Vertebral Column
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/122
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 7:26 PM on 2/1/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
123 Terms
1
New cards
What are the regions of the vertebral column?
Cervical (neck)
Thoracic (ribcage)
Lumbar (lower back)
Sacrum
Coccyx
Thoracic (ribcage)
Lumbar (lower back)
Sacrum
Coccyx
2
New cards
What part of a vertebra bears most of the weight?
vertebral body
3
New cards
The vertebral body of a vertebra is made up of bone derived from what?
centrum
4
New cards
What epiphyseal rim of a vertebra is make of smooth bone derived from what?
anular epiphysis
5
New cards
Where does the spinal cord reside? In the vertebral foramen or the vertebral canal?
vertebral canal
6
New cards
Intervertebral foramina
formed partially by adjacent vertebral notches and transmit (serves as passageway) spinal nerves
7
New cards
What part of vertebra protects the spinal cord?
vertebral arch
8
New cards
What is the vertebral arch made up of?
pedicles and laminae
9
New cards
What part of vertebra provide a mechanical advantage for muscle attachments and movement?
transverse and spinous processes
10
New cards
What part of vertebra have facets for synovial joints that guide and limit motion (restriction of motion)?
articular processes
11
New cards
What part of vertebra supports the body weight?
vertebral body
12
New cards
What forms the skeleton of the neck and back?
the vertebral column
13
New cards
What comprises the axial skeleton?
Vertebral column
Cranium
Rib Cage
Sternum
Cranium
Rib Cage
Sternum
14
New cards
The following are functions of what?
* Supports and positions the head and trunk in the erect position.
* Provides an axis for the body and transmits the weight through the pelvic girdle to the lower limbs.
* Suspends the rib cage.
* Protects the spinal cord and nerves.
* Supports and positions the head and trunk in the erect position.
* Provides an axis for the body and transmits the weight through the pelvic girdle to the lower limbs.
* Suspends the rib cage.
* Protects the spinal cord and nerves.
The vertebral column
15
New cards
How many vertebra make up the vertebral column?
33 vertebrae
16
New cards
How many regions are there of the vertebral column?
5 regions
17
New cards
What are the 5 regions of the vertebral column?
Cervical
Thoracic
Lumbar
Sacrum
Coccyx
Thoracic
Lumbar
Sacrum
Coccyx
18
New cards
How many vertebrae make up the cervical region?
\
A. 4 vertebrae
B. 5 vertebrae
C. 7 vertebrae
D. 12 vertebrae
\
A. 4 vertebrae
B. 5 vertebrae
C. 7 vertebrae
D. 12 vertebrae
C. 7 vertebrae
19
New cards
How many vertebrae make up the lumbar region?
\
A. 4 vertebrae
B. 5 vertebrae
C. 7 vertebrae
D. 12 vertebrae
\
A. 4 vertebrae
B. 5 vertebrae
C. 7 vertebrae
D. 12 vertebrae
B. 5 vertebrae
20
New cards
How many vertebrae make up the thoracic region?
\
A. 4 vertebrae
B. 5 vertebrae
C. 7 vertebrae
D. 12 vertebrae
\
A. 4 vertebrae
B. 5 vertebrae
C. 7 vertebrae
D. 12 vertebrae
D. 12 vertebrae
21
New cards
How many vertebrae make up the sacral region?
\
A. 4 vertebrae
B. 5 vertebrae
C. 7 vertebrae
D. 12 vertebrae
\
A. 4 vertebrae
B. 5 vertebrae
C. 7 vertebrae
D. 12 vertebrae
B. 5 vertebrae
22
New cards
How many vertebrae make up the coccyx region?
\
A. 4 vertebrae
B. 5 vertebrae
C. 7 vertebrae
D. 12 vertebrae
\
A. 4 vertebrae
B. 5 vertebrae
C. 7 vertebrae
D. 12 vertebrae
A. 4 vertebrae
23
New cards
What is unique about the spinal curvature of newborns?
one continuous C-shaped curve (the primary curvature)
24
New cards
What are the two curvatures of the vertebral column?
Primary curve
Secondary curve
Secondary curve
25
New cards
What curvature of the spine develops prior to birth and are concave anteriorly?
