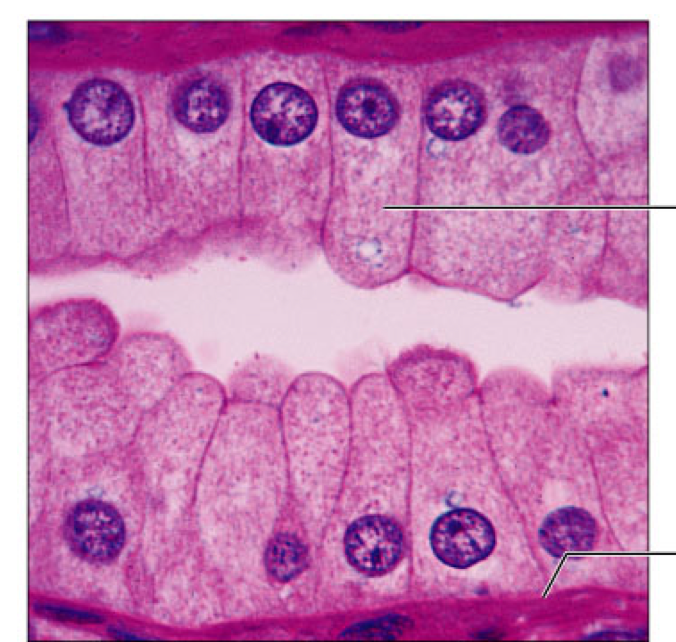
Epithelia: Simple Columnar
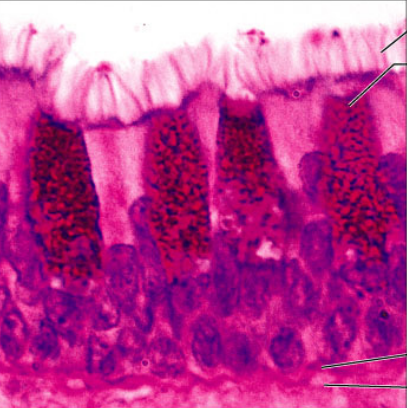
Pseudostratified Ciliated Columnar
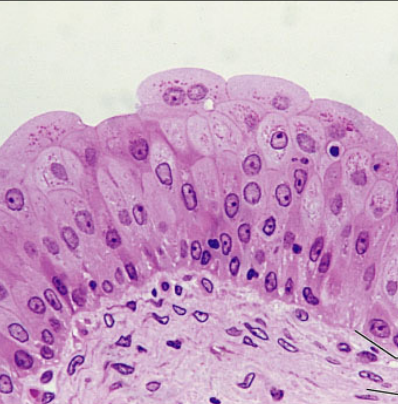
Epithelia: Transitional
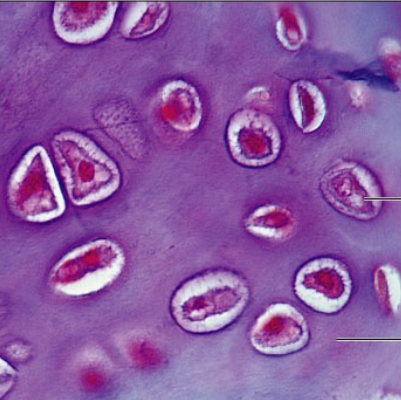
Connective Tissue: Hyaline Cartilage
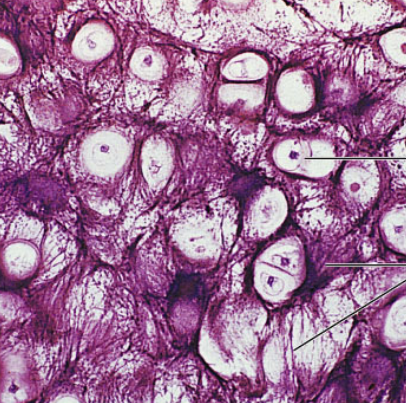
Connective Tissue: Elastic Cartilage
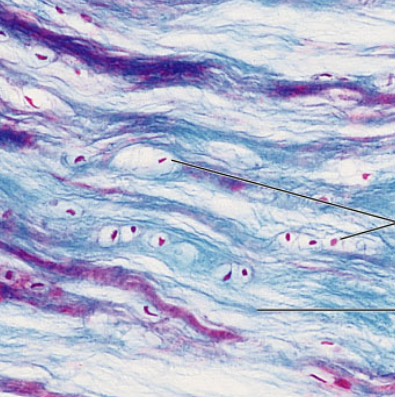
Connective Tissue: Fibrocartilage Cartilage
diffusion
The movement of solute across a semi permeable membrane
isotonic
even flow of concentartaion (low & high)
hypertonic
when comparing two solutions, the solution with the greater concentration, leading to shrinkage
hypotonic
Having a lower concentration of solute than another solution, expands
osmosis
The movement of water across a semipermeable membrane
What is Cell Permeability?
