Biological Rhythms & Sleep: Brain Regions, Sleep Disorders, & Drugs that Affect Sleep
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Made by @agreyr
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
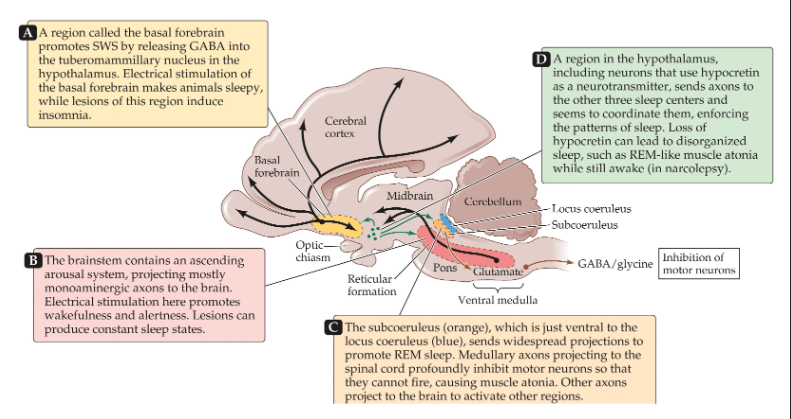
How the brain controls sleep
Forebrain system that generates SWS
Brainstem system that activates the sleeping forebrain to wakefulness (reticular activating system of the brainstem)
Pontine system that triggers REM sleep (REM sleep nuclei in the pons)
Hypothalamic system that coordinates the others
Sleep disorders
Insomnia, hypersomnia, sleep apnea, unreliable respiration, nocturnal myoclonus, narcolepsy, nightmares, night terror, REM behavior disorder, sleep paralysis
Sleep apnea
Unreliable respiration
Nocturnal myoclonus
Restless leg syndrome
Nightmares vs night terror
Nightmares are frightening dreams; night terror is arousal from SWS, intense fear
Narcolepsy
Daytime sleep attacks, cataplexy, sleep hallucinations
REM behavior disorder
Act out a dream while sleeping
Sleep paralysis
Inability to talk/move upon waking or falling asleep
Drugs that affect sleep
Hypnotic drugs and anti-hypnotic drugs
Hypnotic drugs
Benzodiazepines, Ambien, Melatonin
Anti-hypnotic drugs
Stimulants and tricyclic antidepressants
Benzodiazepines
Hypnotic drug
Short-term effects: increase drowsiness, decrease time it takes to fall asleep, reduce number of awakenings, increase total sleep time
Chronic use not recommended; tolerance develops, cessation of use causes insomnia, chronic use causes addiction, they distort the normal pattern of sleep
Ambien
Hypnotic drug
FDA approved for short-term treatment of insomnia; non-benzodiazepine hypnotic but binds to the benzodiazepine site of GABA
Side effects: drowsiness, sleepiness, headache, dizziness, memory impairment, muscle and joint pain
Tolerance, dependance, and withdrawal are possible
Melatonin
Hypnotic drug; a hormone synthesized from serotonin in the pineal gland
Circulating levels of melatonin display circadian rhythms (SCN of the hypothalamus; highest levels associated with darkness and sleep, usefulness is disputable
Stimulants and tricyclic antidepressants
Increase activity of catecholamines by increasing release, blocking reuptake, or both
They act preferentially on REM sleep; can totally suppress REM sleep
Chronic use not recommended; highly addictive, adverse side effects, can interfere with normal sleep