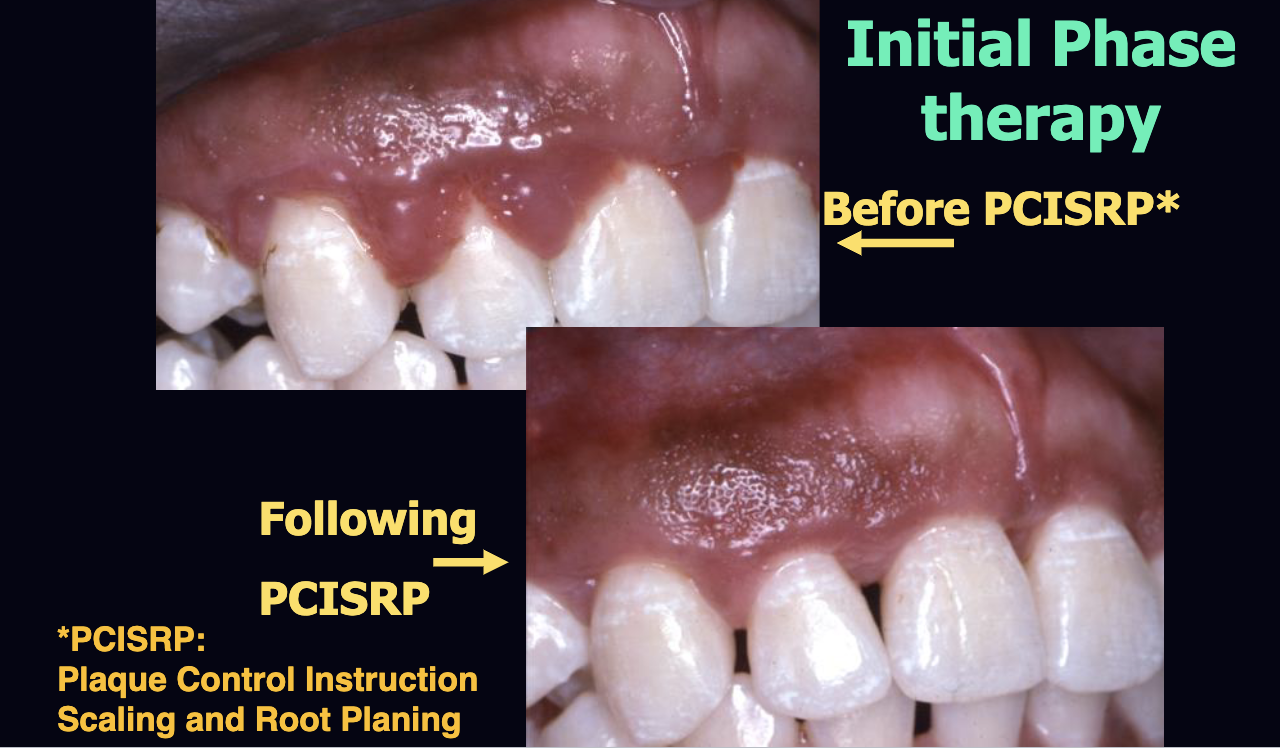
46 Perio: Ecology
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
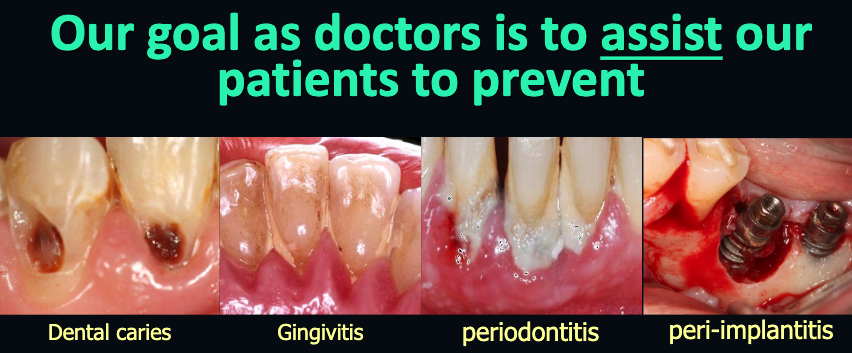
The discussion of Oral Ecology is primary in understanding the primary cause of
caries and periodontal/peri-implant diseases.