The ability of a cell membrane to control the flow of substances in and out of the cell.
What is a thin sheet of material called when it only allows certain molecules to travel from one side to another?
Semi-Permeable Membrane
When water passes across a semipermeable membrane through osmosis, what direction along the concentration gradient does it travel?
up the concentration gradient, from low to high tonicity
When solute passes across a semipermeable membrane through diffusion, what direction along the concentration gradient does it travel?
down the concentration gradient, from high to low
Passive transport
a type of membrane transport that does not require energy to move substances across cell membranes.
Active transport
a type of membrane transport that requires energy to move substances across cell membranes.
facilitated diffusion
diffusion of large molecules assisted by membrane proteins
Primary active transport
uses ATP directly to move molecules against the concentration gradient.
Secondary Active Transport
uses the energy from a primary active transport to move other molecules across the concentration gradient
superficial
towards the outside of body, surface
distal
away from the point of attachment
inferior
towards the bottom, away from head
deep
toward the inside of the body
posterior
towards the back; behind
lateral
away from the midline
caudal
toward the tail, away from the head
oblique plane
divides body at an angle, top to bottom (diagonally)
proximal
towards the point of attachment
superior
toward head; above
anterior
towards front; in front of
quadrupeds
animals that walk on all fours
frontal plane
Divides the body into front and back portions, front to back
transverse plane
line that divides the body into upper and lower sections, top to bottom
median plane
divides the body into equal left and right halves, left to right
apparatus
the technical equipment or machinery needed for a particular activity or purpose
appendicular
arms, legs
axial skeleton
head, neck, trunk
bipedal
animals that walk upright on 2 legs
what is catalase?
Enzyme used to break down Hydrogen peroxide, Optimal conditions for this enzyme are a pH 7, at 37C
what is an enzyme?
a protein that acts as a catalyst for chemical reactions, meaning it speeds up chemical reactions in living things, and is essential for all bodily functions
What does a positive result for glucose using benedicts solution look like?
green, yellow, orange/rusty
What does a positive result for NaCl using silver nitrate look like?
solution forms white precipitate forms or cloudiness
What does a negative result for Glucose using benedicts solution look like?
solution remains blue
What is the enzyme equation
Enzyme + Substrate → Enzyme Substrate Complex → Enzyme Product
(E + S → ES(complex) → E + P
What happens to catalase (or other enzymes) when they are heated beyond their ideal temperature
they denature, meaning they unravel and permanently lose their shape making them unable to be used as they no longer have the correct shape to bind with their substrates.
what does benedicts solution do?
it is a solution to test for glucose.
what is the name for NaCl?
sodium chloride
what does lugols iodine test for in a solution?
starch
What does a positive result for Starch using lugols iodine look like?
black or dark colored solution
What does a negative result for NaCl using silver nitrate look like?
no white or cloudiness, clear
What does a negative result for Starch using lugols iodine look like?
not black or dark colored, solution remains clear
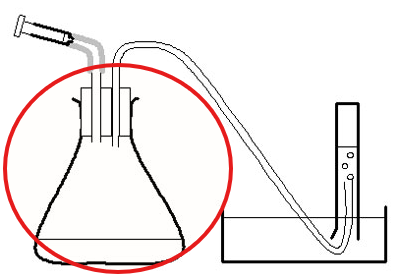
Flask
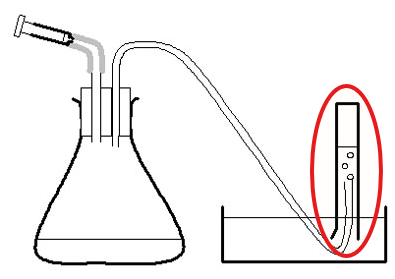
Burette (or buret)
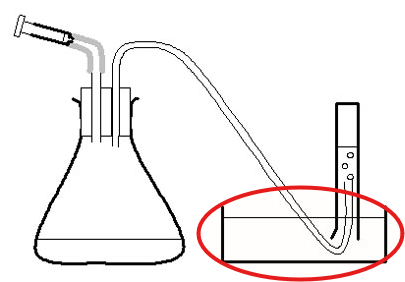
Finger Bowl
What Is left in the flask after the catalase reaction occurs
Oxygen, Water, Catalase
dorsal cavity
includes the cranial (brian) and vertebral (spine) cavities
visceral serosa
lines outside of organs
serosal fluid
fills space between visceral and parietal serosae, keeps organs from sticking
parietal serosa
tissue lining each ventral cavity
ventral cavity
thoracic cavity and abdominopelvic cavity
Cranial Cavity
Houses the Brain
Vertebral Cavity
Houses the spinal cord
Thoracic Cavity
Houses the vital organs, heart, lungs, etc. Contains the pleural, mediastinum, and pericardial cavities.
