Dental Anatomy Board Review
1/148
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
149 Terms
Anatomical Crown
Entire crown of tooth completely covered by enamel (erupted or not)
Anatomic Root
Entire root below the CEJ
Cementum
Similar to bone, is thickest at the apex
calculus detection issues
CEJ irregularities cause
Acellular cementum
cementum that covers entire anatomic root
Cellular cementum
cementum that is at the apex, and can continually reproduce
cementoblasts
cementum is produced by
Clinical Crown
part of the crown seen superior to the gingival margin.
Clinical Root
Unerupted part of the root below the gingival crest
Dentin
Largest portion of both root and crown, produced out of 70% inorganic material
Secondary Dentin
Dentin that forms after tooth eruption
Reparative Dentin
Dentin that forms in response to trauma or caries to reduce sensitivity
Erosion
Caries
Toothbrush abrasion
Root planing
Dentin exposure can be caused by:
increased sensitivity
Exposed dentinal tubules =
dentinoblasts
dentin is produced by
enamel
White, protective external surface layer of the anatomic crown
amleoblasts
enamel is produced by
96%
enamel is ___ inorganic
crown tips
enamel is thickest at
CEJ
enamel is thinnest at
Pulp
soft tissue within a tooth, containing nerves and blood vessels
odontoblasts
pulp produces ___ that form dentin
nourish the tooth
the function of the pulp is to
pain
pulp stimulation =
age
function attrition
trauma
Pulp chamber at coronal portion is affected by
Line angle
Separates 2 surfaces of teeth at the point where 2 junctions meet
Point Angle
Point where 3 surfaces meet.
Lobes
Crowth growth centers (usually 4 or more)
Developmental Grooves
Groves formed when lobes fuse during development
Fossae
Shallow depression
Lingual Fossa
Fossa located on the lingual surface between the mesial and distal marginal ridges and incisal to the cingulum
Pit
Pinpoint hole in fossa or groove
Cusp
Pyramidal elevation with a peak called a cusp tip
Ridges
Linear prominence of enamel converging toward the cusp tip run in a line
4
all cusps have ___ ridges: buccal, lingual, mesial, distal
Marginal Ridges
Rounded borders of enamel
Oblique Ridge
crosses the occlusal surface obliquely (diagonally) and is made up of one ridge on the mesiolingual cusp joining with the triangular ridge of the distobuccal cusp
maxillary molars
oblique ridge is ONLY on
Triangular ridge
Extends from a cusp tip toward the depression (sulcus) near the middle of the occlusal surface faciolingually
proximal surface
triangular ridge is most easily identified when viewing the
Transverse Ridge
Triangular ridge from a buccal cusp joins with a triangular ridge from a lingual cusp, these two ridges together form a longer ridge - a transverse ridge which crosses the occlusal surface of posterior teeth in a more or less buccolingual direction
Cingulum
The prominence or bulge in the cervical third of the lingual surface of the crown (incisors and canines)
Root-to-crown Ratio
Root length divided by crown length
Occlusal Table
The occlusal surface that is bounded by the continuous cusp ridges and marginal ridges
Mamelons
Three small bulges or tubercles on the incisal edge of newly erupted incisors
Perikymata
Numerous, minute horizontal ridges on teh enamel of newly erupted permanent teeth
Occlusal Sulcus
Broar V-shaped depression or valley on the occlusal surface of each posterior teeth running mesiodistally between the buccal and lingual cusps
Supplemental Grooves
Small irregular extra grooves
junction of lobes
major portions of tooth
same location on the same type of teeth
supplemental grooves do not occur at
Central Groove
Developmental groove that separates the buccal from the lingual cusps and is located near the buccolingual center of the tooth sulcus
central groove
Most prominent groove
Crests of Curvature
Curvature which begins at the tip of canines and follows cusp tips of premolars and molars posteriorly
Embrasure
when adjacent teeth contact, the continuous space that surrounds each contact area can be divided into four somewhat triangular spaces
Contact Areas
Where two adjacent teeth touch
positive contact of all teeth within each arch solidifies the position of teeth within each arch.
When chewing, these contacts prevent food from being forced between the teeth where it could contribute to decay and gum and bone disease
Contact protects the thin interdental papillae of the gingiva by diverting food buccally and lingually.
Important Functions of Contact Areas:
anterior teeth
Teeth that contact area is on incisal edge.
canines
Teeth that contact area is on distal contact at middle ⅓
premolar
teeth thats contact area is on cervical junction of the occlusal and middle third
Posterior teeth
teeth thats contact area is on middle third
A
Stage of tooth development that is the bud stage
B
Stage of tooth development that is the cap stage
C
Stage of tooth development that is the bell stage
D and E
Stage of tooth development that is the dentinogenesis and amelogenesis stage
F
Stage of tooth development that is the crown formation stage
G
Stage of tooth development that is the root formation and eruption stage
H
Stage of tooth development in which the functional tooth is developed.