\
A. Primary Curve
B. Secondary Curve
\
A. Primary Curve
B. Secondary Curve
A. Primary Curve
26
New cards
What curvature of the spine develops during the post-natal period and are concave posteriorly?
\
A. Primary Curve
B. Secondary Curve
\
A. Primary Curve
B. Secondary Curve
B. Secondary Curve
27
New cards
What are the two types of secondary curves?
Cervical curve
Lumbar curve
Lumbar curve
28
New cards
What secondary curve becomes evident when the infant raises its head?
\
A. Cervical curve
B. Lumbar curve
\
A. Cervical curve
B. Lumbar curve
A. Cervical curve
29
New cards
What secondary curve becomes evident in crawling, sitting, and standing?
\
A. Cervical curve
B. Lumbar curve
\
A. Cervical curve
B. Lumbar curve
B. Lumbar curve
30
New cards
Where does the spinal cord reside?
\
A. Vertebral canal
B. Vertebral foramen
\
A. Vertebral canal
B. Vertebral foramen
A. Vertebral canal
31
New cards
How is the intervertebral foramina formed?
partially by adjacent vertebral notches
32
New cards
What transmits spinal nerves?
\
A. Vertebral canal
B. Vertebral foramen
\
A. Vertebral canal
B. Vertebral foramen
B. Vertebral foramen
33
New cards
What part of the vertebra functions for weight-bearing?
\
A. Articular processes
B. Transverse and Spinous Processes
C. Vertebral arch
D. Vertebral body
\
A. Articular processes
B. Transverse and Spinous Processes
C. Vertebral arch
D. Vertebral body
D. Vertebral body
34
New cards
What part of the vertebra protects the spinal cord?
\
A. Articular processes
B. Transverse and Spinous Processes
C. Vertebral arch
D. Vertebral body
\
A. Articular processes
B. Transverse and Spinous Processes
C. Vertebral arch
D. Vertebral body
C. Vertebral arch
35
New cards
What part of the vertebra provides a mechanical advantage for muscle attachments?
\
A. Articular processes
B. Transverse and Spinous Processes
C. Vertebral arch
D. Vertebral body
\
A. Articular processes
B. Transverse and Spinous Processes
C. Vertebral arch
D. Vertebral body
B. Transverse and Spinous Processes
36
New cards
What part of the vertebra has facets for synovial joints that guide and limit motion?
\
A. Articular processes
B. Transverse and Spinous Processes
C. Vertebral arch
D. Vertebral body
\
A. Articular processes
B. Transverse and Spinous Processes
C. Vertebral arch
D. Vertebral body
A. Articular processes
37
New cards
What vertebrae have transverse processes with foramina and a large vertebral foramen?
\
A. Cervical
B. Lumbar
C. Thoracic
\
A. Cervical
B. Lumbar
C. Thoracic
A. Cervical
38
New cards
What vertebrae have costal facets with long spinous processes?
\
A. Cervical
B. Lumbar
C. Thoracic
\
A. Cervical
B. Lumbar
C. Thoracic
C. Thoracic
39
New cards
What vertebrae have a large body with short blunt spinous processes?
\
A. Cervical
B. Lumbar
C. Thoracic
\
A. Cervical
B. Lumbar
C. Thoracic
B. Lumbar
40
New cards
The following are characteristics of what vertebrae?
* Transverse process
* Triangular vertebral foramen
* Bifid spinous process
* Oblique, relatively horizontal articular facets directed primarily superiorly and inferiorly
* Perforated transverse processes with anterior and posterior tubercles
* Foramen transversarium
* Rectangular bodies with concave superior and convex inferior surfaces
* Uncus of body (uncinate process)
\
A. Cervical vertebrae
B. Lumbar vertebrae
C. Thoracic vertebrae
* Transverse process
* Triangular vertebral foramen
* Bifid spinous process
* Oblique, relatively horizontal articular facets directed primarily superiorly and inferiorly
* Perforated transverse processes with anterior and posterior tubercles
* Foramen transversarium
* Rectangular bodies with concave superior and convex inferior surfaces
* Uncus of body (uncinate process)
\
A. Cervical vertebrae
B. Lumbar vertebrae
C. Thoracic vertebrae
A. Cervical vertebrae
41
New cards
The following are characteristics of what vertebrae?