Diaphragm
muscle that separates the thoracic and abdominal cavities
Abdominal cavity
Houses the digestive system
Abdominopelvic cavity
Houses the abdominal cavity and pelvic cavity
Pelvic cavity
houses urinary system and reproductive organs
Orbital cavity
houses the eyes
Nasal cavity
posterior and within the nose
oral and digestive cavities
mouth and cavities of the digestive organs
middle ear cavity
contains bones that transmit sound vibrations (ossicles)
synovial cavities
joint cavities
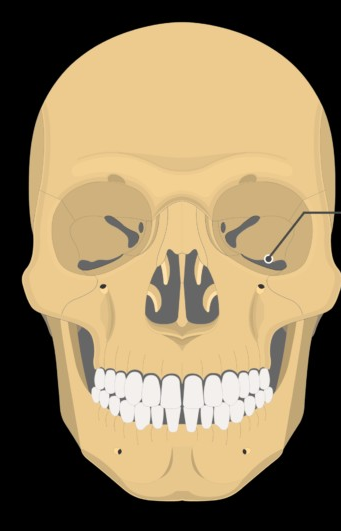
inferior orbital fissure
What is this?
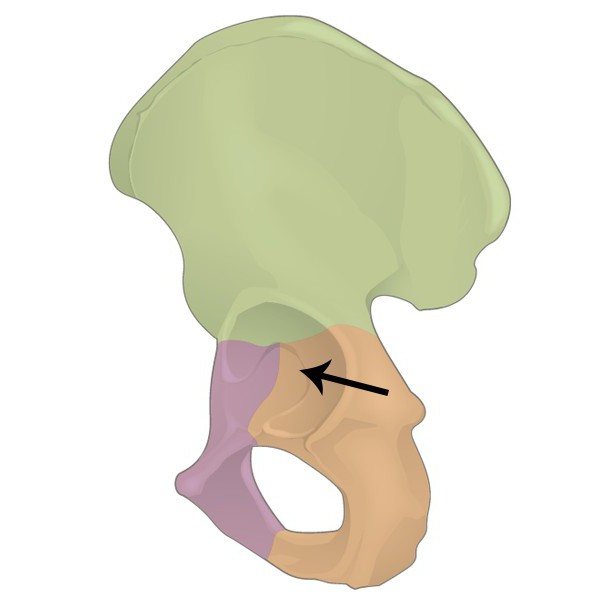
Acetabulum
What Feature is this?
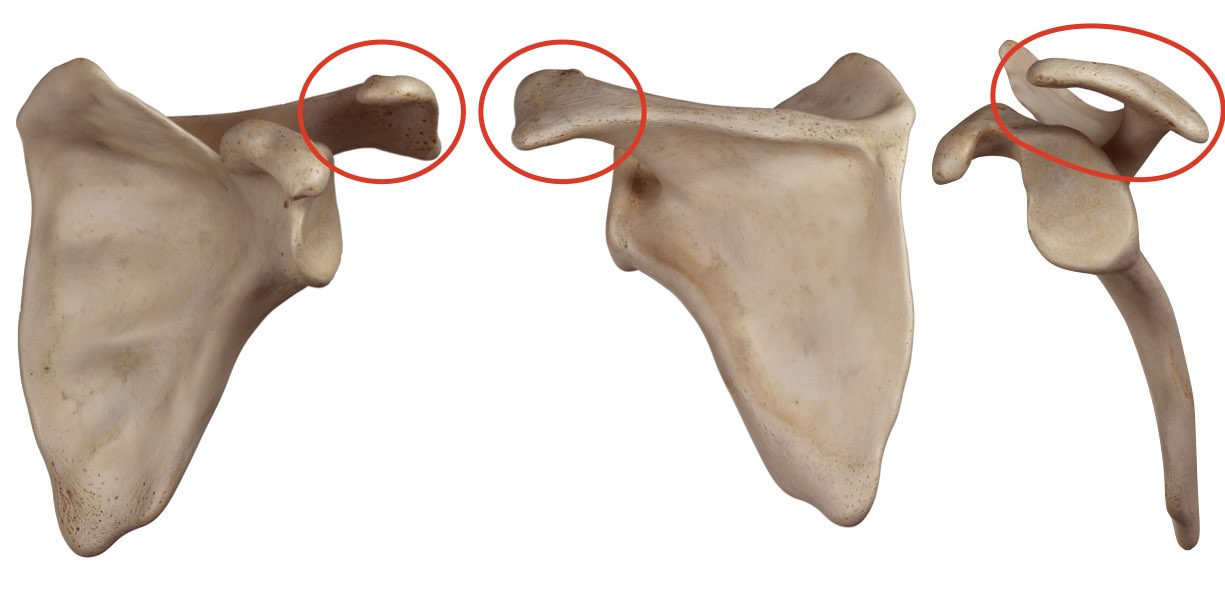
Acromion
What Feature is this?