oral epithelial cells
underlying mesenchymal cells
In humans, primary and permanent teeth develop from interaction of the
the basic development process is similar for all teeth
Each developing tooth grows as an anatomically distinct unit, BUT
Oral epithelial cells
cells form the enamel
mesenchymal cells
developmental cells that form the dental papilla (dentin)
bud
cap
bell
teeth develop through the stages of
odontoblasts
amleoblasts
Hard tissue formative stages of dentinogenesis and amelogenesis produce
odontoblast
form dentin
amleoblasts
form enamel
cementoblasts
fibroblasts
Root formation follows crown development by
Cementoblasts
form cementum
fibroblasts
form periodontal ligament fibers
dentition
arch
side
type
Class
when documenting,
For each tooth you must record:
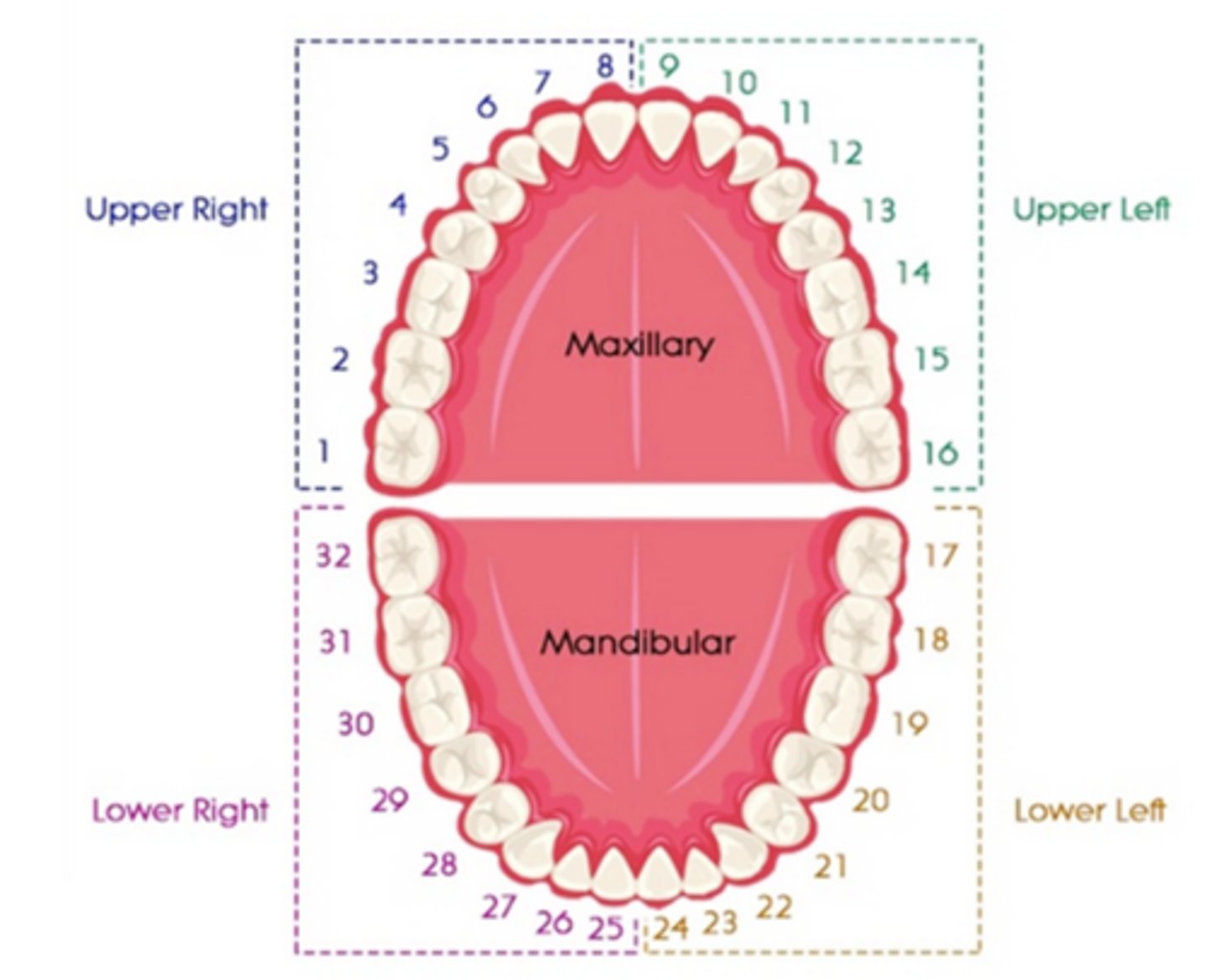
Universal Numbering System