caries, gingivitis, periodontitis, peri-implantitis all have a bacterial etiology with the
biofilm attached to the tooth/implant
the study/science of the relationships or
interactions between living organisms and their
environments
ecology
the waste products from oral Bacteria
Dental plaque
shedding vs non-shedding surfaces
shedding = gingiva, alveolar mucosa, tongue (covered with epithelium)
non-shedding = tooth (not covered with epithelium)
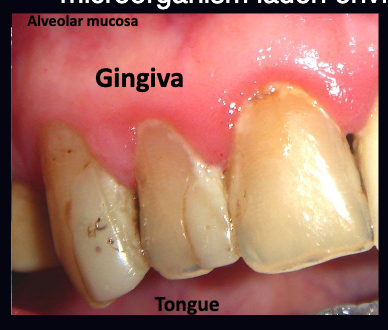
what makes the oral cavity unique?
only part of body that has both shedding and non-shedding surfaces
what are the components of the mouth that serve as a source of microbial nutrients
gingival crevice w ginigval crevice fluid
saliva
colonies of bacteria attached to the tooth produced dental plaque remain attached unless
mechanically dislodged
how many bacterial species can colonize the oral cavity?
1500-1700 (most are host compatible but a subset are responsible caries and periodontal disease)
how many bacterial species in subgingival plaque?
500
what do oral bacterial species colonize?
hard (teeth) and soft tissues + saliva
2 most common infections of mankind
dental caries
periodontal disease
Bacteria including other microorganisms (viruses, yeasts, fungus) that can and often do inhabit the oral cavity are collectively called
microbial flora
the microbial flora of the healthy oral cavity is highly diverse and ____ and ____ specific
site and subject specific
Dental plaque contains bacterial cells and waste products from microbial metabolism; however, the clinical disease comes from the body’s immune response to
those waste products (rather than effect of bacteria eating up/damaging tissue)
what are bulk fluids?
saliva and Gingival Crevice Fluid (GCF) provide nutrients for bacterial life and can affect the change from health to disease
what is the primary bulk fluid? what does it affect?
saliva → supragingival bacterial colonies (above gum line)
what is the secondary bulk fluid? what does it affect?
gingival crevice fluid (GCF) → subgingival bacterial colonies and might affect supragingival bacterial colonies
how do bulk fluids affect the oral microbial ecosystem by…?
