Organizational Behavior Final Quiz
1/310
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
311 Terms
personality
The structures and propensities inside people that explain their characteristic patterns of thought, emotion, and behavior. Personality reflects what people are like and creates their social reputation.
traits
Recurring trends in people's responses to their environment.
cultural values
Shared beliefs about desirable end states or modes of conduct in a given culture that influence the expression of traits.
five personality dimensions (Big Five)
1) Agreeableness
2) Extroversion
3) Conscientiousness
4) Openness to experience
5) Neuroticism
conscientiousness
One of the "Big Five" dimensions of personality reflecting traits like being dependable, organized, reliable, ambitious, hardworking, and persevering.
agreeableness
One of the "Big Five" dimensions of personality reflecting traits like being kind, cooperative, sympathetic, helpful, courteous, and warm.
neuroticism
One of the "Big Five" dimensions of personality reflecting traits like being nervous, moody, emotional, insecure, jealous, and unstable.
Openness
One of the "Big Five" dimensions of personality reflecting traits like being curious, imaginative, creative, complex, refined, and sophisticated.
extraversion
One of the "Big Five" dimensions of personality reflecting traits like being talkative, sociable, passionate, assertive, bold, and dominant.
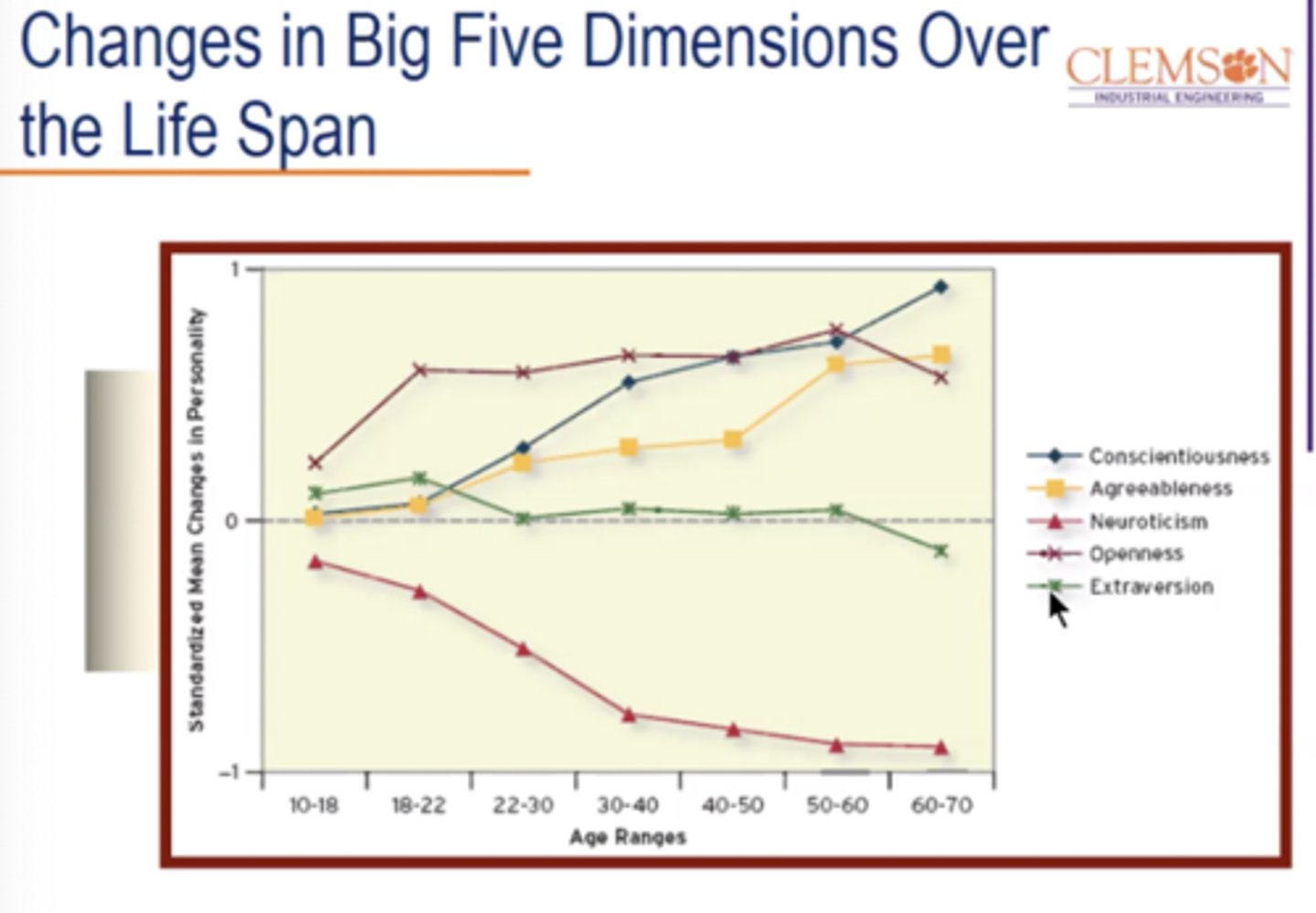
changes in big five dimensions over the life span
Extraversion remains quite stable throughout a person's life. Openness to experience also remains stable, after a sharp increase from the teenage years to college age. The other three dimensions, however, change quite significantly over a person's life span.
accomplishment striving
A strong desire to accomplish task-related goals as a means of expressing personality.
communion striving
A strong desire to obtain acceptance in personal relationships as a means of expressing personality.
zero aquaintance
Situations in which two people have just met.