* Long, strong transverse processes extend posterolaterally
* Circular vertebral foramen, relatively small compared to size of body
* Nearly vertical articular facets directed primarily posteriorly and anteriorly
* Spinous process long and sloping; overlaps inferior vertebra
* Costal facets (2 on each side of body and 1 on each transverse process)
* Columnar bodies, heart-shaped in superior view
\
A. Cervical vertebrae
B. Lumbar vertebrae
C. Thoracic vertebrae
* Long, strong transverse processes extend posterolaterally
* Circular vertebral foramen, relatively small compared to size of body
* Nearly vertical articular facets directed primarily posteriorly and anteriorly
* Spinous process long and sloping; overlaps inferior vertebra
* Costal facets (2 on each side of body and 1 on each transverse process)
* Columnar bodies, heart-shaped in superior view
\
A. Cervical vertebrae
B. Lumbar vertebrae
C. Thoracic vertebrae
C. Thoracic vertebrae
42
New cards
The following are characteristics of what vertebrae?
* Massive columnar body, kidney-shaped in superior view
* Vertebral foramen triangular, intermediate in size
* Nearly vertical articular facets directed primarily medially and laterally
* Transverse processes long and slender, directed laterally
* Short, broad and blunt spinous process
\
A. Cervical vertebrae
B. Lumbar vertebrae
C. Thoracic vertebrae
* Massive columnar body, kidney-shaped in superior view
* Vertebral foramen triangular, intermediate in size
* Nearly vertical articular facets directed primarily medially and laterally
* Transverse processes long and slender, directed laterally
* Short, broad and blunt spinous process
\
A. Cervical vertebrae
B. Lumbar vertebrae
C. Thoracic vertebrae
B. Lumbar vertebrae
43
New cards
What vertebra is the most prominent and referred to as vertebra prominens when the spine is flexed?
C7
44
New cards
What is another word for the C1 vertebra?
Atlas
45
New cards
What vertebra has the following characteristics?
* No body
* Lateral masses that have superior articular surfaces for articulation with the occipital condyles of the skull
* Has a posterior tubercle but no spinous process
* Has anterior tubercle
* Has an articular facet for the dens of C2 vertebra
* Has transverse processes with foramina
* No body
* Lateral masses that have superior articular surfaces for articulation with the occipital condyles of the skull
* Has a posterior tubercle but no spinous process
* Has anterior tubercle
* Has an articular facet for the dens of C2 vertebra
* Has transverse processes with foramina
C1 vertebra
46
New cards
What is another name for the C2 vertebra?
axis
47
New cards
The following are characteristics of what vertebra?
* Has a large centrally located process (dens, odontoid process) projecting cranially from its body
* Has two large superior articular facets
* Has a large bifid spinous process
* Has a large centrally located process (dens, odontoid process) projecting cranially from its body
* Has two large superior articular facets
* Has a large bifid spinous process
C2 vertebra
48
New cards
Atlantoaxial Joint
a type of synovial joint that is classified as a biaxial, pivot joint and resides in the upper part of the neck between the first and second cervical vertebrae (aka the atlas and axis)
49
New cards
What does the vertebral artery pass through?
the transverse foramina of the upper 6 cervical vertebrae
50
New cards
What does the vertebral artery pass over?
the posterior arch of the atlas (C1 vertebra)
51
New cards
What facets articular with the 5th lumbar vertebra?
the superior articular facets
52
New cards
What can be seen in the posterior view of the sacrum?
sacral hiatus
53
New cards
What can be used to deliver epidural anesthesia?
sacral hiatus
54
New cards
In what region of the spinal cord is the intervertebral foramina located?
\
A. Cervical
B. Coccyx
C. Lumbar
D. Sacrum
E. Thoracic
\
A. Cervical
B. Coccyx
C. Lumbar
D. Sacrum
E. Thoracic
D. Sacrum
55
New cards
In a synovial joint, the bones are united by what?
a joint capsule
56
New cards
What comprises the joint capsule?
Outer fibrous layer
Inner synovial membrane
Inner synovial membrane
57
New cards
What part of the joint capsule is a vascular connective tissue that produces synovial fluid, which lubricates and provides nutrients to articular cartilage?