Uses numbers 1 through 32 for the 32 teeth in the permanent dentition
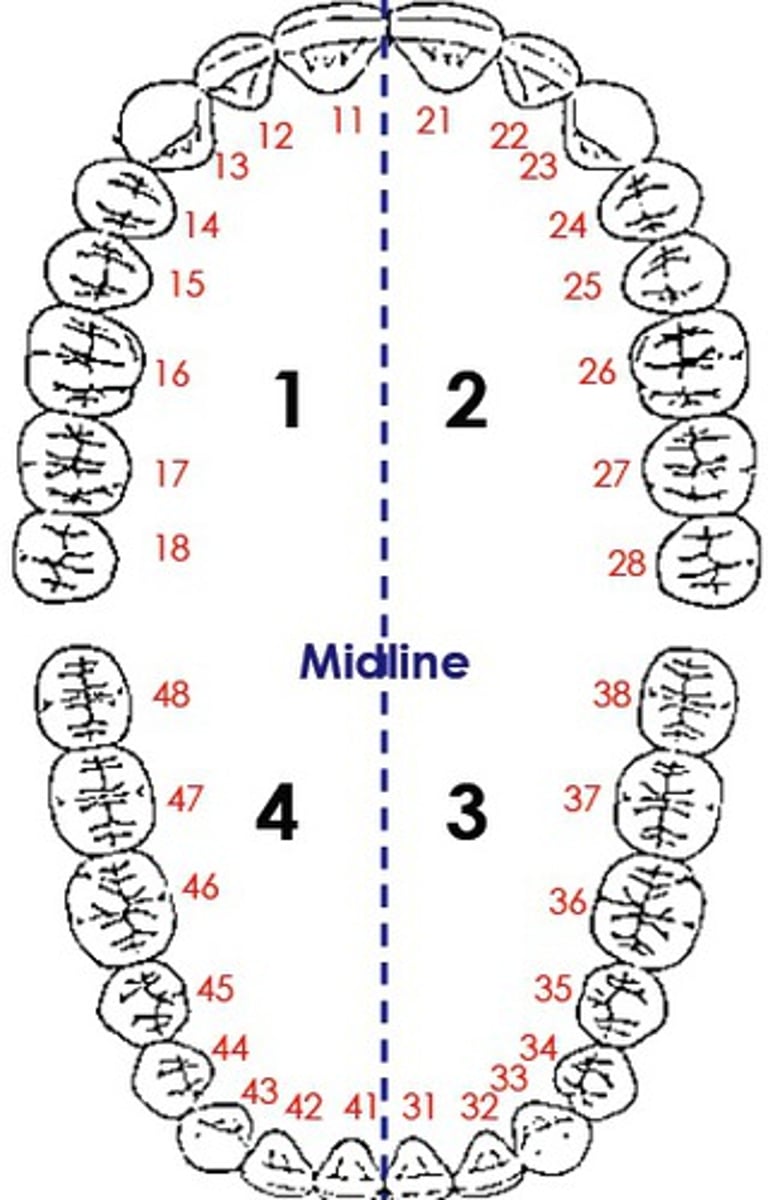
FDI system
Uses two digits for each permanent or primary tooth. The first digit denotes a specific quadrant (right or left), arch (maxillary or mandibular), and dentition (permanent or primary)
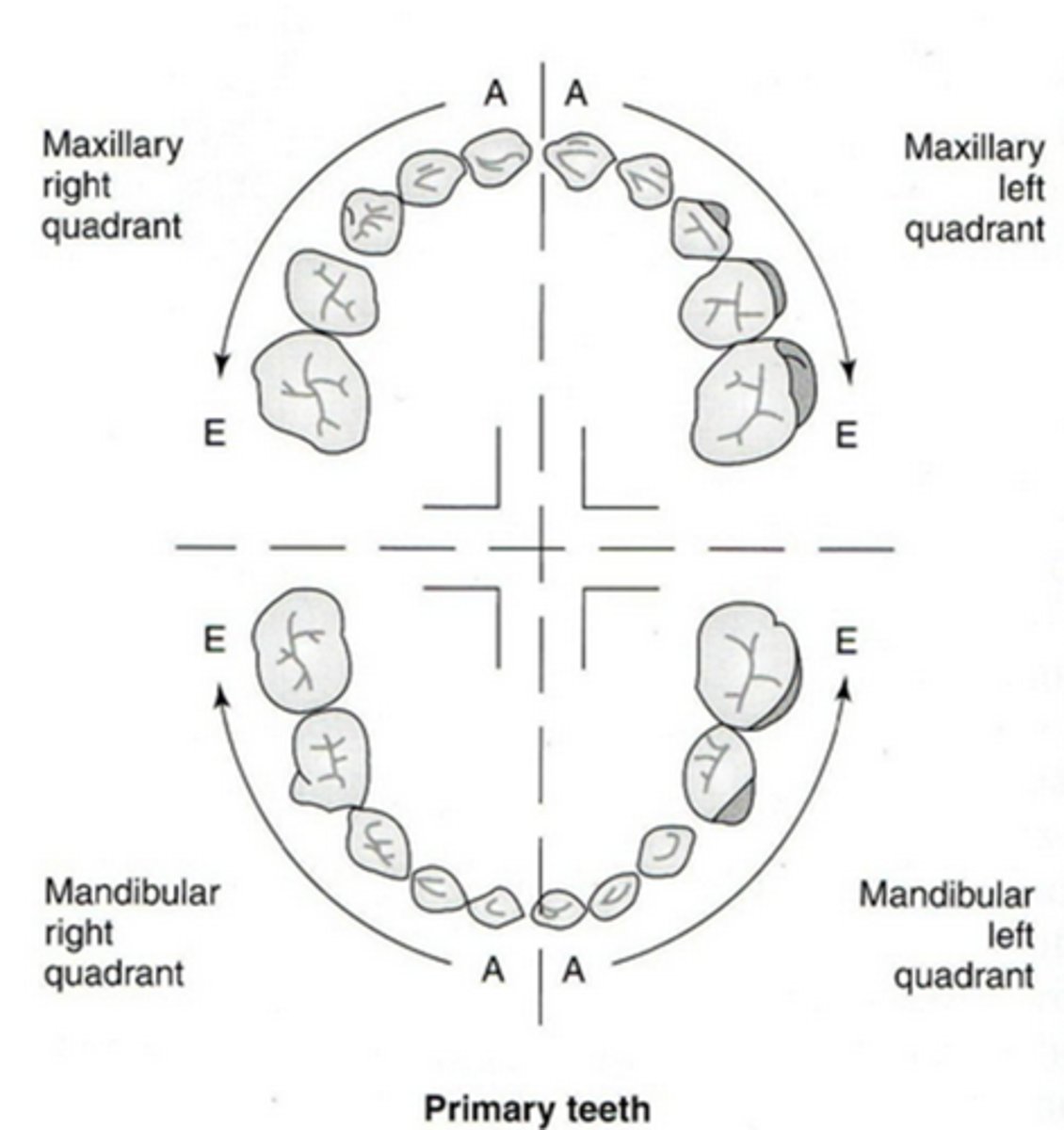
Palmer notation System
used by many orthodontists, utilizes four different bracket shapes to denote each of the four quadrants. The specific bracket surrounds a number (or letter), which denotes the specific tooth within that quadrant.
Occlusion
Relationship between the upper and lower teeth when they close together or contact one another during movement or rest.
Class I
Ideal Occlusion, The mesiobuccal cusp of the maxillary first molar occludes in the mesiobuccal groove of the mandibular first molar.