Positive Affectivity
a dispositional tendency to experience pleasant, engaging moods such as enthusiasm, excitement, and elation

negative affectivity
tendency to experience negative emotions and moods, feel distressed, and be critical of oneself and others
gripe index
your degree of satisfaction with something: dissatisfied, neutral, and satisfied
Differential exposure
Being more likely to appraise day-to-day situations as stressful, thereby feeling that stressors are encountered more frequently
differential reactivity
Being less likely to believe that one can cope with the stressors experienced on a daily basis
locus of control
Whether people believe the events that occur around them are self-driven or driven by the external environment.
external locus of control
the perception that chance or outside forces beyond your personal control determine your fate.
internal locus of control
the perception that you control your own fate
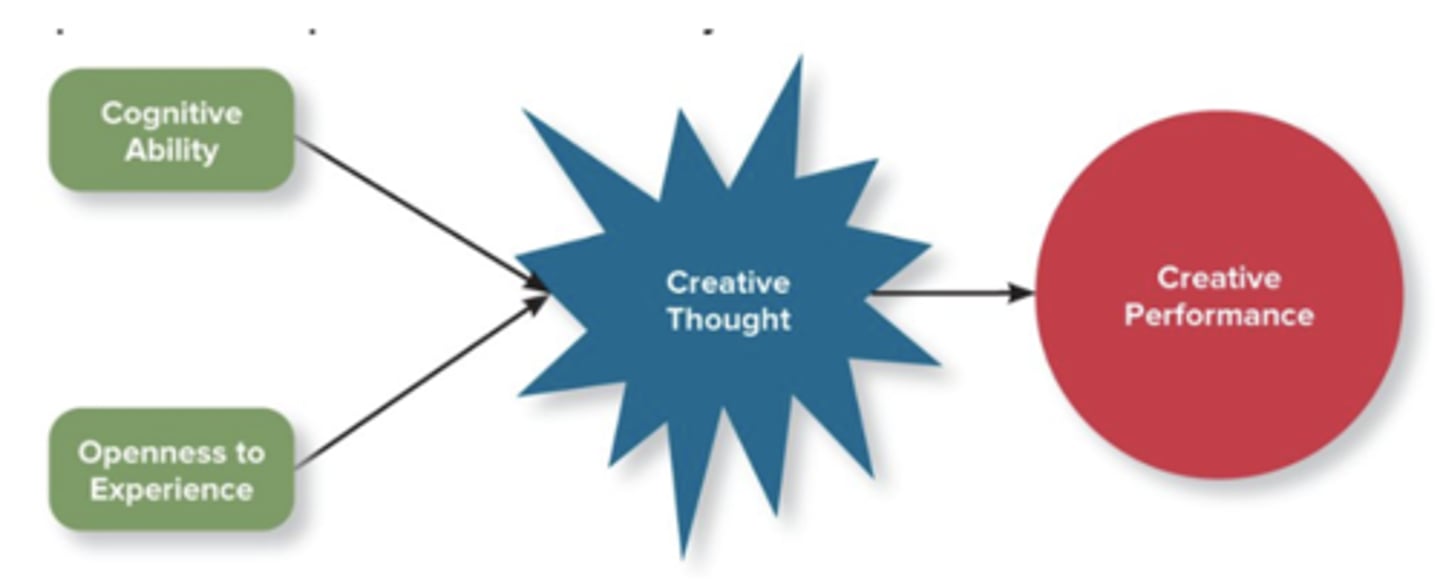
openness to experience and creativity
cognitive ability + openness to experience -> creative thought -> creative performance
Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI)
A personality framework that evaluates people on the basis of four types or preferences: extraversion versus introversion, sensing versus intuition, thinking versus feeling, and judging versus perceiving.
extraversion vs introversion, sensing vs. intuition, thinking vs. feeling, judging vs. perceiving
Extraversion versus Introversion (E or I)
whether a person tends to be outgoing and sociable or shy and quiet
Sensing versus Intuitive (S or N)
whether a person tends to focus on details or on the big picture when dealing with problems
Thinking versus feeling (T or F)
whether a person tends to rely on logic or emotions when dealing with problems
Judging versus perceiving (J or P)
whether a person prefers order and control or acts with flexibility and spontaneity
interests
Expressions of personality that influence behavior through preferences for certain environments and activities.
RIASEC model
An interest framework summarized by six different personality types, including realistic, investigative, artistic, social, enterprising, and conventional.
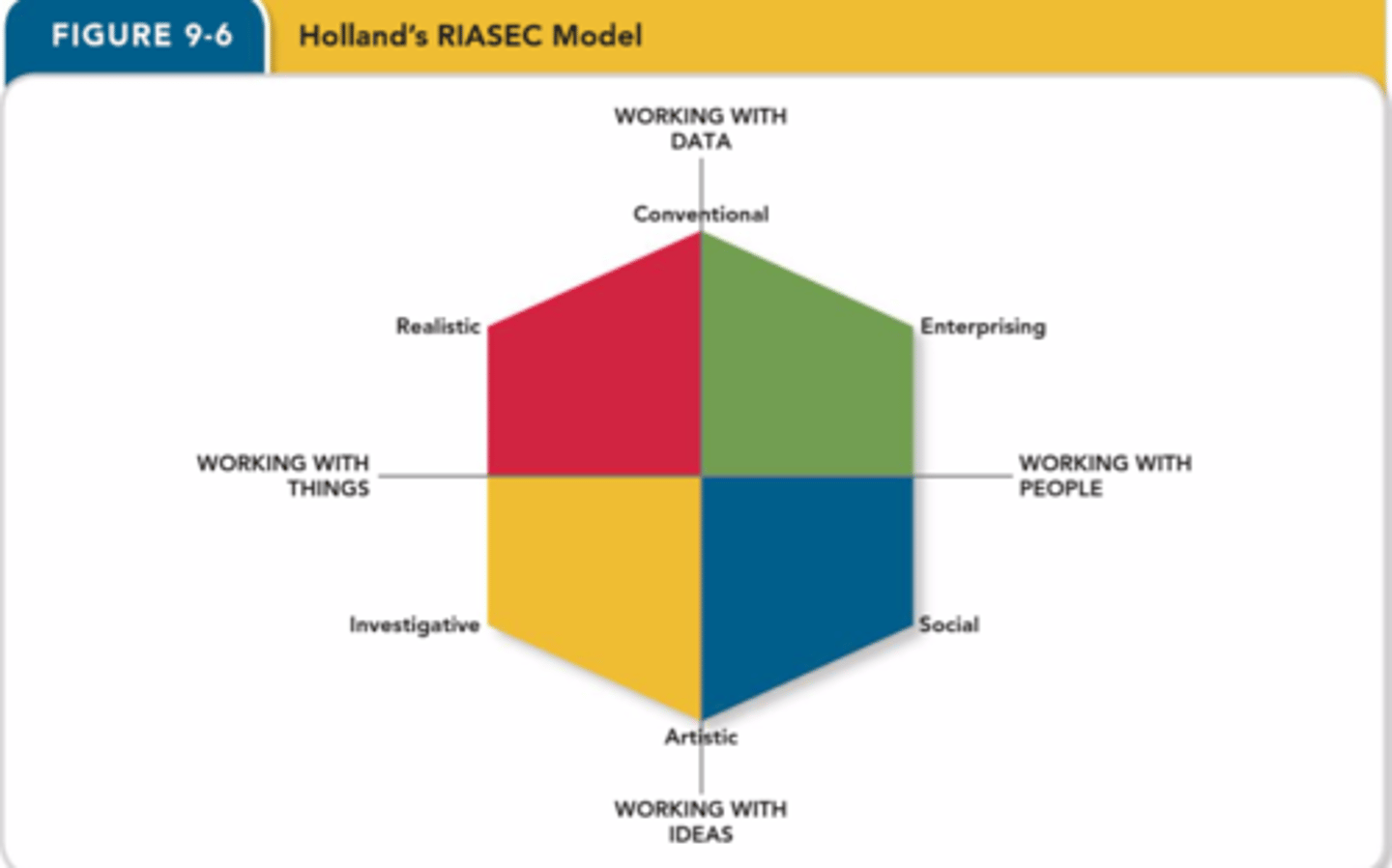
realistic (RIASEC)
Enjoys practical, hands-on, real-world tasks. Tends to be frank, practical, determined, and rugged.
investigative (RIASEC)
Enjoys abstract, analytical, theory-oriented tasks. Tends to be analytical, intellectual, reserved, and scholarly
artistic (RIASEC)
Enjoys entertaining and fascinating others using imagination. Tends to be original, independent, impulsive, and creative.
social (RIASEC)
enjoys helping, serving, or assisting others. tends to be helpful, inspiring, informative, and empathic