Ala
What Feature is this?
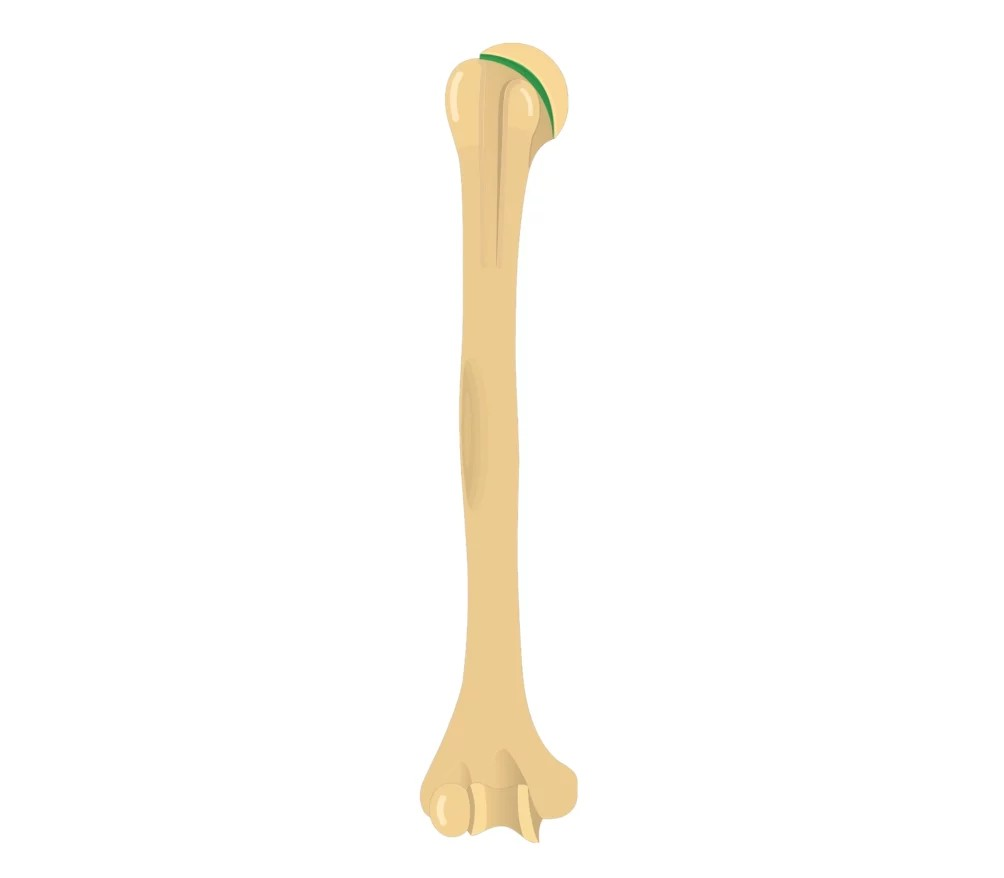
anatomical neck
What is this?
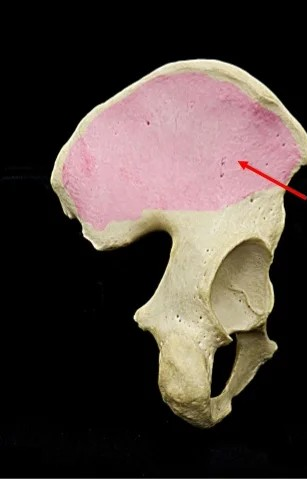
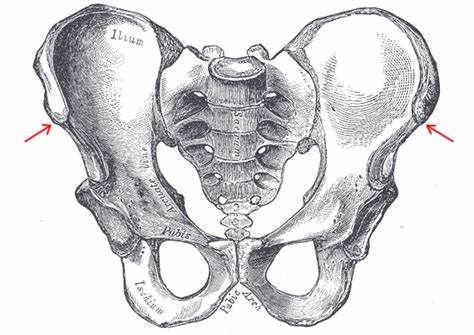
anterior superior iliac spine
What is this?