providing nutrients for microbial metabolism
removing waste products
acting as transport vehicle for bacterial cells from site to site throughout the mouth and likely from person to person
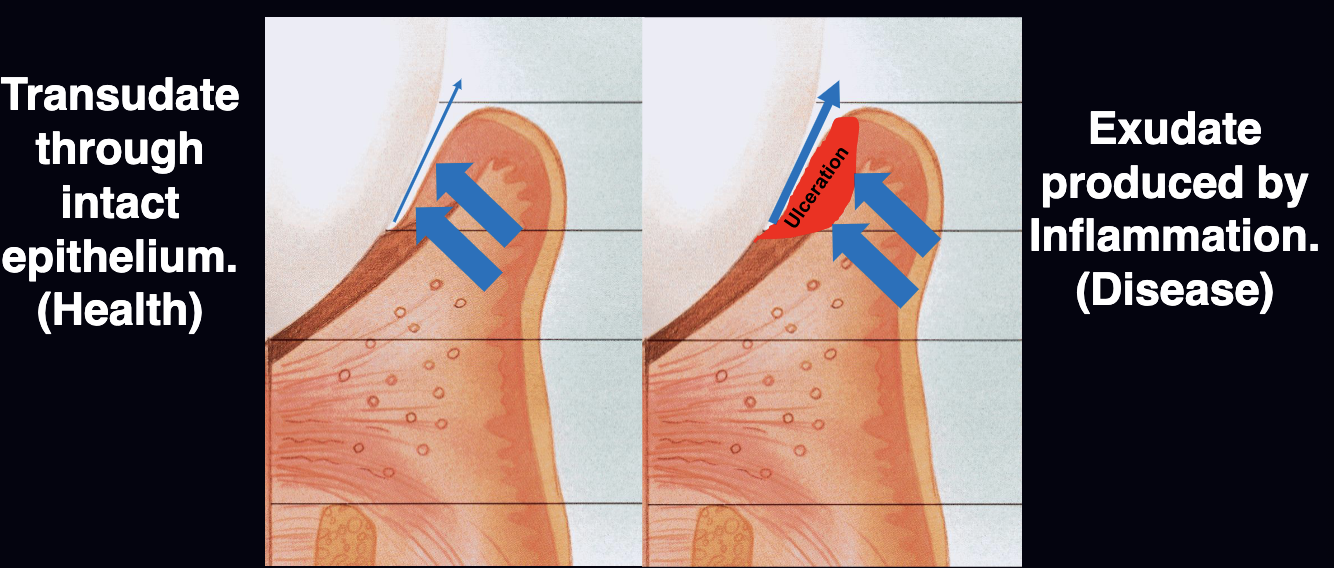
An extravascular, serum-like fluid secreted from the underlying connective tissue through the epithelium into sulcular spaces
gingival crevice fluid (GCF)
how does gingival crevice fluid (GCF) act as a part of the body’s defense mechanism?
transport inflammatory mediators (cytokines), antibodies, and certain systemically administered drugs (antibiotics)
GCF is found in…? and it is increased in quantity and flow in the presence of…?
healthy gingival sulcus (transudate); inflammation (exudate)
transudate vs exudate GCF serum
transudate is through intact epithelium (healthy)
exudate produced by inflammation (disease)
biofilm/plaque is caused by?
Communities of microorganisms attached to a solid surface by a surface glycocalyx. They become embedded in their metabolic waste products.
what is the extracellular/pericellular polymeric material (glycoprotein and glycolipid) produced by some bacterial, epithelial, and other cells.
glycocalyx
glycocalyx is a ______
mucopolysaccharide
what is the function of bacterial glycocalyx?
to promote the adhesion of the bacterial cell to living (epithelial) and inert surfaces, non shedding surfaces, such as a natural tooth, an implant or a prosthesis and the subsequent formation of the adherent, glycocalyx-enclosed populations that are called biofilms
rules for bacterial colonization
bacteria must be at right place at right time
must have ability to survive under changing conditions
presence of nutrients (saliva, GCF)
must tolerate environment (pH, O2 levels, temperature, osmotic pressure, oxidation-reduction potential)
ability to survive host resistance
ability to survive other bacterial species present in that location
capability to grow as fast as other microorganism
ability to adhere to surfaces by creating a glycocalyx
what is a community comprised of?
organisms inhabiting a specific site and containing populations of many individual microbial species
what is a climax community?
A stabilized community of microorganisms that develops an equilibrium with the environment and with other microorganisms within the community
what dental treatment disturbs the biofilm, which then returns to the original equilibrium, climax community, within a day or two following termination of the treatment.
A “dental prophylaxis” (PDHT)
Most dental plaques (biofilms) represent ________ communities.
climax
If a new climax community is established as a result of using chemotherapeutics and/or mechanically altering the plaque, the new climax community must be
host compatible* for it to remain, or the original climax community will return
what factors influence climax communities (the microbial component of biofilm taken from supra and subgingival sites)?
microbial composition of subgingival biofilms (competition)
surfaces on which microbiota colonize (tooth, dental implant, calculus)
bulk fluids
what are the 3 components necessary for bacterial colonization/formation of biofilms?
surfaces for attachment
presnece of community (unless just removed)
flow of bulk fluid passing over and through biofilm ot provide nutrients/waste removal
Tooth surface---Actinomyces species.