enterprising (RIASEC)
Enjoys persuading, leading, or outperforming others. Tends to be energetic, sociable, ambitious, and risk-taking.
conventional (RIASEC)
Enjoys organizing, counting, or regulating people or things. Tends to be careful, conservative, self-controlled, and structured.
Culture
The shared values, beliefs, motives, identities, and interpretations that result from common experiences of members of a society and are transmitted across generations.
Geert Hofstede
Created a framework of culture (Hofstede's Dimensions of Culture). employees in different countries tended to prioritize different values
Individualism/Collectivism
The degree to which a culture has a loosely knit social framework (individualism) or a tight social framework (collectivism).
power distance
The degree to which a culture prefers equal power distribution (low power distance) or an unequal power distribution (high power distance).
Uncertainty Avoidance
The degree to which a culture tolerates ambiguous situations (low uncertainty avoidance) or feels threatened by them (high uncertainty avoidance).
motivation toward achievement/success
The degree to which a culture values competition and excellence as a definition of success (decisive) or consensus and quality of life as a definition of success (consensus).
short-term versus long-term orientation
The degree to which a culture stresses values that are past- and present-oriented (short-term orientation) or future-oriented (long-term orientation).
indulgence versus restraint
The degree to which a culture values expression, freedom, and leisure versus strict social norms and order.
GLOBE project
A collection of 170 researchers from 62 cultures who examine the impact of culture on the effectiveness of leader attributes, behaviors, and practices.
Gender Egalitarianism
the culture promotes gender equality and minimizes role differences between men and women
Assertiveness
the culture values assertiveness, confrontation, and aggressiveness in social relationships
future orientation
the culture engages in planning and investment in the future while delaying individual or collective gratification
performance orientation
the culture encourages and rewards members for excellence and performance improvements
Humane Orientation
the culture encourages and rewards members for being generous, caring, kind, fair, and altruistic
ethnocentrism
a propensity to view one's own cultural values as "right" and those of other cultures as "wrong"
cultural mosaic
A metaphor for understanding the multiple cultural influences that can shape an individual's values. An employee's cultural mosaic includes demographic, geographic, and associative tiles that combine to form a picture of that employee's potential values.