\
A. Fibrous capsule
B. Synovial membrane
\
A. Fibrous capsule
B. Synovial membrane
B. Synovial membrane
58
New cards
What part of the joint capsule has numerous nerve endings for pain and proprioception (position sense)?
\
A. Fibrous capsule
B. Synovial membrane
\
A. Fibrous capsule
B. Synovial membrane
A. Fibrous capsule
59
New cards
Where are the zygapophysial joints located?
between the superior and inferior articular processes
60
New cards
What makes up the symphysis joint?
the intervertebral disc and adjacent vertebral bodies
61
New cards
What joint permits movement and absorbs shock?
symphysis joint
62
New cards
What forms the symphysis between adjacent vertebral bodies?
Hyaline cartilage
Intervertebral disc
Intervertebral disc
63
New cards
What makes up the intervertebral disc?
An outer anulus fibrosus
An inner nucleus pulposus
An inner nucleus pulposus
64
New cards
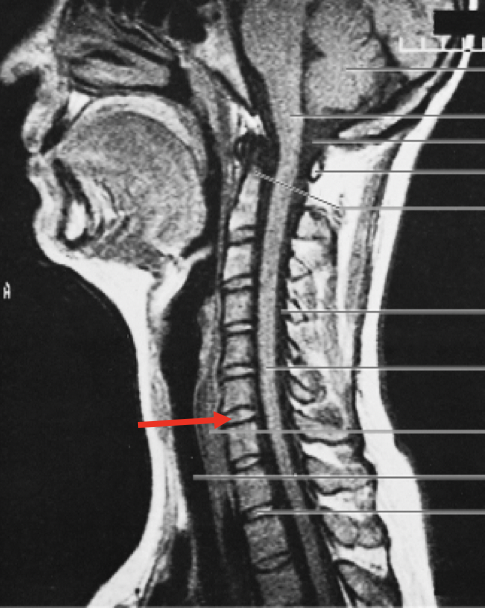
What is the red arrow pointing to?
the nucleus pulpous of the intervertebral disc
65
New cards
What ligament is attached anteriorly to the vertebral bodies and the intervertebral discs?
Anterior longitudinal ligament
66
New cards
What ligament is attached posteriorly to the vertebral bodies and the intervertebral discs but is narrower?
Posterior longitudinal ligament
67
New cards
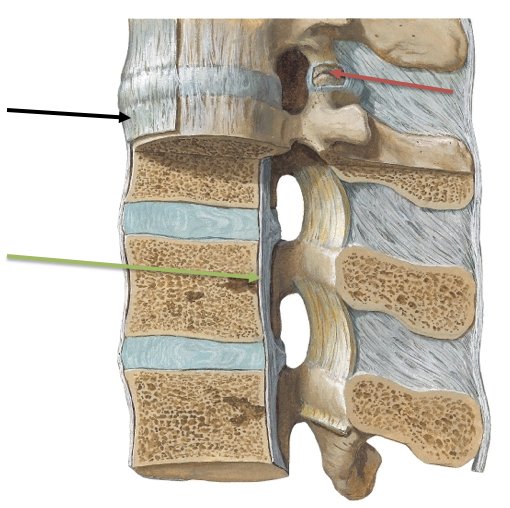
What is the black arrow pointing at?
\
A. Anterior longitudinal ligament
B. Facet Joint and Capsule
C. Posterior longitudinal ligament
\
A. Anterior longitudinal ligament
B. Facet Joint and Capsule
C. Posterior longitudinal ligament
A. Anterior longitudinal ligament
68
New cards
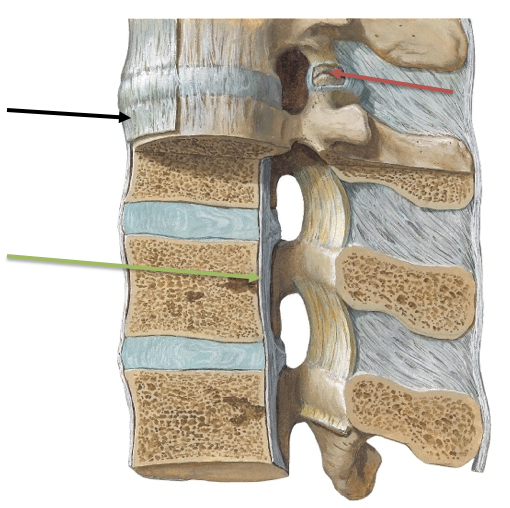
What is the green arrow pointing at?