Horizontal Overlap (class I)
incisal edges of the maxillary anterior teeth horizontally overlap the mandibular teeth so that the incisal edges of upper are labial to the incisal edges of the lower
Vertical Overlap (class I)
incisal edges of the maxillary anterior teeth extend below the incisal edges of the lower teeth so that the incisal of lower incisors are hidden
buccal
in class I occlusion,
Maxillary posterior teeth should be positioned just slightly _____ to mandibular posterior teeth
Labioversion/Buccoversion
A tooth that is out of alignment to the labial or buccal compared to the ideal arch form of other teeth if referring to a posterior tooth
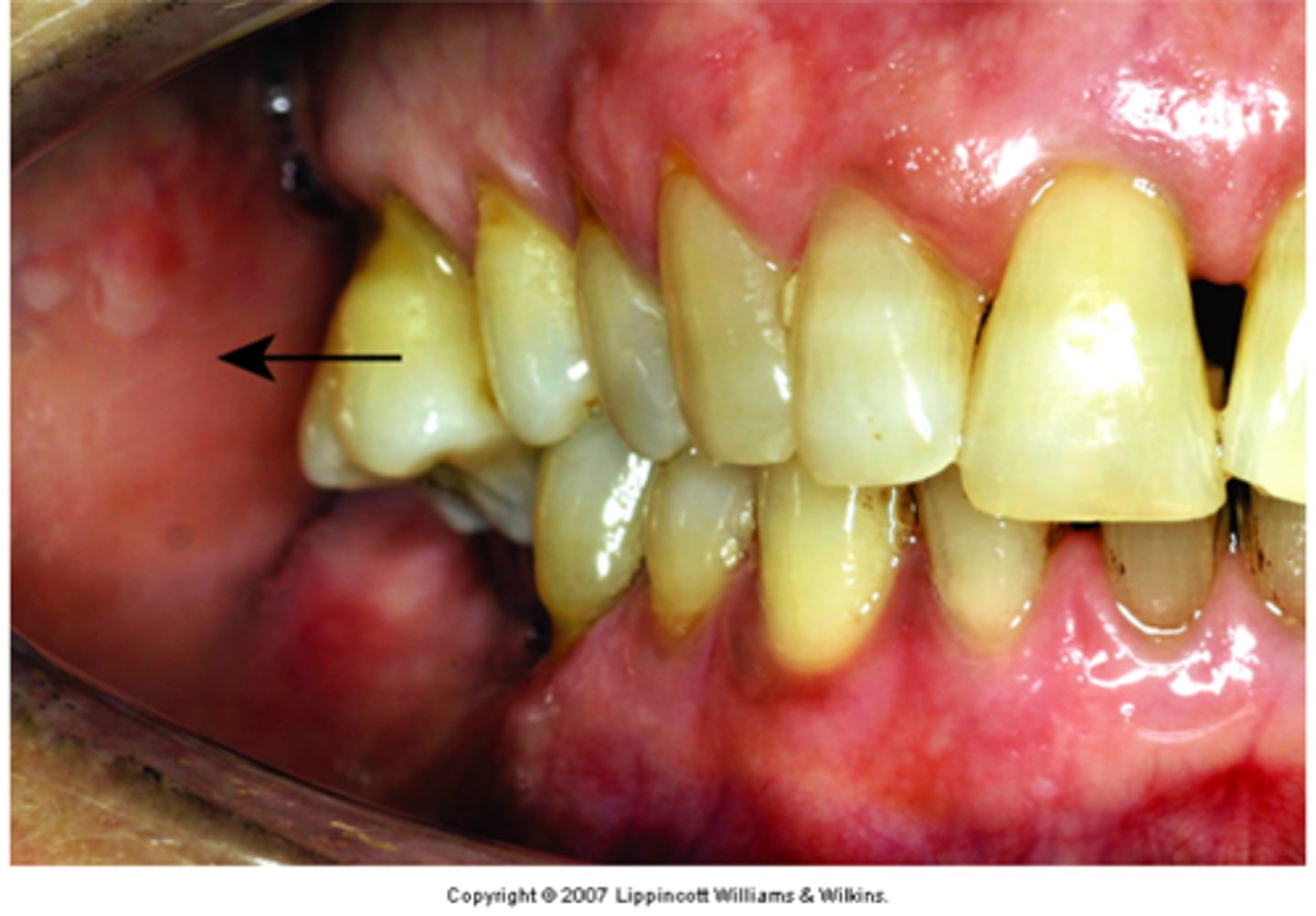
Linguoversion
A tooth that is out of alignment to the lingual compared to other teeth in the arch
Torsiversion
A tooth that is twisted (rotated) around its tooth axis
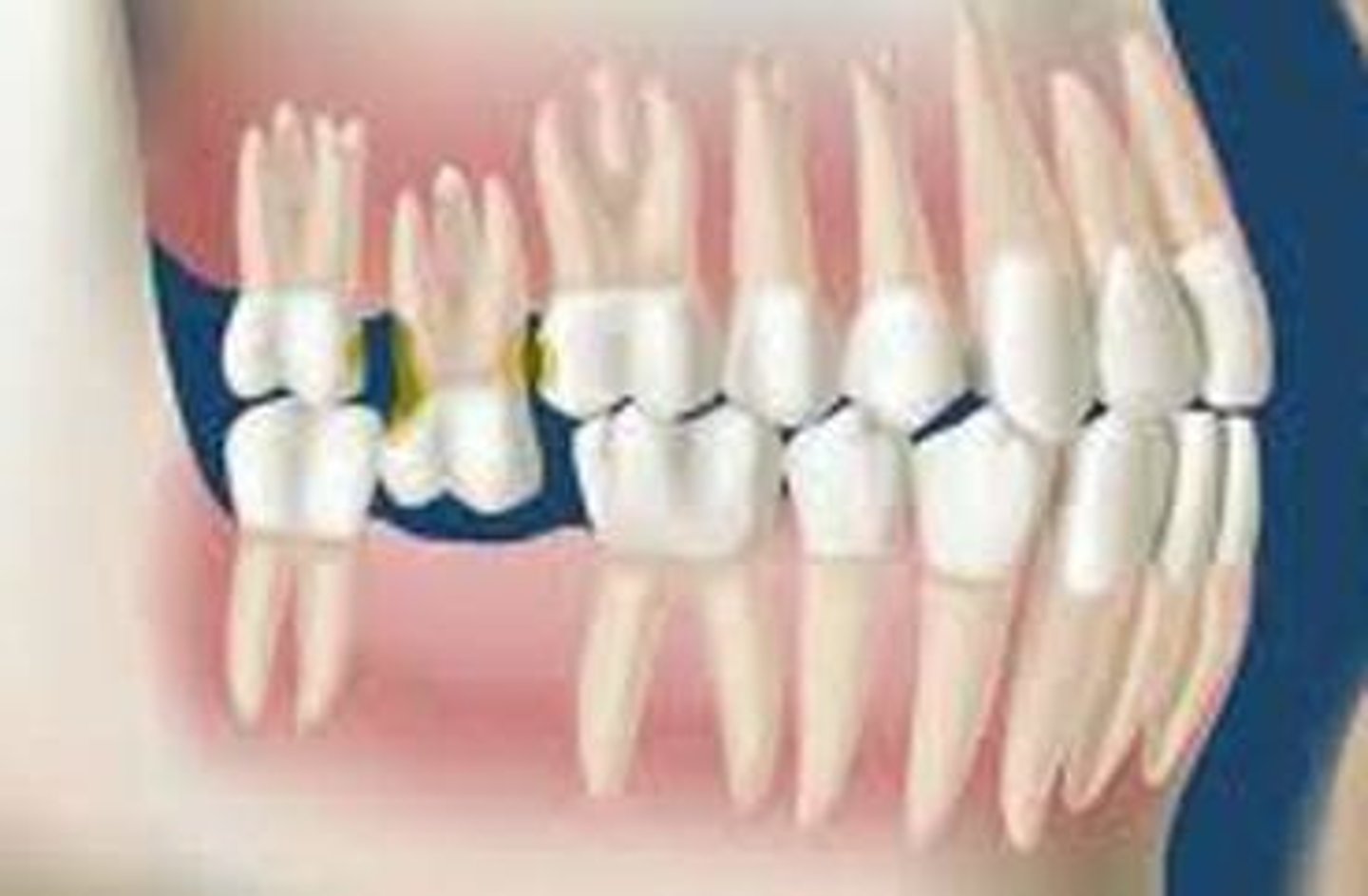
Supraeruption/Extrusion
A tooth that is overerupted is abnormally long relative to the rest of the occlusal surfaces