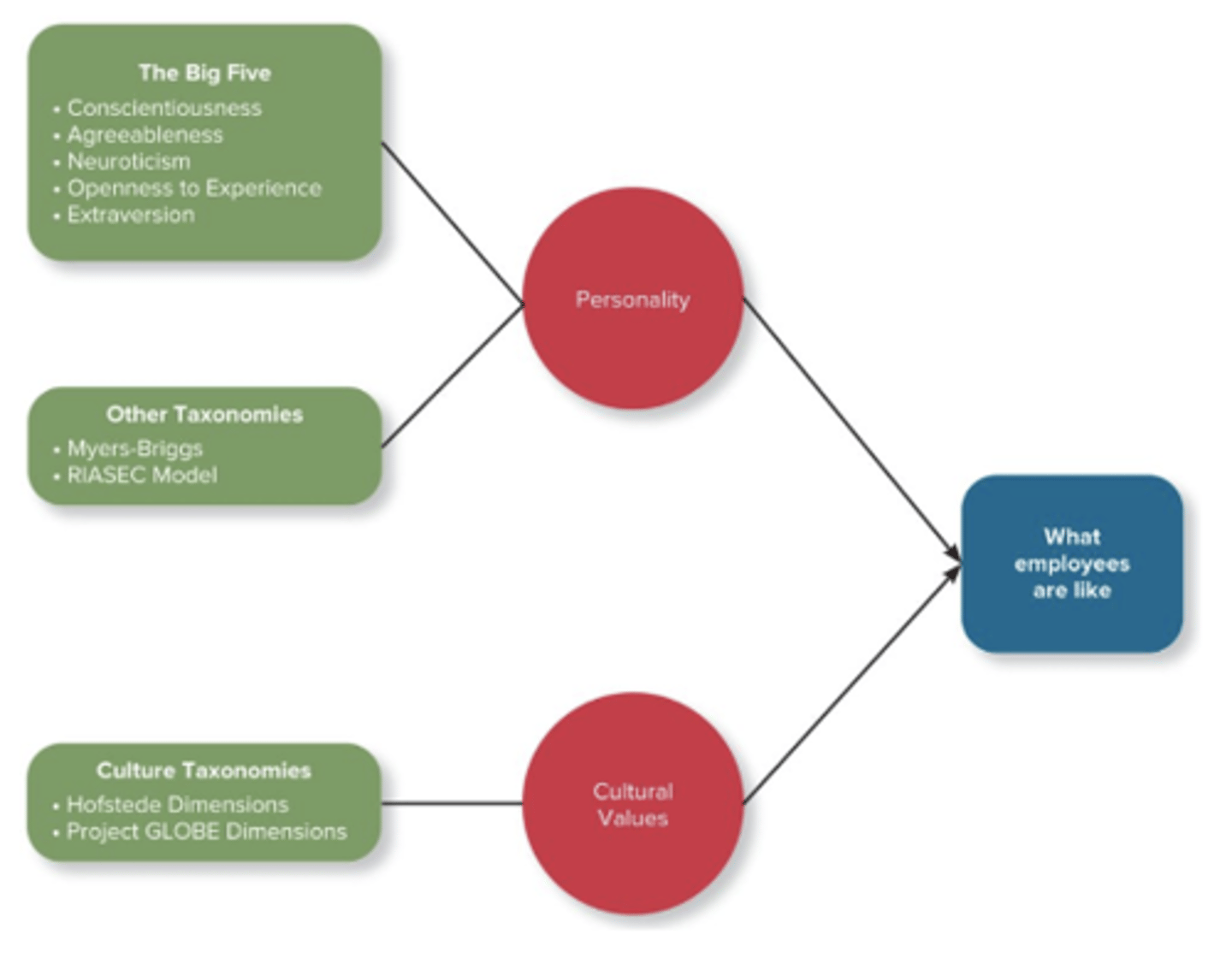
how can we describe what employees are like?
the big five, other taxonomies, culture taxonomies
Typical Performance
Performance in the routine conditions that surround daily job tasks.
Maximum Performance
Performance in brief, special circumstances that demand a person's best effort.
situational strength
The degree to which situations have clear behavioral expectations, incentives, or instructions that make differences between individuals less important.
Trait activation
The degree to which situations provide cues that trigger the expression of a given personality trait.
integrity tests
personality tests that focus specifically on a predisposition to engage in theft and other counterproductive behaviors
Clear purpose tests
Integrity tests that ask about attitudes toward dishonesty, beliefs about the frequency of dishonesty, desire to punish dishonesty, and confession of past dishonesty.
Veiled purpose tests
Integrity tests that do not directly ask about dishonesty, instead assessing more general personality traits associated with dishonest acts.
faking
Exaggerating responses to a personality test in a socially desirable fashion.
team
Two or more people who work interdependently over some time period to accomplish common goals related to some task-oriented purpose.
common goals and task-oriented purpose
working in teams
work team
A relatively permanent team in which members work together to produce goods and/or provide services. Four to eight members.
management teams
A relatively permanent team that participates in managerial-level tasks that affect the entire organization.
parallel teams
A team composed of members from various jobs within the organization that meets to provide recommendations about important issues.
project teams
A team formed to take on one-time tasks, most of which tend to be complex and require input from members from different functional areas.
action teams
A team of limited duration that performs complex tasks in contexts that tend to be highly visible and challenging.
Multiple team membership
A work arrangement in which employees are assigned to multiple teams simultaneously.
virtual teams
A team in which the members are geographically dispersed, and interdependent activity occurs through e-mail, web conferencing, and instant messaging.
forming
The first stage of team development, during which members try to get a feel for what is expected of them, what types of behaviors are out of bounds, and who's in charge.
storming
The second stage of team development, during which conflict occurs due to members' ongoing commitment to ideas they bring with them to the team.
norming
The third stage of team development, during which members realize that they need to work together to accomplish team goals and consequently begin to cooperate.
Performing
The fourth stage of team development, during which members are comfortable working within their roles, and the team makes progress toward goals.
adjourning
The final stage of team development, during which members experience anxiety and other emotions as they disengage and ultimately separate from the team.
model of team development
1. Forming
2. Storming
3. Norming
4. Performing
5. Adjourning

punctuated equilibrium
A sequence of team development during which not much gets done until the halfway point of a project, after which teams make necessary changes to complete the project on time.