Saliva/GCF---Prevotella melaninogenica, gram negative rods.
Soft tissues---Streptococcus mitis, oralis.
The studies to determine the above reveal that the source of most bacteria in saliva is the
tongue surface (various surfaces influence composition of bacterial plaque)
what is a habitat?
site/location at which a population or community grows, reproduces or survives
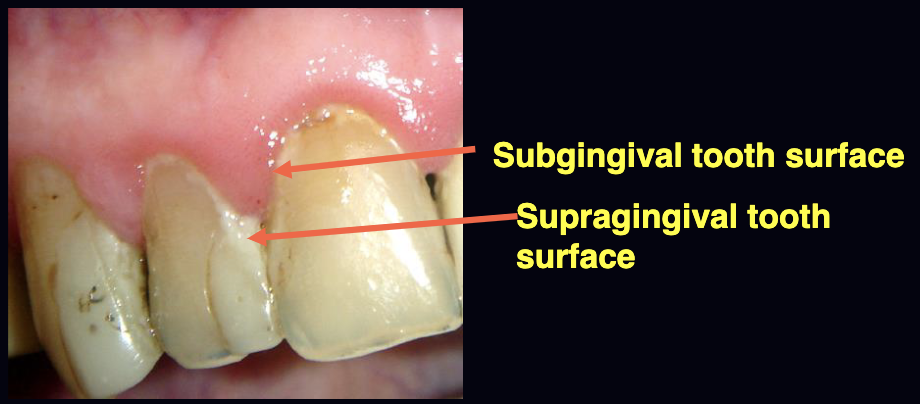
The habitat (shedding and/or non-shedding sites) may be affected by factors such as
geographic location, race and ethnicity, genetic background, smoking, obesity, other systemic diseases, and organisms colonizing within other individuals with whom he/she interacts
what type of surfaces allow the development of ocmplex biofilms?
non-shedding intraoral surfaces
Receptors on the tooth are likely _________ deposited during pellicle formation
salivary proteins (differ from person to person depending on genetic makeup)
what is a niche?
function of an organism in a habitat
what are pioneer organisms?
the first to colonize. their niche is to alter the habitat to allow for the colonization of other species of organisms. Often, they are replaced
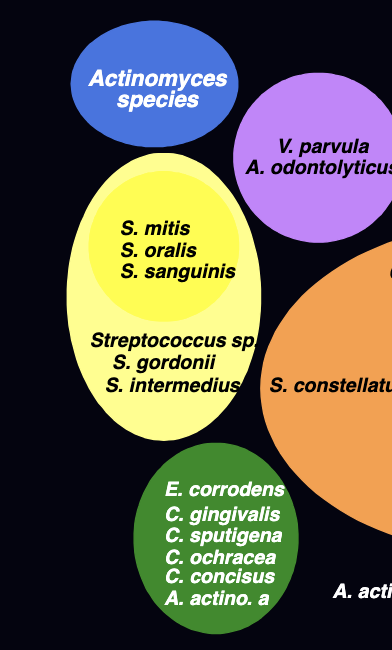
what are these?
subgingival microbial complexes that are NOT associated with causing periodontal disease. they set the stage/lead to orange/red complex bacteria that ARE responsible for periodontal disease
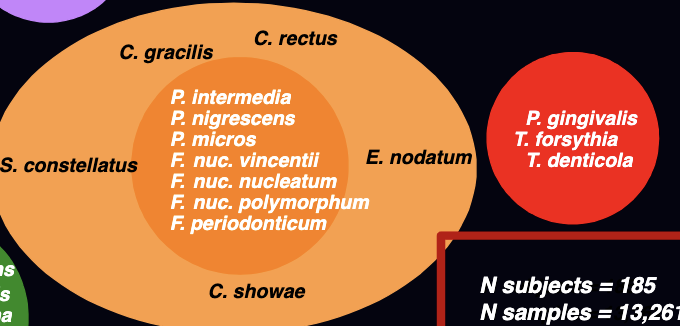
what are these?