\
A. Anterior longitudinal ligament
B. Facet Joint and Capsule
C. Posterior longitudinal ligament
\
A. Anterior longitudinal ligament
B. Facet Joint and Capsule
C. Posterior longitudinal ligament
C. Posterior longitudinal ligament
69
New cards
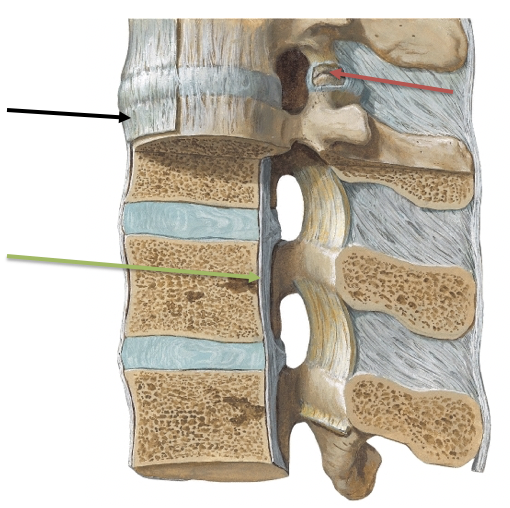
What is the red arrow pointing at?
\
A. Anterior longitudinal ligament
B. Facet Joint and Capsule
C. Posterior longitudinal ligament
\
A. Anterior longitudinal ligament
B. Facet Joint and Capsule
C. Posterior longitudinal ligament
B. Facet Joint and Capsule
70
New cards
Whiplash injury is common with rear end auto collisions. It causes traumatic hyperextension of the neck and may cause strain/tear to what longitudinal ligament?
\
A. Anterior longitudinal ligament
B. Posterior longitudinal ligament
\
A. Anterior longitudinal ligament
B. Posterior longitudinal ligament
A. Anterior longitudinal ligament
71
New cards
What ligament is located within the vertebral canal, posterior to the vertebral bodies and provides less support to the intervertebral disc due to being narrow?
Posterior longitudinal ligament
72
New cards
Intervertebral disc herniation frequently occurs in what direction?
posterolateral direction
73
New cards
Where is the ligamentum flava, interspinous ligament, and the supraspinous ligament located?
in the vertebral column
74
New cards
What ligament of the vertebral column connects adjacent laminae?
\
A. Interspinous ligament
B. Ligamentum flava
C. Supraspinous ligament
\
A. Interspinous ligament
B. Ligamentum flava
C. Supraspinous ligament
A. Interspinous ligament
75
New cards
What ligament of the vertebral column connects spinous processes?
\
A. Interspinous ligament
B. Ligamentum flava
C. Supraspinous ligament
\
A. Interspinous ligament
B. Ligamentum flava
C. Supraspinous ligament
A. Interspinous ligament
76
New cards
What ligament of the vertebral column connects the tips of the spinous processes?
\
A. Interspinous ligament
B. Ligamentum flava
C. Supraspinous ligament
\
A. Interspinous ligament
B. Ligamentum flava
C. Supraspinous ligament
C. Supraspinous ligament
77
New cards
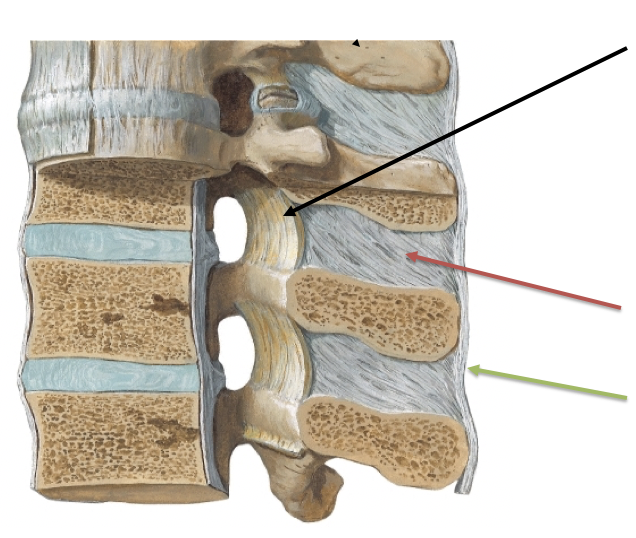
What ligament is the black arrow pointing to?