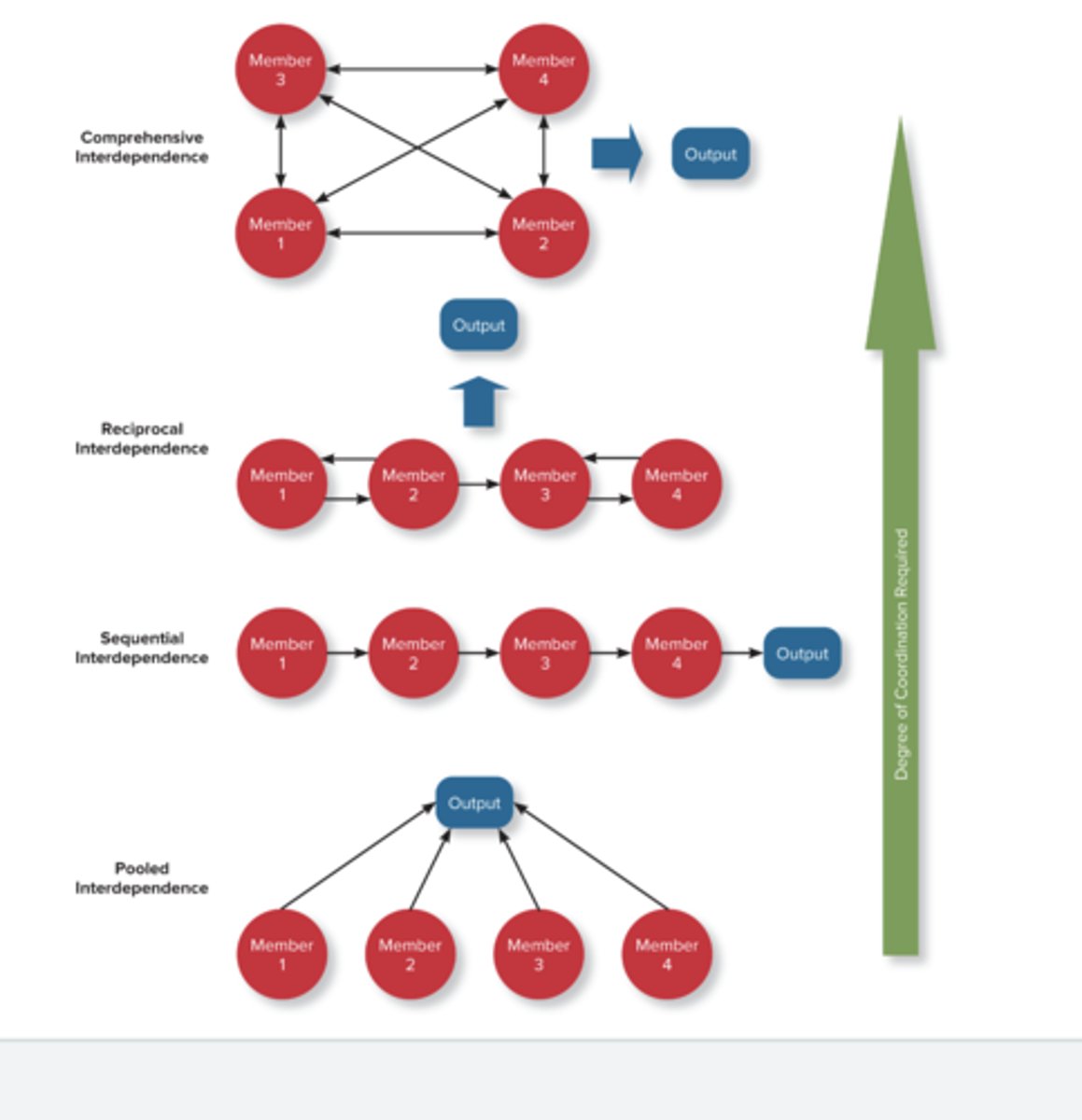
interdependence
Mutual dependence in a team
task interdependence
The degree to which team members interact with and rely on other team members for information, materials, and resources needed to accomplish work for the team.
pooled interdependence
A form of task independence in which group members complete their work assignments independently, and then their work is simply added together to represent the group's output.
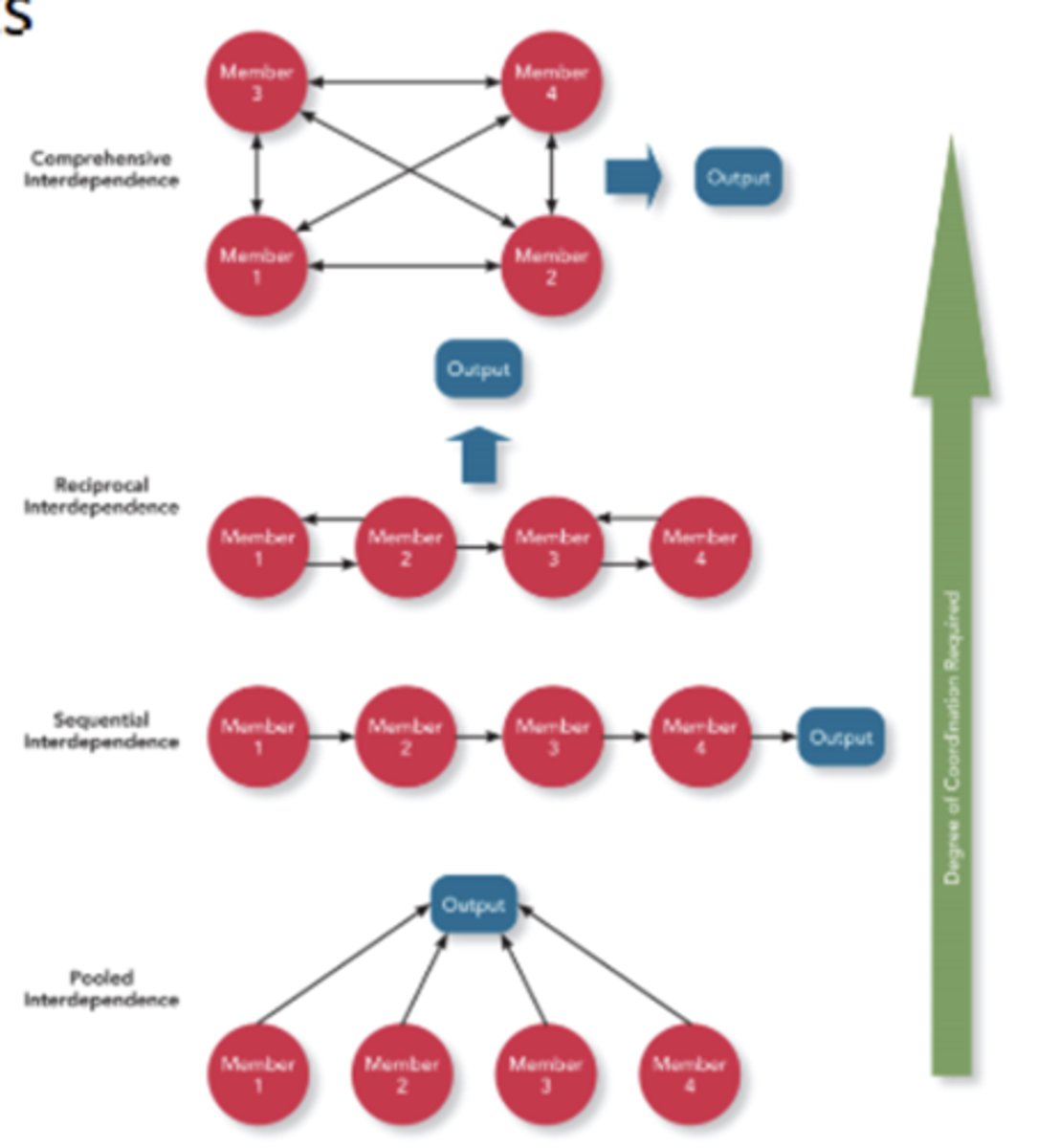
sequential interdependence
A form of task interdependence in which group members perform different tasks in a prescribed sequence, and members depend on only the member who comes before them in the sequence.