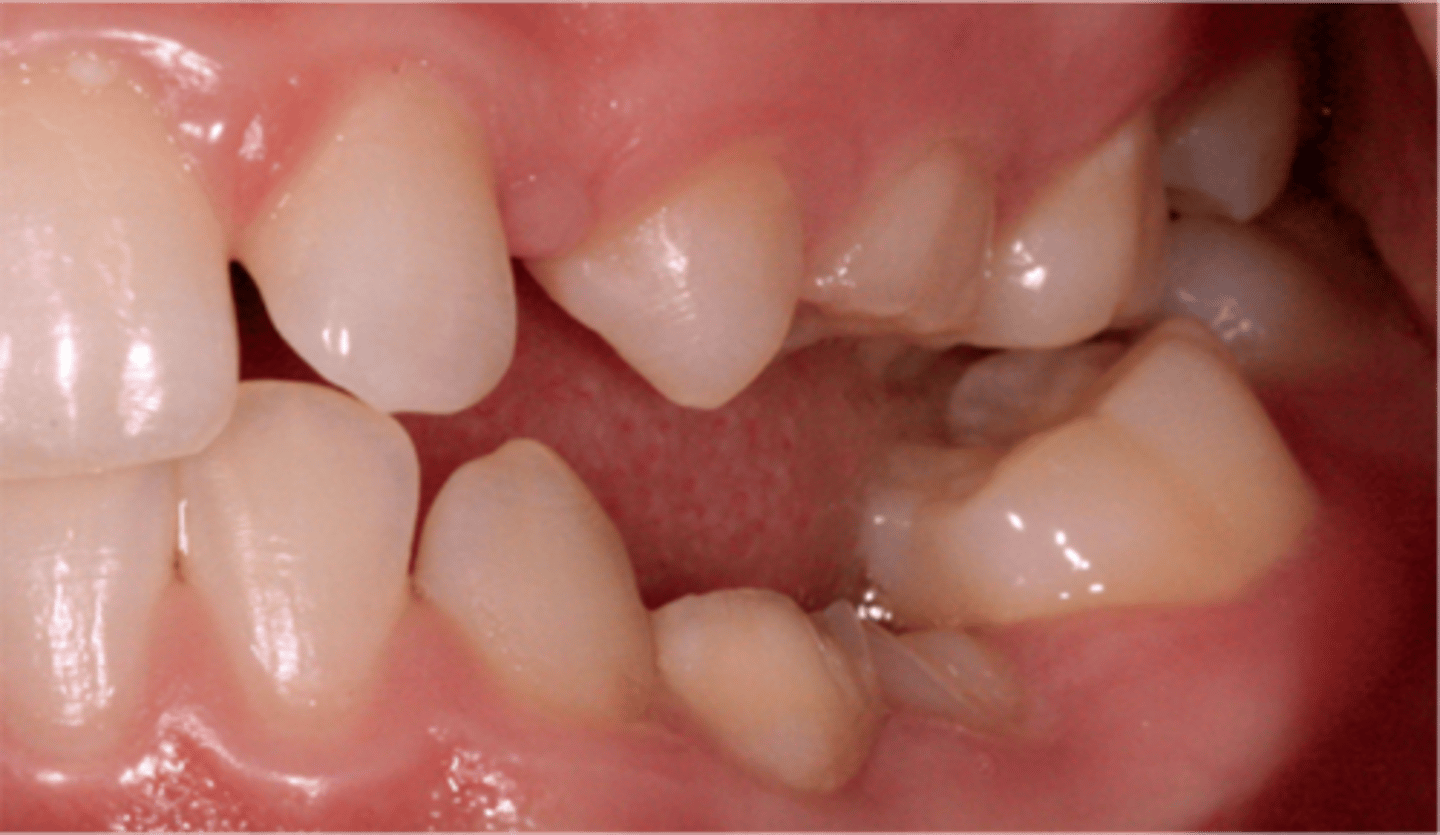
Infraocclusion/Infraversion
If a tooth is abnormally short as opposed to the rest of the occlusal plane
Ankylosis
Fusion of cementum to bone
Anterior Crossbite (reverse articulation)
When mandibular anterior teeth are facial to maxillary anterior teeth
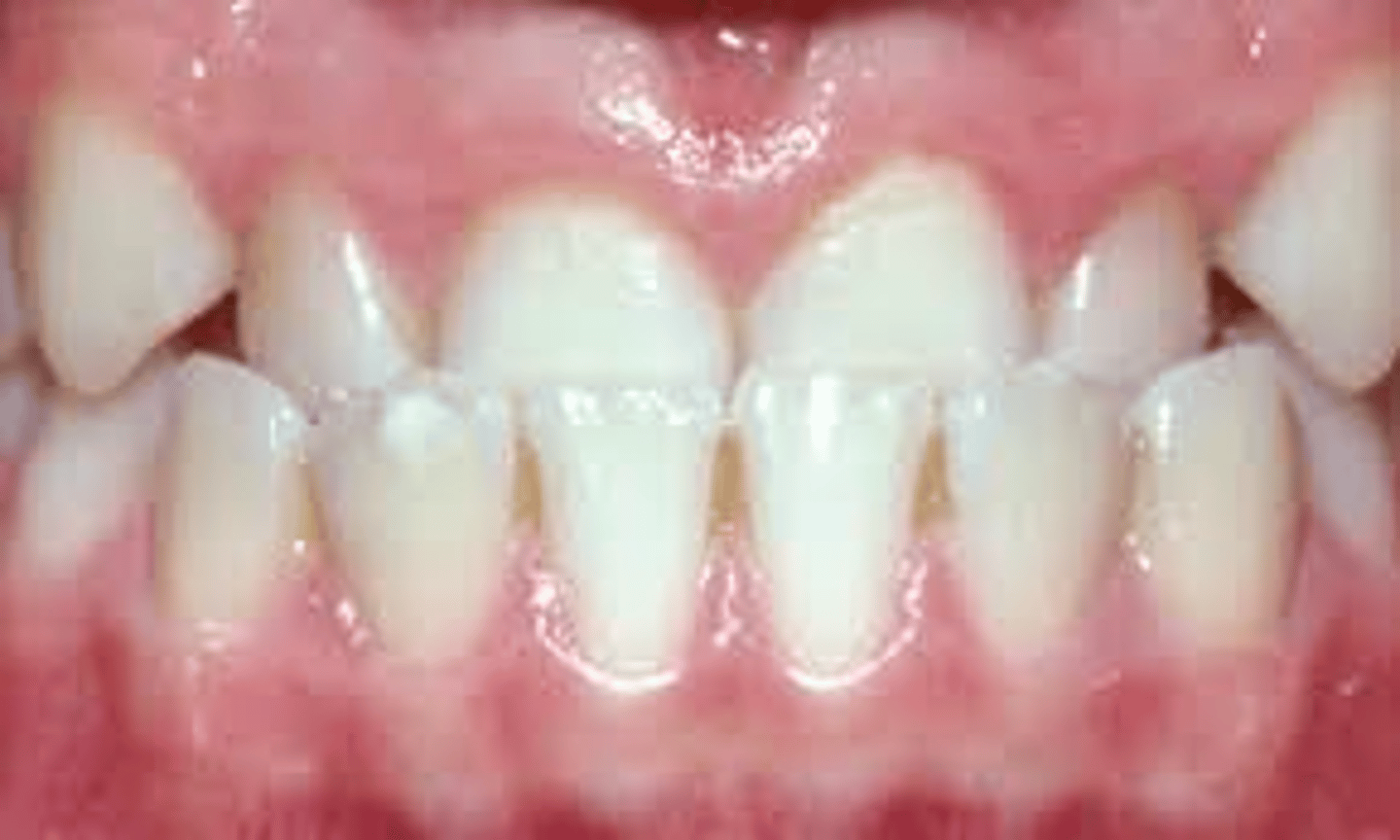
Severe Overbite
when maxillary incisors overlap mandibular incisors down to the level of the cervical lines of the mandibular incisors hiding them from view