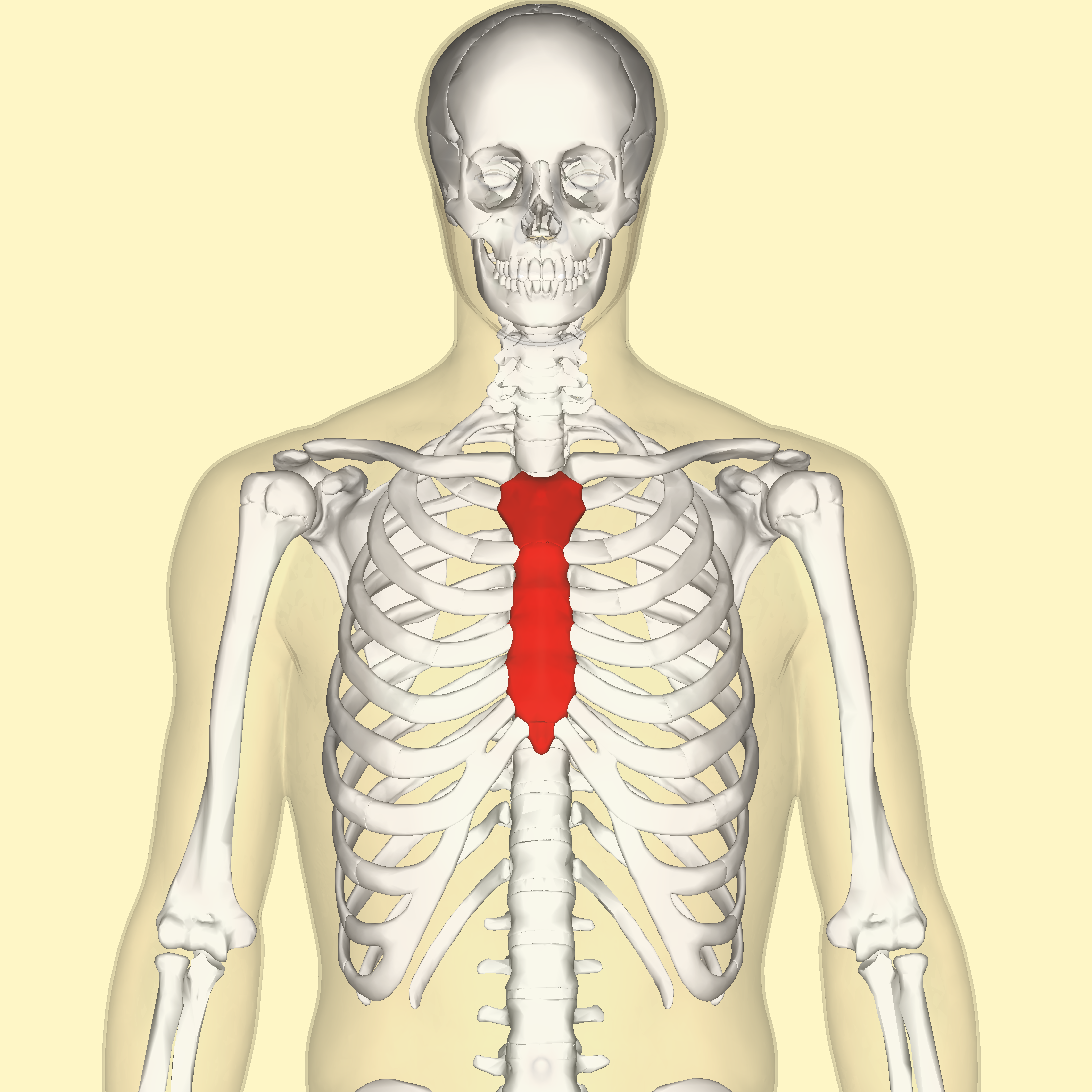
body of sternum
What is this?
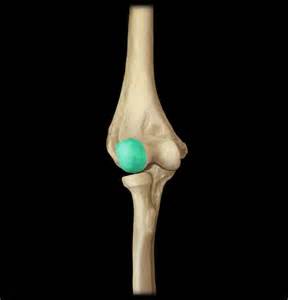
capitulum
What is this?
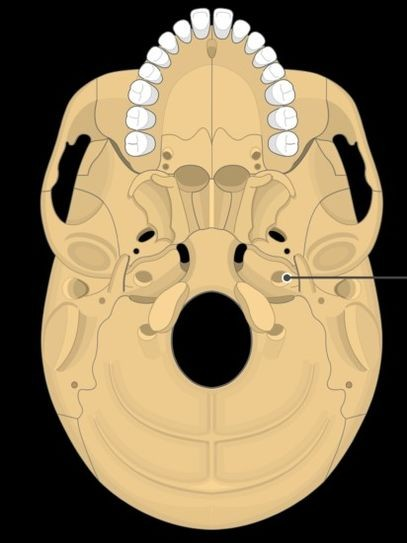
carotid canal
What is this?