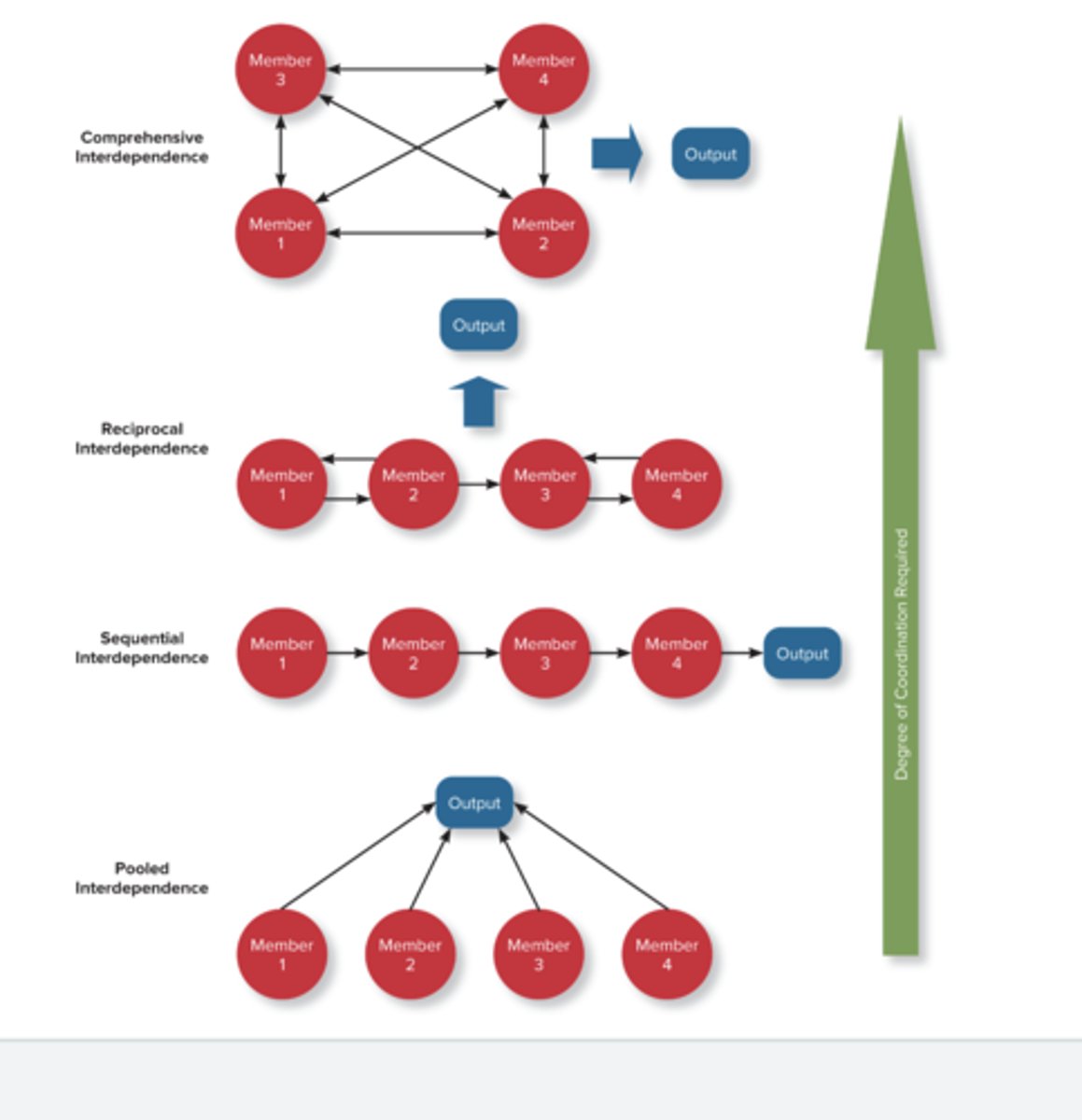
reciprocal interdependence
A form of task interdependence in which group members interact with only a limited subset of other members to complete the team's work.