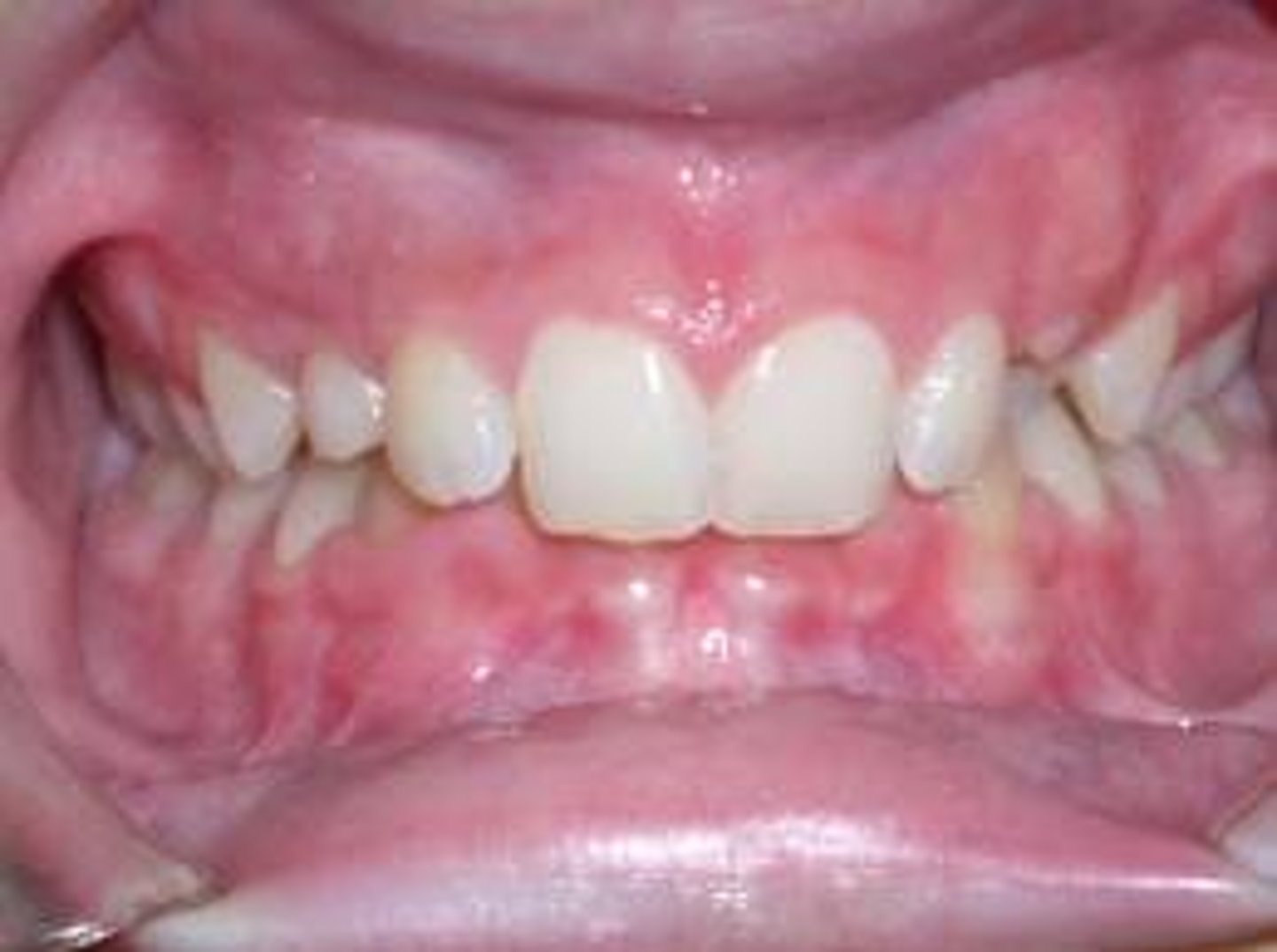
Class II (disto-occlusion)
type of malocclusion where a person may have a mandible that is too small, or a maxilla too large, or both (22% of the population)
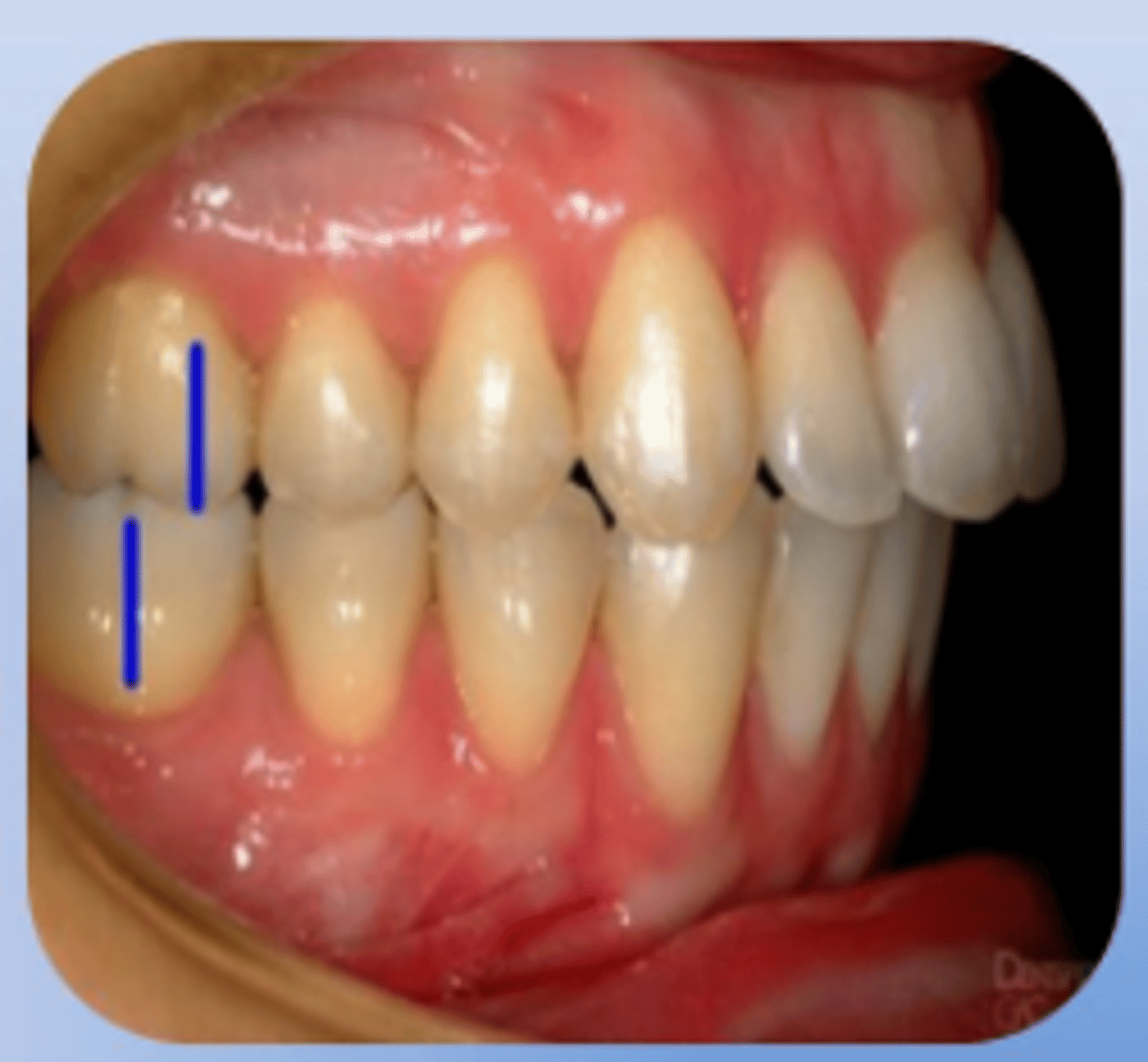
Class II Division 1 Disto-occlusion
a severe horizontal overjet of maxillary incisors labial to mandibular incisors and supra eruption of mandibular incisors.
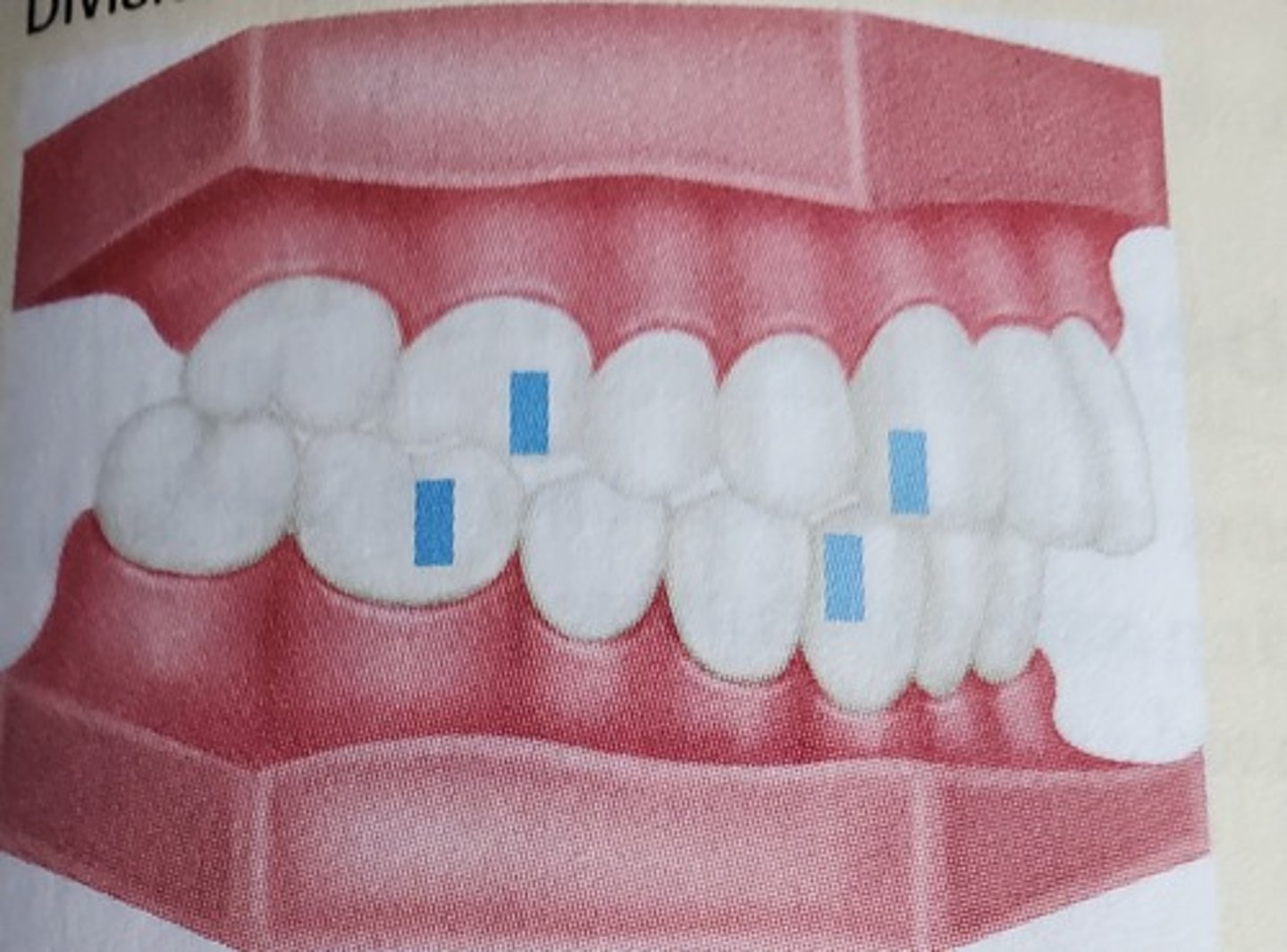
Class II Division 2 Disto-occlusion