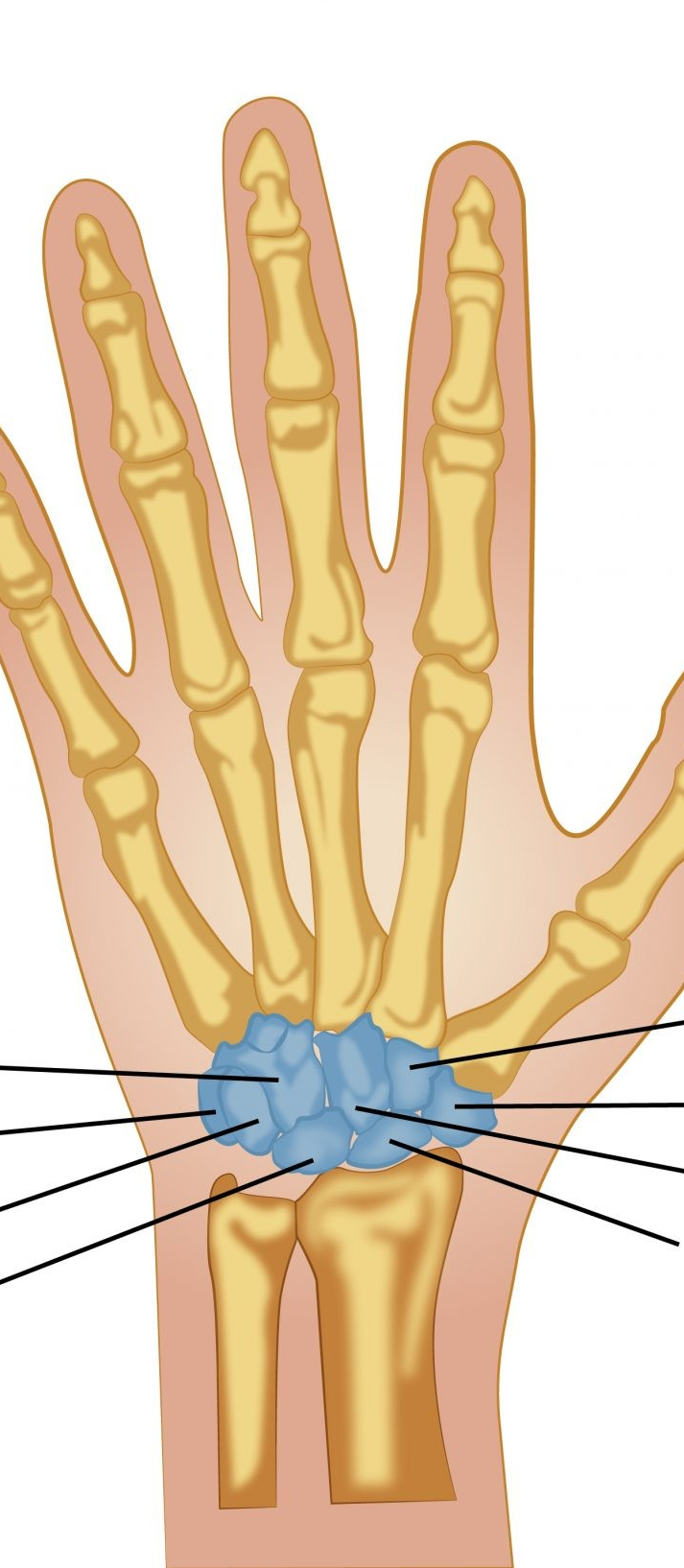
Carpals
What is this?
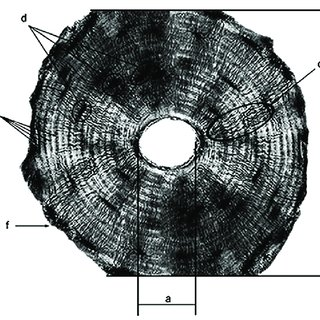
Central Canal
What is this?