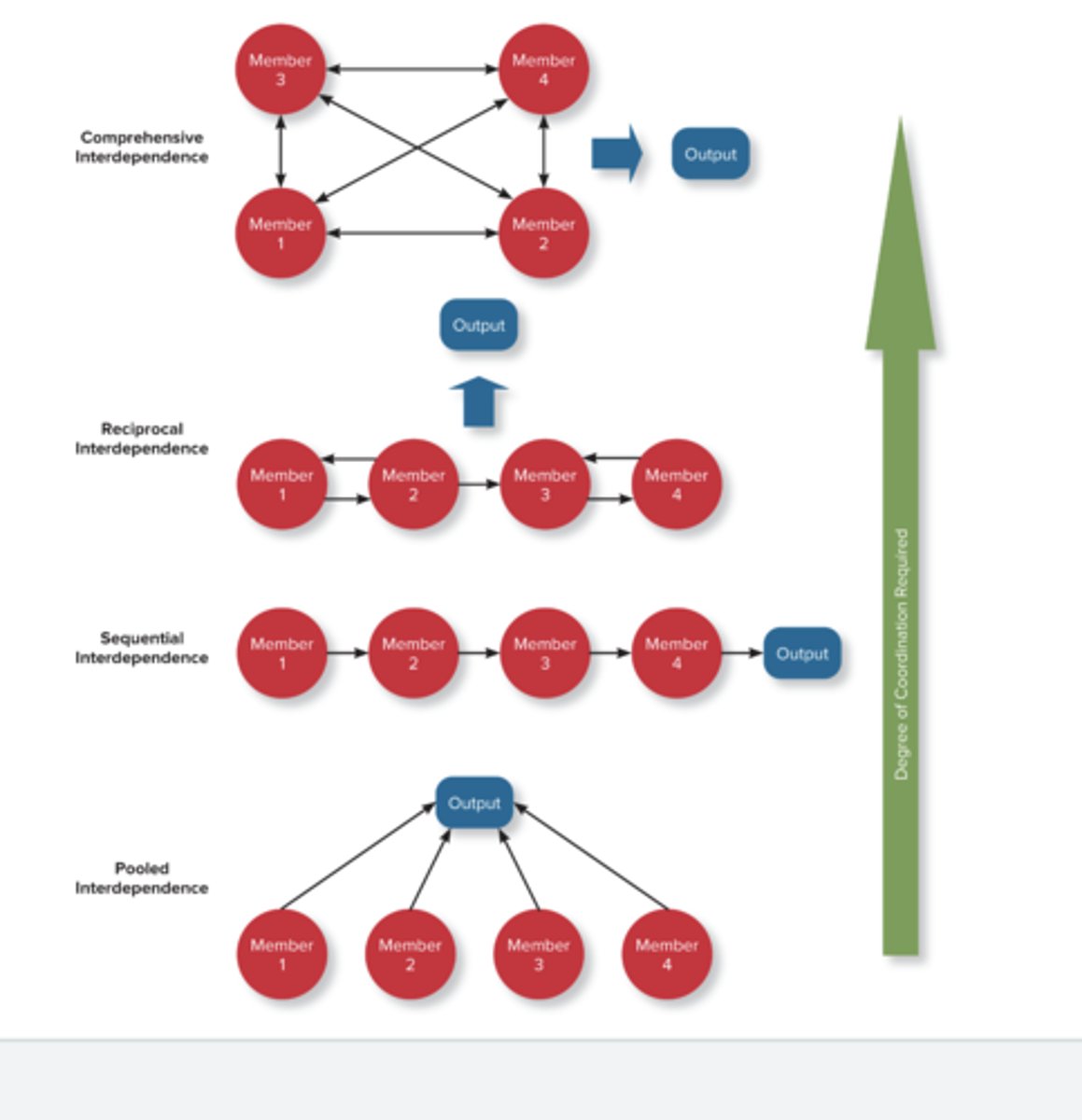
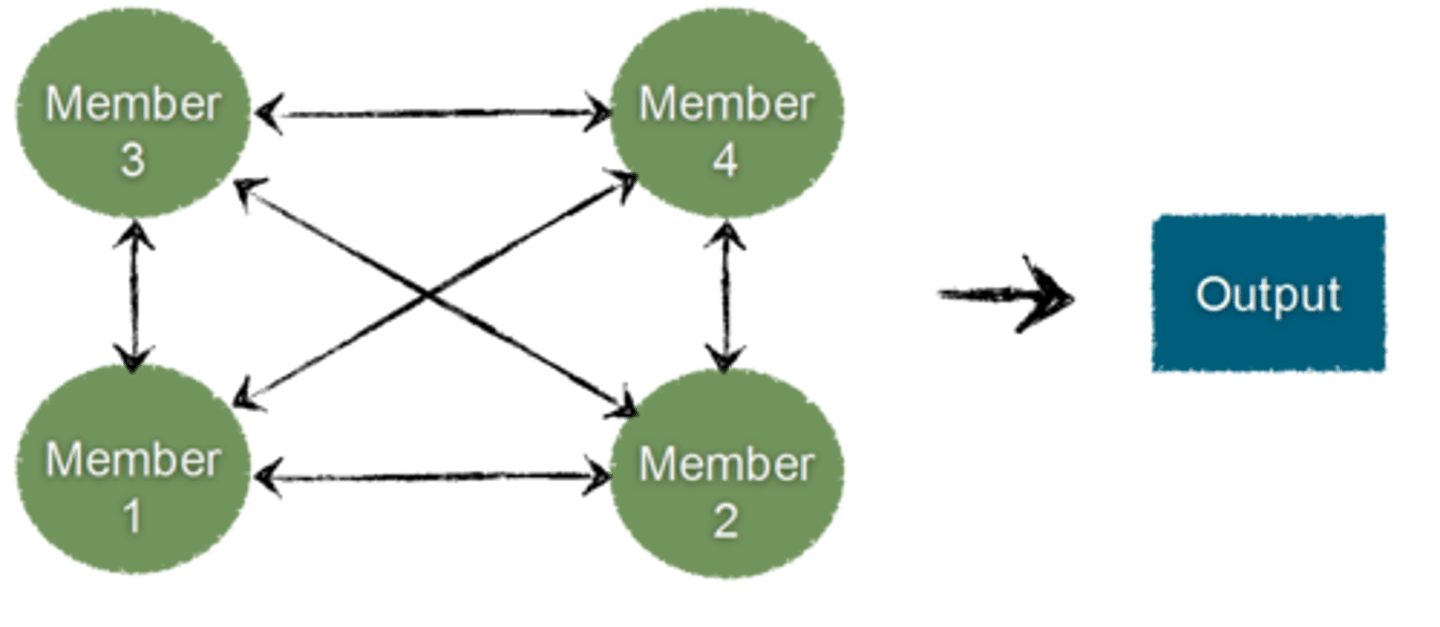
comprehensive interdependence
A form of task interdependence in which team members have a great deal of discretion in terms of what they do and with whom they interact in the course of the collaboration involved in accomplishing the team's work.