\
A. Interspinous ligament
B. Ligamentum flava
C. Supraspinous ligament
\
A. Interspinous ligament
B. Ligamentum flava
C. Supraspinous ligament
B. Ligamentum flava
78
New cards
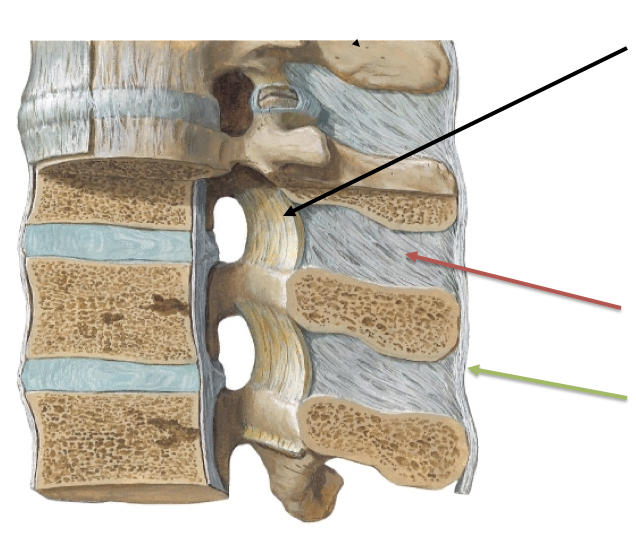
What ligament is the red arrow pointing to?
\
A. Interspinous ligament
B. Ligamentum flava
C. Supraspinous ligament
\
A. Interspinous ligament
B. Ligamentum flava
C. Supraspinous ligament
A. Interspinous ligament
79
New cards
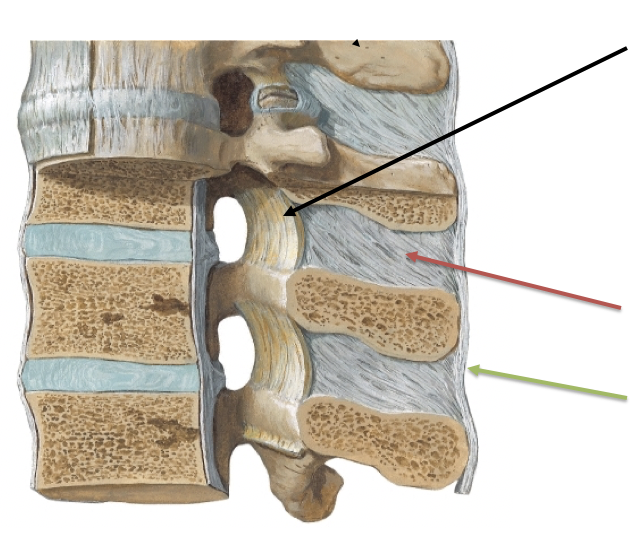
What ligament is the green arrow pointing to?
\
A. Interspinous ligament
B. Ligamentum flava
C. Supraspinous ligament
\
A. Interspinous ligament
B. Ligamentum flava
C. Supraspinous ligament
C. Supraspinous ligament
80
New cards
In what part of the spine is the nuchal ligament (ligamentum nuchae) found?
the cervical spine
81
New cards
What type of tissue does the Nuchal ligament (ligamentum nuchae) contain?
fibroelastic tissue
82
New cards
What ligament attaches from the external occipital protuberance to a cervical spinous processes?
Nuchal ligament (ligamentum nuchae)
83
New cards
The following are functions of what ligament of the cervical spine?
* Resists flexion
* Aids returning head to anatomical position from flexion
* Resists flexion
* Aids returning head to anatomical position from flexion
Nuchal ligament (ligamentum nuchae)
84
New cards
Does the Nuchal ligament (ligamentum nuchae) provide attachment sites for muscles?