disease producing complex of bacterial organisms
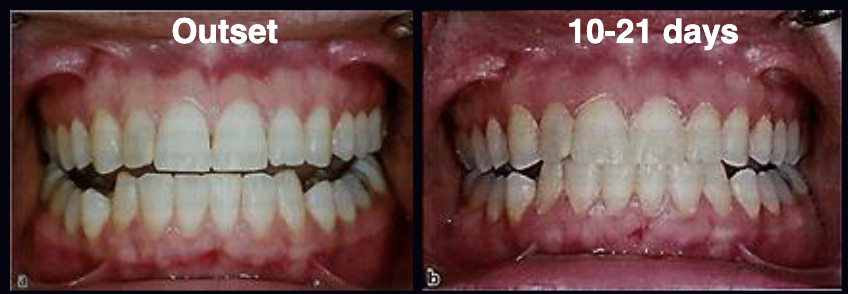
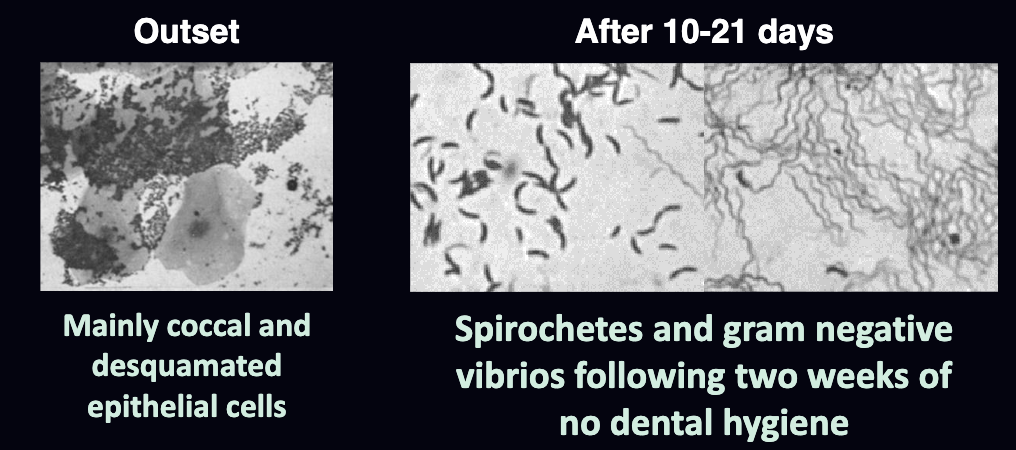
A classic study by Harold Löe et al. (1965) involved the withdrawal of oral hygiene measures in 12 healthy students resulting in plaque accumulation and clinically evident gingivitis after 10-21 days. What is the takehome message? What kinds of bacteria were isolated at the outset vs after 10-21 days?
Removal of plaque leads to resolution of gingival inflammation.