Goal Interdependence
The degree to which team members have a shared goal and align their individual goals with that vision.
outcome interdependence
The degree to which team members share equally in the feedback and rewards that result from the team achieving its goals.
Team Composition
The mix of the various characteristics that describe the individuals who work in the team
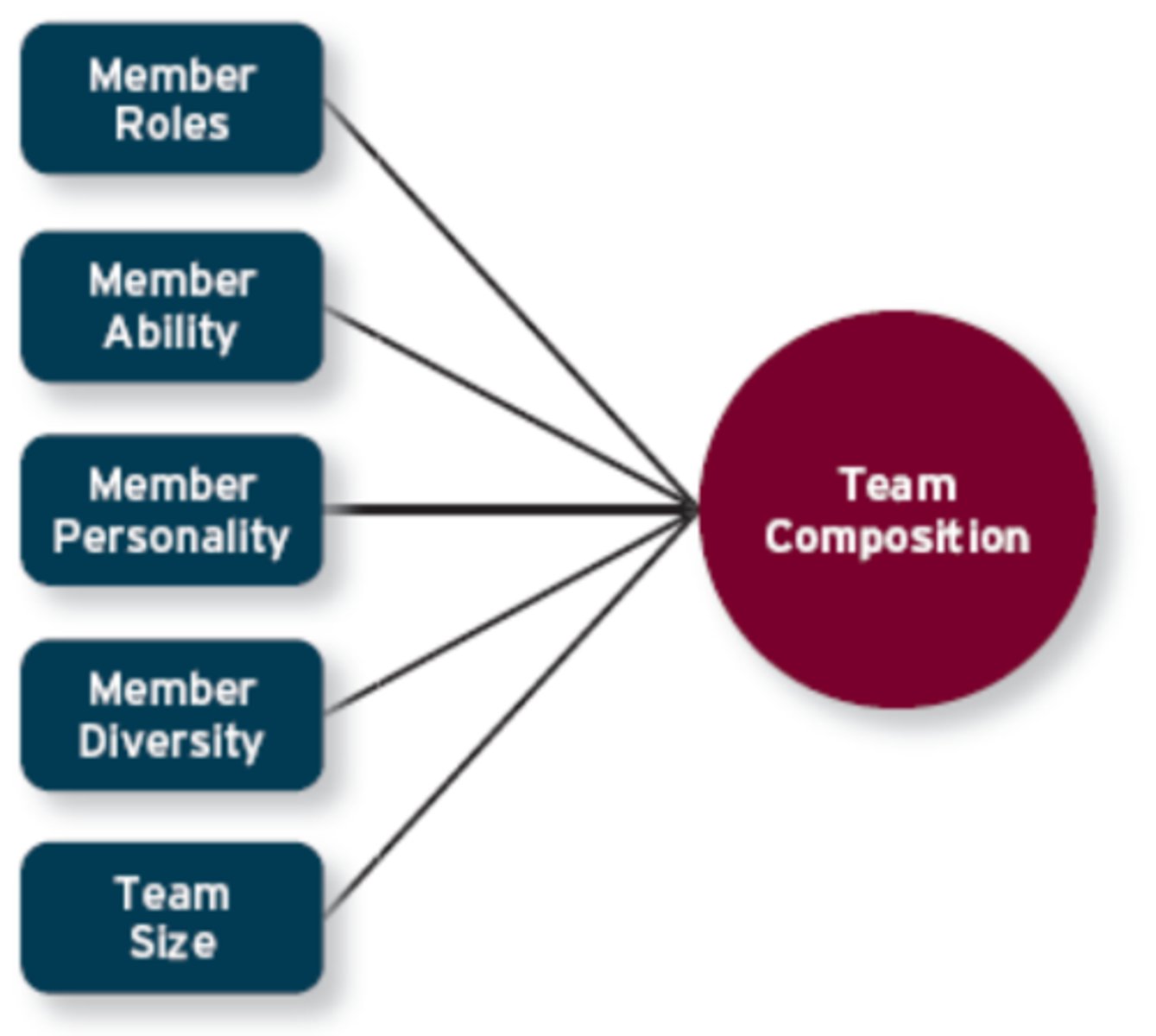
Five Aspects of Team Composition
member roles, member ability, member personality, team diversity, team size
role
The behavior a person is generally expected to display in a given context.
leader-staff teams
A type of team that consists of members who make recommendations to the leader who is ultimately responsible for team decisions.
Initiator-contributor
proposes new ideas
coordinator
tries to coordinate activities among team members
orienter
determines the direction of the team's discussion
devil's advocate
offers challenges to the team's status quo
energizer
motivates the team to strive to do better
procedural technician
performs routine tasks needed to keep progress moving
team-building roles
behaviors that influence the quality of the team's social climate
encourager
praises the contributions of other teams
Harmonizer
mediates the differences between other members
compromiser
attempts to find the halfway point to end conflict
Gatekeeper-expediter
encourages participation from teammates
standard setter
expresses goals for the team to achieve