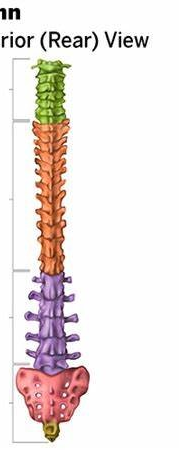
cervical curvature
What is this? (green)
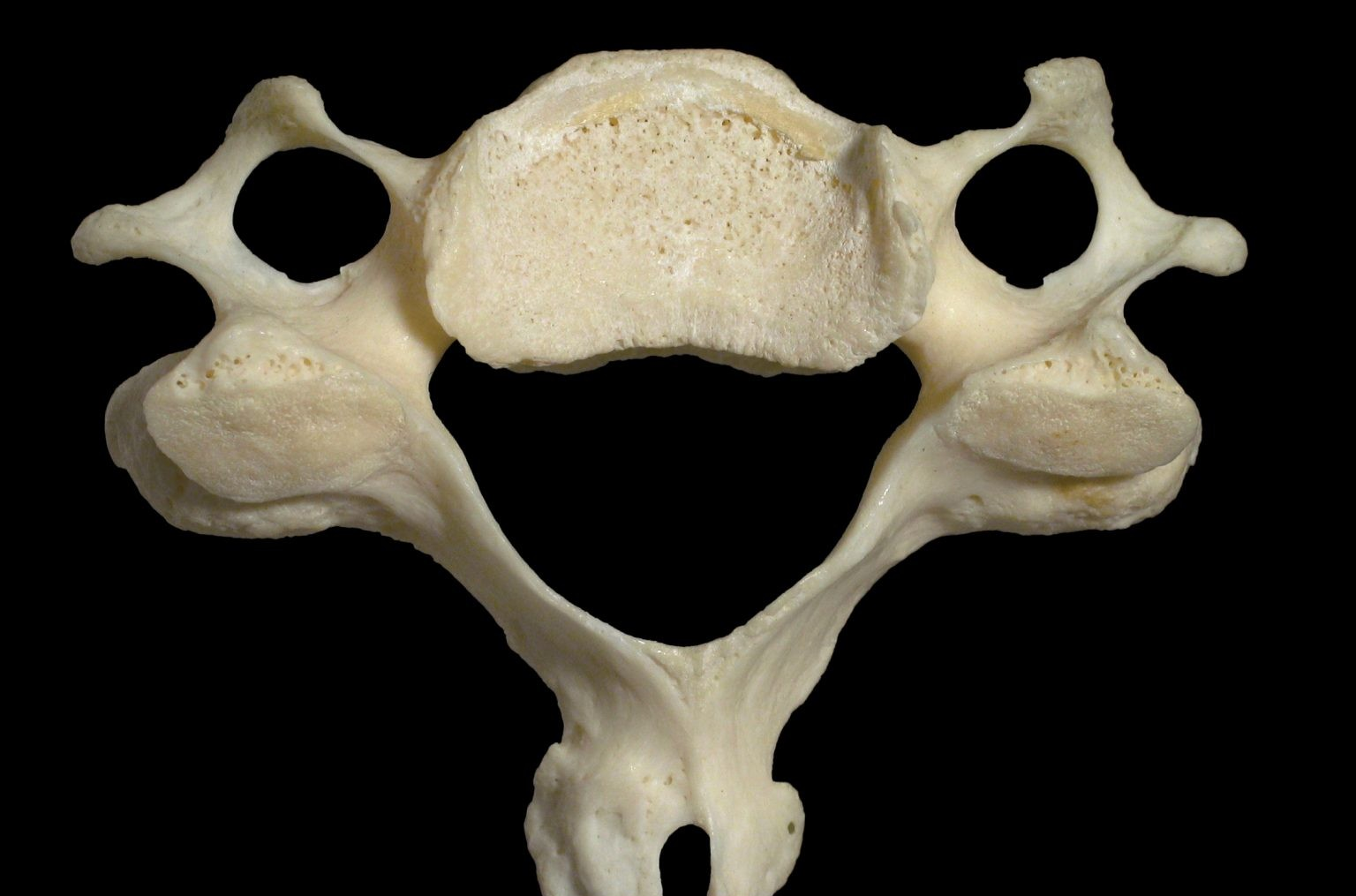
Cervical Vertebrae
What is this?
Clavicle
What is this?
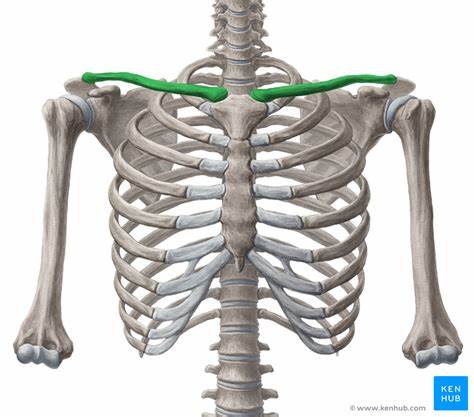
Clavicular Notch
What is this?