Yes
85
New cards
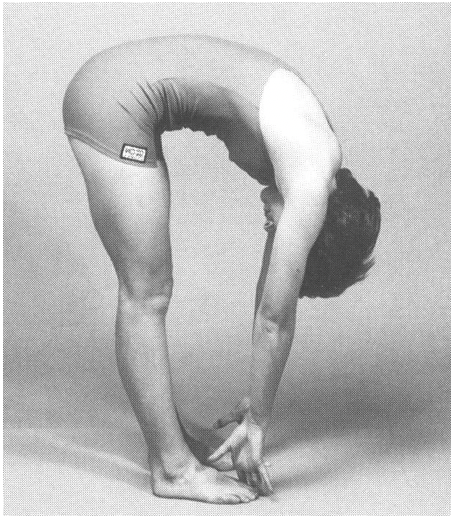

What ligaments become taught in flexion of the vertebral column?
–Posterior longitudinal
–Ligamentum flavum
–Interspinous
–Supraspinous
–Ligamentum flavum
–Interspinous
–Supraspinous
86
New cards

Extension of the vertebral column is limited by what ligament?
the anterior longitudinal ligament
87
New cards
In what region of the spine is the amount of motion the greatest?
A. Cervical
B. Coccyx
C. Lumbar
D. Sacrum
E. Thoracic
A. Cervical
B. Coccyx
C. Lumbar
D. Sacrum
E. Thoracic
A. Cervical
88
New cards
In what region of the spine is flexion of the vertebral column the greatest?
A. Cervical
B. Coccyx
C. Lumbar
D. Sacrum
E. Thoracic
A. Cervical
B. Coccyx
C. Lumbar
D. Sacrum
E. Thoracic
A. Cervical
89
New cards
In what region of the spine is rotation the greatest movement available?
A. Cervical
B. Coccyx
C. Lumbar
D. Sacrum
E. Thoracic
A. Cervical
B. Coccyx
C. Lumbar
D. Sacrum
E. Thoracic
E. Thoracic
90
New cards
What limits the motion of the thoracic vertebral column--especially flexion/extension?
the rib cage
91
New cards
In what region of the spine is extension marked?
A. Cervical
B. Coccyx
C. Lumbar
D. Sacrum
E. Thoracic
A. Cervical
B. Coccyx
C. Lumbar
D. Sacrum
E. Thoracic
C. Lumbar
92
New cards
The atlantoccipital joint (OA) allows for what type of movement?
Nodding the head (flexion and extension)
Lateral flex
Lateral flex
93
New cards
What is the only motion available in the atlantoaxial (AA) joint?
rotation
94
New cards
Rotation in the atlantoaxial (AA) joint is limited by what ligaments?
the alar ligaments
95
New cards
Roughly 1/2 of the total rotation in the cervical region occurs at what joint?
Atlantoaxial (AA) joint
96
New cards
Because 1/2 of the total rotation in the cervical region occurs at the atlantoaxial (AA) joint, where does the rest of the cervical rotation occur?
between the C2-C7 vertebrae
97
New cards
What ligament of the atlas keeps the dens of the C2 vertebra from moving posterior and impinging upon the spinal cord?
the transverse ligament
98
New cards
Dislocation secondary to a rupture of the transverse ligament is likely to cause what?
spinal cord compression
99
New cards
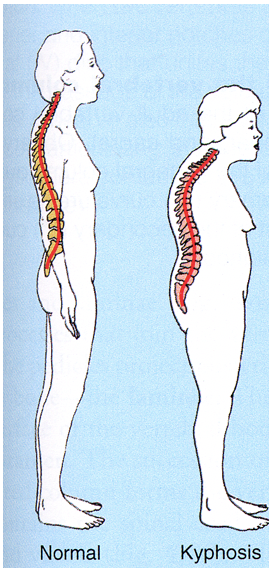
What is excessive thoracic kyphosis?
an increase in thoracic curvature
100
New cards
What are contributing factors to excessive thoracic kyphosis?
Postural change with aging and poor postural habit
Compression fracture of a thoracic vertebral body due to osteoporosis
Compression fracture of a thoracic vertebral body due to osteoporosis