An incisor relationship where the maxillary central incisors are retruded with a severe lingual inclination, often with the lateral incisors inclined labially compared to the centrals - maxillary central incisors tilt to the lingual.
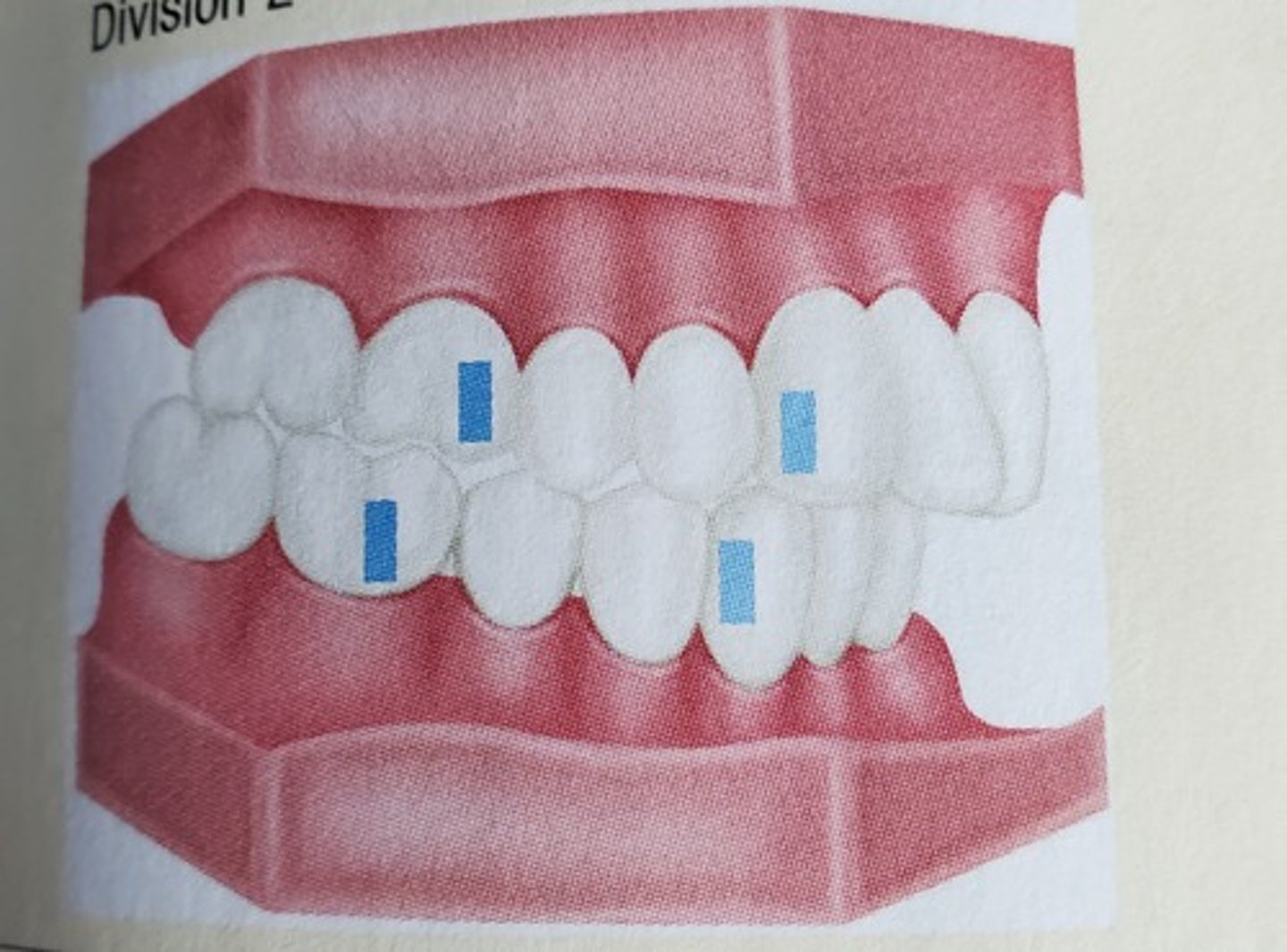
Class II Division 3 Mesio-Occlusion
when the mandibular dental arch is anterior (or mesial) to the maxillary dental arch
Eruption
Sequence
Facial Development
Growth
Occlusion is affected by:
Canine Rise
Describes the actual occlusal contact made during lateral excursion