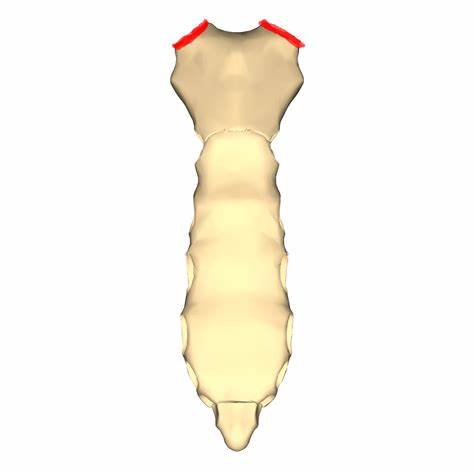
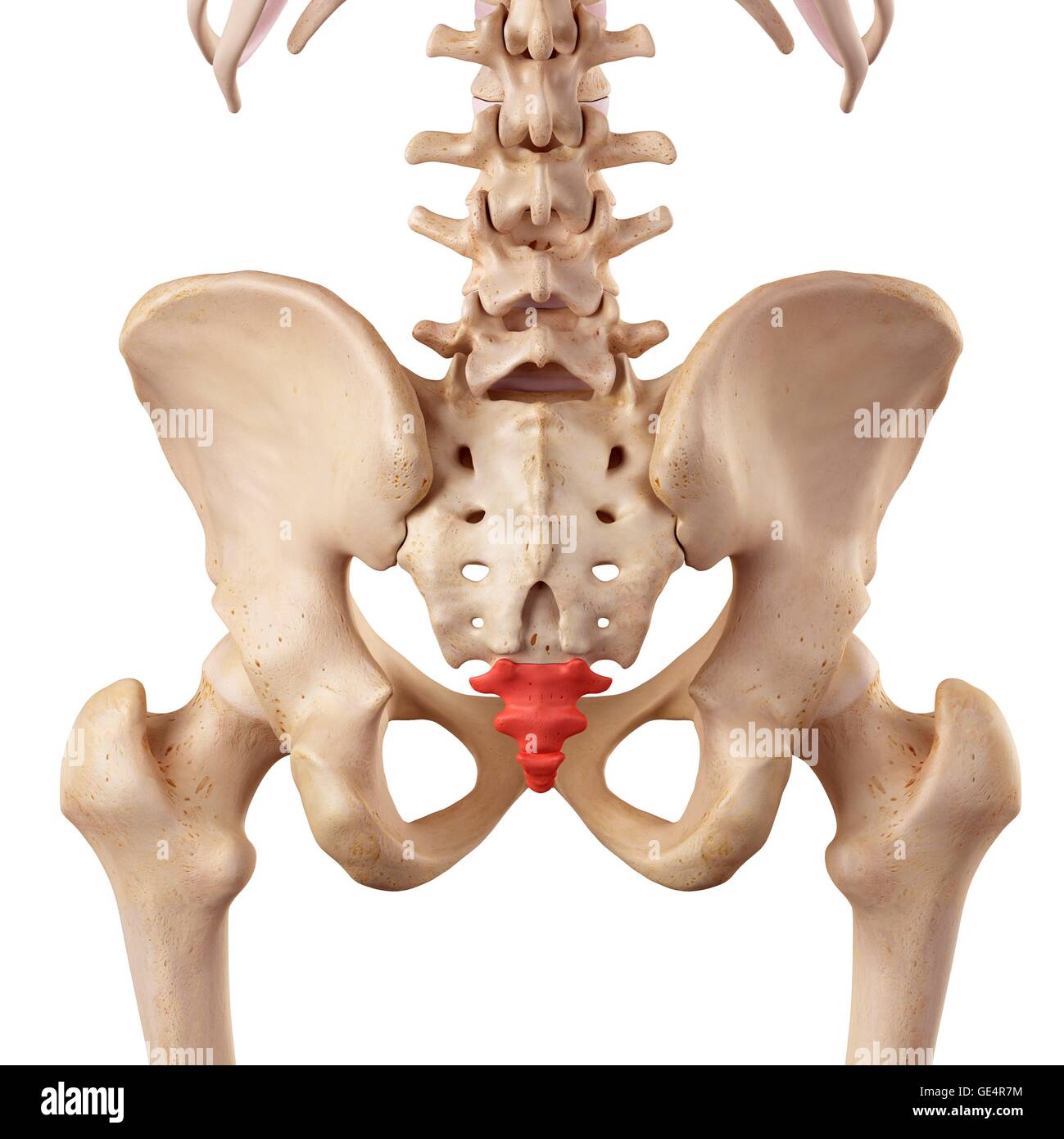
Coccyx
What is this?