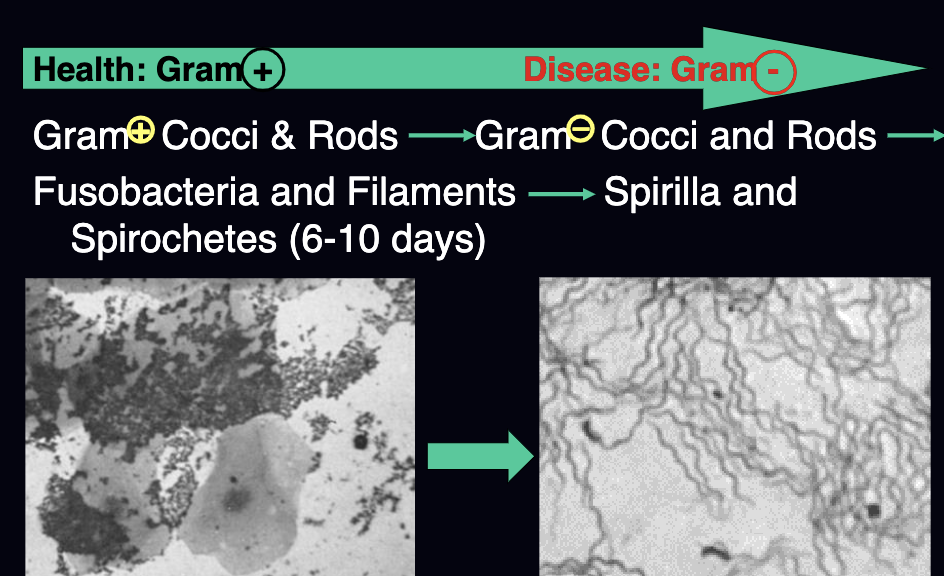
describe the microbial succession from health to disease?
health = gram (+)
disease = gram (-)
what is quorum sensing?
The quantity of bacterial cells affects the gene expression by these cells. Population density creates system of stimuli and responses by microbial cells related to the population. Thus, a non-virulent bacterial cell can become virulent by a change in gene expression due to the quantity of specific bacteria
t/f: Treatment of periodontitis only from a microbiological point of view is possible.
false (not yet possible)
what is a reservoir of microorganisms?
Centers of dispersal from which species of bacteria have spread or are spreading. At the reservoir site conditions are favorable for an increase in density of the species
The tongue is a ________ containing the type of bacteria that can produce periodontitis.
reservoir
types of movement/spread of organisms
active movement
passive movement
what is active movement?
Growth or motility can move an organism from one habitat to another within the mouth
what is passive movement?
Spread within the oral cavity and from subject to subject in saliva. From parent to child and from spouse to spouse.
t/f: in infectious disease, the host must be susceptible to invasion by the colonized organisms
true
The production of antibodies to a colonizing species may change the size, activity or survival of bacteria within a community. This is referring to
environmental feedback
what passive spread of organisms was transmitted among troops in WWII and civilian populations?
ANUG/P (trench mouth) caused by spirochetes and P. gingivalis
Healthy sites of periodontally diseased subjects harbored these organisms more frequently than healthy sites of periodontally healthy subjects. Speculation is that the deep pockets were acting as reservoirs
what 2 factors seem to be the major influences as to the presence and amount of red and orange complex microorganisms present subgingivally.?
Pocket depth and gingival health
Smokers show more/less red and orange complex bacteria in shallow pockets (<4mm) than in non-smokers.
more
which bacteria is seen in greater amounts in smokers vs non-smokers and obese vs overweight/normal individuals
Tanerella forsythia
t/f: Smokers have a higher resistance to the effects of the bacterial toxins than non-smokers
false (lower resistance)
t/f: obese individuals (BMI >35) show greater amounts of periodontitis, plaque, and greater pocket depths than normal weight subjects.
true
what gene is responsible for an increased inflammatory response to an irritant.
(IL)-1 gene
Polymorphisms in the (IL)-1 gene may relate to
the periodontal disease status of non-smoking individuals
In deep pockets (> 6mm), red and orange complex bacteria are decreased/elevated in (IL)-1 positive individuals
elevated (This might relate to increased cytokine production and greater amounts of GCF)
the prevention of dental disease is straightforward and inovles
self-motivation (daily plaque removal)
Knowledge of correct plaque removal techniques.
Having accessibility to the teeth or implants for complete plaque removal.
Regular Professional Dental Hygiene Therapy (PDHT) is essential for coaching and for removing what the patient cannot remove.
what is PCISRP?
plaque control instruction scaling and root planing